Cataphract: Difference between revisions
not correct anywhere, Replaced: humourous → humorous,, typos fixed: archaelogical → archaeological, developement → development (2), fufilled → fulfilled, occured using AWB |
m Please don't revert spelling conventions in this article to suit your personal tastes, as it stands the article is written in predominantly British English convetions, keep it consistent |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
''"... But no sooner had the first light of day appeared, than the glittering coats of mail, girt with bands of steel, and the gleaming cuirasses, seen from afar, showed that the king's forces were at hand."'' |
''"... But no sooner had the first light of day appeared, than the glittering coats of mail, girt with bands of steel, and the gleaming cuirasses, seen from afar, showed that the king's forces were at hand."'' |
||
[[Ammianus Marcellinus]], renowned [[Ancient Rome|Roman]] general and ancient historian, describing the sight of [[Sassanid Empire|Persian]] cataphracts approaching [[Roman legion|Roman infantry]] in [[Asia Minor]], circa [[4th Century BC]].<ref>Ammianus Marcellinus, (353 AD) ''Roman Antiquities'', Boox XXV pp. 477</ref> |
[[Ammianus Marcellinus]], renowned [[Ancient Rome|Roman]] general and ancient historian, describing the sight of [[Sassanid Empire|Persian]] cataphracts approaching [[Roman legion|Roman infantry]] in [[Asia Minor]], circa [[4th Century BC]]. <ref>Ammianus Marcellinus, (353 AD) ''Roman Antiquities'', Boox XXV pp. 477</ref> |
||
Cataphracts served as either the elite cavalry or assault force for most empires and nations that fielded them, primarily used for impetuous charges to break through infantry formations. Chronicled by many historians from the earliest days of [[classical antiquity|Antiquity]] up until the [[High Middle Ages]], they are in part or wholly believed to have given rise to the [[Feudalism|Age of Feudalism]] in Europe and the later European equivalents of [[Knights]] and [[Paladins]], via contact with the [[Byzantine Empire]].<ref name="Nell, Grant S. 1995">Nell, Grant S. (1995) ''The Savaran: The Original Knights''. University of Oklahoma Press.</ref> |
Cataphracts served as either the elite cavalry or assault force for most empires and nations that fielded them, primarily used for impetuous charges to break through infantry formations. Chronicled by many historians from the earliest days of [[classical antiquity|Antiquity]] up until the [[High Middle Ages]], they are in part or wholly believed to have given rise to the [[Feudalism|Age of Feudalism]] in Europe and the later European equivalents of [[Knights]] and [[Paladins]], via contact with the [[Byzantine Empire]].<ref name="Nell, Grant S. 1995">Nell, Grant S. (1995) ''The Savaran: The Original Knights''. University of Oklahoma Press.</ref> |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
There appears to be some confusion of the term in the [[late antiquity|late Roman period]], as armored cavalrymen of any sort which were traditionally referred to as [[Equites]] in the [[Roman Republic|Republican period]], later became exclusively designated as "cataphracts". [[Vegetius]] writing in the 4th century described armor of any sort as "cataphracts" - which at the time of writing would have been either ''[[lorica segmentata]]'' or ''[[lorica hamata]]''. [[Ammianus Marcellinus]], noted Roman general and historian of [[4th century]], mentions the: "''cataphracti equites (quos clibanarios dictitant)''" – the "cataphract cavalry which the they call [[Clibanarii]]," (implying clibanarii is a foreign term, not used in Roman Latin). |
There appears to be some confusion of the term in the [[late antiquity|late Roman period]], as armored cavalrymen of any sort which were traditionally referred to as [[Equites]] in the [[Roman Republic|Republican period]], later became exclusively designated as "cataphracts". [[Vegetius]] writing in the 4th century described armor of any sort as "cataphracts" - which at the time of writing would have been either ''[[lorica segmentata]]'' or ''[[lorica hamata]]''. [[Ammianus Marcellinus]], noted Roman general and historian of [[4th century]], mentions the: "''cataphracti equites (quos clibanarios dictitant)''" – the "cataphract cavalry which the they call [[Clibanarii]]," (implying clibanarii is a foreign term, not used in Roman Latin). |
||
'''Clibanarii''' is a [[Latin]] word for "mail-clad riders", itself a derivative of the {{lang-el|κλιβανοφόροι}} ''Klibanophoroi'' meaning “camp oven-bearers” from the Greek word κλίβανος, meaning "camp oven" or "metallic furnace". However it appears with more frequency in Latin sources than in Greek throughout antiquity. The origins of the original Greek term are twofold: that it was either a |
'''Clibanarii''' is a [[Latin]] word for "mail-clad riders", itself a derivative of the {{lang-el|κλιβανοφόροι}} ''Klibanophoroi'' meaning “camp oven-bearers” from the Greek word κλίβανος, meaning "camp oven" or "metallic furnace". However it appears with more frequency in Latin sources than in Greek throughout antiquity. The origins of the original Greek term are twofold: that it was either a humourous reference to the heavily armored cataphracts (as men encased in armor would heat up very quickly much like an oven) or that it was further derived from the [[Old Persian]] word: ''*griwbanar'' (or ''*grivbanvar''), itself composed of the [[Iranian languages|Iranian]] roots: ''griva-pana-bara'', which translates into "neck-guard wearer".<ref name="Nicolle, David 1992">Nicolle, David (1992) ''Romano-Byzantine Armies, 4th–9th Centuries''. Osprey Publishing.</ref> |
||
Roman chroniclers and historians [[Arrian]], [[Aelianus Tacticus|Aelian]] and [[Asclepiodotus (philosopher)|Asclepiodotus]] use the term cataphract in their military treatises to describe any type of cavalry with either partial or full horse and rider armor. The [[Byzantine]] historian [[Leo the Deacon|Leo Diaconis]] on the other hand, calls them: "πανσιδήρους ιππότας", which would translate as "fully iron-clad knights."<ref>Leo Diaconis, Historiae 4.3, 5.2, 8.9</ref> |
Roman chroniclers and historians [[Arrian]], [[Aelianus Tacticus|Aelian]] and [[Asclepiodotus (philosopher)|Asclepiodotus]] use the term cataphract in their military treatises to describe any type of cavalry with either partial or full horse and rider armor. The [[Byzantine]] historian [[Leo the Deacon|Leo Diaconis]] on the other hand, calls them: "πανσιδήρους ιππότας", which would translate as "fully iron-clad knights."<ref>Leo Diaconis, Historiae 4.3, 5.2, 8.9</ref> |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Refimprovesect|date=October 2009}} |
{{Refimprovesect|date=October 2009}} |
||
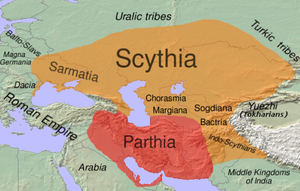
[[Image:Scythia-Parthia 100 BC.png|thumb|right|300px|The extent of the early [[Iranian peoples|Iranian]] [[Scythians]] and [[Parthian Empire|Parthians]] at approximately [[100 BC]], to whom the first recorded use of true, cataphract-like cavalry can be attributed to in [[Classical Antiquity]].]] |
[[Image:Scythia-Parthia 100 BC.png|thumb|right|300px|The extent of the early [[Iranian peoples|Iranian]] [[Scythians]] and [[Parthian Empire|Parthians]] at approximately [[100 BC]], to whom the first recorded use of true, cataphract-like cavalry can be attributed to in [[Classical Antiquity]].]] |
||
The reliance on cavalry as a means of warfare in general lies with the ancient inhabitants of the [[Central Asia]]n [[steppes]] in [[Ancient Near East|early antiquity]], who were one of the first peoples to [[Domestication of the horse|domesticate the horse]] and pioneered the development of the [[chariot]]<ref>Mielczarek, Mariusz (1993) Cataphracti and Clibanarii. Studies on the Heavy Armored Cavalry of the Ancient World, p. 14</ref>. Most of these nomadic tribes and wandering pastoralists circa [[2000 BC]] were largely [[Bronze-Age]], [[Indo-Iranians|Indo-Iranian]] (or [[Indo-Aryan]]) populations, who migrated from the steppes of Central Asia into the [[Iranian Plateau]] and [[Greater Iran]] from around [[1000 BC]] to [[800 BC]] (see [[Indo-Aryan migration]]). Two of these tribes are attested based upon |
