Amphibian: Difference between revisions
Br'er Rabbit (talk | contribs) Adding/improving reference(s) | Assisted by Citation bot r419 |
|||
| (96 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{pp-vandalism|expiry=2 August 2012|small=yes}} |
|||
{{other uses}} |
{{other uses}} |
||
{{pp-move-indef}} |
{{pp-move-indef}} |
||
{{automatic taxobox |
{{automatic taxobox |
||
| name=Amphibians |
| name = Amphibians |
||
| fossil_range= {{fossil range|Late Devonian|present}} |
| fossil_range = {{fossil range|Late Devonian|present}} |
||
| image = Lissamphibia.jpg |
| image = Lissamphibia.jpg |
||
| image_width = 280px |
| image_width = 280px |
||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
:: Order [[Anura]] |
:: Order [[Anura]] |
||
:: Order [[Salamander|Caudata]] |
:: Order [[Salamander|Caudata]] |
||
:: Order [[Caecilian|Gymnophiona]] |
:: Order [[Caecilian|Gymnophiona]]</div> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Amphibians''', members of the [[Class (biology)|class]] '''Amphibia''', whose living forms include [[frog]]s, [[salamander]]s, [[newt]]s and [[caecilian]]s, are [[ectotherm]]ic [[tetrapod]] [[vertebrates]] whose [[amniote|non-amniote]] eggs are not surrounded by membranes. Most amphibians lay their eggs in water, with their [[larva]]e undergoing [[metamorphosis]] from a juvenile form with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Some, however, like the [[Common Coquí]] frog develop directly into the adult form, while others like [[Mudpuppy|Mudpuppies]] and [[olm]]s are [[Pedomorphosis|paedomorphs]] that retain the juvenile gilled water-breathing form throughout life. Adult amphibians also use their skin for respiration, with some small terrestrial salamanders even lacking lungs. |
|||
'''Amphibians''' are members of the [[Class (biology)|class]] '''Amphibia''', whose living forms include frogs, toads, salamanders, newts and caecilians. They are cold-blooded, [[tetrapod]] vertebrates. Most have four limbs and live in fresh water or on land but the caecilians, though included in the group, live in burrows in damp soil and are limbless. Amphibians typically have a larval stage that lives in water but there are many different behavioural adaptations that have developed among species to bypass this necessity. The young undergo [[metamorphosis]] from a larval form with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians also use their skin for respiration and some small terrestrial salamanders rely entirely on this and have no lungs. |
|||
The earliest amphibians evolved in the [[Devonian Period]] from [[sarcopterygian]] fish with lungs and bony-limbed fins,<ref name="evoamphib">[http://sci.waikato.ac.nz/evolution/AnimalEvolution.shtml#evolutionofamphibian Waikato - Evolution of amphibians]</ref> features that were helpful in adapting to dry land. They diversified and became dominant during the [[Carboniferous]] and [[Permian]] periods,<ref name="preamphib">[http://dinosaurs.about.com/od/otherprehistoriclife/a/prehistoric-amphibians.htm About.com - Prehistoric amphibians]</ref> but were later displaced by reptiles and other vertebrates. Over time, amphibians shrank in size and decreased in diversity, leaving only the modern subclass [[Lissamphibia]]. |
|||
The earliest amphibians evolved in the [[Devonian Period]] from [[sarcopterygian]] fish with lungs and bony-limbed fins,<ref name="evoamphib">[http://sci.waikato.ac.nz/evolution/AnimalEvolution.shtml#evolutionofamphibian Waikato – Evolution of amphibians]</ref> features that were helpful in adapting to dry land. They diversified and became dominant during the [[Carboniferous]] and [[Permian]] periods,<ref name="preamphib">[http://dinosaurs.about.com/od/otherprehistoriclife/a/prehistoric-amphibians.htm About.com – Prehistoric amphibians]</ref> but were later displaced by reptiles and other vertebrates. Over time, amphibians shrank in size and decreased in diversity, leaving only the modern subclass [[Lissamphibia]]. |
|||
The three modern orders of amphibians are the [[Anura]] (frogs and toads), [[Caudata]] (salamanders and newts) and [[Gymnophiona]] (caecilians, limbless amphibians that resemble large earthworms with jaws). The total number of known amphibian species is approximately 7,000.<ref name=species>[http://fds.oup.com/www.oup.com/pdf/13/9780199541188_chapter1.pdf Amphibian diversity and life history].</ref> They are superficially similar to [[reptile]]s, but reptiles, along with mammals and birds, are [[amniotes]], having impervious membranes that surround the egg. With their often complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often [[ecological indicator]]s,<ref name=Waddle>[http://etd.fcla.edu/UF/UFE0016760/waddle_j.pdf Waddle, J, Use of amphibians as ecosystem indicator species]</ref> and in recent decades there has been a dramatic [[decline in amphibian populations]] of many species around the globe. The smallest vertebrate in the world is the [[New Guinea]] frog, ''[[Paedophryne amauensis]]''.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Rittmeyer |first1=Eric N. |last2=Allison |first2=Allen |last3=Gründler |first3=Michael C. |last4=Thompson |first4=Derrick K. |last5=Austin |first5=Christopher C. |year=2012 |title=Ecological guild evolution and the discovery of the world's smallest vertebrate |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages= |publisher= |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0029797 |url=http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0029797 |accessdate=2012-01-11 }}</ref> The largest amphibian is the Chinese Giant Salamander, ''[[Andrias davidianus]]''.<ref>{{cite book | author = Wood, Gerald |url = | title =The Guinness Book of Animal Facts and Feats| year = 1983 | isbn = 978-0-85112-235-9}}</ref> The study of amphibians is called batrachology while the study of both [[reptile]]s and amphibians is called [[herpetology]]. |
|||
The three modern orders of amphibians are the [[Anura]] (frogs and toads), [[Caudata]] (salamanders and newts) and [[Gymnophiona]] (caecilians, limbless amphibians that resemble large earthworms with jaws). The total number of known amphibian species is approximately 7,000 of which nearly 90% are frogs.<ref name="species">[http://fds.oup.com/www.oup.com/pdf/13/9780199541188_chapter1.pdf Amphibian diversity and life history].</ref> They are superficially similar to [[reptile]]s, but reptiles, along with mammals and birds, are [[amniotes]], having impervious membranes that surround the egg. With their often complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often [[ecological indicator]]s,<ref name="Waddle">[http://etd.fcla.edu/UF/UFE0016760/waddle_j.pdf Waddle, J, Use of amphibians as ecosystem indicator species]</ref> and in recent decades there has been a dramatic [[decline in amphibian populations]] of many species around the globe. The smallest vertebrate in the world is the [[New Guinea]] frog, ''[[Paedophryne amauensis]]''.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Rittmeyer |first1=Eric N. |last2=Allison |first2=Allen |last3=Gründler |first3=Michael C. |last4=Thompson |first4=Derrick K. |last5=Austin |first5=Christopher C. |year=2012 |title=Ecological guild evolution and the discovery of the world's smallest vertebrate |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages= e29797|publisher= |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0029797 |url=http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0029797 |accessdate=2012-01-11 |editor1-last=Etges |editor1-first=William J |pmid=22253785 |pmc=3256195 }}</ref> The largest amphibian is the Chinese Giant Salamander, ''[[Andrias davidianus]]''.<ref>{{cite book | author = Wood, Gerald |url = | title =The Guinness Book of Animal Facts and Feats| year = 1983 | isbn = 978-0-85112-235-9}}</ref> The study of amphibians is called batrachology while the study of both [[reptile]]s and amphibians is called [[herpetology]]. |
|||
==Etymology== |
|||
[[File:Paratype of Paedophryne amauensis (LSUMZ 95004).png|thumb|right|The world's smallest [[vertebrate]], ''[[Paedophryne amauensis]]'' sitting on a [[Dime (United States coin)|U.S. dime]], 17.91mm, for scale]] |
|||
== Etymology == |
|||
[[File:Paratype of Paedophryne amauensis (LSUMZ 95004).png|thumb|The world's smallest [[vertebrate]], ''[[Paedophryne amauensis]]'' sitting on a [[Dime (United States coin)|U.S. dime]], 17.91mm, for scale]] |
|||
''Amphibian'' is derived from the [[Ancient Greek]] term ἀμφίβιος (''amphíbios''), which means "both kinds of life", ''amphi'' meaning "of both kinds" and ''bio'' meaning "life". The term was initially used generally as an adjective for animals that could live on land or in water, including seals and otters. The word ''amphibian'' became restricted in the taxonomical sense to what we now use around 1600 with the taxon "Amphibia" first published in scientific classification ''circa'' 1819.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=amphibian |title=Amphibian (Adj.) |publisher=Online Etymology Dictionary |year=2012 |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref> |
''Amphibian'' is derived from the [[Ancient Greek]] term ἀμφίβιος (''amphíbios''), which means "both kinds of life", ''amphi'' meaning "of both kinds" and ''bio'' meaning "life". The term was initially used generally as an adjective for animals that could live on land or in water, including seals and otters. The word ''amphibian'' became restricted in the taxonomical sense to what we now use around 1600 with the taxon "Amphibia" first published in scientific classification ''circa'' 1819.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=amphibian |title=Amphibian (Adj.) |publisher=Online Etymology Dictionary |year=2012 |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref> |
||
== |
== Evolution == |
||
[[File:Lissamphibian phylogeny.jpg|thumb|Possible paths of Lissamphibia evolution.]] |
|||
The amphibians are [[tetrapod]]s, a [[class (biology)|class]] of vertebrate animals with four limbs. They are [[Amniote|non-amniotes]], which means that their eggs are not surrounded by the several membranes, some impervious, which enable mammals, reptiles and birds to reproduce on land. Amphibians typically reproduce in fresh water and are not found in the sea, with the exception of one or two frogs that live in [[brackish water]] in [[mangrove]] swamps.<ref>{{cite book |title=Introduction to the biology of marine life |last=Sumich |first=James L. |authorlink= |coauthors= Morrissey, John F. |year=2004 |publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning |location= |isbn=0-7637-3313-X, 9780763733131 |page=171 |pages= |url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?ei=tVpsT7bwCMX-8QOah4zADQ&id=Y8vTCze3dHgC&dq=%22+amphibians+in+the+sea%3F%22&q=Amphibians#v=snippet&q=Amphibians&f=false |accessdate=}}</ref> Most amphibians lay eggs that have a gelatinous coating, which swells when it comes in contact with water. The larvae that hatch from the eggs are mostly quite dissimilar to the adult form. In the case of frogs and toads they have a large head and a dorsally flattened tail and are known as tadpoles. They are vegetarians and breathe with gills. They have no limbs at first, the back limbs thrusting through then skin at a later stage, followed by the fore limbs after which the tail is reabsorbed. After this [[metamorphosis]] the juveniles look like miniature versions of the adult. Newt and salamander larvae have long bodies and feathery gills. They are carnivorous and the front legs develop before the back ones. They do not undergo metamorphosis in the same way that frogs and toads do.<ref name=Collins>{{cite book |title=Reptiles and Amphibians of Britain and Europe |last=Arnold |first=Nicholas |authorlink= |coauthors=Denys Ovenden |year=2002 |publisher=Harper Collins Publishers Ltd |location=London |isbn= |page= |pages=13–18 |url= }}</ref> The caecilians either produce live young or lay eggs in damp positions in their burrows.<ref name=Britannica>[[s:1911 Encyclopædia Britannica/Caecilia|Caecilia]] 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved 2012-03-24.</ref> |
|||
{{main|Labyrinthodontia}} |
|||
{{see also|List of prehistoric amphibians}} |
|||
The first major groups of amphibians developed in the [[Devonian|Devonian period]] from [[Sarcopterygii|lobe-finned fish]] similar to the modern [[coelacanth]] and [[lungfish]],<ref name="evoamphib" /> which had evolved multi-jointed leg-like fins with digits that enabled them to crawl along the sea bottom. Some fish [[lungfish|had developed primitive lungs]] to help them breathe air when the stagnant pools of the Devonian swamps were lacking in oxygen. They could also use their strong fins to hoist themselves out of the water and onto dry land if circumstances required it. Eventually, their bony fins would evolve into limbs and they would become the ancestors to all [[tetrapod]]s, including modern amphibians, [[reptile]]s, [[bird]]s, and [[mammal]]s. Despite being able to crawl on land, many of these prehistoric [[tetrapodomorph]] fish still spent most of their time in the water. They had started to develop lungs but still breathed predominantly with gills.<ref name="Caldwell">{{cite web |url=http://www.michellecaldwell.com/linkfiles/scaredcricket/articles/other/evolution.html |title=Evolution of Amphibians and Reptiles: The Paleozoic Era |author=Caldwell, Michelle |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-08-16}}</ref> |
|||
''[[Ichthyostega]]'' was one of the first primitive amphibians, with nostrils and more efficient lungs. It had four sturdy limbs, a neck, a tail with fins and a skull very similar to the lobe-finned fish, ''[[Eusthenopteron]]''.<ref name="evoamphib" /> Amphibians evolved adaptations that allowed them to stay out of the water for longer periods. Their lungs improved and their skeletons became heavier and stronger, better able to cope with the increased gravitational effect of life on land. They developed "hands" and "feet" with five digits. Their skin evolved and became more capable of retaining body fluids and resisting desiccation.<ref name="Caldwell" /> The fish's [[hyomandibula]] bone in the [[hyoid bone|hyoid]] region behind the gills diminished in size and became the [[stapes]] of the amphibian ear, an adaptation necessary for hearing on dry land.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Lombard, R. E.; Bolt, J. R. |year=1979 |title=Evolution of the tetrapod ear: an analysis and reinterpretation |journal=Biological Journal of the Linnean Society |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=19–76 |doi=10.1111/j.1095-8312.1979.tb00027.x }}</ref> An affinity between the amphibians and the [[teleost]] fish is the labyrinthic structure of the teeth and the paired supra-occipital bones at the back of the head, both features not found elsewhere in the animal kingdom.<ref name="Spoczynska" /> |
|||
Amphibians are [[Ectotherm|cold blooded]] animals and unable to maintain their body temperature above that of their surroundings. This means that they are only able to be active when the temperature is high enough. There is great variability in the sensitivity of different species to cold. Many species hibernate in winter, going into a state of torpor either in an underground chamber or underwater. In colder climates, they may be in a state of hibernation for more than half the year. In hot weather they may aestivate underground, sometimes buried in the mud of a dried up pond, reviving when cooler weather and rain restores their habitat. An advantage of being cold blooded is that little energy is required to provide body heat. This means that they can go without food for prolonged periods without coming to harm.<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
In the late [[Devonian]] and early [[Carboniferous]], the seas, rivers and lakes were teeming with life but the land was the realm of early plants and devoid of animal life. In the early [[Carboniferous]] ({{Ma|362|290}}) the climate became wet and warm and extensive swamps developed with [[mosse]]s, [[fern]]s, [[horsetail]]s and [[calamite]]s. Air breathing arthropods began to evolve and invaded the land where they provided food for the carnivorous amphibians that began to emerge from the waters. There were no other tetrapods on the land and the amphibians were at the top of the food chain and occupying the ecological position currently held by the crocodile. Though equipped with limbs and the ability to breathe air, most still had a long tapering body and strong tail.<ref name="Spoczynska">{{cite book |title=Fossils: A Study in Evolution |last=Spoczynska |first=J. O. I. |year=1971 |publisher=Frederick Muller Ltd |isbn=0-584-10093-0 |pages=120–125 }}</ref> They were the top land predators, sometimes reaching several meters in length, preying on the large insects of the period and many types of fish in the water. They still needed to return to water to lay their shell-less eggs and even modern amphibia have a fully aquatic larval stage with gills like their ancestral fish. It was the development of the amniotic egg, which prevents the developing embryo from drying out, that enabled the reptiles to reproduce on land and which led to their dominance in the period that followed.<ref name="evoamphib" /> |
|||
===Anura=== |
|||
The order [[Anura]] includes the frogs and toads. Members of this order with smooth skins are commonly referred to as frogs while those with warted skins are known as toads. The difference is not a formal one taxonomically, but members of the family [[Bufonidae]] are known as true toads. Frogs and toads have broad heads and plump bodies with short, stout fore limbs and long hind limbs that fold underneath them. Although most species are associated with water and damp habitats, some are specialised to live in trees and in deserts. They are found worldwide.<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
During the [[Triassic|Triassic Period]], the reptiles began to out-compete the amphibians, leading to a reduction in both their size and their importance in the [[biosphere]]. According to the fossil record, [[Lissamphibia]], which includes all modern amphibians and is the only surviving lineage, may have branched off from the extinct groups [[Temnospondyli]] and [[Lepospondyli]] at some period between the Late [[Carboniferous]] and the Early [[Triassic]]. The relative scarcity of fossil evidence prevents an exact date being known <ref name="preamphib" /> but the most recent molecular study, based on multi-locus data, suggest a Late Carboniferous – Early [[Permian]] origin of extant amphibians.<ref>{{cite journal|last=San Mauro|first=D. |year=2010|title=A multilocus timescale for the origin of extant amphibians|journal=Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution |volume=56 |pages=554–561 |doi=10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.019 |pmid=20399871|issue=2}}</ref> |
|||
===Caudata=== |
|||
The order [[Caudata]] includes the salamanders and one of its constituent [[Family (biology)|families]], [[Salamandridae]], includes the true salamanders and the newts. Salamanders and newts have pointed heads, long cylindrical bodies, four similar sized, short legs and long tails. They may be terrestrial or aquatic but many spend part of the year in each habitat. When on land, they mostly spend the day hidden under stones or logs or in dense vegetation, emerging in the evening and night to forage for worms, insects and other invertebrates. They are found in the [[Holarctic]] region of the northern hemisphere and in Central and South America north of the [[Amazon Basin]].<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
The origins and evolutionary relationships between the three main groups of amphibians is a matter for debate. A 2005 molecular phylogeny based on [[Ribosomal DNA|rDNA]] analysis suggests that salamanders and caecilians are more closely related to each other than they are to frogs. It also appears that divergence of the three groups took place in the [[Paleozoic]] or early [[Mesozoic]] before the breakup of the supercontinent [[Pangaea]] and soon after their divergence from the lobe-finned fish. The briefness of this period and the swiftness with which radiation took place would help account for the relative scarcity of primitive amphibian fossils.<ref>{{cite journal |author=San Mauro, Diego; Vences, Miguel; Alcobendas, Marina; Zardoya, Rafael; Meyer, Axel |year=2005 |title=Initial Diversification of living amphibians predated the breakup of Pangaea |journal=The American Naturalist |volume=165 |issue=5 |pages=590‑599 |jstor=429523 |doi=10.1086/429523 }}</ref> There are large gaps in the [[fossil record]] but the discovery of a batrachian from the Early Permian in Texas in 2008 provided a missing link with a lot of the characteristics of modern frogs. [[Molecular phylogenetics|Molecular analysis]] suggests that the frog–salamander divergence took place considerably earlier than the palaeontological evidence indicates.<ref name="Anderson">{{cite journal |author=Anderson, J.; Reisz, R.; Scott, D.; Fröbisch, N.; Sumida, S |year=2008 |title=A stem batrachian from the Early Permian of Texas and the origin of frogs and salamanders |journal=Nature |volume=453 |issue= 7194|pages=515–518 |publisher= |doi=10.1038/nature06865 |pmid= 18497824|pmc= |url=http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v453/n7194/full/nature06865.html |accessdate= }}</ref> [[File:Fossilised frog.jpg|thumb|A fossilized frog from the [[Czech Republic]], possibly ''[[Palaeobatrachus gigas]]'']] |
|||
===Gymnophiona=== |
|||
The order [[Gymnophiona]] includes the caecilians. These are long, cylindrical, limbless animals that resemble [[snake]]s or [[Annelid|worms]]. Their skin has circular folds, increasing their similarity to the segments of earthworms. Some are aquatic but most live underground in burrows they hollow out. Many caecilians give birth to live young, and in the animals that do not do this, the eggs may undergo metamorphosis before they hatch. Caecilians are found in tropical Africa, Asia and Central and South America.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
== Classification == |
|||
==Evolution== |
|||
[[File:2009 Andrias davidianus.JPG|thumb|a small specimen of the [[Chinese giant salamander]]]] |
|||
[[File:Lissamphibian phylogeny.jpg|thumb|right|Possible paths of Lissamphibia evolution.]] |
|||
Traditionally, amphibians includes all [[tetrapod]] vertebrates that are not [[amniote]]s. Amphibia in its widest sense (''[[sensu lato]]'') was divided into three [[Class (biology)|subclasses]], two of which are extinct:<ref>{{cite journal |author=Morell, Virginia |year=1993 |title=Classification of the major taxa of Amphibia and Reptilia |journal=Science |pages=764‑765 |url=http://mcb.berkeley.edu/courses/bio1a/Lab/downloads/Bio1AL_Diveristy_Amphibia+Reptilia.pdf |doi=10.1126/science.259.5096.764 |volume=259 |issue=5096 }}</ref> |
|||
{{Main|Labyrinthodontia}} |
|||
* Subclass [[Labyrinthodontia]]† (diverse Paleozoic and early Mesozoic group) |
|||
{{see also|List of prehistoric amphibians}} |
|||
* Subclass [[Lepospondyli]]† (small Paleozoic group, sometimes included in the Labyrinthodontia, which may actually be more closely related to amniotes than Lissamphibia) |
|||
The first major groups of amphibians developed in the [[Devonian|Devonian period]] from [[Sarcopterygii|lobe-finned fish]] similar to the modern [[coelacanth]] and [[lungfish]],<ref name="evoamphib"/> which had evolved multi-jointed leg-like fins with digits that enabled them to crawl along the sea bottom. Some fish [[lungfish|had developed primitive lungs]] to help them breathe air when the stagnant pools of the Devonian swamps were lacking in oxygen. They could also use their strong fins to hoist themselves out of the water and onto dry land if circumstances required it. Eventually, their bony fins would evolve into limbs and they would become the ancestors to all [[tetrapod]]s, including modern amphibians, [[reptile]]s, [[bird]]s, and [[mammal]]s. Despite being able to crawl on land, many of these prehistoric [[tetrapodomorph]] fish still spent most of their time in the water. ''[[Ichthyostega]]'' was one of these tetrapods and had four sturdy limbs, a neck, a tail with fins and a skull very similar to the lobe-finned fish, ''[[Eusthenopteron]]''.<ref name="evoamphib"/> Amphibians evolved adaptations that allowed them to stay out of the water for longer periods. Their lungs became more efficient and their limbs stronger. The [[hyomandibula]] bone in the [[hyoid bone|hyoid]] region of the fish behind the gills diminished in size and became the [[stapes]] of the ear, an adaptation necessary for hearing on dry land.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Lombard, R. E.; Bolt, J. R. |year=1979 |title=Evolution of the tetrapod ear: an analysis and reinterpretation |journal=Biological Journal of the Linnean Society |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=19–76 |doi=10.1111/j.1095-8312.1979.tb00027.x }}</ref> An affinity between the amphibians and the [[teleost]] fish is the labyrinthic structure of the teeth and the paired supra-occipital bones at the back of the head, both features not found elsewhere in the animal kingdom.<ref name=Spoczynska/> |
|||
* Subclass [[Lissamphibia]] (all modern amphibians including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts and caecilians) |
|||
** Family [[Albanerpetontidae]]—Jurassic to Miocene (extinct) |
|||
** Superorder [[Salientia]] |
|||
*** Genus ''[[Triadobatrachus]]''—Triassic (extinct)—a stem Anuran |
|||
*** Order Anura ([[frog]]s and [[toad]]s): Jurassic to recent—5,602 recent species in 48 families |
|||
*** Order Caudata or Urodela ([[salamander]]s, [[newt]]s): Jurassic to recent—571 recent species in 10 families |
|||
*** Order Gymnophiona ([[caecilian]]s): Jurassic to recent—190 recent species in 10 families |
|||
The actual number of species in each group depends on the taxonomic classification followed, the two most common systems being the classification adopted by the website AmphibiaWeb, University of California (Berkeley) and the classification by [[Herpetology|herpetologist]] Darrel Frost and the [[American Museum of Natural History]], available as the online reference database [[List of amphibians|Amphibian Species of the World]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://research.amnh.org/vz/herpetology/amphibia/ |title= American Museum of Natural History: Amphibian Species of the World 5.5, an Online Reference |author=Frost, Darell |year=2011 |work=Herpetology |publisher=The American Museum of Natural History |accessdate=2012-08-09}}</ref> The numbers of species cited above follow Frost. |
|||
In the late [[Devonian]] and early [[Carboniferous]], the seas, rivers and lakes were teeming with life but the land was the realm of early plants and devoid of animal life. In the early [[Carboniferous]] ({{Ma|362|290}}) the climate became wet and warm and extensive swamps developed with [[mosse]]s, [[fern]]s, [[horsetail]]s and [[calamite]]s. Air breathing arthropods began to evolve and invaded the land where they provided food for the carnivorous amphibians that began to emerge from the waters. There were no other tetrapods on the land and the amphibians were at the top of the food chain and occupying the ecological position currently held by the crocodile. Though equipped with limbs and the ability to breathe air, most still had a long tapering body and strong tail.<ref name=Spoczynska>{{cite book |title=Fossils: A Study in Evolution |last=Spoczynska |first=J. O. I. |year=1971 |publisher=Frederick Muller Ltd |isbn=584 10093 0 |pages=120–125 }}</ref> They were the top land predators, sometimes reaching several meters in length, preying on the large insects on land and many types of fish in the water. They still needed to return to water to lay their shell-less eggs and even modern amphibia have a fully aquatic larval stage with gills like their ancestral fish. It was the development of the amniotic egg, which prevented the developing embryo from drying out, that enabled the reptiles to reproduce on land and which led to their dominance in the period that followed.<ref name="evoamphib"/> |
|||
