Member states of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
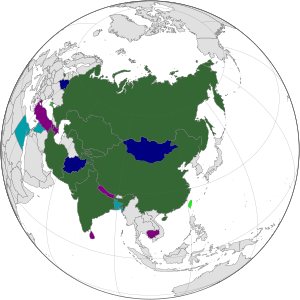
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is an international alliance that consists of 8 member states and 4 observers from Eurasia. It was established on 26 April 1996 as the Shanghai Five. In addition to the 8 member states and 4 observers, the SCO currently has 9 dialogue partners and 4 guest attendance entries.
Member states
| Flag | Country |
Capital |
Largest city |
Area (km²) |
Population (2016) |
Density (/km²) |
GDP per cap. (PPP)[1] |
HDI[2] | Currency |
Official languages | Leaders | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| India Republic of India |
New Delhi | Mumbai | 3,287,240 | 1,284,480,000 | 364.4 | 8,484 | 0.640 | Indian rupee (₹) (INR) |
Hindi (Devanagari script), English & 21 others. Also see Languages of India |
Head of State: Ram Nath Kovind Head of Government: Narendra Modi |
2017-06-09[3] | |
| Pakistan Islamic Republic of Pakistan |
Islamabad | Karachi | 796,095 | 192,779,818 | 214.3 | 4,749 | 0.538 | Pakistani rupee (Rs) (PKR) |
Urdu (National) English |
Head of State: Arif Alvi Head of Government: Shehbaz Sharif |
2017-06-09[3] | |
| China[a] People's Republic of China |
Beijing | Shanghai (metropolitan area) Chongqing (city proper) |
9,640,011[b] | 1,374,820,000 | 139.6 | 13,224 | 0.727 | Renminbi (Chinese yuan, ¥) (CNY) |
Standard Chinese[4] written in simplified characters[4] see also languages of China |
Head of State: Xi Jinping Head of Government: Li Keqiang |
1996-04-26 | |
| Kazakhstan Republic of Kazakhstan |
Astana | Almaty | 2,724,900 | 17,670,900 | 5.94 | 24,108 | 0.788 | Kazakhstani tenge (₸) (KZT) |
Kazakh (National) Russian |
Head of State: Kassym-Jomart Tokayev Head of Government: Askar Mamin |
1996-04-26 | |
| Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyz Republic |
Bishkek | 199,900 | 6,008,600 | 27.4 | 3,262 | 0.655 | Kyrgyzstani som (som) (KGS) |
Kyrgyz (National) Russian |
Head of State: Sadyr Japarov Head of Government: Ulukbek Maripov |
1996-04-26 | ||
| Russia Russian Federation |
Moscow | 17,075,400 | 146,519,759 | 8.3 | 24,449 | 0.798 | Russian rouble (₽) (RUB) |
Russian also see Languages of Russia |
Head of State: Vladimir Putin Head of Government: Mikhail Mishustin |
1996-04-26 | ||
| Tajikistan Republic of Tajikistan |
Dushanbe | 143,100 | 8,352,000 | 48.6 | 2,698 | 0.624 | Tajikistani somoni (SM) (TJS) |
Tajik Persian | Head of State: Emomalii Rahmon Head of Government: Kokhir Rasulzoda |
1996-04-26 | ||
| Uzbekistan Republic of Uzbekistan |
Tashkent | 447,400 | 31,022,500 | 61.4 | 5,630 | 0.675 | Uzbekistani soum (soum) (UZS) |
Uzbek | Head of State: Shavkat Mirziyoyev Head of Government: Abdulla Oripov |
2001-06-15 | ||
Military personnel
The following list is sourced from the 2018 edition of "The Military Balance" published annually by the International Institute for Strategic Studies.
| Country | Active military | Reserve military | Paramilitary | Total | Per 1000 capita (total) |
Per 1000 capita (active) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China[5] | 2,035,000 | 510,000 | 1,500,000 | 4,045,000 | 2.9 | 1.5 | |
| India[6] | 1,440,000 | 2,096,000 | 1,585,950 | 5,121,950 | 4 | 1.1 | |
| Kazakhstan[7] | 39,000 | 0 | 31,500 | 70,500 | 3.8 | 2.1 | |
| Kyrgyzstan[8] | 10,900 | 0 | 9,500 | 20,400 | 3.5 | 1.9 | |
| Pakistan[9] | 653,000 | 0 | 0 | 653,000 | 3.1 | 3.1 | |
| Russian Federation[10][Note 1] | 1,013,628 | 2,572,500 | 2,310,859 | 5,896,987 | 41.5 | 7.1 | |
| Tajikistan[11] | 8,800 | 0 | 7,500 | 16,300 | 1.9 | 1 | |
| Uzbekistan[12] | 48,000 | 0 | 20,000 | 68,000 | 2.3 | 1.6 |
- Notes
- ^ The potential reserve personnel of Russia may be as high as 20 million, depending on how the figures are counted. However, an est. 2 million have seen military service within the last 5 years.