The reliance on cavalry as a means of warfare in general lies with the ancient inhabitants of the [[Central Asia]]n [[steppes]] in [[Ancient Near East|early antiquity]], who were one of the first peoples to [[Domestication of the horse|domesticate the horse]] and pioneered the development of the [[chariot]]<ref>Mielczarek, Mariusz (1993) Cataphracti and Clibanarii. Studies on the Heavy Armored Cavalry of the Ancient World, p. 14</ref>. Most of these nomadic tribes and wandering pastoralists circa [[2000 BC]] were largely [[Bronze-Age]], [[Indo-Iranians|Indo-Iranian]] (or [[Indo-Aryan]]) populations, who migrated from the steppes of Central Asia into the [[Iranian Plateau]] and [[Greater Iran]] from around [[1000 BC]] to [[800 BC]] (see [[Indo-Aryan migration]]). Two of these tribes are attested based upon archaelogical evidence: the [[Mitanni]] and the [[Kassites]]. Although evidence is scant, they are believed to have raised and bred horses for specific purposes, as is evidenced by the large archaeological record of their use of the chariot and several treatises on the training of chariot horses<ref>Robert Drews, "The Coming of the Greeks: Indo-European Conquests in the Aegean and the Near East.", Princeton University Press, Chariot Warfare. pg 61</ref>. The one founding prerequisite towards the development of cataphract cavalry in the [[Ancient Near East]], apart from advanced [[History of ferrous metallurgy|metalworking]] techniques and the necessary grazing pastures for raising horses, was the evolution of [[Horse breeding|selective breeding]] and [[animal husbandry]]. Cataphract cavalry needed to be immensely strong and endurant horses, and without selectively breeding horses for muscular strength and hardiness they would have surely not been able to bear the immense loads of armor and a rider during the strain of battle<ref>Perevalov, S. M. (translated M. E. Sharpe) (Spring 2002). "The Sarmatian Lance and the Sarmatian Horse-Riding Posture". Anthropology & Archeology of Eurasia 41 (4): 7–21.</ref>. The [[Near East]] is generally believed to have been the focal point for where this first occurred. |
||
The above early [[Indo-Iranians|Indo-Iranian]] kingdoms and statehoods were to a large degree the ancestors of the [[Medians]] who would found the very first [[Persian Empire]] in [[625 BC]], and of the [[Scythians|north-eastern Iranian tribes]]. It was the Median Empire that left the first written proof of horse breeding around the [[7th century BC]], being the first to propagate a specific [[horse breed]] known as the [[Nisean horse|Nisean]], which originated in the [[Zagros Mountains]], for use as heavy cavalry<ref name="Farrokh, Kaveh 2005">Farrokh, Kaveh (2005) ''Sassanian Elite Cavalry, AD224-642''. Osprey Publishing.</ref>. The Nisean would go on to become renowned in the Ancient World and particularly in [[Ancient Persia]], being the mount of nobility and of their warhorses, sometimes referred to as "''Nisaean chargers''", who were highly sought after by the Greeks and are believed to have influenced many modern horse breeds. With the growing aggressiveness played by the role of cavalry in warfare, protection of the rider and the horse became paramount. This was especially true of peoples who treated cavalry as the basic arm of their military, and indeed, the backbone of the [[Military history of Iran|Ancient Persian military]] such as that of the Medes or the successive [[Persian Empire|Persian dynasties]] that followed them, was the horse. To a larger extent, the same can said of all the [[Ancient Iranian peoples]], as second only to perhaps the [[bow]], horses were held in reverence and importance in these societies as their preferred and mastered medium of warfare, due to an intrinsic link throughout history with the domestication and evolution of the horse. |
The above early [[Indo-Iranians|Indo-Iranian]] kingdoms and statehoods were to a large degree the ancestors of the [[Medians]] who would found the very first [[Persian Empire]] in [[625 BC]], and of the [[Scythians|north-eastern Iranian tribes]]. It was the Median Empire that left the first written proof of horse breeding around the [[7th century BC]], being the first to propagate a specific [[horse breed]] known as the [[Nisean horse|Nisean]], which originated in the [[Zagros Mountains]], for use as heavy cavalry<ref name="Farrokh, Kaveh 2005">Farrokh, Kaveh (2005) ''Sassanian Elite Cavalry, AD224-642''. Osprey Publishing.</ref>. The Nisean would go on to become renowned in the Ancient World and particularly in [[Ancient Persia]], being the mount of nobility and of their warhorses, sometimes referred to as "''Nisaean chargers''", who were highly sought after by the Greeks and are believed to have influenced many modern horse breeds. With the growing aggressiveness played by the role of cavalry in warfare, protection of the rider and the horse became paramount. This was especially true of peoples who treated cavalry as the basic arm of their military, and indeed, the backbone of the [[Military history of Iran|Ancient Persian military]] such as that of the Medes or the successive [[Persian Empire|Persian dynasties]] that followed them, was the horse. To a larger extent, the same can said of all the [[Ancient Iranian peoples]], as second only to perhaps the [[bow]], horses were held in reverence and importance in these societies as their preferred and mastered medium of warfare, due to an intrinsic link throughout history with the domestication and evolution of the horse. |
||
These early riding traditions, which were strongly tied to the ruling [[caste]] of nobility (as only those of noble birth or caste could become cavalry warriors), now spread throughout the [[Eurasian steppe]]s and [[Iranian plateau]] from around [[600 BC]] and onwards due to contact with [[Median Empire]]'s vast expanse across Central Asia, which was the native homeland of the early, north-eastern Iranian ethnic groups such as the [[Massagetae]], [[Scythians]], [[Sakas]], and [[Dahae]].<ref name="Farrokh, Kaveh 2005"/> The successive [[Persian Empire]]s which followed the Medes after their downfall in [[550 BC]] took these already long-standing military tactics and horse breeding traditions and infused their centuries of experience and |
These early riding traditions, which were strongly tied to the ruling [[caste]] of nobility (as only those of noble birth or caste could become cavalry warriors), now spread throughout the [[Eurasian steppe]]s and [[Iranian plateau]] from around [[600 BC]] and onwards due to contact with [[Median Empire]]'s vast expanse across Central Asia, which was the native homeland of the early, north-eastern Iranian ethnic groups such as the [[Massagetae]], [[Scythians]], [[Sakas]], and [[Dahae]].<ref name="Farrokh, Kaveh 2005"/> The successive [[Persian Empire]]s which followed the Medes after their downfall in [[550 BC]] took these already long-standing military tactics and horse breeding traditions and infused their centuries of experience and veterency from conflicts against the [[Greek city-states]], [[Babylonian]]s, [[ancient Assyrians|Assyrians]], [[Indo-Scythians]], and [[North Arabian]] tribes, with the significant role cavalry played not only in warfare but everyday life, to form a military reliant almost entirely upon armored horses for battle. |
||
== Spread to Central Asia and the Near East == |
== Spread to Central Asia and the Near East == |
||