With the [[Phylogenetics|phylogenetic]] classification, the taxon Labyrinthodontia has been discarded as it is a [[Paraphyly|paraphyletic]] group without unique defining features apart from [[Cladistics#plesiomorphy|shared primitive characteristics]]. Classification varies according to the preferred [[Phylogenetics|phylogeny]] of the author and whether they use a [[Cladistics#Three definitions of clade|stem-based or a node-based]] classification. Traditionally, amphibians as a class are defined as all [[tetrapod]]s with a larval stage, while the group that includes the common ancestors of all living amphibians (frogs, salamanders and caecilians) and all their descendants is called Lissamphibia. The phylogeny of [[Paleozoic]] amphibians is uncertain, and Lissamphibia may possibly fall within extinct groups like the [[Temnospondyli|temnospondyls]] (traditionally placed in the subclass Labyrinthodontia), and the Lepospondyls, and in some analysis even the [[amniote]]s. This means that advocates of [[phylogenetic nomenclature]] have removed a large number of [[basal (phylogenetics)|basal]] [[Devonian]] and [[Carboniferous]] amphibian-type [[tetrapod]] groups that were formerly placed in Amphibia in [[Linnaean taxonomy]] and included them elsewhere under [[cladistic taxonomy]].<ref name="Zug">{{cite book |title=Herpetology, Second Edition: An Introductory Biology of Amphibians and Reptiles |last=Zug |first=G. R. |authorlink= |coauthors=Vitt, L. J.; Caldwell, J. P. |year=2001 |publisher=Academic Press }}</ref> |
|||
During the [[Triassic|Triassic Period]], the better-adapted reptiles began to compete with amphibians, leading to a reduction in their size and importance in the [[biosphere]]. [[Lissamphibia]], which includes all modern amphibians and is the only surviving lineage of amphibians left, may have branched off from the extinct groups [[Temnospondyli]] or [[Lepospondyli]] at some time between the Late [[Carboniferous]] and the Early [[Triassic]] according to the fossil record. The relative scarcity of fossil evidence prevents an exact date being known <ref name="preamphib"/> but the most recent molecular clock study based on multi-locus data suggest a Late Carboniferous – Early [[Permian]] origin of extant amphibians.<ref>{{cite journal|last=San Mauro|first=D. |year=2010|title=A multilocus timescale for the origin of extant amphibians|journal=Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution |volume=56 |pages=554–561 |doi=10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.019 |pmid=20399871|issue=2}}</ref> |
|||
All recent amphibians are included in the subclass Lissamphibia, superorder Salientia, which is usually considered a [[clade]], a group of species that have evolved from a common ancestor. It has also been suggested that salamanders arose separately from a Temnospondyl-like ancestor, and even that caecilians are the sister group of the advanced [[reptiliomorpha|reptiliomorph]] amphibians, and thus of amniotes.<ref name="Anderson" /><ref>Carroll, 2007</ref> |
|||
There are large gaps in the [[fossil record]] but the discovery of a batrachian from the Early Permian in Texas in 2008 provided a missing link with a lot of the characteristics of modern frogs. [[Molecular phylogenetics|Molecular analysis]] suggests that the frog–salamander divergence took place considerably earlier than the palaeontological evidence indicates. However the date of the divergence of the caecilians deduced by molecular phylogenetics agrees with the fossil record.<ref name=Anderson>{{cite journal |author=Anderson, J.; Reisz, R.; Scott, D.; Fröbisch, N.; Sumida, S |year=2008 |title=A stem batrachian from the Early Permian of Texas and the origin of frogs and salamanders |journal=Nature |volume=453 |issue= 7194|pages=515–518 |publisher= |doi=10.1038/nature06865 |pmid= 18497824|pmc= |url=http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v453/n7194/full/nature06865.html |accessdate= }}</ref> |
|||
Authorities also disagree as to whether Salientia is a superorder that includes the order Anura, or whether Anura is a sub-order of the order Salientia. Practical considerations seem to favour using the former arrangement. The Lissamphibia, superorder Salientia, are traditionally divided into three [[Order (biology)|orders]], but an extinct salamander-like family, the Albanerpetontidae, is now considered part of the Lissamphibia alongside the superorder Salientia. Furthermore, Salientia includes all three recent orders plus the [[Triassic]] proto-frog, ''[[Triadobatrachus]]''.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://tolweb.org/Salientia/14938 |title=Salientia |author=David Cannatella |date=1995 |publisher=Tree of Life Web Project |accessdate=2012-08-31}}</ref> |
|||
==Classification== |
|||
[[File:2009 Andrias davidianus.JPG|thumb|right|a small specimen of the [[Chinese giant salamander]]]] |
|||
Traditionally, amphibians includes all [[tetrapod]] vertebrates that are not [[amniote]]s. Amphibia in its widest sense (''[[sensu lato]]'') was divided into three [[Class (biology)|subclasses]], two of which are extinct: |
|||
* Subclass [[Labyrinthodontia]]† (diverse Paleozoic and early Mesozoic group) |
|||
* Subclass [[Lepospondyli]]† (small Paleozoic group, sometimes included in the Labyrinthodontia, which may actually be more closely related to amniotes than Lissamphibia) |
|||
* Subclass [[Lissamphibia]] (frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, etc.) |
|||
== Characteristics == |
|||
Of these only Lissamphibia includes recent species. |
|||
The amphibians are [[tetrapod]]s, a [[class (biology)|class]] of vertebrate animals with four limbs. They are [[Amniote|non-amniotes]], which means that their eggs are not surrounded by the several membranes, some impervious, which enable mammals, reptiles and birds to reproduce on land. Amphibians typically reproduce in fresh water and are not found in the sea, with the exception of one or two frogs that live in [[brackish water]] in [[mangrove]] swamps.<ref>{{cite book |title=Introduction to the biology of marine life |last=Sumich |first=James L. |coauthors= Morrissey, John F. |year=2004 |publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning |location= |isbn=0-7637-3313-X, 9780763733131 |page=171 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=Y8vTCze3dHgC&dq=%22+amphibians+in+the+sea%3F%22&q=Amphibians#v=snippet&q=Amphibians&f=false }}</ref> Amphibians evolved from lunged fish and had to make certain adaptations for living on land. They needed to develop new means of locomotion to replace the sideways thrust of their tails that had been used for swimming. Their vertebral columns, limbs, limb girdles and musculature needed to be strong enough to raise them off the ground for locomotion and feeding. Terrestrial adults needed to discard their lateral line systems and adapt their sensory systems to receive stimuli via the medium of air. They needed to develop new methods to regulate their body heat in order to cope with fluctuations in ambient temperatures. They needed to develop behaviours suitable for reproduction in a terrestrial environment. Their skins were exposed to harmful ultraviolet rays that had previously been absorbed by the water and needed to become more protective membranes that prevented excessive water loss. Amphibians are restricted to moist habitats because their skin needs to be kept damp and they need to produce copious amounts of dilute urine. They also require water bodies for reproduction, although some species have developed various strategies for protecting or bypassing the vulnerable aquatic larval stage.<ref name="DorAmph">{{cite book |title=Zoology |last=Dorit |first=R. L. |coauthors=Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. |year=1991 |publisher=Saunders College Publishing |isbn=0-03-030504-7 |page=843‑859 }}</ref> |
|||
Amphibians are [[Ectotherm|cold blooded]] vertebrates. Their metabolic rate is low and as a result, their food and energy requirements are limited. In the adult state they have tear ducts and movable eyelids and most species have ears that can detect airborne or ground vibrations. They have a muscular tongue which in many species can be protruded. Modern amphibians have fully ossified vertebrae with articular processes. Their ribs are usually short and may be fused to the vertebrae. Their skulls are mostly broad and short and are often incompletely ossified. Their skin contains little [[keratin]] and lacks scales, apart from a few fish-like scales in certain caecilians. It contains many mucous glands and in some species, poison glands. The hearts of amphibians have three chambers. The left and right atria receive oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood respectively. On contraction, these pass the blood to a single ventricle which pumps it round the body and to the lungs. The two blood streams remain largely separate in the process. Amphibians have a urinary bladder and nitrogenous waste products are excreted primarily as urea. Most amphibians lay their eggs in water and have aquatic larvae that undergo metamorphosis to become terrestrial adults. Amphibians breathe by means of a bucco-pharyngeal pump but supplement this with gas exchange through the skin.<ref name="DorAmph" /> |
|||
With the [[Phylogenetics|phylogenetic]] classification, the taxon Labyrinthodontia has been discarded as it is a [[Paraphyly|paraphyletic]] group without unique defining features apart from [[Cladistics#plesiomorphy|shared primitive characteristics]]. Classification varies according to the preferred [[Phylogenetics|phylogeny]] of the author and whether they use a [[Cladistics#Three definitions of clade|stem-based or a node-based]] classification. Traditionally, amphibians as a class are defined as all [[tetrapod]]s with a larval stage, while the group that includes the common ancestors of all living amphibians (frogs, salamanders and caecilians) and all their descendants is called Lissamphibia. The phylogeny of [[Paleozoic]] amphibians is uncertain, and Lissamphibia may possibly fall within extinct groups like the [[Temnospondyli|temnospondyls]] (traditionally placed in the subclass Labyrinthodontia), and the Lepospondyls, and in some analysis even the [[amniote]]s. This means that advocates of [[phylogenetic nomenclature]] have removed a large number of [[basal (phylogenetics)|basal]] [[Devonian]] and [[Carboniferous]] amphibian-type [[tetrapod]] groups that were formerly placed in Amphibia in [[Linnaean taxonomy]] and included them elsewhere under [[cladistic taxonomy]].<ref name=Zug>{{cite book |title=Herpetology, Second Edition: An Introductory Biology of Amphibians and Reptiles |last=Zug |first=G. R. |authorlink= |coauthors=Vitt, L. J.; Caldwell, J. P. |year=2001 |publisher=Academic Press |location= |isbn= |page= |pages= |url= |accessdate=}}</ref> |
|||
=== Anura === |
|||
All recent amphibians are included in the subclass Lissamphibia, superorder Salientia, which is usually considered a [[clade]] (which means that it is thought that they evolved from a common ancestor apart from other extinct groups), although it has also been suggested that salamanders arose separately from a Temnospondyl-like ancestor, and even that caecilians are the sister group of the advanced [[reptiliomorpha|reptiliomorph]] amphibians, and thus of amniotes.<ref name=Anderson/><ref>Carroll, 2007</ref> |
|||
The order [[Anura]] (from the [[Ancient Greek]] ''an-'', without and ''oura'', tail) comprises the frogs and toads. These usually have long hind limbs that fold underneath them, shorter forelimbs, webbed toes with no claws, no tails, large eyes and glandular moist skin.<ref name="Stebbins3">{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |page=3 }}</ref> Members of this order with smooth skins are commonly referred to as frogs while those with warted skins are known as toads. The difference is not a formal one taxonomically and there are numerous exceptions to this rule. Members of the family [[Bufonidae]] are known as the "true toads".<ref>{{cite book |title=Frogs |last=Badger |first=D. |coauthors=Netherton, J. |year=1995 |publisher=Airlife Publishing |isbn=1853107409 |page=19 }}</ref> Frogs range in size from the {{convert|30|cm}} [[goliath frog]] (''Conraua goliath'') of West Africa <ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/past-exhibitions/frogs-a-chorus-of-colors/frog-fun-facts |title=Frog fun facts |date=2010-01-12 |publisher=American Museum of Natural History |accessdate=2012-08-29}}</ref> to the {{convert|7.7|mm}} long [[Paedophryne amauensis]], first described in Papua New Guinea in 2012. This latter is also the smallest known vertebrate.<ref>{{cite news |title=World's smallest frog discovered in Papua New Guinea |author=Challenger, David |url=http://articles.cnn.com/2012-01-12/asia/world_asia_new-frogs_1_frog-papua-new-guinea-body-size?_s=PM:ASIA |newspaper=CNN |date=2012-01-12 |accessdate=2012-08-29}}</ref> Although most species are associated with water and damp habitats, some are specialised to live in trees and in deserts. They are found worldwide except for polar areas.<ref name="Collins">{{cite book |title=Reptiles and Amphibians of Britain and Europe |last=Arnold |first=Nicholas |authorlink= |coauthors=Denys Ovenden |year=2002 |publisher=Harper Collins Publishers Ltd |location=London |isbn= |page= |pages=13–18 |url= }}</ref> Anura is divided into three suborders which are broadly accepted by the scientific community but the relationships between some families remains unclear. Future [[molecular genetics|molecular]] studies should provide further insights into their evolutionary relationships.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Faivovich| first=J.| coauthors=Haddad, C. F. B.; Garcia, P. C. A.; Frost, D. R.; Campbell, J. A.; Wheeler, W. C.| title=Systematic review of the frog family Hylidae, with special reference to Hylinae: Phylogenetic analysis and revision| journal=Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History| volume=294| pages=1‑240| doi=10.1206/0003-0090(2005)294[0001:SROTFF]2.0.CO;2| year=2005}}</ref> |
|||
The suborder [[Archaeobatrachia]] contains four families of primitive frogs. These comprise the families [[Ascaphidae]], [[Bombinatoridae]], [[Discoglossidae]] and [[Leiopelmatidae]].<ref name="Ford">{{cite journal|last=Ford| first=L.S.| coauthors= Cannatella, D. C.| year=1993| title=The major clades of frogs| journal=Herpetological Monographs| volume=7| pages=94‑117| doi=10.2307/1466954| jstor=1466954}}</ref> |
|||
Authorities also disagree as to whether Salientia is a superorder that includes the order Anura, or whether Anura is a sub-order of the order Salientia. Practical considerations seem to favor using the former arrangement. The Lissamphibia, superorder Salientia, are traditionally divided into three [[Order (biology)|order]]s, but an extinct salamander-like family, the Albanerpetontidae, is now considered part of the Lissamphibia, besides the superorder Salientia. Furthermore, Salientia includes all three recent orders plus a single [[Triassic]] proto-frog, ''[[Triadobatrachus]]''. |
|||
The suborder [[Mesobatrachia]] contains six families of more evolutionary advanced frogs. These comprise the families [[Megophryidae]], [[Pelobatidae]], [[Pelodytidae]], [[Scaphiopodidae]], [[Rhinophrynidae]] and [[Pipidae]].<ref name="Ford" /> |
|||
Class '''Amphibia''' |
|||
* Subclass [[Lissamphibia]] |
|||
** Family [[Albanerpetontidae]]—Jurassic to Miocene (extinct) |
|||
** Superorder [[Salientia]] |
|||
*** Genus ''[[Triadobatrachus]]''—Triassic (extinct)—A stem Anuran |
|||
*** Order Anura ([[frog]]s and [[toad]]s): Jurassic to recent—5,602 recent species in 48 families |
|||
*** Order Caudata or Urodela ([[salamander]]s, [[newt]]s): Jurassic to recent—571 recent species in 10 families |
|||
*** Order Gymnophiona ([[caecilian]]s): Jurassic to recent—190 recent species in 10 families |
|||
The suborder [[Neobatrachia]] is by far the largest group and includes the remaining families of modern frogs, including most common species. Ninety six percent of the over 5000 extant species of frog are neobatrachians.<ref>{{cite journal | last = San Mauro | first = Diego | title = Initial diversification of living amphibians predated the breakup of Pangaea | url = http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/AN/journal/issues/v165n5/40546/40546.html | journal = American Naturalist | volume = 165 | pages = 590‑599 | year = 2005 | coauthors = Vences, Miguel; Alcobendas, Marina; Zardoya, Rafael; Meyer, Axel | doi = 10.1086/429523 | issue = 5 }}</ref> |
|||
The actual number of species partly also depends on the taxonomic classification followed, the two most common classifications being the classification of the website AmphibiaWeb, University of California (Berkeley) and the classification by [[Herpetology|herpetologist]] Darrel Frost and The American Museum of Natural History, available as the online reference database Amphibian Species of the World.<ref>[http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/ Amphibian Species of the World] The online database by Darrel Frost and The American Museum of Natural History</ref> The numbers of species cited above follow Frost. |
|||
=== Caudata === |
|||
==Anatomy and physiology== |
|||
The order [[Caudata]] (from the Latin ''cauda'' meaning "tail") consists of the salamanders, elongated, low-slung animals that mostly resemble lizards in form, though this is a [[Symplesiomorphy|symplesiomorphic trait]] and the two groups are no more closely related than salamanders are to mammals.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://palaeo.gly.bris.ac.uk/benton/vertclass.html |title=Classification of the vertebrates |author=Benton, Michael J. |date=2004 |work=Vertebrate Palaeontology |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |accessdate=2012-08-25}}</ref> Salamanders lack claws, have a scale-free skin, either smooth or covered with [[tubercle]]s, and a tail that is usually flattened from side to side and often finned. They range in size from the [[Chinese giant salamander]] (''Andrias davidianus''), which can grow to a length of {{convert|1.8|m}},<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.arkive.org/chinese-giant-salamander/andrias-davidianus/ |title=Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) |publisher=ARKive |accessdate=2012-08-25}}</ref> to the diminutive (''Thorius pennatulus'') from Mexico which seldom exceeds {{convert|20|mm}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://amphibiaweb.org/cgi/amphib_query?where-genus=Thorius&where-species=pennatulus |title=cite web |author=Wake, David B. |date=2000-11-08 |publisher=AmphibiaWeb |accessdate=2012-08-25}}</ref> Salamanders are distributed widely in the [[Holarctic]] region of the northern hemisphere. The family [[Plethodontidae]] are also found in Central and South America north of the [[Amazon Basin]].<ref name="Collins" /> Urodela is a name sometimes used for all the [[extant taxon|extant]] species of salamander.<ref name="larson">{{Cite journal| last =Larson | first =A. | last2 =Dimmick | first2 =W. | year = 1993| title = Phylogenetic relationships of the salamander families: an analysis of the congruence among morphological and molecular characters| journal = Herpetological Monographs| volume =7| issue = 7| pages = 77‑93| doi =10.2307/1466953| jstor =1466953}}</ref> Members of several families of salamanders have become [[Neoteny|paedomorphic]] and either fail to complete their metamorphosis or retain some larval characteristics as adults.<ref name="Dorit852">{{cite book |title=Zoology |last=Dorit |first=R. L. |coauthors=Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. |year=1991 |publisher=Saunders College Publishing |isbn=0-03-030504-7 |page=852 }}</ref> Most salamanders are under {{convert|15|cm}} long. They may be terrestrial or aquatic but many spend part of the year in each habitat. When on land, they mostly spend the day hidden under stones or logs or in dense vegetation, emerging in the evening and night to forage for worms, insects and other invertebrates.<ref name="Collins" /> |
|||
===Integumentary system=== |
|||
[[File:Salamander-olympus.jpg|thumb|right|The [[fire salamander]] has brightly colored yellow spots, indicating that it secretes toxins.]] |
|||
Amphibian skin is permeable to water and contains many mucous glands that keep the skin from drying out. Gas exchange can take place through the skin and this allows adult amphibians to hibernate at the bottom of ponds.<ref name=Collins/> To compensate for their thin and delicate skin, all amphibians have evolved poison glands as a defense mechanism, although toxicity varies by species. Some amphibian toxins can be lethal to humans while others have little effect.<ref name=amphibfacts>{{cite web|url=http://animals.about.com/od/amphibians/a/amphibian-facts.htm|title=Amphibian Facts - About.com|accessdate=February 5, 2012}}</ref> The main poison-producing glands, the [[Parotoid gland|paratoids]], contain the neurotoxin [[bufotoxin]] and are located behind the ears of certain frogs and toads and behind the eyes of salamanders.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lookd.com/frogs/characteristics.html |title=Physical characteristics |author= |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref> The integumentary structure contains some typical characteristics common to terrestrial vertebrates, such as the presence of highly cornified outer layers, renewed periodically through a molting process controlled by the pituitary and thyroid glands. Local thickenings (often called warts) are common, such as those found on toads. The outside of the skin is shed periodically more or less in one piece in contrast to mammals and birds where it is shed in flakes. Amphibians often eat the sloughed skin.<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
The suborder [[Cryptobranchoidea]] contains the primitive salamanders. A number of fossil cryptobranchids have been found but there are only three living species, the Chinese giant salamander (''Andrias davidianus''), the [[Japanese giant salamander]] (''Andrias japonicus '') and the [[hellbender]] (''Cryptobranchus alleganiensis'') from North America. These large amphibians retain several larval characteristics in their adult state; gills slits are present and the eyes are unlidded. A unique feature is their ability to feed by suction using only one half of the lower jaw at a time.<ref name="ADWCrypto">{{cite web |url=http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Cryptobranchidae.html |title=cite web |author=Heying, Heather |date=2003 |work=Animal Diversity Web |publisher=University of Michigan |accessdate=2012-08-25}}</ref> The males excavate nests, persuade females to lay their egg strings inside them and guard them. As well as breathing with lungs, they respire through the many folds in their skin which is thin with the capillaries close to the surface.<ref name="EHSAR">{{cite web |url=http://www.fws.gov/midwest/es/soc/amphibians/eahe-sa.pdf |title=Eastern Hellbender Status Assessment Report |author=Mayasich, J.; Grandmaison, D.; Phillips, C. |date=2003-06-01 |publisher=U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service |accessdate=2012-08-25}}</ref> |
|||
The skin color of amphibians is produced by three layers of pigment cells called [[chromatophore]]s. These three cell layers consist of the melanophores (occupying the deepest layer), the guanophores (forming an intermediate layer and containing many granules, producing a blue-green color) and the lipophores (yellow, the most superficial layer). The color change experienced by many species is caused by secretions from the pituitary gland. Unlike bony fish, there is no direct control by the nervous system of the pigment cells. Therefore, the color change is slower. Bright colors usually indicate that the species produces an exceptionally toxic poison.<ref>{{cite book |title=The integument: A Textbook of Skin Biology |last=Spearman |first=R. I. C. |authorlink= |coauthors= |year=1973 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location= |isbn=0-521-20048-2, 9780521200486 |page=81 |pages= |url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=F7A8AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA81&lpg=PA81&dq=Amphibian+%22skin+colour%22&source=bl&ots=M68LMfq0ou&sig=TdgdZYVTMFmvywKSApTusPGAk7c&hl=en&sa=X&ei=2PpuT6ehOoa-0QWu1_TCBw&ved=0CGYQ6AEwCQ#v=onepage&q=Amphibian%20%22skin%20colour%22&f=false |accessdate=}}</ref> |
|||
The suborder [[Salamandroidea]] contains the advanced salamanders. They differ from the cryptobranchids by having the prearticular bones in their lower jaw fused and reproduction is by internal fertilisation. In salamandrids, the male deposits a bundle of sperm, the spermatophore, and the female picks it up and inserts it into her cloaca where the sperm is stored until the eggs are laid.<ref name="BritCaudata">{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/100353/Caudata |title=Caudata |author=Wake, David B. |work=Encyclopedia Brittanica |accessdate=2012-08-25}}</ref> The largest family in this group is Plethodontidae, the lungless salamanders, which includes sixty percent of all salamander species. The [[Family (biology)|family]] [[Salamandridae]] includes the true salamanders and the name "[[newt]]" is given to members of its subfamily [[Pleurodelinae]].<ref name="Stebbins3" /> |
|||
===Skeletal system=== |
|||
The skeletal system of amphibians is structurally homologous to other [[tetrapod]]s, though with a number of variations. They possess a cranium, spine, rib cage, long bones such as the [[humerus]] and [[femur]], and short bones such as the [[phalanges]], [[metacarpals]], and [[metatarsals]]. Most have four limbs except for caecilians. Bones in most amphibians are hollow and lightweight.<ref name=AmphibAnat>{{cite web |url=http://www.amphibanat.org/ |title=AmphibAnat |author=Maglia, A.M.; Leopold, J.L.; Pugener, A.L.; Gauch, S. |year=2007 |work=The Amphibian Anatomical Ontology web project. |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref><ref name=Anatomy>{{cite web |url=http://www.lookd.com/frogs/anatomy.html |title=Anatomy of the frog |author= |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref> |
|||
The third suborder [[Sirenoidea]] contains the sirens, consisting of four species in a single family, [[Sirenidae]]. Members of this order are [[eel]]-like aquatic salamanders with much reduced forelimbs and no hind limbs. Some of their features are primitive while others are derived.<ref>{{cite book |editor=Cogger, H. G.; Zweifel, R. G.|author= Lanza, B.; Vanni, S.; Nistri, A. |year=1998 |title=Encyclopedia of Reptiles and Amphibians |publisher= Academic Press |pages= 69‑70|isbn= 0-12-178560-2}}</ref> Fertilisation is likely to be external as sirenids lack the cloacal glands used by male salamandrids to produce spermatophores and the females lack spermathecae for sperm storage. Despite this, the eggs are laid singly, a behaviour not conducive for external fertilisation.<ref name="BritCaudata" /> |
|||
The shoulder girdle of early amphibians is almost identical to that of their predecessors the osteolepiformes, except for the presence of a new dermal bone, the interclavicular (which has been lost in modern amphibians). The pelvic girdle is much more developed. In all tetrapods it consists of three main bones: the ilium in the dorsal and ventral, the pubis in the anterior and the ischium in a posterior position. The meeting point of these three bones forms the [[acetabulum]], which articulates with the femur. |
|||
=== Gymnophiona === |
|||
===Circulatory and nervous systems=== |
|||
The order [[Gymnophiona]] (from the [[Greek language|Greek]], ''gymnos'' and ''ophis'' meaning "naked serpent") comprise the caecilians. These are long, cylindrical, limbless animals with a [[snake]] or [[Annelid|worm-like]] form. The adults vary in length from 8 to 75 centimetres (3 to 30 inches) with the exception of [[Caecilia thompsoni|Thomson's caecilian]] (''Caecilia thompsoni'') which can reach 150 centimetres (5 feet). A caecilian's skin has a large number of transverse folds and in some species contains tiny embedded dermal scales. It has rudimentary eyes covered in skin which are probably limited to discerning differences in light intensity. It also has a pair of short [[tentacle]]s near the eye that can be extended and which have [[Somatosensory system|tactile]] and [[Olfaction|olfactory]] functions. Some caecilians are aquatic but most live underground in burrows in damp soil, in rotten wood and under plant debris.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |page=4 }}</ref> Most species lay their eggs underground and when the larvae hatch, they make their way to adjacent bodies of water. Others brood their eggs and the larvae undergo metamorphosis before the eggs hatch. A few species give birth to live young, nourishing them with glandular secretions while they are in the oviduct.<ref name="Dorit858">{{cite book |title=Zoology |last=Dorit |first=R. L. |coauthors=Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. |year=1991 |publisher=Saunders College Publishing |isbn=0-03-030504-7 |page=858 }}</ref> Caecilians are found in tropical Africa, Asia and Central and South America.<ref name="Britannica">[[s:1911 Encyclopædia Britannica/Caecilia|Caecilia]] 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved 2012-03-24.</ref> |