Observer states
| Flag | Country |
Capital |
Area (km²) |
Population (2016) |
Density (/km²) |
GDP per cap. (PPP)[1] |
HDI[2] | Currency |
Official languages | Leaders | Status gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan[13] | Kabul | 652,230 | 27,101,365 | 43.5 | 1,944 | 0.465 | Afghan afghani (Af) (AFN) |
Pashto Dari |
De facto head of state: Hibatullah Akhundzada De facto head of government: Hasan Akhund |
2012-06-07 | |
| Belarus Republic of Belarus |
Minsk | 207,595 | 9,498,700 | 45.8 | 18,246 | 0.798 | Belarusian rubel (Rbl) (BYR) |
Belarusian Russian |
Head of State: Alexander Lukashenko Head of Government: Roman Golovchenko |
2010-04-28 | |
| Iran Islamic Republic of Iran |
Tehran | 1,648,195 | 79,011,700 | 48.0 | 17,443 | 0.766 | Iranian rial (Rl) (IRR) |
Persian | Head of State: Ali Khamenei Head of Government: Ebrahim Raisi |
2005-06-23 | |
| Mongolia | Ulaanbaatar | 1,564,115 | 3,067,550 | 1.75 | 11,919 | 0.727 | Mongolian tögrög (₮) (MNT) |
Mongolian | Head of State: Ukhnaagiin Khürelsükh Head of Government: Luvsannamsrain Oyun-Erdene |
2004-06-17 |
Dialogue partner entries
| Flag | Country |
Capital |
Area (km²) |
Population (2016) |
Density (/km²) |
GDP per cap. (PPP)[1] |
HDI[2] | Currency |
Official languages | Leaders | Status gained |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armenia Republic of Armenia |
Yerevan | 29,743 | 2,998,600 | 102.0 | 8,164 | 0.733 | Armenian dram (֏) (AMD) |
Armenian | Head of State: Armen Sarkissian Head of Government: Nikol Pashinyan |
2015-07-10 | |
| Azerbaijan Republic of Azerbaijan |
Baku | 86,600 | 9,696,800 | 109.0 | 17,761 | 0.751 | Azerbaijani manat (₼) (AZN) |
Azeri | Head of State: Ilham Aliyev Head of Government: Ali Asadov |
2015-07-10 | |
| Cambodia Kingdom of Cambodia |
Phnom Penh | 181,035 | 15,626,444 | 84.0 | 3,276 | 0.555 | Cambodian riel (CR) (KHR) |
Khmer | Monarch: Norodom Sihamoni Head of Government: Hun Sen |
2015-07-10 | |
| Nepal Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal |
Kathmandu | 147,181 | 28,431,500 | 180.0 | 2,388 | 0.548 | Nepalese rupee (Rs) (NPR) |
Nepali | Head of State: Bidhya Devi Bhandari Head of Government: Sher Bahadur Deuba |
2015-07-10 | |
| Sri Lanka Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka |
Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte (Administrative) Colombo (Commercial) |
65,610 | 20,966,000 | 309.0 | 10,410 | 0.757 | Sri Lankan rupee (Rs) (LKR) |
Sinhalese Tamil |
Head of State and Government: Gotabaya Rajapaksa | 2009-06-16 | |
| Turkey Republic of Turkey |
Ankara | 783,562 | 78,741,053 | 102.0 | 19,698 | 0.761 | Turkish lira (₺) (TRY) |
Turkish | Head of State and Government: Recep Tayyip Erdoğan | 2012-06-07 |
Future participation
Observer Iran has submitted an application for full membership.[14] On September 17, 2021, the SCO has officially launched the procedures of Iran's accession to the SCO as a full member, which are expected to take "a fair amount of time".[15][16]
Meanwhile, in 2012 Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, East Timor, Nepal and Sri Lanka applied for observer status within the organization.[17] Egypt[18] and Syria has also submitted an application for observer status,[14] while Egypt, Israel,[19] Maldives and Ukraine have applied for dialogue partner status.[20][21] Saudi Arabia,[22][23][24] Bahrain and Qatar has officially applied to join the SCO.[25][26] In 2022, Erdogan announced that Turkey would seek full SCO membership status.[27]
Guest attendance entries
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS)
- Turkmenistan
Notes
- ^ The sovereignty of China is disputed. Since the conclusion of the Chinese Civil War, the Republic of China (ROC), which was formally established on 1 January 1912 following the Xinhai Revolution, which succeeded the former Qing dynasty's territories on mainland China, while the islands of Taiwan and Penghu were under Japanese rule at the time. The ROC gained control over the latter after the surrender of Japan in 1945, but soon lost its control of mainland to the communists due to the Chinese Civil War. The ROC government was relocated to Taipei in 7th December 1949 as its provisional capital and retains actual rule over the islands of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, the Matsu, and other minor islands, all of which are collectively known as "Free Area" or Taiwan Area in contrast to Mainland China being under communist rule, thus making it a de facto island nation, and has become known colloquially as simply "Taiwan" due to