When discussing the evolution of the heavily armored horseman, it should be noted that it was not isolated to one focal point during a specific era (such as the [[Iranian plateau]]), but rather developed simultaneously in different parts of [[Central Asia]] (especially among the peoples inhabiting the [[Silk Road]]) as well as within the [[Greater Iran|Iranian subcontinent]]. [[Assyrian Empire|Assyria]] and the [[Khwarezm]] region bear significant importance in fostering |
When discussing the evolution of the heavily armored horseman, it should be noted that it was not isolated to one focal point during a specific era (such as the [[Iranian plateau]]), but rather developed simultaneously in different parts of [[Central Asia]] (especially among the peoples inhabiting the [[Silk Road]]) as well as within the [[Greater Iran|Iranian subcontinent]]. [[Assyrian Empire|Assyria]] and the [[Khwarezm]] region bear significant importance in fostering developement of Cataphract-like cavalry during the [[1st millennium BC]]. Reliefs discovered in the ancient ruins of [[Nimrud]] (the ancient Assyrian city founded by king [[Shalmaneser I]] during the [[13th Century BC]]), depict for the first time riders wearing mail shirts of metal scale, presumably deployed to provide the Assyrians with a tactical advantage over the unprotected mounted archers of their nomadic enemies, primarily the [[Aramaeans]], [[Mushki]], North Arabian tribes and the [[Neo-Babylonian Empire|Babylonians]]. The [[Tiglath-Pileser III]] (745–727 BC) period under which the [[Neo-Assyrian Empire]] was formed and reached its military peak, is believed to have been the first context within which the Assyrian kingdom formed crude regiments of cataphract-like cavalary. Though armed only with a [[Pike (weapon)|pike]], these early horseman still rather qualified as mounted cavalrymen, but when provided with a bow under [[Sennacherib]] (705-681 BC), eventually became capable both of long-range and hand-to-hand combat, mirroring the developement of dual-purpose cataphract archers by the [[Parthian Empire]] during the [[1st Century BC]].<ref>{{harvnb|Eadie|1967|pp=161f.}}</ref> |
||
Archaeological excavations also indicate that by the [[6th century BC]] similar experimentation had taken place among the [[Ancient_Iranian_peoples#List|Iranian peoples]] inhabitating the [[Khwarezm]] region and [[Aral Sea]] basin, such as the [[Massagetae]], [[Dahae]] and [[Saka]]. While the offensive weapons of these prototype cataphracts were identical to those of the Assyrians, they differed in that not only the mount but also the head and flanks of the horse were protected by armour. Whether this development was influenced by the Assyrians, as Rubin postulates,<ref>{{harvnb|Rubin|1955|p=266}}</ref> or perhaps the [[Achaemenid Empire]], or whether they |
Archaeological excavations also indicate that by the [[6th century BC]] similar experimentation had taken place among the [[Ancient_Iranian_peoples#List|Iranian peoples]] inhabitating the [[Khwarezm]] region and [[Aral Sea]] basin, such as the [[Massagetae]], [[Dahae]] and [[Saka]]. While the offensive weapons of these prototype cataphracts were identical to those of the Assyrians, they differed in that not only the mount but also the head and flanks of the horse were protected by armour. Whether this development was influenced by the Assyrians, as Rubin postulates,<ref>{{harvnb|Rubin|1955|p=266}}</ref> or perhaps the [[Achaemenid Empire]], or whether they occured spontaneously and entirely unnrelated to the advances in heavily armored cavalry made in the [[Ancient Near East]], cannot be discerned by the archaeological records left by these mounted nomads.<ref>{{harvnb|Eadie|1967|p=162}}</ref> |
||
The further evolution of these early forms of heavy cavalry in Western Eurasia is not entirely clear. Heavily-armored riders on large horses appear in [[4th century BC]] frescos in the northern [[Black Sea]] region, notably at a time when the [[Scythians]] who relied on light horse archers were superseded by the [[Sarmatians]].<ref>{{harvnb|Rubin|1955|pp=269-270}}</ref> By the [[3rd century BC]], light cavalry units were used in most eastern armies, but still only ''"relatively few states in the East or West attempted to imitate the Assyrian and Chorasmian experiments with mailed cavalry"''.<ref>{{harvnb|Eadie|1967|p=163}}</ref> |
The further evolution of these early forms of heavy cavalry in Western Eurasia is not entirely clear. Heavily-armored riders on large horses appear in [[4th century BC]] frescos in the northern [[Black Sea]] region, notably at a time when the [[Scythians]] who relied on light horse archers were superseded by the [[Sarmatians]].<ref>{{harvnb|Rubin|1955|pp=269-270}}</ref> By the [[3rd century BC]], light cavalry units were used in most eastern armies, but still only ''"relatively few states in the East or West attempted to imitate the Assyrian and Chorasmian experiments with mailed cavalry"''.<ref>{{harvnb|Eadie|1967|p=163}}</ref> |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
Nations in the East occasionally fielded cataphracts mounted on [[camel]]s rather than on horses (the Romans also adopted this practice, calling camel mounted cavalrymen ''[[dromedarii]]''), with obvious benefits for use in arid regions, as well as the fact that the smell of the camels, if up wind, was a guaranteed way of panicking enemy cavalry units that they came into contact with. Balanced against this is the relatively greater vulnerability of camel mounted units to [[caltrops]], due to their having soft padded soles to their feet rather than hooves. |
Nations in the East occasionally fielded cataphracts mounted on [[camel]]s rather than on horses (the Romans also adopted this practice, calling camel mounted cavalrymen ''[[dromedarii]]''), with obvious benefits for use in arid regions, as well as the fact that the smell of the camels, if up wind, was a guaranteed way of panicking enemy cavalry units that they came into contact with. Balanced against this is the relatively greater vulnerability of camel mounted units to [[caltrops]], due to their having soft padded soles to their feet rather than hooves. |
||
Ancient [[War elephants]], although not cavalry per se, |
Ancient [[War elephants]], although not cavalry per se, fufilled a role very similar to that of heavy cavalry such as cataphracts in their use in antiquity. War elephants correspondingly were also heavily armored much like cataphracts, particularly those fielded by the [[Seleucid Empire]], [[Carthaginian Empire]] and the [[Persian Empire]]s (see [[Persian war elephants]]), who incorporated [[scale armor]] and large crested [[howdah]]s (or large carriages mounted directly on the back) onto the elephants, which effectively turned them into mobile missile platforms that could also charge enemy positions. This is analogous to the Eastern cataphract [[horse archer]]s mentioned previously, who carried both bows and lances, and alternated between missile and charge attacks as the terms of a battle dictated. The three to four men manning the howdah, including the driver, known as a [[mahout]], were armed with [[sarissa]]e, [[javelin]]s, [[Pike (weapon)|pikes]] or bows to harass enemy soldiers who attempted to close in and attack the elephants. The tough hide of elephants afforded them considerable protection and the scale armor worn made them almost invulnerable to missiles such as arrows. Cavalry were also easily frightened by the smell and presence of the elephants, particularly if they had never been exposed to them previously, which allowed them to be used as living, mobile fortifications to counter cavalry manoeuvres on the battlefield in addition to artillery platforms.<ref>Ammianus Marcellinus, (353 AD) ''Roman Antiquities'', Boox XXV pp. 483</ref>. |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 07:11, 15 October 2009

A cataphract was a form of heavy cavalry utilised in ancient warfare by a number of peoples in Western Eurasia and the Eurasian Steppe.