|||
[[File:Siphonops paulensis02.jpg|thumb|right|The South American caecilian, [[Siphonops paulensis]]]] |
|||
Amphibians have a juvenile stage and an adult stage and the circulatory systems of the two are distinct. In the juvenile (or tadpole) stage, gills are used to oxygenate blood and movement is similar to that of fish. In the adult stage, amphibians (especially frogs) lose their gills and develop lungs. They have a heart that consists of a ventricle and two atria (it may be considered a single atrium, if not totally or partially divided) that pumps oxygenated blood through arteries and deoxygenated blood through veins to the lungs. Since amphibians are cold-blooded, they must find ways to keep their blood at a constant temperature to maintain [[homeostasis]].<ref name=Anatomy/> |
|||
== Anatomy and physiology == |
|||
The [[nervous system]] is basically the same as in other vertebrates, with a central brain, a spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body.<ref name=Anatomy/> The amphibian brain is less developed compared to that of reptiles, birds, and mammals. It consists of a cerebrum, midbrain, and cerebellum of similar sizes. The olfactory lobe is the center of the sense of smell. The cerebrum integrates behavior and learning. The optic lobe processes information from the eyes. The cerebellum is the center of muscular coordination. The medulla oblongata controls some organ functions, such as heart rate and respiration. The brain sends signals through the spinal cord and nerves to regulate activity in the rest of the body. The pineal body, known to regulate sleep patterns in humans, is thought to produce the hormones involved in hibernation and estivation in amphibians.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://staff.tuhsd.k12.az.us/gfoster/standard/bamphib.htm |title=Amphibian brains |accessdate=February 16, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
=== Skin === |
|||
[[File:Salamander-olympus.jpg|thumb|The [[fire salamander]] has brightly colored yellow spots, indicating that it secretes toxins.]] |
|||
The integumentary structure contains some typical characteristics common to terrestrial vertebrates, such as the presence of highly cornified outer layers, renewed periodically through a moulting process controlled by the pituitary and thyroid glands. Local thickenings (often called warts) are common, such as those found on toads. The outside of the skin is shed periodically more or less in one piece in contrast to mammals and birds where it is shed in flakes. Amphibians often eat the sloughed skin.<ref name="Collins" /> Caecilians are unique among amphibians in having mineralized dermal scales embedded in the [[dermis]] between the furrows in the skin. The similarity of these to the scales of bony fish is largely superficial. [[Squamata|Lizards]] and some frogs have somewhat similar [[osteoderm]]s forming bony deposits in the dermis but this is an example of convergent evolution with similar structures having arisen independently in diverse vertebrate lineages.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Zylberberg, Louise; Wake, Marvalee H. |year=1990 |title=Structure of the scales of ''Dermophis'' and ''Microcaecilia'' (Amphibia: Gymnophiona), and a comparison to dermal ossifications of other vertebrates |journal=Journal of Morphology |volume=206 |issue=1 |pages=25‑43 |doi=10.1002/jmor.1052060104 }}</ref> |
|||
Amphibian skin is permeable to water. Gas exchange can take place through the skin and this allows adult amphibians to respire without rising to the surface of water and to hibernate at the bottom of ponds.<ref name="Collins" /> To compensate for their thin and delicate skin, amphibians have evolved mucous glands, principally on their heads, backs and tails. The secretions produced by these help keep the skin moist. In addition, most species of amphibian have granular glands that secrete distasteful or poisonous substances. Some amphibian toxins can be lethal to humans while others have little effect.<ref name="amphibfacts">{{cite web|url=http://www.eoearth.org/article/Amphibian_morphology_and_reproduction |title=Amphibian morphology and reproduction |date=2008-10-12 |author=Biodiversity Institute of Ontario; Hebert, Paul D. N. |work=Encyclopedia of Earth |accessdate=2012-08-15}}</ref> The main poison-producing glands, the [[Parotoid gland|paratoids]], produce the neurotoxin [[bufotoxin]] and are located behind the ears of certain frogs and toads and behind the eyes of salamanders.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lookd.com/frogs/characteristics.html |title=Physical characteristics |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref> |
|||
===Digestive and excretory systems=== |
|||
Amphibians swallow their prey whole, with some chewing done in the oral cavities of some species, so they possess voluminous stomachs. [[Sphincter]]s separate the esophagus from both the oral cavity and the stomach. The relatively short esophagus is lined with [[cilia]] that help transport food and secretions to the stomach. [[Mucus]] and [[pepsin]], a digestive enzyme, are secreted by glands lining the esophagus. The stomach is separated from the intestine by a pyloric sphincter. The duodenum controls the transport of food into the intestine from the stomach.<ref name=Anatomy/> |
|||
The skin colour of amphibians is produced by three layers of pigment cells called [[chromatophore]]s. These three cell layers consist of the melanophores (occupying the deepest layer), the guanophores (forming an intermediate layer and containing many granules, producing a blue-green colour) and the lipophores (yellow, the most superficial layer). The colour change experienced by many species is caused by secretions from the [[pituitary gland]]. Unlike bony fish, there is no direct control of the pigment cells by the nervous system which results in the colour change taking place more slowly. Bright colours usually indicate that the species is toxic, a defence against predators.<ref>{{cite book |title=The integument: A Textbook of Skin Biology |last=Spearman |first=R. I. C. |year=1973 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=0-521-20048-2 |page=81 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=F7A8AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA81&lpg=PA81&dq=Amphibian+%22skin+colour%22#v=onepage&q=Amphibian%20%22skin%20colour%22&f=false |accessdate=}}</ref> |
|||
Amphibians possess a [[pancreas]], [[liver]] and [[gall bladder]]. Like mammals, the liver functions as the central metabolic organ that regulates blood sugar, and also produces the final metabolic products and transports them through the vascular system to the kidneys, and finally to excretion. The liver in most amphibians is large with two lobes. The size of the liver is determined by its vital function as a glycogen and fat storage unit, and may change proportionally with the seasons with increasing or decreasing activity. In aquatic amphibians, the liver plays only a small role in processing nitrogen for excretion, and ammonia is diffused mainly through the skin and excretion. The liver of terrestrial amphibians converts ammonia to urea, a less toxic, water soluble nitrogenous compound, as a means of water conservation. In some species, urea is further converted into uric acid. The liver secretions from the liver collect in the gall bladder, and flow into the small intestine. Salamanders lack a valve separating the small intestine from the large intestine. In the small intestine, enzymes digest carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Salt and water absorption occur in the large intestine, as well as mucous secretion to aid in the transport of fecal matter, which is passed out through the [[cloaca]]. Amphibians have two [[kidney]]s located dorsally, near the roof of the body cavity. Their job is to filter the blood of waste and transport it to the urinary bladder where it passes out of the cloacal vent.<ref name=Anatomy/> |
|||
=== |
=== Skeletal system and locomotion === |
||
The skeletal system of amphibians is structurally homologous to other [[tetrapod]]s, though with a number of variations. They possess a cranium, spine, rib cage, long bones such as the [[humerus]] and [[femur]], and short bones such as the [[phalanges]], [[metacarpals]], and [[metatarsals]]. They have four limbs except for the legless caecilians and a few species of salamander. The bones are hollow and lightweight.<ref name="AmphibAnat">{{cite web |url=http://www.amphibanat.org/ |title=AmphibAnat |author=Maglia, A.M.; Leopold, J.L.; Pugener, A.L.; Gauch, S. |year=2007 |work=The Amphibian Anatomical Ontology web project |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref><ref name="Anatomy">{{cite web |url=http://www.lookd.com/frogs/anatomy.html |title=Anatomy of the frog |accessdate=2012-03-25}}</ref> The skeletomuscular system is strong to enable it to support the head and body. The bones are fully ossified and the vertebrae interlock with each by means of overlapping processes. The pectoral girdle is supported by muscle and the well developed pelvic girdle is attached to the backbone by a pair of sacral ribs. The ilium slopes forward and the body is held closer to the ground than in mammals.<ref name="Dorit846">{{cite book |title=Zoology |last=Dorit |first=R. L. |coauthors=Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. |year=1991 |publisher=Saunders College Publishing |isbn=0-03-030504-7 |page=846 }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Ambystoma mexicanum at Vancouver Aquarium.jpg|thumb|right|[[Leucistic]] [[axolotl]]s at [[Vancouver Aquarium]]]] |
|||
The lungs in amphibians are primitive compared to those of [[amniote]]s, possessing few internal [[alveolar septum|septa]] and large [[Pulmonary alveolus|alveoli]] and consequently having a comparatively slow diffusion rate for oxygen entering the blood. Ventilation is accomplished by [[buccal pumping]]. Most amphibians, however, are able to exchange gases with the water or air via their skin. To enable sufficient cutaneous respiration, the surface of their highly vascularized skin must remain moist in order to allow the oxygen to diffuse at a sufficiently high rate.<ref name=Anatomy/> Because oxygen concentration in the water increases at both low temperatures and high flow rates, aquatic amphibians in these situations can rely primarily on cutaneous respiration, as in the [[Telmatobius culeus|Titicaca water frog]] and the [[Cryptobranchus|hellbender salamander]]. In air, where oxygen is more concentrated, some small species can rely solely on cutaneous gas exchange, most famously the [[Plethodontidae|plethodontid salamanders]], which have neither lungs nor gills. Many aquatic salamanders and all tadpoles have gills in their larval stage, with some (such as the [[axolotl]]) retaining gills as aquatic adults.<ref name=Anatomy/> |
|||
In most amphibians, there are four digits on the fore foot and five on the hind foot, but no claws on either. Some salamanders have fewer digits and the [[Amphiuma]]s are eel-like in appearance with tiny stubby legs. The [[Sirenidae|sirens]] are aquatic salamanders with stumpy forelimbs and no hind limbs. The caecilians are limbless. They burrow in the manner of earthworms with zones of muscle contractions moving along the body. On the surface of the ground or in water they move by undulating their body from side to side.<ref name="Locomotion">{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=26‑36 }}</ref> |
|||
===Sensory systems=== |
|||
The eyes of amphibians have lids and associated glands and ducts. They are an improvement on invertebrate eyes and were a first step in the development of more advanced vertebrate eyes. They allow colour vision and depth of focus. In the retinas are green rods, which are receptive to a wide range of wavelengths.<ref name=EBAmphibia>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/21445/amphibian/ |title=Amphibian |author=Duellman, William E.; Zug, George R. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-27}}</ref> |
|||
In frogs, the hind legs are larger than the fore legs, especially so in those species that principally move by jumping or swimming. In the walkers and runners the hind limbs are not so large and the burrowers mostly have short limbs and broad bodies. The feet have adaptations for the way of life with webbing between the toes for swimming, broad adhesive toe pads for climbing and [[keratin]]ised [[tubercle]]s on the hind feet for digging (frogs usually dig backwards into the soil). In most salamanders, the limbs are short and more or less the same length and project at right angles from the body. Locomotion on land is by walking and the tail often swings from side to side or is used as a prop, particularly when climbing. In their normal gait, only one leg is advanced at a time in the manner adopted by their ancestors, the [[Sarcopterygii|lobe-finned fish]].<ref name="Dorit846" /> Some salamanders in the genus ''[[Aneides]]'' and certain Plethodontids climb trees and have long limbs, large toepads and prehensile tails.<ref name="BritCaudata" /> In aquatic salamanders, and in frog tadpoles, the tail has dorsal and ventral fins and is moved from side to side as a means of propulsion. Adult frogs do not have tails and caecilians have only very short ones.<ref name="Locomotion" /> |
|||
The tympani, or eardrums, of many frogs are external and lie just behind the eyes. There is also a patch of papilla amphibiorum in the ear, which is unique to amphibians and which can detect low frequency sounds. Another unique feature is the columella-opercular complex, adjoining the auditory capsule, which is involved in the transmission of both airborne and seismic signals. The ears of salamanders and caecilians are less highly developed as they do not normally communicate with each other by sound.<ref name=EBAmphibia/> |
|||
Salamanders use their tails in defence. Some species in the [[Plethodontidae]] have a weak zone at the base of the tail and if the salamander is in danger or if the tail is grabbed by a predator, it breaks off, a process known as [[autotomy]]. Other salamanders are also prepared to drop their tail to save their lives. The tail may continue to twitch after separation which may distract the attacker and both tails and limbs are able to be regenerated.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Beneski, John T. Jr. |year=1989 |title=Adaptive significance of tail autotomy in the salamander, ''Ensatina'' |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=23 |issue=3 |pages=322‑324 |jstor=1564465 |doi=10.2307/1564465 }}</ref> Adult frogs are unable to regrow limbs but tadpoles can do so.<ref name="Locomotion" /> |
|||
==Reproduction== |
|||
[[File:Frogspawn closeup.jpg|thumb|right|Frogspawn]] |
|||
=== Circulatory system === |
|||
For the purpose of [[Biological reproduction|reproduction]] most amphibians require [[fresh water]]. A few (e.g. ''[[Fejervarya raja]]'') can inhabit [[brackish water]] and even survive (though not thrive) in [[seawater]], but there are no true [[marine (ocean)|marine]] amphibians. However, there are reports of particular amphibian populations invading marine waters where their species is normally unable to survive. Such is the case with the [[Black Sea]] invasion of the natural hybrid ''[[Pelophylax esculentus]]'' reported in 2010.<ref name="Froh invasion in Black Sea">[https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:MYycOYYXFiIJ:www.herpetologynotes.seh-herpetology.org/Volume4_PDFs/Natchev_et_al_Herpetology_Notes_Volume4_pages347-351.pdf+frogs+black+sea&hl=bg&gl=bg&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESi9tbbBB4rozxfk6c6Cf5gDcIld_cngMDbC0Pp-qJvRB74fXXflikSNmqTbEl2C9q1CJAS61MLuUEWUHySXbrTFgW16HsngBVx5bdyrjlprkEhlSSunWxmx1wT3d_vV6SGKSWJN&sig=AHIEtbRRzQ7uzcNygo-61Ch2ikoHnHefTA].</ref> |
|||
[[File:Siphonops paulensis02.jpg|thumb|The South American caecilian, [[Siphonops paulensis]]]] |
|||
Amphibians have a juvenile stage and an adult stage and the circulatory systems of the two are distinct. In the juvenile (or tadpole) stage, gills are used to oxygenate blood and movement is similar to that of fish. In the adult stage, amphibians (especially frogs) lose their gills and develop lungs. They have a heart that consists of a ventricle and two atria (it may be considered a single atrium, if not totally or partially divided) that pumps oxygenated blood through arteries and deoxygenated blood through veins to the lungs. Since amphibians are cold-blooded, they must find ways to keep their blood at a constant temperature to maintain [[homeostasis]].<ref name="Anatomy" /> |
|||
=== Nervous and sensory systems === |
|||
The [[nervous system]] is basically the same as in other vertebrates, with a central brain, a spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body.<ref name="Anatomy" /> The amphibian brain is less well developed than that of reptiles, birds and mammals but is similar in morphology and function to that of a fish. It consists of a [[cerebrum]],[[midbrain]] and [[cerebellum]] of approximately equal size. The olfactory lobe is the centre of the sense of smell. The cerebrum integrates behaviour and learning. The optic lobe processes information from the eyes. The cerebellum is the centre of muscular coordination. The [[medulla oblongata]] controls some organ functions including the heart and respiration. The brain sends signals through the spinal cord and nerves to regulate activity in the rest of the body. The pineal body, known to regulate sleep patterns in humans, is thought to produce the hormones involved in hibernation and aestivation in amphibians.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://staff.tuhsd.k12.az.us/gfoster/standard/bamphib.htm |title=Amphibian brains |accessdate=February 16, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Tadpoles retain the lateral line system of their ancestral fishes but this is lost in terrestrial adult amphibians. Some caecilians possess [[Electroreception|electroreceptors]] which allow them to locate objects around them when submerged in water. The ears are well developed in frogs. There is no external ear but the large circular [[Tympanum (anatomy)|eardrum]] lies on the surface of the head just behind the eye. This vibrates and sound is transmitted through a single bone, the stapes, to the inner ear. Only high frequency sounds like mating calls are heard in this way but low frequency noises can be detected through another mechanism.<ref name="Dorit846" /> There is a patch of specialized haircells called "papilla amphibiorum" in the inner ear capable of detecting deeper sounds. Another feature unique to amphibians is the columella-opercular complex, adjoining the auditory capsule, which is involved in the transmission of both airborne and seismic signals. The ears of salamanders and caecilians are less highly developed than frogs as they do not normally communicate with each other by sound.<ref name="EBAmphibia" /> |
|||
Tadpoles' eyes resemble those of fishes in structure but at metamorphosis the cornea becomes more dome-shaped, the lens becomes flatter and eyelids and associated glands and ducts develop.<ref name="Dorit846" /> The adult eyes are an improvement on invertebrate eyes and were a first step in the development of more advanced vertebrate eyes. They allow colour vision and depth of focus. In the retinas are green rods, which are receptive to a wide range of wavelengths.<ref name="EBAmphibia">{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/21445/amphibian/ |title=Amphibian |author=Duellman, William E.; Zug, George R. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-27}}</ref> |
|||
=== Digestive and excretory systems === |
|||
Amphibians swallow their prey whole, with some chewing done in the oral cavities of some species, so they possess voluminous stomachs. [[Sphincter]]s separate the esophagus from both the oral cavity and the stomach. The relatively short esophagus is lined with [[cilia]] that help transport food and secretions to the stomach. [[Mucus]] and [[pepsin]], a digestive enzyme, are secreted by glands lining the esophagus. The stomach is separated from the intestine by a pyloric sphincter. The duodenum controls the transport of food into the intestine from the stomach.<ref name="Anatomy" /> |
|||
Amphibians possess a [[pancreas]], [[liver]] and [[gall bladder]]. Like mammals, the liver functions as the central metabolic organ that regulates blood sugar, and also produces the final metabolic products and transports them through the vascular system to the kidneys, and finally to excretion. The liver in most amphibians is large with two lobes. The size of the liver is determined by its vital function as a glycogen and fat storage unit, and may change proportionally with the seasons with increasing or decreasing activity. In aquatic amphibians, the liver plays only a small role in processing nitrogen for excretion, and ammonia is diffused mainly through the skin and excretion. The liver of terrestrial amphibians converts ammonia to urea, a less toxic, water soluble nitrogenous compound, as a means of water conservation. In some species, urea is further converted into uric acid. The liver secretions from the liver collect in the gall bladder, and flow into the small intestine. Salamanders lack a valve separating the small intestine from the large intestine. In the small intestine, enzymes digest carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Salt and water absorption occur in the large intestine, as well as mucous secretion to aid in the transport of faecal matter, which is passed out through the [[cloaca]].<ref name="Anatomy" /> |
|||
Amphibians have two [[kidney]]s located dorsally, near the roof of the body cavity. Their job is to filter the blood of metabolic waste and transport the urine via ureters to the urinary bladder where it is stored before being passed out periodically through the cloacal vent. Larvae and most aquatic adult amphibians excrete the nitrogen as [[ammonia]] in large quantities of dilute urine while terrestrial species, with a greater need to conserve water, excrete the less toxic product [[urea]]. Some tree frogs with limited access to water excrete most of their metabolic waste as [[uric acid]].<ref name="Dorit849">{{cite book |title=Zoology |last=Dorit |first=R. L. |coauthors=Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. |year=1991 |publisher=Saunders College Publishing |isbn=0-03-030504-7 |page=849 }}</ref> |
|||
=== Respiratory system === |
|||
[[File:Ambystoma mexicanum at Vancouver Aquarium.jpg|thumb|[[Leucistic]] [[axolotl]]s at [[Vancouver Aquarium]]]] |
|||
The lungs in amphibians are primitive compared to those of [[amniote]]s, possessing few internal [[alveolar septum|septa]] and large [[Pulmonary alveolus|alveoli]] and consequently having a comparatively slow diffusion rate for oxygen entering the blood. Ventilation is accomplished by [[buccal pumping]]. Most amphibians, however, are able to exchange gases with the water or air via their skin. To enable sufficient cutaneous respiration, the surface of their highly vascularized skin must remain moist in order to allow the oxygen to diffuse at a sufficiently high rate.<ref name="Anatomy" /> Because oxygen concentration in the water increases at both low temperatures and high flow rates, aquatic amphibians in these situations can rely primarily on cutaneous respiration, as in the [[Telmatobius culeus|Titicaca water frog]] and the [[Cryptobranchus|hellbender salamander]]. In air, where oxygen is more concentrated, some small species can rely solely on cutaneous gas exchange, most famously the [[Plethodontidae|plethodontid salamanders]], which have neither lungs nor gills. Many aquatic salamanders and all tadpoles have gills in their larval stage, with some (such as the [[axolotl]]) retaining gills as aquatic adults.<ref name="Anatomy" /> |
|||
== Reproduction == |
|||
[[File:Frogspawn closeup.jpg|thumb|Frogspawn]] |
|||
For the purpose of [[Biological reproduction|reproduction]] most amphibians require [[fresh water]] although some lay their eggs on land and have developed various ingenious ways of keeping them moist. A few (e.g. ''[[Fejervarya raja]]'') can inhabit [[brackish water]] and even survive (though not thrive) in [[seawater]], but there are no true [[marine (ocean)|marine]] amphibians. However, there are reports of particular amphibian populations invading marine waters where their species is normally unable to survive. Such is the case with the [[Black Sea]] invasion of the natural hybrid ''[[Pelophylax esculentus]]'' reported in 2010.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Natchev, Nikolay; Tzankov, Nikolay; Geme, Richard |year=2011 |title=Green frog invasion in the Black Sea: habitat ecology of the Pelophylax esculentus complex (Anura, Amphibia) population in the region of Shablenska Тuzla lagoon in Bulgaria |journal=Herpetology Notes |volume=4 |pages=347‑351 |url=http://www.herpetologynotes.seh-herpetology.org/Volume4_PDFs/Natchev_et_al_Herpetology_Notes_Volume4_pages347-351.pdf }}</ref> |
|||
Several hundred frog species in [[adaptive radiation]]s (e.g., ''[[Eleutherodactylus]]'', the Pacific Platymantines, the Australo-Papuan microhylids, and many other tropical frogs), however, do not need any water for [[breeding in the wild]]. They reproduce via direct development, an ecological and [[evolution]]ary adaptation that has allowed them to be completely independent from free-standing water. Almost all of these frogs live in wet [[Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|tropical rainforests]] and their eggs hatch directly into miniature versions of the adult, passing through the [[tadpole]] stage within the egg. Reproductive success of many amphibians is dependent not only on the quantity of rainfall, but the seasonal timing.<ref>C.Michael Hogan. 2010. [http://www.eoearth.org/article/Abiotic_factor?topic=49461 ''Abiotic factor''. ''Encyclopedia of Earth''. eds Emily Monosson and C. Cleveland. National Council for Science and the Environment]. Washington DC</ref> |
Several hundred frog species in [[adaptive radiation]]s (e.g., ''[[Eleutherodactylus]]'', the Pacific Platymantines, the Australo-Papuan microhylids, and many other tropical frogs), however, do not need any water for [[breeding in the wild]]. They reproduce via direct development, an ecological and [[evolution]]ary adaptation that has allowed them to be completely independent from free-standing water. Almost all of these frogs live in wet [[Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|tropical rainforests]] and their eggs hatch directly into miniature versions of the adult, passing through the [[tadpole]] stage within the egg. Reproductive success of many amphibians is dependent not only on the quantity of rainfall, but the seasonal timing.<ref>C.Michael Hogan. 2010. [http://www.eoearth.org/article/Abiotic_factor?topic=49461 ''Abiotic factor''. ''Encyclopedia of Earth''. eds Emily Monosson and C. Cleveland. National Council for Science and the Environment]. Washington DC</ref> |
||
In the tropics, many amphibians breed continuously or at any time of year. In temperate regions, breeding is mostly seasonal, usually in the spring, and is triggered by increasing day length, rising temperatures or rainfall. Experiments have shown the importance of temperature but the trigger event, especially in arid regions, is often rainfall. In anurans, males usually arrive at the breeding sites before females and the vocal chorus they produce may stimulate the endocrine activity of males that are not yet reproductively active and ovulation in females.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=140‑141 }}</ref> |