the island of Taiwan forming the majority of the ROC-controlled territories; nonetheless, the ROC has not officially renounced its constitutional-defined territories which include areas effectively controlled by the People's Republic of China, Mongolia, Tuva (a Russian republic) etc. If claimed territories were taken into account, the ROC would not be a borderless country, nor a country centred around a major island. The ROC-controlled territories are also claimed by the People's Republic of China. Constitutionally, the ROC on Taiwan still views itself as the continuation of former Chinese republic, with legitimate sovereignty over mainland China despite no actual control. See: Political status of Taiwan, Retreat of the Republic of China to Taiwan, Four-Stage Theory of the Republic of China, Two Chinas, One-China policy, and Cross-strait relations.
- ^ The actual area under PRC control is 9,596,960.
References
- ^ a b c at purchasing power parity, per capita, in international dollars (rounded IMF 2012)
- ^ a b c at Human Development Index (New 2013 Estimates for 2012)
- ^ a b Bhattacherjee, Kallol (9 June 2017). "India, Pakistan become full members of SCO". The Hindu. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ^ a b Law of the People's Republic of China on the Standard Spoken and Written Chinese Language (Order of the President No.37)
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 249-250
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 260
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 188
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 190
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 291
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 192
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 207
- ^ IISS 2018, pp. 214
- ^ Seiwert, Eva (30 September 2021). "The Shanghai Cooperation Organization Will Not Fill Any Vacuum in Afghanistan". Foreign Policy Research Institute. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ^ a b "Syria applies for observer status at Shanghai security bloc — Russian Foreign Ministry". Russian News Agency TASS. 2015-02-13. Retrieved 2015-07-11.
- ^ "News Analysis: Why is Iran keen on full SCO membership?". Xinhua. 18 September 2021.
- ^ "Iran Joins SCO". Financial Tribune. 17 September 2021.
- ^ "Azerbaijan asks to join a new alliance of China and Russia".
- ^ "Syria, Egypt may join Shanghai Cooperation Organization as observers". Russian News Agency TASS. 2015-06-05. Retrieved 2015-12-21.
- ^ "Syria, Israel, Egypt willing to join SCO's activity - president's special envoy". Interfax. 2016-06-23. Archived from the original on 2016-08-16. Retrieved 2016-06-24.
- ^ "Egypt applies to become dialogue partner of Shanghai security bloc — Kremlin aide". Russian News Agency TASS. 2015-07-06. Retrieved 2015-08-15.
- ^ "Azerbaijan intends to become SCO observer". 2015-02-10. Archived from the original on 2015-08-02. Retrieved 2015-08-15.
- ^ "以色列和沙特提交加入上合组织的相关申请". 环球网. 2019-08-15. Retrieved 2019-11-03.
- ^ "В МИД рассказали о странах, которые хотят участвовать в работе ШОС". RIA Novosti. 2019-08-15. Retrieved 2019-08-21.
- ^ "Саудовская Аравия устремилась в ШОС". Abkhazian Network News Agency. 2018-10-18. Retrieved 2019-08-22.
- ^ "Катар, Бахрейн и Израиль просят о приеме в ШОС". Мир 24. 2017-12-05. Retrieved 2019-08-22.
- ^ "SCO receives membership requests from Qatar, Bahrain". Interfax. 2017-12-05. Archived from the original on 2017-12-07. Retrieved 2019-08-22.
- ^ "Turkey Seeks to Be First NATO Member to Join China-Led SCO". www.bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2022-09-17.
Bibliography
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (3 February 2010). The Military Balance 2010. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1857435573.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2 March 2011). The Military Balance 2011. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1857436068.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (7 March 2012). The Military Balance 2012. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1857436426.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (14 March 2013). The Military Balance 2013. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1857436808.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (3 February 2014). The Military Balance 2014. London: Routledge. ISBN 9781857437225.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (14 February 2018). The Military Balance 2018. London: Routledge. ISBN 9781857439557.