The word in English is derived from the Greek: κατάφρακτος Kataphraktos (plural: κατάφρακτοι Kataphraktoi), literally meaning "armored" or "completely enclosed". Historically the cataphract was a very heavily armored horseman, with both the rider and steed draped from head-to-toe in scale armor, while typically wielding a kontos or lance as their weapon.
"... But no sooner had the first light of day appeared, than the glittering coats of mail, girt with bands of steel, and the gleaming cuirasses, seen from afar, showed that the king's forces were at hand." Ammianus Marcellinus, renowned Roman general and ancient historian, describing the sight of Persian cataphracts approaching Roman infantry in Asia Minor, circa 4th Century BC. [1]
Cataphracts served as either the elite cavalry or assault force for most empires and nations that fielded them, primarily used for impetuous charges to break through infantry formations. Chronicled by many historians from the earliest days of Antiquity up until the High Middle Ages, they are in part or wholly believed to have given rise to the Age of Feudalism in Europe and the later European equivalents of Knights and Paladins, via contact with the Byzantine Empire.[2]
Notable peoples and states deploying cataphracts at some point in their history include: the Scythians, Assyrians, Sarmatians, Parthian dynasties, Achaemenid Empire, Sakas Armenia, Seleucids, Pergamenes, the Sassanid Empire, the Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire.
In the West, the fashion for heavily armored Roman cavalry seems to have been a response to the Eastern campaigns of the Parthians and Sassanids in the region referred to as Asia Minor, as well as numerous defeats at the hands of cataphracts across the steppes of Eurasia, the most notable of which is the Battle of Carrhae. Traditionally Roman Cavalry was neither heavily armored nor all that effective, the Roman Equites corps were mainly comprised of lightly armored horsemen bearing spears and swords to chase down stragglers and routing enemies. The adoption of cataphract-like cavalry formations took hold amongst the late Roman army during the 3rd and 4th Centuries AD. The Emperor Gallienus Augustus (253-268 AD) and his general and would-be usurper Aureolus, bear much of the responsibility for the institution of Roman cataphract contingents in the Late Roman army.
Etymology
The genesis is undoubtedly Greek: "Kataphraktos" (or various transliterations such as: "Cataphraktos", "Cataphractos", "Katafraktos",etc.) is composed of the Greek root words: κατά completely plus φρακτός covered, protected, which is interpreted along the lines of "fully armored" or "closed from all sides". The term first appears substantively in Latin, in the writings of Sisennus: "… loricatos, quos cataphractos vocant …", meaning "… the armored, whom they call cataphract."[3]
There appears to be some confusion of the term in the late Roman period, as armored cavalrymen of any sort which were traditionally referred to as Equites in the Republican period, later became exclusively designated as "cataphracts". Vegetius writing in the 4th century described armor of any sort as "cataphracts" - which at the time of writing would have been either lorica segmentata or lorica hamata. Ammianus Marcellinus, noted Roman general and historian of 4th century, mentions the: "cataphracti equites (quos clibanarios dictitant)" – the "cataphract cavalry which the they call Clibanarii," (implying clibanarii is a foreign term, not used in Roman Latin).
Clibanarii is a Latin word for "mail-clad riders", itself a derivative of the Greek: κλιβανοφόροι Klibanophoroi meaning “camp oven-bearers” from the Greek word κλίβανος, meaning "camp oven" or "metallic furnace". However it appears with more frequency in Latin sources than in Greek throughout antiquity. The origins of the original Greek term are twofold: that it was either a humourous reference to the heavily armored cataphracts (as men encased in armor would heat up very quickly much like an oven) or that it was further derived from the Old Persian word: *griwbanar (or *grivbanvar), itself composed of the Iranian roots: griva-pana-bara, which translates into "neck-guard wearer".[4]
Roman chroniclers and historians Arrian, Aelian and Asclepiodotus use the term cataphract in their military treatises to describe any type of cavalry with either partial or full horse and rider armor. The Byzantine historian Leo Diaconis on the other hand, calls them: "πανσιδήρους ιππότας", which would translate as "fully iron-clad knights."[5]
There is therefore some ambiguity as to determining what exactly cataphracts were in late antiquity, as well as determining whether or not they were distinct from clibanarii. Some historians theorise that cataphracts and clibanarii are one and the same type of cavalry, simply termed differently as a result of their divided geographical locations and linguistic preferences. Cataphract-like cavalry under the command of the Western Roman Empire always bore the Latinized variant of the original Greek name: Cataphractarii, where Latin was the official tongue. Those cataphract-like cavalry stationed in the Eastern Roman Empire had no exclusive term designated to them, with both the Latin variant or the Greek innovation Clibanarii being used in historical sources, largely because of the Byzantine's heavy Greek influence (especially after the 7th century when Latin ceased to be the official language). Contemporary sources however sometimes imply that clibanarii were in fact an even heavier type of cavalryman, or formed special-purpose units (such as the late Equites Sagittarii Clibanarii, a Roman equivalent of horse archers, first mentioned in the Notitia Dignitatum). Therefore either side can be argued, but given the fact that the term was used for more than a millennium by various cultures, it stands to reason that different types of fully armored cavalry, in the armies of different nations bore this name, that was simply ascribed to them by Greek and Roman scholars not familiar with the native names for such cavalry.
Indo-Iranian Origins
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2009) |
The reliance on cavalry as a means of warfare in general lies with the ancient inhabitants of the Central Asian steppes in early antiquity, who were one of the first peoples to domesticate the horse and pioneered the development of the chariot[6]. Most of these nomadic tribes and wandering pastoralists circa 2000 BC were largely Bronze-Age, Indo-Iranian (or Indo-Aryan) populations, who migrated from the steppes of Central Asia into the Iranian Plateau and Greater Iran from around 1000 BC to 800 BC (see Indo-Aryan migration). Two of these tribes are attested based upon archaelogical evidence: the Mitanni and the Kassites. Although evidence is scant, they are believed to have raised and bred horses for specific purposes, as is evidenced by the large archaeological record of their use of the chariot and several treatises on the training of chariot horses[7]. The one founding prerequisite towards the development of cataphract cavalry in the Ancient Near East, apart from advanced metalworking techniques and the necessary grazing pastures for raising horses, was the evolution of selective breeding and animal husbandry. Cataphract cavalry needed to be immensely strong and endurant horses, and without selectively breeding horses for muscular strength and hardiness they would have surely not been able to bear the immense loads of armor and a rider during the strain of battle[8]. The Near East is generally believed to have been the focal point for where this first occurred.