|||
Many amphibians exhibit different kinds of [[Parental investment|parenting behaviour]]. After their hatching, the tadpoles of different species of [[poison dart frog]]s (family ''Dendrobatidae'') are carried by the adults to a suitable place where they can pass metamorphosis. Such places are the [[Rosette (botany)|rosette]]s of many [[bromeliads]] in which water is gathered and used by the plant. The [[Surinam toad]] raises its young in pores at its back and after enough time they appear out of these pores fully developed. The ringed caecilian (''[[Siphonops annulatus]]'') has developed a unique adaptation for the purposes of reproduction. The progeny feeds on a skin layer that is specially developed by the adult. This phenomenon is known as maternal dermatophagy. |
|||
In caecilians, fertilisation is internal, the male extruding an intromittent organ, the phallodeum, and inserting it into the female cloaca. The paired Müllerian glands inside the male cloaca secrete a fluid which resembles that produced by mammalian [[prostate]] glands and which may transport and nourish the sperm. Fertilisation probably takes place in the oviduct.<ref name="Duellman">{{cite book |title=Biology of Amphibians |last=Duellman|first=Willia E. |coauthors= Trueb, Linda |year=1994 |publisher=JHU Press |isbn=080184780X |pages=77‑79 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=CzxVvKmrtIgC&pg=PA77&lpg=PA77&dq=phallodeum#v=onepage&q=phallodeum&f=false }}</ref> |
|||
The majority of salamanders also engage in internal fertilisation. In most of these, the male deposits a [[spermatophore]], a small packet of sperm on top of a gelatinous cone, on the [[Substrate (biology)|substrate]] either on land or in the water. The female takes the sperm packet into her vent by grasping it with the lips of the cloaca. The spermatozoa move to the [[spermotheca]] in the roof of the cloaca where they remain until ovulation which may be many months later. Courtship rituals and methods of transfer of the spermatophore vary between species. In some, the male places the spermatophore into the female cloaca, in others he guides her to it or restrains her with an embrace called [[amplexus]]. Certain primitive salamanders in the families [[Sirenidae]], [[Hynobiidae]] and [[Cryptobranchidae]] practice external fertilisation in a similar manner to frogs, with the female laying the eggs in water and the male releasing sperm onto the egg mass.<ref name="Duellman" /> |
|||
With a few exceptions, frogs use external fertilisation. The male grasps the female tightly with his forelimbs either behind her arms or in front of her back legs, or in the case of ''[[Epipedobates tricolor]]'', round her neck. They remain in amplexus with their cloacae positioned close together while she lays her eggs and he covers them with his sperm. Roughened nuptial pads on his hands help him retain his grip. Often the male collects and retains the egg mass, forming his hind feet into a sort of basket. An exception is the [[granular poison frog]] (''Oophaga granulifera'') where the male and female place their cloacae in close proximity while facing in opposite directions and then release eggs and sperm simultaneously. The [[tailed frog]] (''Ascaphus truei'') exhibits internal fertilisation. The "tail" is only possessed by the male and is an extension of the cloaca and used to inseminate the female. This frog lives in fast flowing streams and internal fertilisation will prevent the sperm being washed away before fertilisation occurs.<ref name="Steb">{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=154‑162 }}</ref> |
|||
Most frogs can be classified as either prolonged or explosive breeders. Typically, prolonged breeders congregate at a breeding site, the males usually arriving first, calling and setting up territories. Other satellite males remain quietly nearby, waiting for their opportunity to take over a territory. The females arrive sporadically, mate selection takes place and eggs are laid. The females depart and territories may change hands and more females appear and in due course, the breeding season comes to an end. Explosive breeders on the other hand are found where temporary pools appear in dry regions after rainfall. These frogs are typically fossorial species that emerge after heavy rains and congregate at a breeding site. They are attracted there by the calling of the first male to find a suitable place, perhaps a pool that forms in the same place each rainy season. The assembled frogs may call in unison and frenzied activity ensues, the males scrambling to mate with the usually smaller number of females.<ref name="Steb" /> |
|||
The ringed caecilian (''[[Siphonops annulatus]]'') has developed a unique adaptation for the purposes of reproduction. The progeny feeds on a skin layer that is specially developed by the adult. This phenomenon is known as maternal dermatophagy. The [[common tree frog]] (''Polypedates leucomystax'') from Asia makes a foam nest on a leaf above an ephemeral pool. When the eggs hatch, the tadpoles work themselves out of the foam and fall into the water below.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://amphibiaweb.org/cgi/amphib_query?where-genus=Polypedates&where-species=leucomystax |title=''Polypedates leucomystax'' |author=Whittaker, Kellie ; Tsai, Gary |date=2005-10-24 |publisher=AmphibiaWeb |accessdate=2012-08-24}}</ref> |
|||
Several species have also adapted to arid and semi-arid environments, but most of them still need water to lay their eggs. [[Symbiosis]] with single celled [[algae]] that lives in the jelly-like layer of the eggs has evolved several times. The larvae of frogs (tadpoles) breathe with exterior [[gill]]s at the start, but soon a pouch is formed that covers the gills and the front legs. Lungs are also formed quite early to assist in breathing. Newt larvae have large external gills that gradually disappear and the larvae of newts are quite similar to the adult form from an early age. |
|||
== Life cycle == |
|||
[[File:Kaulquappen Tadpole 3.JPG|thumb|Tadpoles]] |
|||
Most amphibians go through [[metamorphosis]], a process of significant morphological change after birth. In typical amphibian development, eggs are laid in water and larvae are adapted to an aquatic lifestyle. Frogs, toads and salamanders all hatch from the egg as larvae with external gills. Metamorphosis in amphibians is regulated by [[thyroxin]] concentration in the blood, which stimulates metamorphosis, and [[prolactin]], which counteracts its effect. Specific events are dependent on threshold values for different tissues.<ref>{{cite book |title=International Review of Cytology: Aspects of amphibian metamorphosis: Hormonal control |last=Kikuyama |first=Sakae |authorlink= |coauthors=Kawamura K.; Tanaka, S.; Yamamoto, K. |year=1993 |publisher=Academic Press |location= |isbn= 9780123645487|page= |pages=105–126 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=wfSM70CuYqYC&pg=PA105&dq=amphibian+metamorphosis#v=onepage&q=amphibian%20metamorphosis&f=false |accessdate=}}</ref> Because most embryonic development is outside the parental body, development is subject to many adaptations due to specific ecological circumstances. For this reason tadpoles can have horny ridges for teeth, whiskers and fins. They also make use of the [[lateral line]] organ. After metamorphosis, these organs become redundant and will be reabsorbed by controlled cell death, called [[apoptosis]]. The extent of adaptations to specific ecological circumstances among amphibians is remarkable, with many discoveries still being made.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Newman, Robert A. |year=1992 |title=Adaptive Plasticity in Amphibian Metamorphosis |journal=BioScience |volume=42 |issue=9 |pages=671–678 |publisher= |doi= 10.2307/1312173|pmid= |pmc= |accessdate= |jstor=1312173}}</ref> |
|||
=== Eggs === |
|||
The egg of an amphibian is typically surrounded by a transparent gelatinous covering secreted by the oviducts and containing [[mucoprotein]]s and [[mucopolysaccharide]]s. This capsule is permeable to water and gases and swells considerably as it absorbs water. The ovum is at first rigidly held but in fertilised eggs, the innermost layer liquefies and allows the [[embryo]] to move freely and this also happens in salamander eggs even when they are unfertilised. Eggs of some salamanders and frogs contain unicellular green algae. These penetrate the jelly envelope after the eggs are laid and may increase the supply of oxygen to the embryo through photosynthesis. They seem to both speed up the development of the larvae and reduce mortality.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Gilbert, Perry W. |year=1942 |title=Observations on the eggs of ''Ambystoma maculatum'' with especial reference to the green algae found within the egg envelopes |journal=Ecology |volume=23 |pages=215‑227 |jstor=1931088 |doi=10.2307/1931088 |issue=2 }}</ref> Most eggs contain the pigment [[melanin]] which raises their temperature and protects them against [[ultraviolet radiation]]. Species such as caecilians, plethodontid salamanders and certain frogs that lay eggs underground or in dark locations usually have unpigmented eggs. In the [[Wood Frog|wood frog]] (''Rana sylvatica''), the interior of the globular egg cluster has been found to be up to 6°C (11°F) warmer than its surroundings which is an advantage in its cool northern habitat.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Waldman, Bruce; Ryan, Michael J. |year=1983 |title=Thermal advantages of communal egg mass deposition in wood frogs (''Rana sylvatica'') |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=17 |issue=1 |pages=70‑72 |jstor=1563783 |doi=10.2307/1563783 }}</ref> |
|||
The eggs or spawn may be deposited singly or in small groups or may take the form of spherical egg masses, rafts or long strings. In terrestrial caecilians, the eggs are laid in grape-like clusters in burrows near streams. The amphibious salamander ''[[Ensatina]]'' attaches its similar clusters by stalks to underwater stems and roots. The [[Eleutherodactylus planirostris|greenhouse frog]] (''Eleutherodactylus planirostris'') lays eggs in small groups in the soil where they develop in about two weeks directly into juvenile frogs without an intervening larval stage.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.arkive.org/greenhouse-frog/eleutherodactylus-planirostris/ |title=Greenhouse frog (''Eleutherodactylus planirostris'') |publisher=ARKive |accessdate=2012-08-18}}</ref> The [[tungara frog]] (''Physalaemus pustulosus'') builds a floating nest from foam to protect its eggs. A raft is built first and then eggs are laid in the centre and there is a foam capping. The foam has anti-microbial properties. It contains no detergents but is created by whipping up [[protein]]s and [[lectin]]s secreted by the female.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Dalgetty, Laura; Kennedy, Malcolm W. |year=2010 |title=Building a home from foam: túngara frog foam nest architecture and three-phase construction process {{open access}}|journal=Biology Letters |volume=6 |issue=3 |pages=293–6 |doi=10.1098/rsbl.2009.0934 |pmid=20106853 |pmc=2880057 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gla.ac.uk/schools/lifesciences/staff/malcolmkennedy/malcolmkennedy/proteinsoffrogfoamnests/ |title=Proteins of frog foam nests |publisher=University of Glasgow |accessdate=2012-08-24}}</ref> |
|||
Several species have also adapted to arid and semi-arid environments, but most of them still need water to lay their eggs. [[Symbiosis]] with single celled [[algae]] that lives in the jelly-like layer of the eggs has evolved several times. The larvae of frogs (tadpoles or polliwogs) breathe with exterior [[gill]]s at the start, but soon a pouch is formed that covers the gills and the front legs. Lungs are also formed quite early to assist in breathing. Newt larvae have large external gills that gradually disappear and the larvae of newts are quite similar to the adult form from an early age. |
|||
== |
=== Larvae === |
||
The eggs of amphibians are typically laid in water and hatch into free-living larvae that complete their development in water and later transform into either aquatic or terrestrial adults. In many species of frog and in most lungless salamanders ([[Plethodontidae]]), direct development takes place, the larvae growing within the eggs and emerging as miniature adults. Many caecilians and some other amphibians lay their eggs on land and the newly hatched larvae wriggle or are transported to water bodies. Some caecilians, the [[Alpine salamander]] (''Salamandra atra'') and some of the [[Nectophrynoides|African live-bearing toads]] (''Nectophrynoides spp.'') are [[Vivipary|viviparous]], the larvae feeding on glandular secretions and developing within the female's oviduct, often for long periods. Other amphibians, but not as far as it is known caecilians, are [[Ovoviviparity|ovoviviparous]]. The eggs are retained in or on the parent's body but the larvae subsist on the yolks of their eggs and receive no nourishment from the adult. The larvae emerge at varying stages of their growth, either before or after metamorphosis, according to their species.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=6‑9 }}</ref> The toad genus ''Nectophrynoides'' exhibits all these developmental patterns among its dozen or so members.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://fds.oup.com/www.oup.com/pdf/13/9780199541188_chapter1.pdf |title=Amphibian diversity and life history |author=Crump, Martha L. |date=2009-08-19 |page=14 |accessdate=2012-08-30}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Kaulquappen Tadpole 3.JPG|thumb|right|Tadpoles]] |
|||
Most amphibians go through [[metamorphosis]], a process of significant morphological change after birth. In typical amphibian development, eggs are laid in water and larvae are adapted to an aquatic lifestyle. Frogs, toads and salamanders all hatch from the egg as larvae with external gills. Metamorphosis in amphibians is regulated by [[thyroxin]] concentration in the blood, which stimulates metamorphosis, and [[prolactin]], which counteracts its effect. Specific events are dependent on threshold values for different tissues.<ref>{{cite book |title=International Review of Cytology: Aspects of amphibian metamorphosis: Hormonal control |last=Kikuyama |first=Sakae |authorlink= |coauthors=Kawamura K.; Tanaka, S.; Yamamoto, K. |year=1993 |publisher=Academic Press |location= |isbn= |page= |pages=105–126 |url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=wfSM70CuYqYC&oi=fnd&pg=PA105&dq=amphibian+metamorphosis&ots=iBzh0cUJyH&sig=-s4zVunWmW68k7I22jPGneNI9K8#v=onepage&q=amphibian%20metamorphosis&f=false |accessdate=}}</ref> Because most embryonic development is outside the parental body, development is subject to many adaptations due to specific ecological circumstances. For this reason tadpoles can have horny ridges for teeth, whiskers and fins. They also make use of the [[lateral line]] organ. After metamorphosis, these organs become redundant and will be reabsorbed by controlled cell death, called [[apoptosis]]. The extent of adaptations to specific ecological circumstances among amphibians is remarkable, with many discoveries still being made.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Newman, Robert A. |year=1992 |title=Adaptive Plasticity in Amphibian Metamorphosis |journal=BioScience |volume=42 |issue=9 |pages=671–678 |publisher= |doi= |pmid= |pmc= |accessdate= |jstor=1312173}}</ref> |
|||
=== Frogs |
==== Frogs ==== |
||
[[File:Frog spawn time-lapse.gif|thumb|Frogspawn development]] |
|||
[[File:Metamorphosis frog Meyers.png|thumb|Life cycle of a typical frog]] |
[[File:Metamorphosis frog Meyers.png|thumb|Life cycle of a typical frog]] |
||
Frog larvae are known as tadpoles and typically have oval bodies and long, vertically flattened tails with fins. The free living larvae are normally fully aquatic but the tadpoles of some species such as (''[[Nannophrys ceylonensis]]'') are semi-terrestrial and live among wet rocks.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1P.html|title=Ontogenetic Changes in Diet and Intestinal Morphology in Semi-Terrestrial Tadpoles of ''Nannophrys ceylonensis'' (Dicroglossidae)}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://amphibiaweb.org/cgi-bin/amphib_query?query_src=aw_lists_genera_&table=amphib&where-genus=Nannophrys&where-species=ceylonensis |title=''Nannophrys ceylonensis'' |author=Janzen, Peter |date=2005-05-10 |work=AmphibiaWeb |publisher=University of California, Berkeley |accessdate=2012-07-20}}</ref> Tadpoles have cartilaginous skeletons, gills for respiration (external gills at first, internal gills later), [[lateral line system]]s and large tails which they use for swimming.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-40603/Anura |title=Anura: From tadpole to adult |author=Duellman, W. E.; Zug, G. R. |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-07-13}}</ref> Newly hatched tadpoles soon develop gill pouches which cover the gills and their lungs develop early and are used as accessory breathing organs, the tadpoles rising to the water surface to gulp air. Some species complete their development inside the egg and hatch directly into small frogs. These larvae do not have gills but instead have specialised areas of skin through which respiration takes place. Tadpoles do not have true teeth but, in most species, the jaws have long, parallel rows of small keratinized structures called keradonts surrounded by a horny beak.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=179‑181 }}</ref> Front legs are formed under the gill sac and hind legs become visible a few days later. Tadpoles are typically [[herbivore|herbivorous]], feeding mostly on [[alga]]e, including [[diatom]]s filtered from the water through the [[gill]]s. They are also [[detrivore]]s, stirring up the sediment at the pond bottom and ingesting edible fragments. They have a relatively long, spiral-shaped gut to enable them to digest this diet.<ref name="EBAnura">{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/29023/Anura |title=Anura |author=Duellman, William E.; Zug, George R. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-26}}</ref> Some species are carnivorous at the tadpole stage, eating insects, smaller tadpoles and fish. Young of the [[Cuban tree frog]] (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') can occasionally be [[Cannibalism|cannibalistic]], the younger tadpoles attacking a larger, more developed tadpole when it is undergoing metamorphosis.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Crump, Martha L. |year=1986 |title=Cannibalism by younger tadpoles: another hazard of metamorphosis |journal=Copeia |volume=4 |pages=1007‑1009 |publisher=American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists |jstor=1445301 |doi=10.2307/1445301 |issue=4 }}</ref> |
|||
With frogs and toads, the external gills of the newly hatched tadpole are covered with a gill sac after a few days, and lungs are quickly formed. Front legs are formed under the gill sac, and hind legs are visible a few days later. Following that there is usually a longer stage during which the tadpole has a vegetarian diet, scraping algae off plant surfaces with their horny tooth ridges. Tadpoles have a relatively long, spiral-shaped gut to enable them to digest this diet.<ref name=EBAnura>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/29023/Anura |title=Anura |author=Duellman, William E.; Zug, George R. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-26}}</ref> |
|||
At metamorphosis, rapid changes in the body take place as the lifestyle of the frog changes completely. The spiral‐shaped mouth with horny tooth ridges is reabsorbed together with the spiral gut. The animal develops a big jaw, and its gills disappear along with its gill sac. Eyes and legs grow quickly, a tongue is formed, and all this is accompanied by associated changes in the neural networks (development of stereoscopic vision, loss of the lateral line system, etc.) All this can happen in about a day, so it is truly a metamorphosis. It isn't until a few days later that the tail is reabsorbed, due to the higher thyroxin concentrations required for tail resorption.<ref name="EBAnura" /> |
|||
=== |
==== Salamanders ==== |
||
At hatching, a typical salamander larva has eyes without lids, teeth in both upper and lower jaws, three pairs of feathery external gills and a long, somewhat laterally flattened body and tail with dorsal and ventral fins. The forelimbs may be partially developed and the hind limbs are rudimentary in pond-living species but may be rather more developed in species that reproduce in moving water. Pond-type larvae often have a pair of balancers, rod-like structures on either side of the head which perhaps prevent the gills from getting clogged up with bottom sediment. Some members of the genera ''[[Ambystoma]]'' and ''[[Dicamptodon]]'' have larvae that never fully develop into the adult form but this varies with species and with populations. The [[Northwestern Salamander|northwestern salamander]] (''Ambystoma gracile'') is one of these and, depending on environmental factors, either remains permanently in the larval state, a condition known as [[neoteny]], or transforms into an adult.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Valentine, Barry D.; Dennis, David M. |year=1964 |title=A Comparison of the gill-arch system and fins of three genera of larval salamanders, ''Rhyacotriton'', ''Gyrinophilus'', and ''Ambystoma'' |journal=Copeia |volume=1 |pages=196‑201 |jstor=1440850 |doi=10.2307/1440850 }}</ref> Neoteny occurs when the animal's growth rate is very low. This is usually because of adverse conditions such as low water temperatures which may inhibit the production of thyroxin or prevent the larva from reacting to the [[hormone]] in the normal way. Other factors that may inhibit metamorphosis include lack of food, lack of trace elements and competition from [[conspecific]]s. The [[tiger salamander]] (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') also sometimes behaves in this way and may grow particularly large in the process. The adult tiger salamander is terrestrial but the larva is aquatic and able to breed while still in the larval state. When conditions are particularly inhospitable on land, larval breeding may allow continuation of a population that would otherwise die out. There are fifteen species of obligate neotenic salamanders including ''[[Necturus]]'', ''[[Olm|Proteus]]'' and ''[[Amphiuma]]'', and many examples of facultative ones that adopt this strategy under appropriate environmental circumstances.<ref>{{cite book |title=Biology of Amphibians |last=Duellman |first=William E. |coauthors=Trueb, Linda |year=1994 |publisher=JHU Press |isbn=080184780X |pages=191‑192 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=CzxVvKmrtIgC&pg=PA191&lpg=PA191&dq=salamander+obligate+neoteny#v=onepage&q=salamander%20obligate%20neoteny&f=false }}</ref> |
|||
In newts and salamanders, there is no true metamorphosis because the larvae already feed as predators and continue doing so as adults. Their gills are never covered by a gill sac and will be reabsorbed only just before the animal leaves the water. Just as in tadpoles, their lungs are functional early, but the larvae don't make as much use of them as tadpoles do. They often have an aquatic phase in spring and summer, and a land phase in winter. For adaptation to a water phase, [[prolactin]] is the required hormone, and for adaptation to the land phase, [[thyroxin]]. External gills do not return in subsequent aquatic phases because these are completely absorbed upon leaving the water for the first time.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/100353/Caudata |title=Caudata |author=Wake, David B. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-26}}</ref> |
|||
[[Lungless salamander]]s in the family Plethodontidae are terrestrial and lay a small number of unpigmented eggs in a cluster among damp leaf litter. Each egg has a large yolk sac and the larva feeds on this while it develops inside the egg, emerging fully formed as a juvenile salamander. The female salamander often broods the eggs and in the genus ''[[Ensatinas]]'', she has been observed to coil around them and press her throat area against them, effectively massaging them with a mucous secretion.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |page=196 }}</ref> |
|||
===Caecilians=== |
|||
Most caecilians lay eggs in burrows formed in moist soil close to water. The eggs are watched over by the female and, on hatching, the young make their way into the adjoining pond or stream. They have gill slits but no external gills. In some species, the young are produced by [[vivipary]]. Up to four eggs begin their development in the oviduct. When their yolk has been consumed, the developing larvae feed on maternal secretions and on the cells lining the oviduct, scraping them off with their deciduous teeth.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/29797/Gymnophiona |title=Gymnophiona |author=Duellman, William E. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-26}}</ref> |
|||
In newts and salamanders, metamorphosis is less dramatic than in frogs. This is because the larvae are already carnivorous and continue to feed as predators when they are adults so few changes are needed to their digestive systems. Their lungs are functional early but the larvae don't make as much use of them as do tadpoles. Their gills are never covered by gill sacs and are reabsorbed just before the animals leave the water. Other changes include the reduction in size or loss of tail fins, the closure of gill slits, thickening of the skin, the development of eyelids, and certain changes in dentition and tongue structure. Salamanders are at their most vulnerable at metamorphosis as swimming speeds are reduced and transforming tails are encumbrances on land.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Shaffer, H. Bradley ; Austin, C. C.; Huey, R. B. |year=1991 |title=The consequences of metamorphosis on salamander (''Ambystoma'') locomotor performance |journal=Physiological Zoology |volume=64 |issue=1 |pages=212‑231 |jstor=30158520 }}</ref> Adult salamanders often have an aquatic phase in spring and summer, and a land phase in winter. For adaptation to a water phase, [[prolactin]] is the required hormone, and for adaptation to the land phase, thyroxin. External gills do not return in subsequent aquatic phases because these are completely absorbed upon leaving the water for the first time.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/100353/Caudata |title=Caudata |author=Wake, David B. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-26}}</ref> |
|||
==Diet== |
|||
Adult amphibians are [[Predation|predators]], feeding mainly on live invertebrates. The diet mostly consists of small items of prey that do not move too fast such as beetles, caterpillars, earthworms and spiders. Many amphibians have extensible tongues with sticky tips that can be flicked forward to catch the prey. They usually swallow the food whole but may chew it lightly first in order to subdue it.<ref name=Collins/> The larvae of frogs and toads have a mostly vegetarian diet, using their specialised mouthparts, consisting of a horny beak edged by several rows of labial teeth, to feed on aquatic plants.<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
==== Caecilians ==== |
|||
==Vocalization== |
|||
Most terrestrial caecilians that lay eggs do so in burrows or moist places on land near bodies of water. The development of the young of ''[[Ichthyophis glutinosus]]'', a species from Sri Lanka, has been much studied. The eel-like larvae hatch out of the eggs and make their way to water. They have three pairs of external red feathery gills, a blunt head with two rudimentary eyes, a lateral line system and a short tail with fins. They swim by undulating their body from side to side. They are mostly active at night, soon lose their gills and make sorties onto land. Metamorphosis is gradual but by the age of about ten months they have developed a pointed head with sensory tentacles near the mouth and lost their eyes, lateral line systems and tails. The skin has becomes thicker, embedded scales have developed and the body has become divided into segments. By this time the caecilian has constructed a burrow and is living on land.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Breckenridge, W. R.; Nathanael, S.; Pereira, L. |year=1987 |title=Some aspects of the biology and development of ''Ichthyophis glutinosus'' |journal=Journal of Zoology |volume=211 |pages=437‑449 }}</ref> |
