Triakis tetrahedron
| Triakis tetrahedron | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Catalan solid |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Conway notation | kT |
| Face type | V3.6.6 isosceles triangle |
| Faces | 12 |
| Edges | 18 |
| Vertices | 8 |
| Vertices by type | 4{3}+4{6} |
| Symmetry group | Td, A3, [3,3], (*332) |
| Rotation group | T, [3,3]+, (332) |
| Dihedral angle | 129°31′16″ arccos(−7/11) |
| Properties | convex, face-transitive |
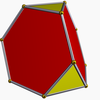 Truncated tetrahedron (dual polyhedron) |
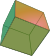
 Net |
In geometry, a triakis tetrahedron is an Archimedean dual solid, or a Catalan solid. Its dual is the truncated tetrahedron.
It can be seen as a tetrahedron with triangular pyramids added to each face; that is, it is the Kleetope of the tetrahedron. This interpretation is expressed in the name.
If the triakis tetrahedron has shorter edge lengths 1, it has area and volume .
Images
Orthogonal projection
| Centered by | Edge normal | Face normal | Edge | Face/vertex |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Truncated tetrahedron |
|
|

|

|
| Triakis tetrahedron |

|
|

|

|
| Projective symmetry |
[1] | [1] | [3] | [4] |
Variations
A triakis tetrahedron with equilateral triangle faces represents a net of the four-dimensional regular polytope known as the 5-cell.
Stellations
This chiral figure is one of thirteen stellations allowed by Miller's rules.
Related polyhedra
The triakis tetrahedron is a part of a sequence of polyhedra and tilings, extending into the hyperbolic plane. These face-transitive figures have (*n32) reflectional symmetry.
| *n32 symmetry mutation of truncated tilings: t{n,3} | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | ||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] | [9i,3] | [6i,3] | |
| Truncated figures |

|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|

|
| Symbol | t{2,3} | t{3,3} | t{4,3} | t{5,3} | t{6,3} | t{7,3} | t{8,3} | t{∞,3} | t{12i,3} | t{9i,3} | t{6i,3} |
| Triakis figures |

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|||
| Config. | V3.4.4 | V3.6.6 | V3.8.8 | V3.10.10 | V3.12.12 | V3.14.14 | V3.16.16 | V3.∞.∞ | |||
| Family of uniform tetrahedral polyhedra | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [3,3], (*332) | [3,3]+, (332) | ||||||

|

|
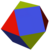
|

|
||||
| {3,3} | t{3,3} | r{3,3} | t{3,3} | {3,3} | rr{3,3} | tr{3,3} | sr{3,3} |
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | |||||||
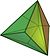
|
|

|

| ||||
| V3.3.3 | V3.6.6 | V3.3.3.3 | V3.6.6 | V3.3.3 | V3.4.3.4 | V4.6.6 | V3.3.3.3.3 |
See also
References
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5, MR730208 (The thirteen semiregular convex polyhedra and their duals, Page 14, Triakistetrahedron)
- The Symmetries of Things 2008, John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 [1] (Chapter 21, Naming the Archimedean and Catalan polyhedra and tilings, page 284, Triakis tetrahedron )