The above early Indo-Iranian kingdoms and statehoods were to a large degree the ancestors of the Medians who would found the very first Persian Empire in 625 BC, and of the north-eastern Iranian tribes. It was the Median Empire that left the first written proof of horse breeding around the 7th century BC, being the first to propagate a specific horse breed known as the Nisean, which originated in the Zagros Mountains, for use as heavy cavalry[9]. The Nisean would go on to become renowned in the Ancient World and particularly in Ancient Persia, being the mount of nobility and of their warhorses, sometimes referred to as "Nisaean chargers", who were highly sought after by the Greeks and are believed to have influenced many modern horse breeds. With the growing aggressiveness played by the role of cavalry in warfare, protection of the rider and the horse became paramount. This was especially true of peoples who treated cavalry as the basic arm of their military, and indeed, the backbone of the Ancient Persian military such as that of the Medes or the successive Persian dynasties that followed them, was the horse. To a larger extent, the same can said of all the Ancient Iranian peoples, as second only to perhaps the bow, horses were held in reverence and importance in these societies as their preferred and mastered medium of warfare, due to an intrinsic link throughout history with the domestication and evolution of the horse.
These early riding traditions, which were strongly tied to the ruling caste of nobility (as only those of noble birth or caste could become cavalry warriors), now spread throughout the Eurasian steppes and Iranian plateau from around 600 BC and onwards due to contact with Median Empire's vast expanse across Central Asia, which was the native homeland of the early, north-eastern Iranian ethnic groups such as the Massagetae, Scythians, Sakas, and Dahae.[9] The successive Persian Empires which followed the Medes after their downfall in 550 BC took these already long-standing military tactics and horse breeding traditions and infused their centuries of experience and veterency from conflicts against the Greek city-states, Babylonians, Assyrians, Indo-Scythians, and North Arabian tribes, with the significant role cavalry played not only in warfare but everyday life, to form a military reliant almost entirely upon armored horses for battle.
Spread to Central Asia and the Near East
When discussing the evolution of the heavily armored horseman, it should be noted that it was not isolated to one focal point during a specific era (such as the Iranian plateau), but rather developed simultaneously in different parts of Central Asia (especially among the peoples inhabiting the Silk Road) as well as within the Iranian subcontinent. Assyria and the Khwarezm region bear significant importance in fostering developement of Cataphract-like cavalry during the 1st millennium BC. Reliefs discovered in the ancient ruins of Nimrud (the ancient Assyrian city founded by king Shalmaneser I during the 13th Century BC), depict for the first time riders wearing mail shirts of metal scale, presumably deployed to provide the Assyrians with a tactical advantage over the unprotected mounted archers of their nomadic enemies, primarily the Aramaeans, Mushki, North Arabian tribes and the Babylonians. The Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727 BC) period under which the Neo-Assyrian Empire was formed and reached its military peak, is believed to have been the first context within which the Assyrian kingdom formed crude regiments of cataphract-like cavalary. Though armed only with a pike, these early horseman still rather qualified as mounted cavalrymen, but when provided with a bow under Sennacherib (705-681 BC), eventually became capable both of long-range and hand-to-hand combat, mirroring the developement of dual-purpose cataphract archers by the Parthian Empire during the 1st Century BC.[10]
Archaeological excavations also indicate that by the 6th century BC similar experimentation had taken place among the Iranian peoples inhabitating the Khwarezm region and Aral Sea basin, such as the Massagetae, Dahae and Saka. While the offensive weapons of these prototype cataphracts were identical to those of the Assyrians, they differed in that not only the mount but also the head and flanks of the horse were protected by armour. Whether this development was influenced by the Assyrians, as Rubin postulates,[11] or perhaps the Achaemenid Empire, or whether they occured spontaneously and entirely unnrelated to the advances in heavily armored cavalry made in the Ancient Near East, cannot be discerned by the archaeological records left by these mounted nomads.[12]
The further evolution of these early forms of heavy cavalry in Western Eurasia is not entirely clear. Heavily-armored riders on large horses appear in 4th century BC frescos in the northern Black Sea region, notably at a time when the Scythians who relied on light horse archers were superseded by the Sarmatians.[13] By the 3rd century BC, light cavalry units were used in most eastern armies, but still only "relatively few states in the East or West attempted to imitate the Assyrian and Chorasmian experiments with mailed cavalry".[14]
Exposure to Western Civilization

The western Greeks then first encountered cataphracts during the Greco-Persian Wars of 400 BC with the Achaemenid Empire. The Ionian Revolt, an uprising against Persian rule in Asia minor which preluded the First Persian invasion of Greece, is very likely the first Western encounter of cataphract cavalry, and to a degree heavy cavalry in general. The cataphract was then widely adopted by the Seleucid Empire, the Hellenistic successors of Alexander the Great's kingdom who reigned over conquered Persia and Asia minor after his death in 323 BC. The Parthians, who wrested control over their native Persia from the last Seleucid Kingdom in the East in 247 BC, were also noted for their reliance upon cataphracts as well as horse archers in battle.
The Romans first encountered cataphracts during their wars with the 6th Seleucid regent, Antiochus III the Great, at the Battle of Thermopylae, in 191 BC. One year later in the Battle of Magnesia, the final chapter in the Roman–Syrian War between Antiochus and Rome, the Seleucid cataphracts managed to rout the Roman infantry but their contribution was not enough for Antiochus to decisively win the battle, and the Romans triumphed once more, leaving a total of four victories against the bitterly defeated Antiochus who was forced to sign an armistice. Yet the battle is the first reported incident of frontal cavalry charge against a heavy infantry phalanx. The first recorded deployment and use of cataphracts by the Roman Empire comes far later in the 2nd Century AD, during the reign of emperor Hadrian (117-138 AD), who created the ala I Gallorum et Pannoniorum catafractata. A key architect in the process of adopting cataphracts for usage in the Roman military was evidently the Roman emperor Gallienus who created a highly mobile force in response to the multiple threats along the northern and eastern frontier.[15]. Rome's contact and drawn-out struggle with their main rival in the east during Classical antiquity, the Parthians, is believed to have inspired their adoption of cataphract cavalry.
The Romans fought a prolonged and indecisive campaign in the east against the Parthians beginning in 53 BC, commencing with the defeat of Marcus Licinius Crassus (close benefactor of Julius Caesar) and his 35,000 legionaries at the Carrhae. This initially unexpected and humiliating defeat for Rome was followed by numerous campaigns over the next two centuries entailing many notable engagements such as: the Battle of Cilician Gates, Mount Gindarus, Mark Antony's Parthian Campaign and finally culminating in the bloody Battle of Nisibis in 217 AD, which resulted in a slight Parthian victory and Emperor Macrinus being forced to concede peace with Parthia[16][17]. As a result of this lingering period of exposure to cataphracts, by the fourth century the Roman Empire had adopted a number of vexillations of mercenary cataphract cavalry (see the Notitia Dignitatum), such as the Sarmatian Auxiliaries[18][19]. The Romans deployed both native and mercenary units of cataphracts throughout the Empire, from Asia Minor all the way to Britain, where a contingent of 5,500 Sarmatian cataphracts were posted in the 3rd century by emperor Marcus Aurelius (see Roman departure from Britain). This tradition was later paralleled by the rise of Feudalism in Christian Europe in the Early Middle Ages, and the establishment of the Knighthood particularly during the Crusades[20], while the Byzantine Empire continued to maintain a very active corps of cataphracts long after their Western counterparts fell in 476 AD.