|||
The noises made by newts, salamanders and caecilians are limited to occasional soft squeaks, grunts or hisses. Frogs and toads however use their voice in the breeding season to attract mates. Each call is characteristic of the species, the presence of which in an area may be easier to detect by its voice than by a fleeting glimpse of the animal itself. In ponds where more than one species breed, it is important for the female to be attracted to the correct partner as male frogs, in their ardour, have been known to attempt to mate with other males, females of the wrong species or inanimate objects.<ref name=Collins/> Besides the attracting call, another vocalization is a release call, used by a frog suffering in this way from advances by the wrong frog. Calling bears the risk of attracting predators. Some males do not call at all but station themselves near others that are calling, with the intention of intercepting a female attracted to the sound. Although calling mainly occurs in the breeding season, sporadic calls may be heard at other times of year in some species.<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
In the majority of species of caecilians, the young are produced by [[vivipary]]. ''[[Typhlonectes compressicauda]]'', a species from South America, is typical of these. Up to nine larvae can develop in the oviduct at any one time. They are elongated and have paired sac-like gills, small eyes and specialised scraping teeth. At first they feed on the yolks of the eggs but as this source of nourishment declines they begin to rasp at the ciliated epithelial cells that line the oviduct. This stimulates the secretion of fluids rich in [[lipid]]s and [[mucoprotein]]s on which they feed along with scrapings from the oviduct wall. They may increase their length sixfold and be two fifths as long as their mother before being born. By this time they have undergone metamorphosis, lost their eyes and gills, developed a thicker skin and mouth tentacles and reabsorbed their teeth. A permanent set of teeth grow through soon after birth.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Wake, Marvalee H. |year=1977 |title=Fetal maintenance and its evolutionary significance in the Amphibia: Gymnophiona |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=379‑386 |jstor=1562719 |doi=10.2307/1562719 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/29797/Gymnophiona |title=Gymnophiona |author=Duellman, William E. |year=2012 |work=Encyclopædia Britannica Online |publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica |accessdate=2012-03-26}}</ref> |
|||
The calls are made by vibrations of the larynx but are often amplified by [[vocal sac]]s, which act as resonators. Sometimes these are fairly small air-filled pouches inside the mouth but in other species they are much larger and cause a ballooning of the elastic skin of the throat and are known as external vocal sacs. Many species have single sacs but members of the family [[Ranidae]] have two, one on each side of the mouth.<ref name=Collins/> |
|||
=== Parental care === |
|||
==Defense mechanisms== |
|||
The care of offspring among amphibians has been little studied but in general, the larger the number of eggs in a batch, the less likely it is that any degree of parental care takes place. Nevertheless, it is estimated that up to twenty percent of amphibian adults play some role in the care of the young.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Crump| first=M. L.| year=1996| title=Parental care among the Amphibia| journal=Advances in the Study of Behavior| volume=25| pages=109‑144| doi=10.1016/S0065-3454(08)60331-9|series=Advances in the Study of Behavior|isbn=9780120045259 }}</ref> Those species that breed in smaller water bodies or other specialised habitats tend to have more complex patterns of behaviour in the care of the young than do others.<ref name="Brown1">{{cite journal | doi = 10.1086/650727 | last1 = Brown | first1 = J. L. | last2 = Morales | first2 = V. | last3 = Summers | first3 = K. | year = 2010 | title = A key ecological trait drove the evolution of biparental care and monogamy in an amphibian | journal = American Naturalist | volume = 175 | issue = 4| pages = 436‑446 | pmid = 20180700 }}</ref> |
|||
Amphibians have soft bodies and are relatively helpless. They are eaten by reptiles, birds and mammals when on land and by fish when in the water. Many are nocturnal and hide during the day, thereby avoiding predators that hunt by sight, apart from owls, which are also nocturnal. Other amphibians use [[camouflage]] to avoid being detected. They have various colorings such as mottled browns, greys and olives to make themselves inconspicuous so that they blend into the background. Other species contain poison glands and use bright colours to warn potential predators of their toxicity. These are mostly black and yellow or black and red, like the [[Fire Salamander|fire salamander]] (''Salamandra salamandra''). Once a predator has tried eating one of these, it is likely to remember the coloration next time it encounters one. In some species, such as the [[fire-bellied toad]] (''Bombina spp.''), the warning coloration is on the belly and these animals adopt a defensive pose when attacked to exhibit the bright colors to the attacker. A few salamanders will [[Autotomy|autotomise]] their tails when attacked, sacrificing this part of their body to enable the main part to escape. The tail is regenerated later. Some frogs and toads inflate themselves to make themselves look large and fierce, and some spadefoot toads (''[[Pelobates]] spp'') scream and leap towards the attacker.<ref name=Collins/> Giant Salamanders of the genus ''[[Andrias]]'', as well as Ceratophrine and ''[[Pyxicephalus]]'' frogs posess sharp teeth and are capable of drawing blood with a defensive bite. |
|||
Many woodland salamanders lay clutches of eggs under dead logs or stones on land. The [[Black Mountain Salamander|black mountain salamander]] does this, the mother brooding the eggs and guarding them from predation as the larvae feed on the yolks of their eggs. They eventually break their way out of the egg capsules and disperse.<ref name="Dorit853–854">{{cite book |title=Zoology |last=Dorit |first=R. L. |coauthors=Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. |year=1991 |publisher=Saunders College Publishing |isbn=0-03-030504-7 |page=853‑854 }}</ref> The male [[hellbender]], a primitive salamander, excavates an underwater nest and encourages females to lay there. He then guards the site for the two to three months before the eggs hatch, undulating his body and fanning them with his skin folds to increase their supply of oxygen.<ref name="EHSAR" /> |
|||
==Conservation== |
|||
The tiny male frog ''[[Colostethus subpunctatus]]'' protects his egg cluster which is hidden under a stone or log. When the eggs hatch, he transports the tadpoles on his back, stuck there by a mucous secretion, to a temporary pool where he dips himself into the water and the tadpoles drop off.<ref>{{cite journal |author= Fandiño, María Claudia; Lüddecke, Horst; Amézquita, Adolfo |year=1997 |title=Vocalisation and larval transportation of male ''Colostethus subpunctatus'' (Anura: Dendrobatidae) |journal=Amphibia-Reptilia |volume=18 |issue=1 |pages=39‑48 |doi=10.1163/156853897X00297 }}</ref> The male [[Common midwife toad|midwife toad]] (''Alytes obstetricans'') winds egg strings round his thighs and carries the eggs around for up to eight weeks. He keeps them moist and when they are ready to hatch, visits a pond or ditch and releases the tadpoles.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.herpfrance.com/amphibian/common_midwife_toad_alytes_obstetricans.php |title=Common midwife toad, ''Alytes obstetricans'' |work=Repties et Amphibiens de France |accessdate=2012-07-30}}</ref> The female [[gastric-brooding frog]] (''Rheobatrachus sp.''), believed to be extinct, swallows her eggs and rears her larvae in her stomach. She stops feeding while they are there and they consume their egg yolks. When they are ready to undergo metamorphosis, she regurgitates them and they hop away from her mouth.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Rheobatrachus_silus.html |title=''Rheobatrachus silus'' |author=Semeyn, E. |year=2002 |work=Animal Diversity Web |publisher=University of Michigan Museum of Zoology |accessdate=2012-08-05}}</ref> The [[pouched frog]] (''Assa darlingtoni'') lays eggs on the ground and, when they hatch, the male carries the tadpoles around in brood pouches on his hind legs.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://frogsaustralia.net.au/frogs/display.cfm?frog_id=3 |title=''Assa darlingtoni'' |year=2005 |work=Frogs Australia Network |accessdate=2012-08-22}}</ref> The aquatic [[Surinam toad]] (''Pipa pipa'') raises its young in pores on its back where they remain until metamorphosis.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/58163/0 |title=''Pipa pipa'' (Suriname Toad) |author= La Marca, Enrique; Azevedo-Ramos, Claudia; Silvano, Débora; Coloma, Luis A.; Ron, Santiago; Hardy, Jerry; Beier, Manfred |date=2010 |work= IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.1 |accessdate=2012-08-24}}</ref> The [[granular poison frog]] (''Oophaga granulifera'') is typical of a number of tree frogs in the poison dart frog family [[Dendrobatidae]]. Its eggs are laid on the forest floor and when they hatch, the tadpoles are carried one by one on the back of an adult to a suitable water filled crevice such as the axil of a leaf or the [[Rosette (botany)|rosette]] of a [[Bromeliaceae|bromeliad]]. The female visits the nursery sites regularly and deposits one or more unfertilised eggs in the water which is consumed by the tadpole.<ref>{{cite journal |author=van Wijngaarden, René; Bolaños, Federico |year=1992 |title=Parental care in ''Dendrobates granuliferus'' (Anura: Dendrobatidae), with a description of the tadpole |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=102‑105 |jstor=1565037 |doi=10.2307/1565037 }}</ref> |
|||
== Feeding and diet == |
|||
With a few exceptions, adult amphibians are [[Predation|predators]], feeding on virtually anything that moves that they can swallow. The diet mostly consists of small items of prey that do not move too fast such as beetles, caterpillars, earthworms and spiders. The sirens (''[[Siren (genus)|Siren spp.]]'') often ingest aquatic plant material with the invertebrates on which they feed <ref>{{cite web |url=http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Siren_intermedia.html |title=''Siren intermedia'': Lesser Siren |author=Gabbard, Jesse |year=2000 |work=Animal Diversity Web |publisher=University of Michigan Museum of Zoology |accessdate=2012-08-11}}</ref> and a Brazilian tree frog ''[[Xenohyla truncata]]'' includes a large quantity of fruit in its diet.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Da Silva, H. R.; De Britto-Pereira, M. C. |year=2006 |title=How much fruit do fruit-eating frogs eat? An investigation on the diet of ''Xenohyla truncata'' (Lissamphibia: Anura: Hylidae) |journal=Journal of Zoology |volume=270 |issue=4 |pages=692‑698 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00192.x }}</ref> The [[Mexican burrowing toad]] (''Rhinophrynus dorsalis'') has a specially adapted tongue for picking up ants and termites. It projects it with the tip foremost whereas other frogs flick out the rear part first, their tongues being hinged at the front.<ref>{{cite journal |author= Trueb, Linda; Gans, Carl |year=1983 |title=Feeding specializations of the Mexican burrowing toad, ''Rhinophrynus dorsalis'' (Anura: Rhinophrynidae) |journal=Journal of Zoology |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=189‑208 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.1983.tb02090.x }}</ref> |
|||
Food is mostly selected by sight, even in conditions of dim light. Movement of the prey triggers a feeding response. Frogs have been caught on fish hooks baited with red flannel and [[Rana clamitans|green frogs]] (''Rana clamitans'') have been found to have stomachs full of elm seeds that they had seen floating past.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Hamilton, W. J. Jr. |year=1948 |title=The food and feeding behavior of the green frog, ''Rana clamitans'' Latreille, in New York State |journal=Copeia |volume=1948 |issue=3 |pages=203‑207 |publisher=American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists |jstor=1438455 |doi=10.2307/1438455 }}</ref> Toads, salamanders and caecilians also use smell to detect prey. This response is mostly secondary because salamanders have been observed to remain stationary near odoriferous prey but only feed if it moves. Cave dwelling amphibians normally hunt by smell and some salamanders seem to have learned to recognize immobile prey even when it has no smell.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |page=56 }}</ref> |
|||
Amphibians usually swallow food whole but may chew it lightly first in order to subdue it.<ref name="Collins" /> They typically have small hinged pediceled teeth. These have bicuspid conical crowns attached by a pedicel to the jaw and are replaced at intervals. Salamanders, caecilians and some frogs have one or two rows of teeth in both jaws but some frogs (''Rana spp.'') lack teeth in the lower jaw and toads (''Bufo spp.'') have no teeth. In many amphibians there are also [[vomerine teeth]] attached to a facial bone in the roof of the mouth.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=57‑58 }}</ref> |
|||
The [[Tiger Salamander|tiger salamander]] (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') is typical of the frogs and salamanders that hide under cover ready to ambush unwary invertebrates. Others amphibians such as the ''Bufo spp.'' toads actively search for prey, while the [[Argentine Horned Frog|Argentine horned frog]] (''Ceratophrys ornata'') lures inquisitive prey closer by raising its hind feet over its back and vibrating its yellow toes.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Radcliffe, Charles W. ; Chiszar, David; Estep, Karen; Murphy, James B.; Smith, Hobart M. |year=1986 |title=Observations on pedal luring and pedal movements in Leptodactylid frogs |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=20 |issue=3 |pages=300‑306 |jstor=1564496 |doi=10.2307/1564496 }}</ref> Among leaf litter frogs in Panama, frogs that actively hunted prey had narrow mouths and were slim, often brightly coloured and toxic, while ambushers had wide mouths and were broad and well camouflaged.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Toft, Catherine A. |year=1981 |title=Feeding ecology of Panamanian litter anurans: patterns in diet and foraging mode |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=139‑144 |jstor=1563372 |doi=10.2307/1563372 }}</ref> Caecilians do not flick their tongues but catch their prey by grabbing it with their slightly backward-pointing teeth. The struggles of the prey and further jaw movements work it inwards and the caecilian usually retreats into its burrow. The subdued prey is gulped down whole.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Bemis, W. E.; Schwenk, K.; Wake, M. H. |year=1983 |title=Morphology and function of the feeding apparatus in ''Dermophis mexicanus'' (Amphibia: Gymnophiona) |journal=Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society |volume=77 |issue=1 |pages=75‑96 |doi=10.1111/j.1096-3642.1983.tb01722.x }}</ref> |
|||
When they are newly hatched, frog larvae feed on the yolk of the egg. When this is exhausted some move on to feed on bacteria, algal crusts, detritus and raspings from submerged plants. Water is drawn in through their mouths, which are usually at the bottom of their heads, and passes through branchial food traps between their mouths and their gills where fine particles are trapped in mucus and filtered out. Others have specialised mouthparts consisting of a horny beak edged by several rows of labial teeth. They scrape and bite food of many kinds as well as stirring up the bottom sediment, filtering out larger particles with the papillae round their mouths. Some, such as the spadefoot toads, have strong biting jaws and are carnivorous or even cannibalistic.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=181‑185 }}</ref> |
|||
== Vocalization == |
|||
The calls made by caecilians and salamanders are limited to occasional soft squeaks, grunts or hisses and have not been much studied. A clicking sound sometimes produced by caecilians may be a means of orientation, as in bats, or a form of communication. Most salamanders are considered voiceless but the [[California Giant Salamander|California giant salamander]] (''Dicamptodon ensatus'') has vocal cords and can produce a rattling or barking sound. Some species of salamander emit a quiet squeak or yelp if attacked.<ref name="calling">{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |pages=76‑77 }}</ref> |
|||
Frogs are much more vocal, especially during the breeding season when they use their voices to attract mates. Each call is characteristic of the species, the presence of which in an area may be easier to detect by its voice than by a fleeting glimpse of the animal itself. In most species, the sound is produced by expelling air from the lungs over the vocal cords into an [[Gular skin|air sac]] or sacs in the throat or at the corner of the mouth. This may distend like a balloon and acts as a resonator, helping to transfer the sound to the atmosphere, or the water at times when the animal is submerged.<ref name="calling" /> The main vocalisation is the male's loud advertisement call which seeks to both encourage a female to approach and discourage other males from intruding on its territory. This call is modified to a quieter courtship call on the approach of a female or to a more aggressive version if a male intruder draws near. Calling bears the risk of attracting predators and involves the expendirure of much energy.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Sullivan, Brian K. |year=1992 |title=Sexual Selection and Calling Behavior in the American Toad (''Bufo americanus'') |journal=Copeia |volume=77 |pages=1‑7 |publisher=American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists |jstor=1446530 |doi=10.2307/1446530 }}</ref> Other calls include those given by a female in response to the advertisement call and a release call given by a male or female during unwanted attempts at amplexus. When a frog is attacked, a distress or fright call is emitted, often resembling a scream.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Toledo, L. F.; Haddad, C. F. B. |year=2007 |title=When frogs scream! A review of anuran defensive vocalizations |journal=Predacao e defesa em anuros: revisao, descricao e evolucao |pages=102–150 |publisher=Instituto de Biociências |url=http://www.athena.biblioteca.unesp.br/exlibris/bd/brc/33004137003P3/2007/pereira_lftr_dr_rcla.pdf#page=110 |accessdate= }}</ref> The usually nocturnal [[Cuban tree frog]] (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') produces a rain call when there is rainfall during daylight hours.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw259 |title=The Cuban Treefrog (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') in Florida |author=Johnson, Steve A. |year=2010 |work=EDIS |publisher=University of Florida |accessdate=2012-08-13}}</ref> |
|||
=== Territorial behaviour === |
|||
Little is known of the territorial behaviour of caecilians but some frogs and salamanders defend home ranges. These are usually feeding, breeding or sheltering sites and it is the males that normally exhibit such behaviour though in some species, females and even juveniles are also involved. Although in many frog species, females are larger than males, this is not the case in most species where males are actively involved in territorial defence. Some of these have specific adaptations such as enlarged teeth for biting or spines on the chest, arms or thumbs.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Shine, Richard |year=1979 |title=Sexual selection and sexual dimorphism in the Amphibia |journal=Copeia |volume=1979 |issue=2 |pages=297‑306 |jstor=1443418 |doi=10.2307/1443418 }}</ref> |
|||
In salamanders, defence of a territory involves adopting an aggressive posture and if necessary attacking the intruder. This may involve snapping, chasing and sometimes biting, occasionally causing the loss of a tail. The behaviour of [[Red Back Salamander|red-backed salamander]]s (''Plethodon cinereus'') has been much studied. It was found that 91% of marked individuals which were later recaptured were within a metre (yard) of their original location (foraging behaviour would have given a different result at night). <ref name="Gergits">{{cite journal |author= Gergits, W. F.; Jaeger, R. G. |year=1990 |title=Site attachment by the red-backed salamander, ''Plethodon cinereus'' |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=24 |issue=1 |pages=91‑93 |jstor=1564297 |doi= 10.2307/1564297 }}</ref> The salamanders left odour marks which deterred the intrusion of others and delineated the boundaries of their territory. A lot of the behaviour seemed stereotyped and did not involve any actual contact between individuals. An aggressive posture involved raising the body off the ground and glaring at the opponent who often turned away submissively. If the intruder persisted, a biting lunge was usually launched at either the tail region or the naso-labial grooves. Damage to either of these areas can reduce the fitness of the rival, either because of the need to regenerate tissue or because it impairs their ability to detect food.<ref name="Gergits" /> |
|||
In frogs, male territorial behaviour is often observed at breeding locations and calling is both an announcement of ownership of part of this resource and an advertisement call to potential mates. In general, a deeper voice represents a heavier and more powerful individual, and this may be sufficient to prevent intrusion by smaller males. Much energy is used in the vocalization and it takes a toll on the territory holder who may be displaced by a fitter individual if he loses too much condition. There is a tendency for males to tolerate the holders of neighbouring territories while vigorously attacking unknown intruders. Holders of territories have a “home” advantage and usually come off better in an encounter between two similar sized frogs. If threats are insufficient, chest to chest tussles may take place. Other fighting methods include pushing and shoving, deflating the opponent’s vocal sac, jumping on his back, biting, chasing, splashing and ducking him and seizing him by the head.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Wells, K. D. |year=1977 |title=Territoriality and male mating success in the green frog (''Rana clamitans'') |journal=Ecology |volume=58 |issue=4 |pages=750‑762 |jstor=1936211 |doi=10.2307/1936211 }}</ref> |
|||
== Defence mechanisms == |
|||
[[File:Taricha granulosa (Rough-skinned newt).JPG|thumb|[[Rough-skinned newt]] (''Taricha granulosa'')]] |
|||
[[File:Tree frog congo.jpg|thumb|[[Common Reed Frog|Common reed frog]] (''Hyperolius viridiflavus'')]] |
|||
Amphibians have soft bodies and thin skins, lack claws, defensive armour or spines and seem relatively helpless. Nevertheless they have evolved various defence mechanisms to keep themselves alive. The first line of defence in salamanders and frogs is the mucous secretions that they produce to keep their skin moist and which make them slippery and difficult to grip. The secretion is often sticky and distasteful or toxic. Snakes have been observed yawning and gaping when trying to swallow an [[African clawed frog]] (''Xenopus spp.'') which gives the frog an opportunity to escape.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Barthalmus, G. T.; Zielinski W. J. |year=1988 |title=''Xenopus'' skin mucus induces oral dyskinesias that promote escape from snakes |journal=Pharmacology, Biochemistry Behavior |volume=30 |issue=4 |pages=:957‑959 |pmid=3227042 |doi=10.1016/0091-3057(88)90126-8 }}</ref> Caecilians have been little studied in this respect but the aquatic (''[[Typhlonectes compressicauda]]'') produces toxic mucous which has caused the death of predatory fish in a feeding experiment in Brazil.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Moodie, G. E. E. |year=1978 |title=Observations on the life history of the caecilian ''Typhlonectes compressicaudus'' (Dumeril and Bibron) in the Amazon basin |journal=Canadian Journal of Zoology |volume=56 |issue=4 |pages=1005‑1008 |doi=10.1139/z78-141 }}</ref> In salamanders, the skin is toxic and in frogs, the main poison glands are at the side of the neck and under the warts on the back and these regions are presented to the attacking animal. The skin of the [[rough-skinned newt]] (''Taricha granulosa'') from North America contains the neurotoxin [[tetrodotoxin]] (TTX), the most toxic non-protein substance known and almost identical to that produced by [[pufferfish]]. Handling the newts does not cause harm but ingestion of even the most minute amounts of the skin is deadly. In feeding trials, fish, frogs, reptiles, birds and mammals were all found to be susceptible. A dose of 0.0002cc of skin was sufficient to kill a mouse in ten minutes.<ref>{{cite journal |author= Brodie, Edmund D. Jr. |year=1968 |title=Investigations on the skin toxin of the adult rough-skinned newt, ''Taricha granulosa'' |journal=Copeia |volume=1968 |issue=2 |pages=307‑313 |jstor=1441757 |doi= 10.2307/1441757 }}</ref> The only predators with some tolerance to the poison are certain populations of [[Common Garter Snake|common garter snake]] (''Thamnophis sirtalis''). In locations where both snake and salamander co-exist, these seems to have developed some immunity through genetic changes and the snakes feed on the newt with impunity.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Geffeney, Shana L.; Fujimoto, Esther; Brodie, Edmund D.; Brodie, Edmund D. Jr.; Ruben, Peter C. |year=2005 |title=Evolutionary diversification of TTX-resistant sodium channels in a predator–prey interaction |journal=Nature |volume=434 |pages=759‑763 |doi=10.1038/nature03444 |issue=7034 }}</ref> [[Coevolution]] occurs with the newt increasing its toxic capabilities at the same rate as the snake further develops its immunity.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Hanifin, Charles T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, Mari; Yasumoto, Takeshi; Brodie, Edmund D.; Brodie, Edmund D. Jr. |year=1999 |title=Toxicity of dangerous prey: variation of tetrodotoxin levels within and among populations of the newt ''Taricha granulosa'' |journal=Journal of Chemical Ecology |volume=25 |issue=9 |pages=2161‑2175 |doi=10.1023/A:1021049125805 |last4=Brodie |last5=Brodie }}</ref> A number of different animal groups have independently evolved to use TTX as a defensive agent. They may obtain it through the [[food chain]] from the bacterium ''[[Vibrio alginolyticus]]'' which is known to synthesize the substance. The link is not firmly established and there remains doubt as to whether the bacteria are truly the source of TTX in animals.<ref>{{Cite journal | author = Chau R.; Kalaitzis, J. A.; Neilan, B. A. | year = 2011 | title = On the origins and biosynthesis of tetrodotoxin | doi=10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.04.001 | journal = Aquatic Toxicology | volume = 104 | pages = 61‑72 | pmid = 21543051 | issue = 1–2}}</ref> |
|||
Poisonous species often use bright colouring to warn potential predators of their toxicity. These warning colours tend to be red or yellow combined with black. The [[Fire Salamander|fire salamander]] (''Salamandra salamandra'') being an example. Once a predator has sampled one of these, it is likely to remember the colouration next time it encounters a similar animal. In some species, such as the [[fire-bellied toad]] (''Bombina spp.''), the warning colouration is on the belly and these animals adopt a defensive pose when attacked, exhibiting their bright colours to the predator. The frog ''[[Allobates zaparo]]'' is not poisonous but [[Batesian mimicry|mimics]] the appearance of other toxic species in its locality, a strategy that may deceive predators.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Darst, Catherine R.; Cummings, Molly E. |year=2006 |title=Predator learning favours mimicry of a less-toxic model in poison frogs |journal=Nature |volume=440 |pages=208‑211 |doi=10.1038/nature04297 |issue=7081 }}</ref> |
|||
Many amphibians are nocturnal and hide during the day, thereby avoiding diurnal predators that hunt by sight. Other amphibians use [[camouflage]] to avoid being detected. They have various colourings such as mottled browns, greys and olives to make themselves inconspicuous so that they blend into the background. Some salamanders adopt defensive poses when faced by a potential predator such as the North American [[Northern Short-tailed Shrew|northern short-tailed shrew]] (''Blarina brevicauda''). Their bodies writhe and they raise and lash their tails which makes it difficult for the predator to avoid contact with their granular glands.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Brodie, Edmund D. Jr.; Nowak, Robert T.; Harvey, William R. |
|||
|year=1979 |title=Antipredator secretions and behavior of selected salamanders against shrews |journal=Copeia |volume=1979 |issue=2 |pages=270‑274 |publisher=American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists |jstor=1443413 |doi=10.2307/1443413 }}</ref> A few salamanders will [[Autotomy|autotomise]] their tails when attacked, sacrificing this part of their anatomy to enable them to escape with their lives. There may have a constricted tail base to allow this to happen easily. The tail is regenerated later but the cost to the animal of replacing it is significant.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Beneski, John T. Jr. |year=1989 |title=Adaptive significance of tail autotomy in the Salamander, ''Ensatina'' |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=23 |issue=3 |pages=322‑324 |jstor=156446 |doi=10.2307/1564465 }}</ref> |
|||
Some frogs and toads inflate themselves to make themselves look large and fierce, and some spadefoot toads (''[[Pelobates]] spp'') scream and leap towards the attacker.<ref name="Collins" /> Giant Salamanders of the genus ''[[Andrias]]'', as well as Ceratophrine and ''[[Pyxicephalus]]'' frogs possess sharp teeth and are capable of drawing blood with a defensive bite. the [[Blackbelly Salamander]] bites an attacking common garter snake (''Thamnophis sirtalis'') two or three times its size on the head and often manages to escape.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Brodie, E. D. Jr. |year=1978 |title=Biting and vocalisation as antipredator mechanisms in terrestrial salamanders |journal=Copeia |volume=1978 |issue=1 |pages=127‑129 |jstor=1443832 |doi=10.2307/1443832 }}</ref> |
|||
== Conservation == |
|||
{{main|Decline in amphibian populations}} |
{{main|Decline in amphibian populations}} |
||
[[ |
[[File:Bufo periglenes1.jpg|thumb|The [[golden toad]] of [[Monteverde]], [[Costa Rica]], was among the first casualties of amphibian declines. Formerly abundant, it was last seen in 1989.]] |
||
Dramatic declines in amphibian populations, including population crashes and mass localized [[extinction]], have been noted in the past two decades from locations all over the world, and amphibian declines are thus perceived as one of the most critical threats to global [[biodiversity]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=McCallum |first1= M. L. |year=2007 |title=Amphibian Decline or Extinction? Current Declines Dwarf Background Extinction Rate |journal=Journal of Herpetology|volume=41 |issue=3 |pages=483–491 |publisher= |doi= 10.1670/0022-1511(2007)41[483:ADOECD]2.0.CO;2|url= https://www.herpconbio.org/~herpconb/McCallum/amphibian%20extinctions.pdf}}</ref> A number of causes are believed to be involved, including [[habitat destruction]] and modification, [[over-exploitation]], [[pollution]], [[introduced species]], [[climate change]], endocrine-disrupting pollutants, destruction of the [[ozone layer]] (ultraviolet radiation has shown to be especially damaging to the skin, eyes, and eggs of amphibians), and diseases like [[chytridiomycosis]]. However, many of the causes of amphibian declines are still poorly understood, and are a topic of ongoing discussion.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.amphibians.org/ |title=Amphibian Specialist Group |
Dramatic declines in amphibian populations, including population crashes and mass localized [[extinction]], have been noted in the past two decades from locations all over the world, and amphibian declines are thus perceived as one of the most critical threats to global [[biodiversity]].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=McCallum |first1= M. L. |year=2007 |title=Amphibian Decline or Extinction? Current Declines Dwarf Background Extinction Rate |journal=Journal of Herpetology|volume=41 |issue=3 |pages=483–491 |publisher= |doi= 10.1670/0022-1511(2007)41[483:ADOECD]2.0.CO;2|url= https://www.herpconbio.org/~herpconb/McCallum/amphibian%20extinctions.pdf}}</ref> A number of causes are believed to be involved, including [[habitat destruction]] and modification, [[over-exploitation]], [[pollution]], [[introduced species]], [[climate change]], endocrine-disrupting pollutants, destruction of the [[ozone layer]] (ultraviolet radiation has shown to be especially damaging to the skin, eyes, and eggs of amphibians), and diseases like [[chytridiomycosis]]. However, many of the causes of amphibian declines are still poorly understood, and are a topic of ongoing discussion.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.amphibians.org/ |title=Amphibian Specialist Group |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> |
||
In many terrestrial ecosystems, amphibians constitute one of the largest parts of the vertebrate biomass. Any decline in amphibian numbers will have an impact on the patterns of predation. The loss of carnivorous species near the top of the food chain will upset the delicate ecosystem balance and may cause dramatic increases in opportunistic species. In the Middle East, a growing appetite for eating frog legs and the consequent gathering of them for food was linked to an increase in [[mosquito]]es.<ref>{{cite book |title=Sustainable redevelopment of regional ecosystems degraded by exploitive development in ''Sustainability Issues for Resource Managers (Bottom, Daniel L.; Reeves, Gordon H.; Brookes, Martha H. (eds.))'' |last=Regier |first=Henry A. |coauthors=Baskerville, Gordon L. |year=1996 |publisher=DIANE Publishing |isbn=0788146998 |pages=36‑38 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=e66hatcSAsUC&pg=PA21&dq=Sustainable+redevelopment+of+regional+ecosystems+degraded+by#v=onepage&q=Sustainable%20redevelopment%20of%20regional%20ecosystems%20degraded%20by&f=false |accessdate=}}</ref> Predators that feed on amphibians are affected by their decline. The [[Western Terrestrial Garter Snake|western terrestrial garter snake]] (''Thamnophis elegans'') in California is largely aquatic and depends heavily on two species of frog that are diminishing in numbers, the [[Yosemite toad]] (''Bufo canorus'') and the [[mountain yellow-legged frog]] (''Rana muscosa''), putting the snake's future at risk. If it were to become scarce, this would affect birds of prey and other predators that feed on it.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Jennings, W. Bryan; Bradford, David F.; Johnson, Dale F. |year=1992 |title=Dependence of the garter snake ''Thamnophis elegans'' on amphibians in the Sierra Nevada of California |journal=Journal of Herpetology |volume=26 |issue=4 |pages=503–505 |jstor=1565132 |doi=10.2307/1565132 }}</ref> Meanwhile, in the ponds and lakes, fewer frogs means fewer tadpoles. These normally play an important role in controlling the growth of algae and also forage on [[detritus]] that accumulates as sediment on the bottom. A reduction in the number of tadpoles or their absence might lead to algal overgrowth and possibly [[eutrophication]], resulting in the water becoming depleted of oxygen when the algae die and decompose. Aquatic invertebrates and fish might then die and there would be unpredictable ecological consequences.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Natural History of Amphibians |last=Stebbins |first=Robert C. |coauthors=Cohen, Nathan W. |year=1995 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-03281-5 |page=249 }}</ref> |
|||
A [[global strategy]] to stem the crisis has been released in the form of the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan. Developed by over 80 leading experts in the field, this call to action details what would be required to curtail amphibian declines and extinctions over the next 5 years—and how much this would cost. The Amphibian Specialist Group of the World Conservation Union (IUCN) is spearheading efforts to implement a comprehensive global strategy for amphibian conservation.<ref name=AmphibianArk>{{cite web |url=http://www.iucn.org/about/union/secretariat/offices/asia/regional_activities/asian_amphibian_crisis/taking_action/amphibian_conservation_action_plan/ |title=Amphibian Conservation Action Plan |author= |date= |work=IUCN |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> [[Amphibian Ark]] is an organization that was formed to implement the ex-situ conservation recommendations of this plan, and they have been working with zoos and aquaria around the world encouraging them to create assurance colonies of threatened amphibians.<ref name=AmphibianArk/> One such project is the Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project that built on existing conservation efforts in Panama to create a country-wide response to the threat of [[chytridiomycosis]] rapidly spreading into eastern Panama.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://amphibianrescue.org/?page_id=91 |title=Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project |author= |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> |
|||
A [[global strategy]] to stem the crisis has been released in the form of the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan. Developed by over 80 leading experts in the field, this call to action details what would be required to curtail amphibian declines and extinctions over the next 5 years—and how much this would cost. The Amphibian Specialist Group of the World Conservation Union (IUCN) is spearheading efforts to implement a comprehensive global strategy for amphibian conservation.<ref name="AmphibianArk">{{cite web |url=http://www.iucn.org/about/union/secretariat/offices/asia/regional_activities/asian_amphibian_crisis/taking_action/amphibian_conservation_action_plan/ |title=Amphibian Conservation Action Plan |author= |date= |work=IUCN |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> [[Amphibian Ark]] is an organization that was formed to implement the ex-situ conservation recommendations of this plan, and they have been working with zoos and aquaria around the world encouraging them to create assurance colonies of threatened amphibians.<ref name="AmphibianArk" /> One such project is the Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project that built on existing conservation efforts in Panama to create a country-wide response to the threat of [[chytridiomycosis]] rapidly spreading into eastern Panama.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://amphibianrescue.org/?page_id=91 |title=Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project |author= |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> |
|||
On January 21, 2008, Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered (EDGE),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.edgeofexistence.org/ |title=Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered |author= |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> in a statement made by chief Helen Meredith, identified nature's most [[endangered]] [[species]]: "The EDGE amphibians are amongst the most remarkable and unusual species on the planet and yet an alarming 85% of the top 100 are receiving little or no conservation attention." The top 10 [[EDGE species|EDGE listed species]] include the [[Chinese giant salamander]], a distant relative of the [[newt]], the tiny [[Gardiner's Seychelles Frog|Gardiner's Seychelles frog]], the limbless [[Boulengerula niedeni|Sagalla caecilian]] from Kenya, South African [[ghost frog]]s, [[lungless salamander]]s from Mexoco, the [[Scaphiophryne gottlebei|Malagasy rainbow frog]], Chile's [[Darwin's frog]] (''Rhinoderma rufum'') and the [[Betic midwife toad]] from Spain.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSL2038808 |title=Reuters, Giant newt, tiny frog identified as most at risk |publisher=Reuters.com |date=2008-01-20 |accessdate=2009-04-07 | first=Jeremy | last=Lovell| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20090220211707/http://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSL2038808| archivedate= 20 February 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2008/jan/21/conservation |title= Drive to save weird and endangered amphibians |accessdate=2009-04-07 | location=London | first=Ian | last=Sample | date=2008-01-20 | work=The Guardian}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation?picture=332110244 |title=Environment, images of the species |publisher=Guardian |date=2008-01-18 |accessdate=2009-04-07 | location=London| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20090326125823/http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation?picture=332110244| archivedate= 26 March 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation |title=Environment, Gallery: the world's strangest amphibians |publisher=Guardian |date=2008-01-18 |accessdate=2009-04-07 | location=London| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20090326125823/http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation| archivedate= 26 March 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref> |
On January 21, 2008, Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered (EDGE),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.edgeofexistence.org/ |title=Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered |author= |date= |work= |publisher= |accessdate=2012-03-30}}</ref> in a statement made by chief Helen Meredith, identified nature's most [[endangered]] [[species]]: "The EDGE amphibians are amongst the most remarkable and unusual species on the planet and yet an alarming 85% of the top 100 are receiving little or no conservation attention." The top 10 [[EDGE species|EDGE listed species]] include the [[Chinese giant salamander]], a distant relative of the [[newt]], the tiny [[Gardiner's Seychelles Frog|Gardiner's Seychelles frog]], the limbless [[Boulengerula niedeni|Sagalla caecilian]] from Kenya, South African [[ghost frog]]s, [[lungless salamander]]s from Mexoco, the [[Scaphiophryne gottlebei|Malagasy rainbow frog]], Chile's [[Darwin's frog]] (''Rhinoderma rufum'') and the [[Betic midwife toad]] from Spain.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSL2038808 |title=Reuters, Giant newt, tiny frog identified as most at risk |publisher=Reuters.com |date=2008-01-20 |accessdate=2009-04-07 | first=Jeremy | last=Lovell| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20090220211707/http://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSL2038808| archivedate= 20 February 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2008/jan/21/conservation |title= Drive to save weird and endangered amphibians |accessdate=2009-04-07 | location=London | first=Ian | last=Sample | date=2008-01-20 | work=The Guardian}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation?picture=332110244 |title=Environment, images of the species |publisher=Guardian |date=2008-01-18 |accessdate=2009-04-07 | location=London| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20090326125823/http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation?picture=332110244| archivedate= 26 March 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation |title=Environment, Gallery: the world's strangest amphibians |publisher=Guardian |date=2008-01-18 |accessdate=2009-04-07 | location=London| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20090326125823/http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/gallery/2008/jan/21/wildlife.conservation| archivedate= 26 March 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
== See also == |
||
*[[Vegetal rotation]] |
* [[Vegetal rotation]] |
||
*[[List of amphibians]] |
* [[List of amphibians]] |
||
==References== |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist| |
{{Reflist|30em}} |
||
== Further reading == |
== Further reading == |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| last = Carroll |
|||
| first = Robert L. |
|||
| title = Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution |
|||
| year = 1988 |
|||
| publisher = W. H. Freeman & Co. |
|||
| location = New York |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| last = Carroll |
|||
| first = Robert L. |
|||
| title = The Rise of Amphibians: 365 Million Years of Evolution |
|||
| year = 2009 |
|||
| publisher = The Johns Hopkins University Press |
|||
| location = Baltimore |
|||
| isbn = 978-0-8018-9140-3 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last = Duellman |
|||
*{{cite book |
|||
| first = William E. |
|||
| coauthors = Linda Trueb |
|||
| title = Biology of Amphibians |
|||
| coauthors = Linda Trueb |
|||
| year = 1994 |
|||
| title = Biology of Amphibians |
|||
| publisher = Johns Hopkins University Press |
|||
| year = 1994 |
|||
| isbn = 978-0-8018-4780-6 |
|||
| publisher = Johns Hopkins University Press |
|||
}} |
|||
| isbn = 978-0-8018-4780-6 |
|||
* {{cite journal |
|||
}} |
|||
| last = Frost |
|||
*{{cite journal |
|||
| first = Darrel R. |
|||
| title = The Amphibian Tree of Life |
|||
| first = Darrel R. |
|||
| id = {{hdl|2246/5781}} |
|||
| title = The Amphibian Tree of Life |
|||
| journal = Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History |
|||
| id = {{hdl|2246/5781}} |
|||
| volume = 297 |
|||
| journal = Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History |
|||
| pages = 1–291 |
|||
| year = 2006 |
|||
| month = March |
|||
| coauthors = Taran Grant, Julián Faivovich, Raoul H. Bain, Alexander Haas, Célio F.B. Haddad, Rafael O. De Sá, Alan Channing, Mark Wilkinson, Stephen C. Donnellan, Christopher J. Raxworthy, Jonathan A. Campbell, Boris L. Blotto, Paul Moler, Robert C. Drewes, Ronald A. Nussbaum, John D. Lynch, David M. Green, Ward C. Wheeler |
|||
| month = March |
|||
| doi = 10.1206/0003-0090(2006)297[0001:TATOL]2.0.CO;2 |
|||
| coauthors = Taran Grant, Julián Faivovich, Raoul H. Bain, Alexander Haas, Célio F.B. Haddad, Rafael O. De Sá, Alan Channing, Mark Wilkinson, Stephen C. Donnellan, Christopher J. Raxworthy, Jonathan A. Campbell, Boris L. Blotto, Paul Moler, Robert C. Drewes, Ronald A. Nussbaum, John D. Lynch, David M. Green, Ward C. Wheeler |
|||
}} |
|||
| doi = 10.1206/0003-0090(2006)297[0001:TATOL]2.0.CO;2 |
|||
* {{cite journal |
|||
}} |
|||
| last = Pounds |
|||
*{{cite journal |
|||
| first = J. Alan |
|||
| title = Widespread amphibian extinctions from epidemic disease driven by global warming |
|||
| first = J. Alan |
|||
| url = http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v439/n7073/full/nature04246.html |
|||
| title = Widespread amphibian extinctions from epidemic disease driven by global warming |
|||
| journal = Nature |
|||
| url = http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v439/n7073/full/nature04246.html |
|||
| volume = 439 |
|||
| issue = 7073 |
|||
| pages = 161–167 |
|||
| year = 2006 |
|||
| month = January |
|||
| pmid = 16407945 |
|||
| doi = 10.1038/nature04246 |
|||
| pmid = 16407945 |
|||
| coauthors = Martín R. Bustamante, Luis A. Coloma, Jamie A. Consuegra, Michael P. L. Fogden, Pru N. Foster, Enrique La Marca, Karen L. Masters, Andrés Merino-Viteri, Robert Puschendorf, Santiago R. Ron, G. Arturo Sánchez-Azofeifa, Christopher J. Still and Bruce E. Young |
|||
| doi = 10.1038/nature04246 |
|||
}} |
|||
| coauthors = Martín R. Bustamante, Luis A. Coloma, Jamie A. Consuegra, Michael P. L. Fogden, Pru N. Foster, Enrique La Marca, Karen L. Masters, Andrés Merino-Viteri, Robert Puschendorf, Santiago R. Ron, G. Arturo Sánchez-Azofeifa, Christopher J. Still and Bruce E. Young |
|||
* {{cite journal |
|||
}} |
|||
| last = Stuart |
|||
*{{cite journal |
|||
| first = Simon N. |
|||
| coauthors = Janice S. Chanson, Neil A. Cox, Bruce E. Young, Ana S. L. Rodrigues, Debra L. Fischman, Robert W. Waller |
|||
| first = Diego |
|||
| title = Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide |
|||
| coauthors = Miguel Vences, Marina Alcobendas, Rafael Zardoya and Axel Meyer |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/306/5702/1783 |
|||
| title = Initial diversification of living amphibians predated the breakup of Pangaea |
|||
| journal = Science |
|||
| volume = 306 |
|||
| journal = American Naturalist |
|||
| issue = 5702 |
|||
| pages = 1783–1786 |
|||
| year = 2004 |
|||
| month = December |
|||
| doi = 10.1126/science.1103538 |
|||
| month = May |
|||
| pmid = 15486254 |
|||
}} |
|||
| doi = 10.1086/429523 |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
}} |
|||
| last = S.N.Stuart, M.Hoffmann, J.S.Chanson, N.A.Cox, R.J.Berridge, P.Ramani, B.E. Young (editors) |
|||
*{{cite journal |
|||
| first = Collective work |
|||
| title = Threatened Amphibians of the World |
|||
| first = Diego |
|||
| publisher = Published by [[Lynx Edicions]], in association with [[IUCN-The World Conservation Union]], [[Conservation International]] and [[NatureServe]]. |
|||
| title = A multilocus timescale for the origin of extant amphibians |
|||
| month = September | year = 2008 |
|||
| journal = Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution |
|||
| url = http://www.hbw.com/lynx/en/lynx-edicions/portada-lynx/MON0017-threatened-amphibians-world.html |
|||
| volume = 56 |
|||
| isbn = 978-84-96553-41-5 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| pages = |
|||
}} 776 pages |
|||
| year = 2010 |
|||
| pmid = 20399871 |
|||
| doi = 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.019 |
|||
}} |
|||
*Solomon Berg Martin, ''Biology'' |
|||
*{{cite journal |
|||
| last = Stuart |
|||
| first = Simon N. |
|||
| coauthors = Janice S. Chanson, Neil A. Cox, Bruce E. Young, Ana S. L. Rodrigues, Debra L. Fischman, Robert W. Waller |
|||
| title = Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide |
|||
| url = http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/306/5702/1783 |
|||
| journal = Science |
|||
| volume = 306 |
|||
| issue = 5702 |
|||
| pages = 1783–1786 |
|||
| year = 2004 |
|||
| month = December |
|||
| doi = 10.1126/science.1103538 |
|||
| pmid = 15486254 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{cite book |
|||
| last = S.N.Stuart, M.Hoffmann, J.S.Chanson, N.A.Cox, R.J.Berridge, P.Ramani, B.E. Young (editors) |
|||
| first = Collective work |
|||
| title = Threatened Amphibians of the World |
|||
| publisher = Published by [[Lynx Edicions]], in association with [[IUCN-The World Conservation Union]], [[Conservation International]] and [[NatureServe]]. |
|||
| month = September | year = 2008 |
|||
| url = http://www.hbw.com/lynx/en/lynx-edicions/portada-lynx/MON0017-threatened-amphibians-world.html |
|||
| isbn = 978-84-96553-41-5 |
|||
| pages = |
|||
}} 776 pages |
|||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{Wikispecies|Amphibia}} |
{{Wikispecies|Amphibia}} |
||
{{Wikibooks|Dichotomous Key|Amphibia}} |
{{Wikibooks|Dichotomous Key|Amphibia}} |
||
* [http://www.savethefrogs.com/ Save the Frogs!] |
|||
* [http://www.amphibians.org/ Amphibian Specialist Group] |
* [http://www.amphibians.org/ Amphibian Specialist Group] |
||
* [http://www.puce.edu.ec/zoologia/vertebrados/amphibiawebec/index.html AmphibiaWebEcuador] |
|||
* [http://marlonstein.com/fotos/natureza/saposepererecas Amphibians photos Brazil] |
|||
* [http://www.amphibianark.org/ Amphibian Ark] |
* [http://www.amphibianark.org/ Amphibian Ark] |
||
* [http://www.amphibiaweb.org/ AmphibiaWeb] |
* [http://www.amphibiaweb.org/ AmphibiaWeb] |
||
* [http://www.edgeofexistence.org/ EDGE] |
|||
* [http://www.globalamphibians.org/ Global Amphibian Assessment] |
* [http://www.globalamphibians.org/ Global Amphibian Assessment] |
||
* [http://www.whose-tadpole.net/ Amphibians of central Europe] |
|||
* [http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/narcam/idguide/index.htm USGS—Online Guide for the Identification of Amphibians in North America north of Mexico] |
|||
* [http://www.livingunderworld.org/ General amphibian biology information—Living UnderWorld] |
|||
* [http://www.amphibianrescue.org Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project] |
|||
* [http://www.atlantabotanicalgarden.org Atlanta Botanical Garden Amphibian Conservation Program] |
|||
* [http://sounds.bl.uk/Browse.aspx?category=Environment&collection=Amphibians Amphibian vocalisations on Archival Sound Recordings] |
* [http://sounds.bl.uk/Browse.aspx?category=Environment&collection=Amphibians Amphibian vocalisations on Archival Sound Recordings] |
||
* [http://www.froglife.org Froglife (British conservation charity)] |
|||
* [http://www.salamandridae.com Salamandridae] |
|||
* [http://www.reptileexpert.org/amphibians/ A guide to Amphibians] |
|||
{{Chordata}} |
{{Chordata}} |
||
| Line 346: | Line 382: | ||
[[gl:Anfibios]] |
[[gl:Anfibios]] |
||
[[ko:양서류]] |
[[ko:양서류]] |
||
[[hy:Երկկենցաղներ]] |
|||
[[hi:उभयचर]] |
[[hi:उभयचर]] |
||
[[hr:Vodozemci]] |
[[hr:Vodozemci]] |
||
Revision as of 21:51, 31 August 2012
| Amphibians Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| File:Lissamphibia.jpg | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Batrachomorpha |
| Class: | Amphibia Linnaeus, 1758 |
| Subclasses and Orders | |
| |
Amphibians are members of the class Amphibia, whose living forms include frogs, toads, salamanders, newts and caecilians. They are cold-blooded, tetrapod vertebrates. Most have four limbs and live in fresh water or on land but the caecilians, though included in the group, live in burrows in damp soil and are limbless. Amphibians typically have a larval stage that lives in water but there are many different behavioural adaptations that have developed among species to bypass this necessity. The young undergo metamorphosis from a larval form with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians also use their skin for respiration and some small terrestrial salamanders rely entirely on this and have no lungs.
The earliest amphibians evolved in the Devonian Period from sarcopterygian fish with lungs and bony-limbed fins,[1] features that were helpful in adapting to dry land. They diversified and became dominant during the Carboniferous and Permian periods,[2] but were later displaced by reptiles and other vertebrates. Over time, amphibians shrank in size and decreased in diversity, leaving only the modern subclass Lissamphibia.
The three modern orders of amphibians are the Anura (frogs and toads), Caudata (salamanders and newts) and Gymnophiona (caecilians, limbless amphibians that resemble large earthworms with jaws). The total number of known amphibian species is approximately 7,000 of which nearly 90% are frogs.[3] They are superficially similar to reptiles, but reptiles, along with mammals and birds, are amniotes, having impervious membranes that surround the egg. With their often complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators,[4] and in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline in amphibian populations of many species around the globe. The smallest vertebrate in the world is the New Guinea frog, Paedophryne amauensis.[5] The largest amphibian is the Chinese Giant Salamander, Andrias davidianus.[6] The study of amphibians is called batrachology while the study of both reptiles and amphibians is called herpetology.