Appearance and Equipment
Cataphracts were almost universally clad in some form of scale armour (Greek: φαλιδωτός "Falidotos", equivalent to the Roman Lorica squamata) which was flexible enough to give the rider and horse a good degree of motion but strong enough to resist the immense impact of a thunderous charge into infantry formations. Scale armour was made from overlapping, rounded plates of bronze or iron (varying in thickness from 4 to 6 millimeters), which had two or four holes drilled into the sides, to be threaded with a bronze wire that was then sewn onto an undergarment of leather or animal hide, worn by the horse. A full set of cataphract armor consisted of approximately 1,300 or so "scales", and could weigh an astonishing 40 kilograms or 88 pounds (not inclusive of the rider's body weight)[4]. Less commonly, plated mail or lamellar armor (which is similar in appearance but divergent in design, as it has no backing) was substituted for scale armor, while for the most part the rider wore chain mail. Specifically, the horse armor was usually sectional (not joined together as a cohesive "suit"), with large plates of scales tied together around the animal's waist, flank, shoulders, neck and head (especially along the breastplate of the saddle) independently to give a further degree of movement for the horse and to allow the armor to be affixed to the horse reasonably tightly so that it should not loosen too much during movement. Usually but not always, a close-fitting helmet that covered the head and neck was worn by the rider; the Persian variants extended this even further, and encased the entire wearer's head in metal, leaving only minute slits for the nose and eyes as openings. Ammianus Marcellinus, a noted Roman historian and general who served in the army of Constantius II in Gaul and Persia, and fought against the Sassanid army under Julian the Apostate, described the sight of a contingent of massed Persian cataphracts in the 4th century:
- "… all the companies were clad in iron, and all parts of their bodies were covered with thick plates, so fitted that the stiff-joints conformed with those of their limbs; and the forms of human faces were so skillfully fitted to their heads, that since their entire body was covered with metal, arrows that fell upon them could lodge only where they could see a little through tiny openings opposite the pupil of the eye, or where through the tip of their nose they were able to get a little breath. Of these some, who were armed with pikes, stood so motionless that you would think them held fast by clamps of bronze."[21]
Cataphracts would often be equipped with an additional side-arm such as a sword or mace, for use in the melee that often followed a charge. Some wore armour that was primarily frontal: providing protection for a charge and against missiles yet offering relief from the weight and encumbrance of a full suit. In yet another variation, cataphracts in some field armies were not equipped with shields at all, particularly if they had heavy body armor, as having both hands occupied with a shield and lance left no room to effectively steer the horse. Eastern and Persian cataphracts, particularly those of the Sassanid Empire carried bows as well as blunt-force weapons, to soften up enemy formations before an eventual attack; reflecting upon the longstanding Persian tradition of horse archery and its use in battle by successive Persian Empires.
Cataphract lances (known in Greek as a Kontos ("oar") or in Latin as a Contus) appeared much like the Greek army's Sarissae used by the famed Greek phalanxes as an anti-cavalry weapon. They were roughly four meters in length, with a capped point made of iron, bronze or even animal bone and usually wielded with both hands. Most had a chain attached to the horse's neck, and at the end by a fastening attached to the horse's hind leg, which supported the use of the lance by transferring the full momentum of a horse's gallop to the thrust of the charge. One reason for this was the lack of stirrups (especially amongst Western armies); although the traditional Roman saddle had four horns with which to secure the rider[22], nevertheless these were largely inadequate for keeping a soldier seated upon the full impact of a charge action. During the Sassanid era, the Persian military developed an innovative solution to overcome the lack of stirrups and effectively "fasten" the rider to the horse's body. Persian horseman had a cantle at the back of the saddle and two guard clamps which curved across the top of the rider's thighs and fastened to the saddle, thereby enabling the rider to stay properly seated, especially during violent contact in battle[23]
Tactics and Deployment

While they varied in design and appearance, cataphracts were universally the heavy assault force of most nations that deployed them, acting as "shock troops" to deliver the bulk of an offensive manoeuvre, while being supported by various forms of infantry and archers (both mounted and unmounted). While their roles in military history often seem to overlap with lancers or generic heavy cavalry, they should not be considered analogous to these forms of cavalry, and instead represent the separate evolution of a very distinct class of heavy cavalry in the Near East that had certain connotations of prestige, nobility and Esprit de corps attached to them. In many armies this reflected upon social stratification or a caste system, as only the wealthiest men of noble birth could afford the panoply of the cataphract, not to mention the costs of supporting several war horses and ample amounts of weaponry and armour.
Fire support was deemed particularly important for the proper deployment of cataphracts. The Parthian army that defeated the Romans at Carrhae in 53 BC operated primarily as a combined arms team of cataphracts and horse archers against the Roman heavy infantry. Archer fire was concentrated on the dense Roman ranks which prompted the legionaries to loosen their formation in order to present a wider target area for the enemy. This then made them fatally susceptible to a massed cataphract charge. The end result was a far smaller force of Parthian Cataphracts and Horse Archers wiping out a Roman cohort four times their size numerically, due to a combination of fire and movement, which pinned the enemy down, wore them out and left them vulnerable to a concluding deathblow.
The cataphract charge was very effective due to the disciplined riders and the large numbers of horses deployed. As early as the 1st Century BC, especially during the expansionist campaigns of the Parthian and Sassanid dynasties, Eastern Iranian cataphracts employed by the Scythians, Sarmatians, Parthians and Sassanids presented a grievous problem for the traditionally less mobile, infantry-dependant Roman Empire. Roman writers throughout imperial history made much of the terror of facing cataphracts, let alone receiving their charge. Parthian armies thus repeatedly repelled Roman incursions across the Euphrates, due in large part to the Roman's ineptness in dealing with mobile warfare and particularly cataphracts.
Persian cataphracts were a contiguous division known as the Savaran (Persian: سواران, literally meaning "rider of the horse") during the era of the Sassanid army, and remained a formidable force from the 3rd to 7th centuries until the collapse of the Sassanid Empire[2]. Initially the Sassanid dynasty continued the cavalry traditions of the Parthians, fielding units of super-heavy cavalry. This gradually fell out of favour and a "universal" cavalryman was developed during the later 3rd century, able to fight as a mounted archer as well as a cataphract. This was perhaps in response to the harassing, nomadic combat style used by the Sassanid's northern neighbours who frequently raided their borders, such as the Huns, Hephthalites, Xiongnu, Scythians and Kushans, all of which favoured hit and run tactics and relied almost solely upon horse archers for combat. However as the Roman-Persian wars intensified to the West, sweeping military reforms were again reestablished. During the 4th century, Shapur II of Persia attempted to reinstate the super-heavy cataphracts of previous Persian dynasties to the counter the formation of the new, Roman Comitatenses, the dedicated, front-line legionaries who were the heavy infantry of the late Roman Empire. The elite of the Persian cataphracts, known as the Pushtigban Body Guards, were sourced from the very best of the Savaran divisions, and were akin in their deployment and military role to their Roman counterparts, the Praetorian Guard, used exclusively by Roman Emperors. Ammianus Marcellinus remarked in his memoirs that members of the Pushtigban were able impale two Roman soldiers on their spears at once with a single furious charge. Persian cataphract archery also seems to have been again revived in late antiquity, perhaps as a response (or even a stimulus) to a an emerging trend of the late Roman army towards mobility and versatility in their means of warfare.