Etymology

Amphibian is derived from the Ancient Greek term ἀμφίβιος (amphíbios), which means "both kinds of life", amphi meaning "of both kinds" and bio meaning "life". The term was initially used generally as an adjective for animals that could live on land or in water, including seals and otters. The word amphibian became restricted in the taxonomical sense to what we now use around 1600 with the taxon "Amphibia" first published in scientific classification circa 1819.[7]
Evolution
The first major groups of amphibians developed in the Devonian period from lobe-finned fish similar to the modern coelacanth and lungfish,[1] which had evolved multi-jointed leg-like fins with digits that enabled them to crawl along the sea bottom. Some fish had developed primitive lungs to help them breathe air when the stagnant pools of the Devonian swamps were lacking in oxygen. They could also use their strong fins to hoist themselves out of the water and onto dry land if circumstances required it. Eventually, their bony fins would evolve into limbs and they would become the ancestors to all tetrapods, including modern amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Despite being able to crawl on land, many of these prehistoric tetrapodomorph fish still spent most of their time in the water. They had started to develop lungs but still breathed predominantly with gills.[8]
Ichthyostega was one of the first primitive amphibians, with nostrils and more efficient lungs. It had four sturdy limbs, a neck, a tail with fins and a skull very similar to the lobe-finned fish, Eusthenopteron.[1] Amphibians evolved adaptations that allowed them to stay out of the water for longer periods. Their lungs improved and their skeletons became heavier and stronger, better able to cope with the increased gravitational effect of life on land. They developed "hands" and "feet" with five digits. Their skin evolved and became more capable of retaining body fluids and resisting desiccation.[8] The fish's hyomandibula bone in the hyoid region behind the gills diminished in size and became the stapes of the amphibian ear, an adaptation necessary for hearing on dry land.[9] An affinity between the amphibians and the teleost fish is the labyrinthic structure of the teeth and the paired supra-occipital bones at the back of the head, both features not found elsewhere in the animal kingdom.[10]
In the late Devonian and early Carboniferous, the seas, rivers and lakes were teeming with life but the land was the realm of early plants and devoid of animal life. In the early Carboniferous (362 to 290 million years ago) the climate became wet and warm and extensive swamps developed with mosses, ferns, horsetails and calamites. Air breathing arthropods began to evolve and invaded the land where they provided food for the carnivorous amphibians that began to emerge from the waters. There were no other tetrapods on the land and the amphibians were at the top of the food chain and occupying the ecological position currently held by the crocodile. Though equipped with limbs and the ability to breathe air, most still had a long tapering body and strong tail.[10] They were the top land predators, sometimes reaching several meters in length, preying on the large insects of the period and many types of fish in the water. They still needed to return to water to lay their shell-less eggs and even modern amphibia have a fully aquatic larval stage with gills like their ancestral fish. It was the development of the amniotic egg, which prevents the developing embryo from drying out, that enabled the reptiles to reproduce on land and which led to their dominance in the period that followed.[1]
During the Triassic Period, the reptiles began to out-compete the amphibians, leading to a reduction in both their size and their importance in the biosphere. According to the fossil record, Lissamphibia, which includes all modern amphibians and is the only surviving lineage, may have branched off from the extinct groups Temnospondyli and Lepospondyli at some period between the Late Carboniferous and the Early Triassic. The relative scarcity of fossil evidence prevents an exact date being known [2] but the most recent molecular study, based on multi-locus data, suggest a Late Carboniferous – Early Permian origin of extant amphibians.[11]
The origins and evolutionary relationships between the three main groups of amphibians is a matter for debate. A 2005 molecular phylogeny based on rDNA analysis suggests that salamanders and caecilians are more closely related to each other than they are to frogs. It also appears that divergence of the three groups took place in the Paleozoic or early Mesozoic before the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea and soon after their divergence from the lobe-finned fish. The briefness of this period and the swiftness with which radiation took place would help account for the relative scarcity of primitive amphibian fossils.[12] There are large gaps in the fossil record but the discovery of a batrachian from the Early Permian in Texas in 2008 provided a missing link with a lot of the characteristics of modern frogs. Molecular analysis suggests that the frog–salamander divergence took place considerably earlier than the palaeontological evidence indicates.[13]

Classification

Traditionally, amphibians includes all tetrapod vertebrates that are not amniotes. Amphibia in its widest sense (sensu lato) was divided into three subclasses, two of which are extinct:[14]
- Subclass Labyrinthodontia† (diverse Paleozoic and early Mesozoic group)
- Subclass Lepospondyli† (small Paleozoic group, sometimes included in the Labyrinthodontia, which may actually be more closely related to amniotes than Lissamphibia)
- Subclass Lissamphibia (all modern amphibians including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts and caecilians)
- Family Albanerpetontidae—Jurassic to Miocene (extinct)
- Superorder Salientia
- Genus Triadobatrachus—Triassic (extinct)—a stem Anuran
- Order Anura (frogs and toads): Jurassic to recent—5,602 recent species in 48 families
- Order Caudata or Urodela (salamanders, newts): Jurassic to recent—571 recent species in 10 families
- Order Gymnophiona (caecilians): Jurassic to recent—190 recent species in 10 families
The actual number of species in each group depends on the taxonomic classification followed, the two most common systems being the classification adopted by the website AmphibiaWeb, University of California (Berkeley) and the classification by herpetologist Darrel Frost and the American Museum of Natural History, available as the online reference database Amphibian Species of the World.[15] The numbers of species cited above follow Frost.
With the phylogenetic classification, the taxon Labyrinthodontia has been discarded as it is a paraphyletic group without unique defining features apart from shared primitive characteristics. Classification varies according to the preferred phylogeny of the author and whether they use a stem-based or a node-based classification. Traditionally, amphibians as a class are defined as all tetrapods with a larval stage, while the group that includes the common ancestors of all living amphibians (frogs, salamanders and caecilians) and all their descendants is called Lissamphibia. The phylogeny of Paleozoic amphibians is uncertain, and Lissamphibia may possibly fall within extinct groups like the temnospondyls (traditionally placed in the subclass Labyrinthodontia), and the Lepospondyls, and in some analysis even the amniotes. This means that advocates of phylogenetic nomenclature have removed a large number of basal Devonian and Carboniferous amphibian-type tetrapod groups that were formerly placed in Amphibia in Linnaean taxonomy and included them elsewhere under cladistic taxonomy.[16]
All recent amphibians are included in the subclass Lissamphibia, superorder Salientia, which is usually considered a clade, a group of species that have evolved from a common ancestor. It has also been suggested that salamanders arose separately from a Temnospondyl-like ancestor, and even that caecilians are the sister group of the advanced reptiliomorph amphibians, and thus of amniotes.[13][17]
Authorities also disagree as to whether Salientia is a superorder that includes the order Anura, or whether Anura is a sub-order of the order Salientia. Practical considerations seem to favour using the former arrangement. The Lissamphibia, superorder Salientia, are traditionally divided into three orders, but an extinct salamander-like family, the Albanerpetontidae, is now considered part of the Lissamphibia alongside the superorder Salientia. Furthermore, Salientia includes all three recent orders plus the Triassic proto-frog, Triadobatrachus.[18]
Characteristics
The amphibians are tetrapods, a class of vertebrate animals with four limbs. They are non-amniotes, which means that their eggs are not surrounded by the several membranes, some impervious, which enable mammals, reptiles and birds to reproduce on land. Amphibians typically reproduce in fresh water and are not found in the sea, with the exception of one or two frogs that live in brackish water in mangrove swamps.[19] Amphibians evolved from lunged fish and had to make certain adaptations for living on land. They needed to develop new means of locomotion to replace the sideways thrust of their tails that had been used for swimming. Their vertebral columns, limbs, limb girdles and musculature needed to be strong enough to raise them off the ground for locomotion and feeding. Terrestrial adults needed to discard their lateral line systems and adapt their sensory systems to receive stimuli via the medium of air. They needed to develop new methods to regulate their body heat in order to cope with fluctuations in ambient temperatures. They needed to develop behaviours suitable for reproduction in a terrestrial environment. Their skins were exposed to harmful ultraviolet rays that had previously been absorbed by the water and needed to become more protective membranes that prevented excessive water loss. Amphibians are restricted to moist habitats because their skin needs to be kept damp and they need to produce copious amounts of dilute urine. They also require water bodies for reproduction, although some species have developed various strategies for protecting or bypassing the vulnerable aquatic larval stage.[20]
Amphibians are cold blooded vertebrates. Their metabolic rate is low and as a result, their food and energy requirements are limited. In the adult state they have tear ducts and movable eyelids and most species have ears that can detect airborne or ground vibrations. They have a muscular tongue which in many species can be protruded. Modern amphibians have fully ossified vertebrae with articular processes. Their ribs are usually short and may be fused to the vertebrae. Their skulls are mostly broad and short and are often incompletely ossified. Their skin contains little keratin and lacks scales, apart from a few fish-like scales in certain caecilians. It contains many mucous glands and in some species, poison glands. The hearts of amphibians have three chambers. The left and right atria receive oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood respectively. On contraction, these pass the blood to a single ventricle which pumps it round the body and to the lungs. The two blood streams remain largely separate in the process. Amphibians have a urinary bladder and nitrogenous waste products are excreted primarily as urea. Most amphibians lay their eggs in water and have aquatic larvae that undergo metamorphosis to become terrestrial adults. Amphibians breathe by means of a bucco-pharyngeal pump but supplement this with gas exchange through the skin.[20]
Anura
The order Anura (from the Ancient Greek an-, without and oura, tail) comprises the frogs and toads. These usually have long hind limbs that fold underneath them, shorter forelimbs, webbed toes with no claws, no tails, large eyes and glandular moist skin.[21] Members of this order with smooth skins are commonly referred to as frogs while those with warted skins are known as toads. The difference is not a formal one taxonomically and there are numerous exceptions to this rule. Members of the family Bufonidae are known as the "true toads".[22] Frogs range in size from the 30 centimetres (12 in) goliath frog (Conraua goliath) of West Africa [23] to the 7.7 millimetres (0.30 in) long Paedophryne amauensis, first described in Papua New Guinea in 2012. This latter is also the smallest known vertebrate.[24] Although most species are associated with water and damp habitats, some are specialised to live in trees and in deserts. They are found worldwide except for polar areas.[25] Anura is divided into three suborders which are broadly accepted by the scientific community but the relationships between some families remains unclear. Future molecular studies should provide further insights into their evolutionary relationships.[26]
The suborder Archaeobatrachia contains four families of primitive frogs. These comprise the families Ascaphidae, Bombinatoridae, Discoglossidae and Leiopelmatidae.[27]
The suborder Mesobatrachia contains six families of more evolutionary advanced frogs. These comprise the families Megophryidae, Pelobatidae, Pelodytidae, Scaphiopodidae, Rhinophrynidae and Pipidae.[27]
The suborder Neobatrachia is by far the largest group and includes the remaining families of modern frogs, including most common species. Ninety six percent of the over 5000 extant species of frog are neobatrachians.[28]
Caudata
The order Caudata (from the Latin cauda meaning "tail") consists of the salamanders, elongated, low-slung animals that mostly resemble lizards in form, though this is a symplesiomorphic trait and the two groups are no more closely related than salamanders are to mammals.[29] Salamanders lack claws, have a scale-free skin, either smooth or covered with tubercles, and a tail that is usually flattened from side to side and often finned. They range in size from the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus), which can grow to a length of 1.8 metres (5 ft 11 in),[30] to the diminutive (Thorius pennatulus) from Mexico which seldom exceeds 20 millimetres (0.79 in).[31] Salamanders are distributed widely in the Holarctic region of the northern hemisphere. The family Plethodontidae are also found in Central and South America north of the Amazon Basin.[25] Urodela is a name sometimes used for all the extant species of salamander.[32] Members of several families of salamanders have become paedomorphic and either fail to complete their metamorphosis or retain some larval characteristics as adults.[33] Most salamanders are under 15 centimetres (5.9 in) long. They may be terrestrial or aquatic but many spend part of the year in each habitat. When on land, they mostly spend the day hidden under stones or logs or in dense vegetation, emerging in the evening and night to forage for worms, insects and other invertebrates.[25]
The suborder Cryptobranchoidea contains the primitive salamanders. A number of fossil cryptobranchids have been found but there are only three living species, the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus), the Japanese giant salamander (Andrias japonicus ) and the hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis) from North America. These large amphibians retain several larval characteristics in their adult state; gills slits are present and the eyes are unlidded. A unique feature is their ability to feed by suction using only one half of the lower jaw at a time.[34] The males excavate nests, persuade females to lay their egg strings inside them and guard them. As well as breathing with lungs, they respire through the many folds in their skin which is thin with the capillaries close to the surface.[35]
The suborder Salamandroidea contains the advanced salamanders. They differ from the cryptobranchids by having the prearticular bones in their lower jaw fused and reproduction is by internal fertilisation. In salamandrids, the male deposits a bundle of sperm, the spermatophore, and the female picks it up and inserts it into her cloaca where the sperm is stored until the eggs are laid.[36] The largest family in this group is Plethodontidae, the lungless salamanders, which includes sixty percent of all salamander species. The family Salamandridae includes the true salamanders and the name "newt" is given to members of its subfamily Pleurodelinae.[21]
The third suborder Sirenoidea contains the sirens, consisting of four species in a single family, Sirenidae. Members of this order are eel-like aquatic salamanders with much reduced forelimbs and no hind limbs. Some of their features are primitive while others are derived.[37] Fertilisation is likely to be external as sirenids lack the cloacal glands used by male salamandrids to produce spermatophores and the females lack spermathecae for sperm storage. Despite this, the eggs are laid singly, a behaviour not conducive for external fertilisation.[36]
Gymnophiona
The order Gymnophiona (from the Greek, gymnos and ophis meaning "naked serpent") comprise the caecilians. These are long, cylindrical, limbless animals with a snake or worm-like form. The adults vary in length from 8 to 75 centimetres (3 to 30 inches) with the exception of Thomson's caecilian (Caecilia thompsoni) which can reach 150 centimetres (5 feet). A caecilian's skin has a large number of transverse folds and in some species contains tiny embedded dermal scales. It has rudimentary eyes covered in skin which are probably limited to discerning differences in light intensity. It also has a pair of short tentacles near the eye that can be extended and which have tactile and olfactory functions. Some caecilians are aquatic but most live underground in burrows in damp soil, in rotten wood and under plant debris.[38] Most species lay their eggs underground and when the larvae hatch, they make their way to adjacent bodies of water. Others brood their eggs and the larvae undergo metamorphosis before the eggs hatch. A few species give birth to live young, nourishing them with glandular secretions while they are in the oviduct.[39] Caecilians are found in tropical Africa, Asia and Central and South America.[40]
Anatomy and physiology
Skin

The integumentary structure contains some typical characteristics common to terrestrial vertebrates, such as the presence of highly cornified outer layers, renewed periodically through a moulting process controlled by the pituitary and thyroid glands. Local thickenings (often called warts) are common, such as those found on toads. The outside of the skin is shed periodically more or less in one piece in contrast to mammals and birds where it is shed in flakes. Amphibians often eat the sloughed skin.[25] Caecilians are unique among amphibians in having mineralized dermal scales embedded in the dermis between the furrows in the skin. The similarity of these to the scales of bony fish is largely superficial. Lizards and some frogs have somewhat similar osteoderms forming bony deposits in the dermis but this is an example of convergent evolution with similar structures having arisen independently in diverse vertebrate lineages.[41]
Amphibian skin is permeable to water. Gas exchange can take place through the skin and this allows adult amphibians to respire without rising to the surface of water and to hibernate at the bottom of ponds.[25] To compensate for their thin and delicate skin, amphibians have evolved mucous glands, principally on their heads, backs and tails. The secretions produced by these help keep the skin moist. In addition, most species of amphibian have granular glands that secrete distasteful or poisonous substances. Some amphibian toxins can be lethal to humans while others have little effect.[42] The main poison-producing glands, the paratoids, produce the neurotoxin bufotoxin and are located behind the ears of certain frogs and toads and behind the eyes of salamanders.[43]
The skin colour of amphibians is produced by three layers of pigment cells called chromatophores. These three cell layers consist of the melanophores (occupying the deepest layer), the guanophores (forming an intermediate layer and containing many granules, producing a blue-green colour) and the lipophores (yellow, the most superficial layer). The colour change experienced by many species is caused by secretions from the pituitary gland. Unlike bony fish, there is no direct control of the pigment cells by the nervous system which results in the colour change taking place more slowly. Bright colours usually indicate that the species is toxic, a defence against predators.[44]
Skeletal system and locomotion
The skeletal system of amphibians is structurally homologous to other tetrapods, though with a number of variations. They possess a cranium, spine, rib cage, long bones such as the humerus and femur, and short bones such as the phalanges, metacarpals, and metatarsals. They have four limbs except for the legless caecilians and a few species of salamander. The bones are hollow and lightweight.[45][46] The skeletomuscular system is strong to enable it to support the head and body. The bones are fully ossified and the vertebrae interlock with each by means of overlapping processes. The pectoral girdle is supported by muscle and the well developed pelvic girdle is attached to the backbone by a pair of sacral ribs. The ilium slopes forward and the body is held closer to the ground than in mammals.[47]
In most amphibians, there are four digits on the fore foot and five on the hind foot, but no claws on either. Some salamanders have fewer digits and the Amphiumas are eel-like in appearance with tiny stubby legs. The sirens are aquatic salamanders with stumpy forelimbs and no hind limbs. The caecilians are limbless. They burrow in the manner of earthworms with zones of muscle contractions moving along the body. On the surface of the ground or in water they move by undulating their body from side to side.[48]
In frogs, the hind legs are larger than the fore legs, especially so in those species that principally move by jumping or swimming. In the walkers and runners the hind limbs are not so large and the burrowers mostly have short limbs and broad bodies. The feet have adaptations for the way of life with webbing between the toes for swimming, broad adhesive toe pads for climbing and keratinised tubercles on the hind feet for digging (frogs usually dig backwards into the soil). In most salamanders, the limbs are short and more or less the same length and project at right angles from the body. Locomotion on land is by walking and the tail often swings from side to side or is used as a prop, particularly when climbing. In their normal gait, only one leg is advanced at a time in the manner adopted by their ancestors, the lobe-finned fish.[47] Some salamanders in the genus Aneides and certain Plethodontids climb trees and have long limbs, large toepads and prehensile tails.[36] In aquatic salamanders, and in frog tadpoles, the tail has dorsal and ventral fins and is moved from side to side as a means of propulsion. Adult frogs do not have tails and caecilians have only very short ones.[48]
Salamanders use their tails in defence. Some species in the Plethodontidae have a weak zone at the base of the tail and if the salamander is in danger or if the tail is grabbed by a predator, it breaks off, a process known as autotomy. Other salamanders are also prepared to drop their tail to save their lives. The tail may continue to twitch after separation which may distract the attacker and both tails and limbs are able to be regenerated.[49] Adult frogs are unable to regrow limbs but tadpoles can do so.[48]
Circulatory system

Amphibians have a juvenile stage and an adult stage and the circulatory systems of the two are distinct. In the juvenile (or tadpole) stage, gills are used to oxygenate blood and movement is similar to that of fish. In the adult stage, amphibians (especially frogs) lose their gills and develop lungs. They have a heart that consists of a ventricle and two atria (it may be considered a single atrium, if not totally or partially divided) that pumps oxygenated blood through arteries and deoxygenated blood through veins to the lungs. Since amphibians are cold-blooded, they must find ways to keep their blood at a constant temperature to maintain homeostasis.[46]
Nervous and sensory systems
The nervous system is basically the same as in other vertebrates, with a central brain, a spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body.[46] The amphibian brain is less well developed than that of reptiles, birds and mammals but is similar in morphology and function to that of a fish. It consists of a cerebrum,midbrain and cerebellum of approximately equal size. The olfactory lobe is the centre of the sense of smell. The cerebrum integrates behaviour and learning. The optic lobe processes information from the eyes. The cerebellum is the centre of muscular coordination. The medulla oblongata controls some organ functions including the heart and respiration. The brain sends signals through the spinal cord and nerves to regulate activity in the rest of the body. The pineal body, known to regulate sleep patterns in humans, is thought to produce the hormones involved in hibernation and aestivation in amphibians.[50]
Tadpoles retain the lateral line system of their ancestral fishes but this is lost in terrestrial adult amphibians. Some caecilians possess electroreceptors which allow them to locate objects around them when submerged in water. The ears are well developed in frogs. There is no external ear but the large circular eardrum lies on the surface of the head just behind the eye. This vibrates and sound is transmitted through a single bone, the stapes, to the inner ear. Only high frequency sounds like mating calls are heard in this way but low frequency noises can be detected through another mechanism.[47] There is a patch of specialized haircells called "papilla amphibiorum" in the inner ear capable of detecting deeper sounds. Another feature unique to amphibians is the columella-opercular complex, adjoining the auditory capsule, which is involved in the transmission of both airborne and seismic signals. The ears of salamanders and caecilians are less highly developed than frogs as they do not normally communicate with each other by sound.[51]
Tadpoles' eyes resemble those of fishes in structure but at metamorphosis the cornea becomes more dome-shaped, the lens becomes flatter and eyelids and associated glands and ducts develop.[47] The adult eyes are an improvement on invertebrate eyes and were a first step in the development of more advanced vertebrate eyes. They allow colour vision and depth of focus. In the retinas are green rods, which are receptive to a wide range of wavelengths.[51]
Digestive and excretory systems
Amphibians swallow their prey whole, with some chewing done in the oral cavities of some species, so they possess voluminous stomachs. Sphincters separate the esophagus from both the oral cavity and the stomach. The relatively short esophagus is lined with cilia that help transport food and secretions to the stomach. Mucus and pepsin, a digestive enzyme, are secreted by glands lining the esophagus. The stomach is separated from the intestine by a pyloric sphincter. The duodenum controls the transport of food into the intestine from the stomach.[46]
Amphibians possess a pancreas, liver and gall bladder. Like mammals, the liver functions as the central metabolic organ that regulates blood sugar, and also produces the final metabolic products and transports them through the vascular system to the kidneys, and finally to excretion. The liver in most amphibians is large with two lobes. The size of the liver is determined by its vital function as a glycogen and fat storage unit, and may change proportionally with the seasons with increasing or decreasing activity. In aquatic amphibians, the liver plays only a small role in processing nitrogen for excretion, and ammonia is diffused mainly through the skin and excretion. The liver of terrestrial amphibians converts ammonia to urea, a less toxic, water soluble nitrogenous compound, as a means of water conservation. In some species, urea is further converted into uric acid. The liver secretions from the liver collect in the gall bladder, and flow into the small intestine. Salamanders lack a valve separating the small intestine from the large intestine. In the small intestine, enzymes digest carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Salt and water absorption occur in the large intestine, as well as mucous secretion to aid in the transport of faecal matter, which is passed out through the cloaca.[46]
Amphibians have two kidneys located dorsally, near the roof of the body cavity. Their job is to filter the blood of metabolic waste and transport the urine via ureters to the urinary bladder where it is stored before being passed out periodically through the cloacal vent. Larvae and most aquatic adult amphibians excrete the nitrogen as ammonia in large quantities of dilute urine while terrestrial species, with a greater need to conserve water, excrete the less toxic product urea. Some tree frogs with limited access to water excrete most of their metabolic waste as uric acid.[52]
Respiratory system

The lungs in amphibians are primitive compared to those of amniotes, possessing few internal septa and large alveoli and consequently having a comparatively slow diffusion rate for oxygen entering the blood. Ventilation is accomplished by buccal pumping. Most amphibians, however, are able to exchange gases with the water or air via their skin. To enable sufficient cutaneous respiration, the surface of their highly vascularized skin must remain moist in order to allow the oxygen to diffuse at a sufficiently high rate.[46] Because oxygen concentration in the water increases at both low temperatures and high flow rates, aquatic amphibians in these situations can rely primarily on cutaneous respiration, as in the Titicaca water frog and the hellbender salamander. In air, where oxygen is more concentrated, some small species can rely solely on cutaneous gas exchange, most famously the plethodontid salamanders, which have neither lungs nor gills. Many aquatic salamanders and all tadpoles have gills in their larval stage, with some (such as the axolotl) retaining gills as aquatic adults.[46]
Reproduction

For the purpose of reproduction most amphibians require fresh water although some lay their eggs on land and have developed various ingenious ways of keeping them moist. A few (e.g. Fejervarya raja) can inhabit brackish water and even survive (though not thrive) in seawater, but there are no true marine amphibians. However, there are reports of particular amphibian populations invading marine waters where their species is normally unable to survive. Such is the case with the Black Sea invasion of the natural hybrid Pelophylax esculentus reported in 2010.[53]
Several hundred frog species in adaptive radiations (e.g., Eleutherodactylus, the Pacific Platymantines, the Australo-Papuan microhylids, and many other tropical frogs), however, do not need any water for breeding in the wild. They reproduce via direct development, an ecological and evolutionary adaptation that has allowed them to be completely independent from free-standing water. Almost all of these frogs live in wet tropical rainforests and their eggs hatch directly into miniature versions of the adult, passing through the tadpole stage within the egg. Reproductive success of many amphibians is dependent not only on the quantity of rainfall, but the seasonal timing.[54]
In the tropics, many amphibians breed continuously or at any time of year. In temperate regions, breeding is mostly seasonal, usually in the spring, and is triggered by increasing day length, rising temperatures or rainfall. Experiments have shown the importance of temperature but the trigger event, especially in arid regions, is often rainfall. In anurans, males usually arrive at the breeding sites before females and the vocal chorus they produce may stimulate the endocrine activity of males that are not yet reproductively active and ovulation in females.[55]
In caecilians, fertilisation is internal, the male extruding an intromittent organ, the phallodeum, and inserting it into the female cloaca. The paired Müllerian glands inside the male cloaca secrete a fluid which resembles that produced by mammalian prostate glands and which may transport and nourish the sperm. Fertilisation probably takes place in the oviduct.[56]
The majority of salamanders also engage in internal fertilisation. In most of these, the male deposits a spermatophore, a small packet of sperm on top of a gelatinous cone, on the substrate either on land or in the water. The female takes the sperm packet into her vent by grasping it with the lips of the cloaca. The spermatozoa move to the spermotheca in the roof of the cloaca where they remain until ovulation which may be many months later. Courtship rituals and methods of transfer of the spermatophore vary between species. In some, the male places the spermatophore into the female cloaca, in others he guides her to it or restrains her with an embrace called amplexus. Certain primitive salamanders in the families Sirenidae, Hynobiidae and Cryptobranchidae practice external fertilisation in a similar manner to frogs, with the female laying the eggs in water and the male releasing sperm onto the egg mass.[56]
With a few exceptions, frogs use external fertilisation. The male grasps the female tightly with his forelimbs either behind her arms or in front of her back legs, or in the case of Epipedobates tricolor, round her neck. They remain in amplexus with their cloacae positioned close together while she lays her eggs and he covers them with his sperm. Roughened nuptial pads on his hands help him retain his grip. Often the male collects and retains the egg mass, forming his hind feet into a sort of basket. An exception is the granular poison frog (Oophaga granulifera) where the male and female place their cloacae in close proximity while facing in opposite directions and then release eggs and sperm simultaneously. The tailed frog (Ascaphus truei) exhibits internal fertilisation. The "tail" is only possessed by the male and is an extension of the cloaca and used to inseminate the female. This frog lives in fast flowing streams and internal fertilisation will prevent the sperm being washed away before fertilisation occurs.[57]
Most frogs can be classified as either prolonged or explosive breeders. Typically, prolonged breeders congregate at a breeding site, the males usually arriving first, calling and setting up territories. Other satellite males remain quietly nearby, waiting for their opportunity to take over a territory. The females arrive sporadically, mate selection takes place and eggs are laid. The females depart and territories may change hands and more females appear and in due course, the breeding season comes to an end. Explosive breeders on the other hand are found where temporary pools appear in dry regions after rainfall. These frogs are typically fossorial species that emerge after heavy rains and congregate at a breeding site. They are attracted there by the calling of the first male to find a suitable place, perhaps a pool that forms in the same place each rainy season. The assembled frogs may call in unison and frenzied activity ensues, the males scrambling to mate with the usually smaller number of females.[57]
The ringed caecilian (Siphonops annulatus) has developed a unique adaptation for the purposes of reproduction. The progeny feeds on a skin layer that is specially developed by the adult. This phenomenon is known as maternal dermatophagy. The common tree frog (Polypedates leucomystax) from Asia makes a foam nest on a leaf above an ephemeral pool. When the eggs hatch, the tadpoles work themselves out of the foam and fall into the water below.[58]
Several species have also adapted to arid and semi-arid environments, but most of them still need water to lay their eggs. Symbiosis with single celled algae that lives in the jelly-like layer of the eggs has evolved several times. The larvae of frogs (tadpoles) breathe with exterior gills at the start, but soon a pouch is formed that covers the gills and the front legs. Lungs are also formed quite early to assist in breathing. Newt larvae have large external gills that gradually disappear and the larvae of newts are quite similar to the adult form from an early age.