In an ironic twist, the elite of the Roman army by the 6th century had become the cataphract, modelled after the very force that had famously defeated and slaughtered their forebears numerous times more than 500 years earlier. During the Iberian and Lazic wars initiated in the Caucasus by Justinian I of the 6th century, it was noted by Procopius that Persian cataphract archers were adept at firing their arrows in very quick succession and saturating enemy positions but with little hitting power, resulting in mostly non-incapacitating limb wounds for the enemy. The newly developed, Roman cataphracts on the other hand released their shots with far more power, able to launch arrows with lethal kinetic energy behind them, albeit at a slower pace.
Later History and Usage in the Early Middle Ages

Some cataphracts fielded by the later Roman Empire were also equipped with heavy, lead-weight darts called Martiobarbuli, akin to the Plumbata used by late Roman infantry. These were to be hurled at the enemy lines during or just before a charge, to disorder the defensive formation immediately before the impact of the lances. With or without darts, a cataphract charge would usually be supported by some kind of missile troops (mounted or unmounted) placed on either flank of the enemy formation. Some armies formalised this tactic by deploying separate types of cataphract, the conventional, very heavily armored, bowless lancer for the primary charge and a dual purpose, lance-and-bow cataphract for supporting units.
Interestingly, references to Byzantine cataphracts seemed to have disappeared in the late 6th century, as the famed manual of war, the Strategikon of Maurice, published during the same period made no mention of cataphracts or their tactical employment. This absence persisted through most of the Thematic period until the cataphracts reappeared in Emperor Leo VI's Sylloge Taktikon, probably reflecting a revival that paralleled the transformation of the Byzantine army from a largely defensive force, into an offensive force. The cataphracts deployed by the Byzantine Empire (most noticeably after the 7th century when Latin ceased to be the official language of the empire) were exclusively referred to as Kataphraktoi, due to the Byzantine Empire's strong Greek influence.
These later Byzantine cataphracts were a much feared force in their heyday. The army of Emperor Nicephorus II, relied on its cataphracts as its nucleus, coupling cataphract archers with cataphract lancers to create a self-perpetuating "hammer blow" tactic where the cataphract lancers would charge the enemy, disengage, and charge again and again until the enemy broke and routed, all the while supported by cataphract archers who continually pelted the enemy with missile barrages.
Contemporary depictions however imply that Byzantine cataphracts were not as completely armored as the earlier Roman and Sassanid incarnation. The horse armour was noticeably lighter than earlier examples, being made of leather scales or quilted cloth rather than metal at all. Byzantine cataphracts of the 10th century were drawn from the ranks of the middle class landowners through the theme system, providing the Byzantine Empire with a motivated and professional force that could support its own war-time expenditures. The previously mentioned term "Clibanarii" (possibly representing a distinct class of cavalry from the cataphract), was brought to the fore in the 10th and 11th centuries of the Byzantine Empire, known in Byzantine Greek as: Klibanophoros, which appeared to be a throwback to the super-heavy cavalry of earlier antiquity. These cataphracts specialised in forming a wedge formation and penetrating enemy formations to create gaps, enabling lighter troops to make a breakthrough. Alternatively, they were used to target the head of the enemy force, typically a foreign emperor.
As with the original cataphracts, the Leonian/Nikephorian units seemed to have fallen out of favour and use with their handlers, making their last, recorded appearance in battle in 970 and the last record of their existence in 1001, referred to as being posted to garrison duty. If they had indeed disappeared, then it is possible that they were revived once again when the Komnenian restoration, a period of thorough financial, territorial and military reform that changed the Byzantine army of previous ages, which is referred to separately as the Komnenian army after the 12th century[24]. Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (1081 to 1118) established a new military force from the ground up, which was directly responsible for transforming the ageing Byzantine Empire from one of the weakest periods in its existence, into a major economic and military power, akin to its existence during the golden age of Justinian I. However, even in this case it seems that the cataphract was eventually superseded by other types of heavy cavalry.
It is difficult to determine when exactly the cataphract saw his final day. After all, cataphracts and knights fulfilled a roughly similar role on the medieval battlefield, and the armored knight survived well into the Early modern era of Europe. The Byzantine army maintained units of heavily armored cavalrymen up until its final years, mostly in the form of Western European Latinikon mercenaries, while neighbouring Bulgars, Serbs, Avars, Russian states, Alans, Lithuanians, Khazars and other eastern European and Eurasian peoples emulated Byzantine military equipment.
As western European metalwork became increasingly sophisticated, the traditional image of the cataphract's awe-inspiring might and presence quickly evaporated. From the 15th century and onwards; chain mail, lamellar armor, and scale armour seemed to fall out of favour with eastern noble cavalrymen as elaborate and robust plate cuirasses arrived from the west, this in combination with the advent of early firearms, cannon and gunpowder rendered the relatively thin and flexible armor of cataphracts obsolete. Despite these advances, the Byzantine army, often unable to afford newer equipment en masse, was left ill-equipped and forced to rely on its increasingly archaic military technology. The cataphract finally passed into the pages of history with the Fall of Constantinople on May the 29th , 1453, when the last nation to refer to its cavalrymen as cataphracts fell (see Decline of the Byzantine Empire).
Cataphracts in East Asia

Comprehensive armor for horses might have been used in China as early as the Three Kingdoms period. It wasn't until the early 4th century AD however, that cataphracts came into widespread use among the Xianbei tribes of inner Mongolia and southern Manchuria, which led to the adoption of cataphracts by the Chinese armies during the Northern and Southern Dynasties era. Numerous burial seals, military figurines, murals, and official reliefs from this period testify to the great importance of armored cavalry in warfare. Later, the Sui empire maintained the use of cataphracts, but the use of horse armour declined in the Tang empire (becoming limited to ceremonial guards of honor) for reasons that remain unclear. The use of cataphracts was then revived in the Liao, Western Xia, and Jin dynasties - the super-heavy cataphracts of the Xia and Jin were especially effective and were known as Iron Sparrowhawks and Iron Pagodas respectively. The Song Empire also developed cataphract units to counter those of the Liao, Xia, and Jin, but the shortage of suitable grazing lands and horse pastures in Song territory made the effective breeding and maintenance of Song cavalry far more difficult, in addition to the Song's vulnerability to continual raids by the emerging Mongol Empire for over two decades, which eventually vanquished them in 1279 at the hands of Kublai Khan. The Yuan Dynasty, successors to the Song, which were a continuation of the Mongolian Empire seem to have all but forgotten the cataphract traditions of their predecessors, and the last remaining traces of cataphracts in Southeast Asia seems to have died with the downfall of the Yuan in 1368.
Other East Asian cultures were also known to have used cataphracts during a similar time period to the Chinese. Korean cataphracts reached their pinnacle in Korea's Three Kingdoms period. Meanwhile, the Tibetan Empire utilized cataphracts as the elite assault force of its armies for much of its history.
Related Cavalry
In addition to ordinary cataphract types the Byzantine Empire sometimes fielded a very heavy type of cavalry known as a clibanarius, literally meaning "boiler boy" (pl. clibanarii), but more properly translating into "camp oven bearers", a sort of humorous reference to that fact that men encased in metal armor would almost certainly feel incredibly hot and perspire rapidly, much like an oven. The clibinarii are vaguely attested in Eastern Roman sources but there is dispute over their actual role and difference from cataphracts in warfare.
The 5th century Notitia Dignitatum mentions a specialist unit of clibanarii known as the Equites Sagittarii Clibanarii - evidently a unit of heavily armored horse archers based on the heavy cavalry of contemporary Persian armies.
An anonymous 6th century Roman military treatise also proposed one exotic experimental unit of scythed chariots with cataphract lancers mounted on the chariot's horses, though there is no evidence that this unit ever materialised.
Nations in the East occasionally fielded cataphracts mounted on camels rather than on horses (the Romans also adopted this practice, calling camel mounted cavalrymen dromedarii), with obvious benefits for use in arid regions, as well as the fact that the smell of the camels, if up wind, was a guaranteed way of panicking enemy cavalry units that they came into contact with. Balanced against this is the relatively greater vulnerability of camel mounted units to caltrops, due to their having soft padded soles to their feet rather than hooves.
Ancient War elephants, although not cavalry per se, fufilled a role very similar to that of heavy cavalry such as cataphracts in their use in antiquity. War elephants correspondingly were also heavily armored much like cataphracts, particularly those fielded by the Seleucid Empire, Carthaginian Empire and the Persian Empires (see Persian war elephants), who incorporated scale armor and large crested howdahs (or large carriages mounted directly on the back) onto the elephants, which effectively turned them into mobile missile platforms that could also charge enemy positions. This is analogous to the Eastern cataphract horse archers mentioned previously, who carried both bows and lances, and alternated between missile and charge attacks as the terms of a battle dictated. The three to four men manning the howdah, including the driver, known as a mahout, were armed with sarissae, javelins, pikes or bows to harass enemy soldiers who attempted to close in and attack the elephants. The tough hide of elephants afforded them considerable protection and the scale armor worn made them almost invulnerable to missiles such as arrows. Cavalry were also easily frightened by the smell and presence of the elephants, particularly if they had never been exposed to them previously, which allowed them to be used as living, mobile fortifications to counter cavalry manoeuvres on the battlefield in addition to artillery platforms.[25].
See also
- Heavy cavalry
- Lancer
- Clibanarii
- Horses in warfare
- Horse archer
- Sassanid army
- Byzantine army
- Komnenian army
- Late Roman army
Footnotes
- ^ Ammianus Marcellinus, (353 AD) Roman Antiquities, Boox XXV pp. 477
- ^ a b Nell, Grant S. (1995) The Savaran: The Original Knights. University of Oklahoma Press.
- ^ Nikonorov, Valerii P. (1998) Cataphracti, Catafractarii and Clibanarii: Another Look at the old problem of their Identifications. In Voennaia arkheologiia: Oruzhie i voennoe delo v istoricheskoi i sotsial.noi perspektive (Military Archaeology: Weaponry and Warfare in the Historical and Social Perspective). St. Petersburg:. pp. 131-138.
- ^ a b Nicolle, David (1992) Romano-Byzantine Armies, 4th–9th Centuries. Osprey Publishing.
- ^ Leo Diaconis, Historiae 4.3, 5.2, 8.9
- ^ Mielczarek, Mariusz (1993) Cataphracti and Clibanarii. Studies on the Heavy Armored Cavalry of the Ancient World, p. 14
- ^ Robert Drews, "The Coming of the Greeks: Indo-European Conquests in the Aegean and the Near East.", Princeton University Press, Chariot Warfare. pg 61
- ^ Perevalov, S. M. (translated M. E. Sharpe) (Spring 2002). "The Sarmatian Lance and the Sarmatian Horse-Riding Posture". Anthropology & Archeology of Eurasia 41 (4): 7–21.
- ^ a b Farrokh, Kaveh (2005) Sassanian Elite Cavalry, AD224-642. Osprey Publishing.
- ^ Eadie 1967, pp. 161f.
- ^ Rubin 1955, p. 266
- ^ Eadie 1967, p. 162
- ^ Rubin 1955, pp. 269–270
- ^ Eadie 1967, p. 163
- ^ Eadie 1967, p. 168
- ^ Eadie 1967, pp. 163f.
- ^ Perevalov 2002, p. 10
- ^ Perevalov 2002, pp. 10ff.
- ^ Eadie 1967, p. 166
- ^ Kaveh Farrokh. Dr. David Khoupenia. http://www.ghandchi.com/iranscope/Anthology/KavehFarrokh/Khoupenia/index.html. Retrieved 3 September 2009.
- ^ Ammianus Marcellinus, (353 AD) Roman Antiquities, Boox XXV pp. 481
- ^ Driel-Murray, C. van; Connolly, P. (1991) The Roman cavalry saddle. Britannia 22, pp. 33-50
- ^ Shahbazi, A. Sh. (2009) Sassanian Army.
- ^ J. Birkenmeier in "The development of the Komnenian army: 1081-1180"
- ^ Ammianus Marcellinus, (353 AD) Roman Antiquities, Boox XXV pp. 483
References
- Bivar, A. D. H. (1972), "Cavalry Equipment and Tactics on the Euphrates Frontier", Dumbarton Oaks Papers, 26: 271–291
- Campbell, Brian (1987), "Teach Yourself How to Be a General", Journal of Roman Studies, 77: 13–29
- Eadie, John W. (1967), "The Development of Roman Mailed Cavalry", Journal of Roman Studies, 57 (1/2): 161–173
- Nikonorov, Valerii P. (1985a) The Parthian Cataphracts In Chetvertaia vsesoiuznaia shkola molodykh vostokovedov. T. I. Moscow. pp. 65–67.
- Smith, William et al. (1890) A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities. 3rd edition. Article Cataphracti. The text of this book is now in the public domain.
- Nikonorov, Valerii P. (1985b) The Development of Horse Defensive Equipment in the Antique Epoch.In Kruglikova, I. T. (ed.), Zheleznyi vek Kavkaza, Srednei Azii i Sibiri. Kratkie soobshcheniia Instituta arkheologii Akademii nauk SSSR. 184. Moscow: Nauka, 1985, pp. 30–35.
- Nikonorov, Valerii P. (1998) Cataphracti, Catafractarii and Clibanarii: Another Look at the old problem of their Identifications. In Voennaia arkheologiia: Oruzhie i voennoe delo v istoricheskoi i sotsial.noi perspektive (Military Archaeology: Weaponry and Warfare in the Historical and Social Perspective). St. Petersburg:. pp. 131–138.
- Perevalov, S. M. (2002), "The Sarmatian Lance and the Sarmatian Horse-Riding Posture", Anthropology & Archeology of Eurasia, 41 (4): 7–21
- Rubin, Berthold (1955), "Die Entstehung der Kataphraktenreiterei im Lichte der chorezmischen Ausgrabungen", Historia, 4: 264–283
- Warry, John Gibson (1980) Warfare in the classical world: an illustrated encyclopedia of weapons, warriors, and warfare in the ancient civilisations of Greece and Rome. New York, St. Martin's Press.
- Macdowall, Simon (1995) Late Roman Cavalryman, 236-565AD. Osprey Publishing.
- Farrokh, Kaveh (2005) Sassanian Elite Cavalry, AD224-642. Osprey Publishing.
- Nell, Grant S. (1995) The Savaran: The Original Knights. University of Oklahoma Press.
- Marcellinus, Ammianus (353 AD), Roman Antiquities, Boox XXV pp. 481.
External links
- Types of cavalry unit in the army of ancient Rome
- Military units and formations of the Hellenistic world
- Late Roman military units
- Military units and formations of the Sassanid Empire
- Military units and formations of the Byzantine Empire
- Military history of the Parthian empire
- Sarmatians
- History of Armenia
- Tang Dynasty