Life cycle

Most amphibians go through metamorphosis, a process of significant morphological change after birth. In typical amphibian development, eggs are laid in water and larvae are adapted to an aquatic lifestyle. Frogs, toads and salamanders all hatch from the egg as larvae with external gills. Metamorphosis in amphibians is regulated by thyroxin concentration in the blood, which stimulates metamorphosis, and prolactin, which counteracts its effect. Specific events are dependent on threshold values for different tissues.[59] Because most embryonic development is outside the parental body, development is subject to many adaptations due to specific ecological circumstances. For this reason tadpoles can have horny ridges for teeth, whiskers and fins. They also make use of the lateral line organ. After metamorphosis, these organs become redundant and will be reabsorbed by controlled cell death, called apoptosis. The extent of adaptations to specific ecological circumstances among amphibians is remarkable, with many discoveries still being made.[60]
Eggs
The egg of an amphibian is typically surrounded by a transparent gelatinous covering secreted by the oviducts and containing mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides. This capsule is permeable to water and gases and swells considerably as it absorbs water. The ovum is at first rigidly held but in fertilised eggs, the innermost layer liquefies and allows the embryo to move freely and this also happens in salamander eggs even when they are unfertilised. Eggs of some salamanders and frogs contain unicellular green algae. These penetrate the jelly envelope after the eggs are laid and may increase the supply of oxygen to the embryo through photosynthesis. They seem to both speed up the development of the larvae and reduce mortality.[61] Most eggs contain the pigment melanin which raises their temperature and protects them against ultraviolet radiation. Species such as caecilians, plethodontid salamanders and certain frogs that lay eggs underground or in dark locations usually have unpigmented eggs. In the wood frog (Rana sylvatica), the interior of the globular egg cluster has been found to be up to 6°C (11°F) warmer than its surroundings which is an advantage in its cool northern habitat.[62]
The eggs or spawn may be deposited singly or in small groups or may take the form of spherical egg masses, rafts or long strings. In terrestrial caecilians, the eggs are laid in grape-like clusters in burrows near streams. The amphibious salamander Ensatina attaches its similar clusters by stalks to underwater stems and roots. The greenhouse frog (Eleutherodactylus planirostris) lays eggs in small groups in the soil where they develop in about two weeks directly into juvenile frogs without an intervening larval stage.[63] The tungara frog (Physalaemus pustulosus) builds a floating nest from foam to protect its eggs. A raft is built first and then eggs are laid in the centre and there is a foam capping. The foam has anti-microbial properties. It contains no detergents but is created by whipping up proteins and lectins secreted by the female.[64][65]
Larvae
The eggs of amphibians are typically laid in water and hatch into free-living larvae that complete their development in water and later transform into either aquatic or terrestrial adults. In many species of frog and in most lungless salamanders (Plethodontidae), direct development takes place, the larvae growing within the eggs and emerging as miniature adults. Many caecilians and some other amphibians lay their eggs on land and the newly hatched larvae wriggle or are transported to water bodies. Some caecilians, the Alpine salamander (Salamandra atra) and some of the African live-bearing toads (Nectophrynoides spp.) are viviparous, the larvae feeding on glandular secretions and developing within the female's oviduct, often for long periods. Other amphibians, but not as far as it is known caecilians, are ovoviviparous. The eggs are retained in or on the parent's body but the larvae subsist on the yolks of their eggs and receive no nourishment from the adult. The larvae emerge at varying stages of their growth, either before or after metamorphosis, according to their species.[66] The toad genus Nectophrynoides exhibits all these developmental patterns among its dozen or so members.[67]
Frogs
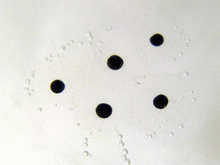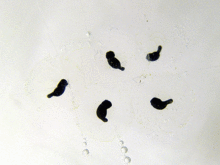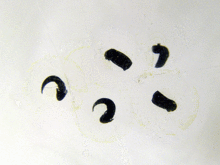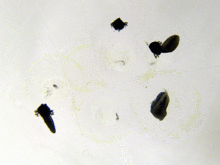

Frog larvae are known as tadpoles and typically have oval bodies and long, vertically flattened tails with fins. The free living larvae are normally fully aquatic but the tadpoles of some species such as (Nannophrys ceylonensis) are semi-terrestrial and live among wet rocks.[68][69] Tadpoles have cartilaginous skeletons, gills for respiration (external gills at first, internal gills later), lateral line systems and large tails which they use for swimming.[70] Newly hatched tadpoles soon develop gill pouches which cover the gills and their lungs develop early and are used as accessory breathing organs, the tadpoles rising to the water surface to gulp air. Some species complete their development inside the egg and hatch directly into small frogs. These larvae do not have gills but instead have specialised areas of skin through which respiration takes place. Tadpoles do not have true teeth but, in most species, the jaws have long, parallel rows of small keratinized structures called keradonts surrounded by a horny beak.[71] Front legs are formed under the gill sac and hind legs become visible a few days later. Tadpoles are typically herbivorous, feeding mostly on algae, including diatoms filtered from the water through the gills. They are also detrivores, stirring up the sediment at the pond bottom and ingesting edible fragments. They have a relatively long, spiral-shaped gut to enable them to digest this diet.[72] Some species are carnivorous at the tadpole stage, eating insects, smaller tadpoles and fish. Young of the Cuban tree frog (Osteopilus septentrionalis) can occasionally be cannibalistic, the younger tadpoles attacking a larger, more developed tadpole when it is undergoing metamorphosis.[73]
At metamorphosis, rapid changes in the body take place as the lifestyle of the frog changes completely. The spiral‐shaped mouth with horny tooth ridges is reabsorbed together with the spiral gut. The animal develops a big jaw, and its gills disappear along with its gill sac. Eyes and legs grow quickly, a tongue is formed, and all this is accompanied by associated changes in the neural networks (development of stereoscopic vision, loss of the lateral line system, etc.) All this can happen in about a day, so it is truly a metamorphosis. It isn't until a few days later that the tail is reabsorbed, due to the higher thyroxin concentrations required for tail resorption.[72]
Salamanders
At hatching, a typical salamander larva has eyes without lids, teeth in both upper and lower jaws, three pairs of feathery external gills and a long, somewhat laterally flattened body and tail with dorsal and ventral fins. The forelimbs may be partially developed and the hind limbs are rudimentary in pond-living species but may be rather more developed in species that reproduce in moving water. Pond-type larvae often have a pair of balancers, rod-like structures on either side of the head which perhaps prevent the gills from getting clogged up with bottom sediment. Some members of the genera Ambystoma and Dicamptodon have larvae that never fully develop into the adult form but this varies with species and with populations. The northwestern salamander (Ambystoma gracile) is one of these and, depending on environmental factors, either remains permanently in the larval state, a condition known as neoteny, or transforms into an adult.[74] Neoteny occurs when the animal's growth rate is very low. This is usually because of adverse conditions such as low water temperatures which may inhibit the production of thyroxin or prevent the larva from reacting to the hormone in the normal way. Other factors that may inhibit metamorphosis include lack of food, lack of trace elements and competition from conspecifics. The tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) also sometimes behaves in this way and may grow particularly large in the process. The adult tiger salamander is terrestrial but the larva is aquatic and able to breed while still in the larval state. When conditions are particularly inhospitable on land, larval breeding may allow continuation of a population that would otherwise die out. There are fifteen species of obligate neotenic salamanders including Necturus, Proteus and Amphiuma, and many examples of facultative ones that adopt this strategy under appropriate environmental circumstances.[75]
Lungless salamanders in the family Plethodontidae are terrestrial and lay a small number of unpigmented eggs in a cluster among damp leaf litter. Each egg has a large yolk sac and the larva feeds on this while it develops inside the egg, emerging fully formed as a juvenile salamander. The female salamander often broods the eggs and in the genus Ensatinas, she has been observed to coil around them and press her throat area against them, effectively massaging them with a mucous secretion.[76]
In newts and salamanders, metamorphosis is less dramatic than in frogs. This is because the larvae are already carnivorous and continue to feed as predators when they are adults so few changes are needed to their digestive systems. Their lungs are functional early but the larvae don't make as much use of them as do tadpoles. Their gills are never covered by gill sacs and are reabsorbed just before the animals leave the water. Other changes include the reduction in size or loss of tail fins, the closure of gill slits, thickening of the skin, the development of eyelids, and certain changes in dentition and tongue structure. Salamanders are at their most vulnerable at metamorphosis as swimming speeds are reduced and transforming tails are encumbrances on land.[77] Adult salamanders often have an aquatic phase in spring and summer, and a land phase in winter. For adaptation to a water phase, prolactin is the required hormone, and for adaptation to the land phase, thyroxin. External gills do not return in subsequent aquatic phases because these are completely absorbed upon leaving the water for the first time.[78]
Caecilians
Most terrestrial caecilians that lay eggs do so in burrows or moist places on land near bodies of water. The development of the young of Ichthyophis glutinosus, a species from Sri Lanka, has been much studied. The eel-like larvae hatch out of the eggs and make their way to water. They have three pairs of external red feathery gills, a blunt head with two rudimentary eyes, a lateral line system and a short tail with fins. They swim by undulating their body from side to side. They are mostly active at night, soon lose their gills and make sorties onto land. Metamorphosis is gradual but by the age of about ten months they have developed a pointed head with sensory tentacles near the mouth and lost their eyes, lateral line systems and tails. The skin has becomes thicker, embedded scales have developed and the body has become divided into segments. By this time the caecilian has constructed a burrow and is living on land.[79]
In the majority of species of caecilians, the young are produced by vivipary. Typhlonectes compressicauda, a species from South America, is typical of these. Up to nine larvae can develop in the oviduct at any one time. They are elongated and have paired sac-like gills, small eyes and specialised scraping teeth. At first they feed on the yolks of the eggs but as this source of nourishment declines they begin to rasp at the ciliated epithelial cells that line the oviduct. This stimulates the secretion of fluids rich in lipids and mucoproteins on which they feed along with scrapings from the oviduct wall. They may increase their length sixfold and be two fifths as long as their mother before being born. By this time they have undergone metamorphosis, lost their eyes and gills, developed a thicker skin and mouth tentacles and reabsorbed their teeth. A permanent set of teeth grow through soon after birth.[80][81]
Parental care
The care of offspring among amphibians has been little studied but in general, the larger the number of eggs in a batch, the less likely it is that any degree of parental care takes place. Nevertheless, it is estimated that up to twenty percent of amphibian adults play some role in the care of the young.[82] Those species that breed in smaller water bodies or other specialised habitats tend to have more complex patterns of behaviour in the care of the young than do others.[83]
Many woodland salamanders lay clutches of eggs under dead logs or stones on land. The black mountain salamander does this, the mother brooding the eggs and guarding them from predation as the larvae feed on the yolks of their eggs. They eventually break their way out of the egg capsules and disperse.[84] The male hellbender, a primitive salamander, excavates an underwater nest and encourages females to lay there. He then guards the site for the two to three months before the eggs hatch, undulating his body and fanning them with his skin folds to increase their supply of oxygen.[35]
The tiny male frog Colostethus subpunctatus protects his egg cluster which is hidden under a stone or log. When the eggs hatch, he transports the tadpoles on his back, stuck there by a mucous secretion, to a temporary pool where he dips himself into the water and the tadpoles drop off.[85] The male midwife toad (Alytes obstetricans) winds egg strings round his thighs and carries the eggs around for up to eight weeks. He keeps them moist and when they are ready to hatch, visits a pond or ditch and releases the tadpoles.[86] The female gastric-brooding frog (Rheobatrachus sp.), believed to be extinct, swallows her eggs and rears her larvae in her stomach. She stops feeding while they are there and they consume their egg yolks. When they are ready to undergo metamorphosis, she regurgitates them and they hop away from her mouth.[87] The pouched frog (Assa darlingtoni) lays eggs on the ground and, when they hatch, the male carries the tadpoles around in brood pouches on his hind legs.[88] The aquatic Surinam toad (Pipa pipa) raises its young in pores on its back where they remain until metamorphosis.[89] The granular poison frog (Oophaga granulifera) is typical of a number of tree frogs in the poison dart frog family Dendrobatidae. Its eggs are laid on the forest floor and when they hatch, the tadpoles are carried one by one on the back of an adult to a suitable water filled crevice such as the axil of a leaf or the rosette of a bromeliad. The female visits the nursery sites regularly and deposits one or more unfertilised eggs in the water which is consumed by the tadpole.[90]
Feeding and diet
With a few exceptions, adult amphibians are predators, feeding on virtually anything that moves that they can swallow. The diet mostly consists of small items of prey that do not move too fast such as beetles, caterpillars, earthworms and spiders. The sirens (Siren spp.) often ingest aquatic plant material with the invertebrates on which they feed [91] and a Brazilian tree frog Xenohyla truncata includes a large quantity of fruit in its diet.[92] The Mexican burrowing toad (Rhinophrynus dorsalis) has a specially adapted tongue for picking up ants and termites. It projects it with the tip foremost whereas other frogs flick out the rear part first, their tongues being hinged at the front.[93]
Food is mostly selected by sight, even in conditions of dim light. Movement of the prey triggers a feeding response. Frogs have been caught on fish hooks baited with red flannel and green frogs (Rana clamitans) have been found to have stomachs full of elm seeds that they had seen floating past.[94] Toads, salamanders and caecilians also use smell to detect prey. This response is mostly secondary because salamanders have been observed to remain stationary near odoriferous prey but only feed if it moves. Cave dwelling amphibians normally hunt by smell and some salamanders seem to have learned to recognize immobile prey even when it has no smell.[95]
Amphibians usually swallow food whole but may chew it lightly first in order to subdue it.[25] They typically have small hinged pediceled teeth. These have bicuspid conical crowns attached by a pedicel to the jaw and are replaced at intervals. Salamanders, caecilians and some frogs have one or two rows of teeth in both jaws but some frogs (Rana spp.) lack teeth in the lower jaw and toads (Bufo spp.) have no teeth. In many amphibians there are also vomerine teeth attached to a facial bone in the roof of the mouth.[96]
The tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) is typical of the frogs and salamanders that hide under cover ready to ambush unwary invertebrates. Others amphibians such as the Bufo spp. toads actively search for prey, while the Argentine horned frog (Ceratophrys ornata) lures inquisitive prey closer by raising its hind feet over its back and vibrating its yellow toes.[97] Among leaf litter frogs in Panama, frogs that actively hunted prey had narrow mouths and were slim, often brightly coloured and toxic, while ambushers had wide mouths and were broad and well camouflaged.[98] Caecilians do not flick their tongues but catch their prey by grabbing it with their slightly backward-pointing teeth. The struggles of the prey and further jaw movements work it inwards and the caecilian usually retreats into its burrow. The subdued prey is gulped down whole.[99]
When they are newly hatched, frog larvae feed on the yolk of the egg. When this is exhausted some move on to feed on bacteria, algal crusts, detritus and raspings from submerged plants. Water is drawn in through their mouths, which are usually at the bottom of their heads, and passes through branchial food traps between their mouths and their gills where fine particles are trapped in mucus and filtered out. Others have specialised mouthparts consisting of a horny beak edged by several rows of labial teeth. They scrape and bite food of many kinds as well as stirring up the bottom sediment, filtering out larger particles with the papillae round their mouths. Some, such as the spadefoot toads, have strong biting jaws and are carnivorous or even cannibalistic.[100]
Vocalization
The calls made by caecilians and salamanders are limited to occasional soft squeaks, grunts or hisses and have not been much studied. A clicking sound sometimes produced by caecilians may be a means of orientation, as in bats, or a form of communication. Most salamanders are considered voiceless but the California giant salamander (Dicamptodon ensatus) has vocal cords and can produce a rattling or barking sound. Some species of salamander emit a quiet squeak or yelp if attacked.[101]
Frogs are much more vocal, especially during the breeding season when they use their voices to attract mates. Each call is characteristic of the species, the presence of which in an area may be easier to detect by its voice than by a fleeting glimpse of the animal itself. In most species, the sound is produced by expelling air from the lungs over the vocal cords into an air sac or sacs in the throat or at the corner of the mouth. This may distend like a balloon and acts as a resonator, helping to transfer the sound to the atmosphere, or the water at times when the animal is submerged.[101] The main vocalisation is the male's loud advertisement call which seeks to both encourage a female to approach and discourage other males from intruding on its territory. This call is modified to a quieter courtship call on the approach of a female or to a more aggressive version if a male intruder draws near. Calling bears the risk of attracting predators and involves the expendirure of much energy.[102] Other calls include those given by a female in response to the advertisement call and a release call given by a male or female during unwanted attempts at amplexus. When a frog is attacked, a distress or fright call is emitted, often resembling a scream.[103] The usually nocturnal Cuban tree frog (Osteopilus septentrionalis) produces a rain call when there is rainfall during daylight hours.[104]
Territorial behaviour
Little is known of the territorial behaviour of caecilians but some frogs and salamanders defend home ranges. These are usually feeding, breeding or sheltering sites and it is the males that normally exhibit such behaviour though in some species, females and even juveniles are also involved. Although in many frog species, females are larger than males, this is not the case in most species where males are actively involved in territorial defence. Some of these have specific adaptations such as enlarged teeth for biting or spines on the chest, arms or thumbs.[105]
In salamanders, defence of a territory involves adopting an aggressive posture and if necessary attacking the intruder. This may involve snapping, chasing and sometimes biting, occasionally causing the loss of a tail. The behaviour of red-backed salamanders (Plethodon cinereus) has been much studied. It was found that 91% of marked individuals which were later recaptured were within a metre (yard) of their original location (foraging behaviour would have given a different result at night). [106] The salamanders left odour marks which deterred the intrusion of others and delineated the boundaries of their territory. A lot of the behaviour seemed stereotyped and did not involve any actual contact between individuals. An aggressive posture involved raising the body off the ground and glaring at the opponent who often turned away submissively. If the intruder persisted, a biting lunge was usually launched at either the tail region or the naso-labial grooves. Damage to either of these areas can reduce the fitness of the rival, either because of the need to regenerate tissue or because it impairs their ability to detect food.[106]
In frogs, male territorial behaviour is often observed at breeding locations and calling is both an announcement of ownership of part of this resource and an advertisement call to potential mates. In general, a deeper voice represents a heavier and more powerful individual, and this may be sufficient to prevent intrusion by smaller males. Much energy is used in the vocalization and it takes a toll on the territory holder who may be displaced by a fitter individual if he loses too much condition. There is a tendency for males to tolerate the holders of neighbouring territories while vigorously attacking unknown intruders. Holders of territories have a “home” advantage and usually come off better in an encounter between two similar sized frogs. If threats are insufficient, chest to chest tussles may take place. Other fighting methods include pushing and shoving, deflating the opponent’s vocal sac, jumping on his back, biting, chasing, splashing and ducking him and seizing him by the head.[107]
Defence mechanisms


Amphibians have soft bodies and thin skins, lack claws, defensive armour or spines and seem relatively helpless. Nevertheless they have evolved various defence mechanisms to keep themselves alive. The first line of defence in salamanders and frogs is the mucous secretions that they produce to keep their skin moist and which make them slippery and difficult to grip. The secretion is often sticky and distasteful or toxic. Snakes have been observed yawning and gaping when trying to swallow an African clawed frog (Xenopus spp.) which gives the frog an opportunity to escape.[108] Caecilians have been little studied in this respect but the aquatic (Typhlonectes compressicauda) produces toxic mucous which has caused the death of predatory fish in a feeding experiment in Brazil.[109] In salamanders, the skin is toxic and in frogs, the main poison glands are at the side of the neck and under the warts on the back and these regions are presented to the attacking animal. The skin of the rough-skinned newt (Taricha granulosa) from North America contains the neurotoxin tetrodotoxin (TTX), the most toxic non-protein substance known and almost identical to that produced by pufferfish. Handling the newts does not cause harm but ingestion of even the most minute amounts of the skin is deadly. In feeding trials, fish, frogs, reptiles, birds and mammals were all found to be susceptible. A dose of 0.0002cc of skin was sufficient to kill a mouse in ten minutes.[110] The only predators with some tolerance to the poison are certain populations of common garter snake (Thamnophis sirtalis). In locations where both snake and salamander co-exist, these seems to have developed some immunity through genetic changes and the snakes feed on the newt with impunity.[111] Coevolution occurs with the newt increasing its toxic capabilities at the same rate as the snake further develops its immunity.[112] A number of different animal groups have independently evolved to use TTX as a defensive agent. They may obtain it through the food chain from the bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus which is known to synthesize the substance. The link is not firmly established and there remains doubt as to whether the bacteria are truly the source of TTX in animals.[113]
Poisonous species often use bright colouring to warn potential predators of their toxicity. These warning colours tend to be red or yellow combined with black. The fire salamander (Salamandra salamandra) being an example. Once a predator has sampled one of these, it is likely to remember the colouration next time it encounters a similar animal. In some species, such as the fire-bellied toad (Bombina spp.), the warning colouration is on the belly and these animals adopt a defensive pose when attacked, exhibiting their bright colours to the predator. The frog Allobates zaparo is not poisonous but mimics the appearance of other toxic species in its locality, a strategy that may deceive predators.[114]
Many amphibians are nocturnal and hide during the day, thereby avoiding diurnal predators that hunt by sight. Other amphibians use camouflage to avoid being detected. They have various colourings such as mottled browns, greys and olives to make themselves inconspicuous so that they blend into the background. Some salamanders adopt defensive poses when faced by a potential predator such as the North American northern short-tailed shrew (Blarina brevicauda). Their bodies writhe and they raise and lash their tails which makes it difficult for the predator to avoid contact with their granular glands.[115] A few salamanders will autotomise their tails when attacked, sacrificing this part of their anatomy to enable them to escape with their lives. There may have a constricted tail base to allow this to happen easily. The tail is regenerated later but the cost to the animal of replacing it is significant.[116]
Some frogs and toads inflate themselves to make themselves look large and fierce, and some spadefoot toads (Pelobates spp) scream and leap towards the attacker.[25] Giant Salamanders of the genus Andrias, as well as Ceratophrine and Pyxicephalus frogs possess sharp teeth and are capable of drawing blood with a defensive bite. the Blackbelly Salamander bites an attacking common garter snake (Thamnophis sirtalis) two or three times its size on the head and often manages to escape.[117]
Conservation

Dramatic declines in amphibian populations, including population crashes and mass localized extinction, have been noted in the past two decades from locations all over the world, and amphibian declines are thus perceived as one of the most critical threats to global biodiversity.[118] A number of causes are believed to be involved, including habitat destruction and modification, over-exploitation, pollution, introduced species, climate change, endocrine-disrupting pollutants, destruction of the ozone layer (ultraviolet radiation has shown to be especially damaging to the skin, eyes, and eggs of amphibians), and diseases like chytridiomycosis. However, many of the causes of amphibian declines are still poorly understood, and are a topic of ongoing discussion.[119]
In many terrestrial ecosystems, amphibians constitute one of the largest parts of the vertebrate biomass. Any decline in amphibian numbers will have an impact on the patterns of predation. The loss of carnivorous species near the top of the food chain will upset the delicate ecosystem balance and may cause dramatic increases in opportunistic species. In the Middle East, a growing appetite for eating frog legs and the consequent gathering of them for food was linked to an increase in mosquitoes.[120] Predators that feed on amphibians are affected by their decline. The western terrestrial garter snake (Thamnophis elegans) in California is largely aquatic and depends heavily on two species of frog that are diminishing in numbers, the Yosemite toad (Bufo canorus) and the mountain yellow-legged frog (Rana muscosa), putting the snake's future at risk. If it were to become scarce, this would affect birds of prey and other predators that feed on it.[121] Meanwhile, in the ponds and lakes, fewer frogs means fewer tadpoles. These normally play an important role in controlling the growth of algae and also forage on detritus that accumulates as sediment on the bottom. A reduction in the number of tadpoles or their absence might lead to algal overgrowth and possibly eutrophication, resulting in the water becoming depleted of oxygen when the algae die and decompose. Aquatic invertebrates and fish might then die and there would be unpredictable ecological consequences.[122]
A global strategy to stem the crisis has been released in the form of the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan. Developed by over 80 leading experts in the field, this call to action details what would be required to curtail amphibian declines and extinctions over the next 5 years—and how much this would cost. The Amphibian Specialist Group of the World Conservation Union (IUCN) is spearheading efforts to implement a comprehensive global strategy for amphibian conservation.[123] Amphibian Ark is an organization that was formed to implement the ex-situ conservation recommendations of this plan, and they have been working with zoos and aquaria around the world encouraging them to create assurance colonies of threatened amphibians.[123] One such project is the Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project that built on existing conservation efforts in Panama to create a country-wide response to the threat of chytridiomycosis rapidly spreading into eastern Panama.[124]
On January 21, 2008, Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered (EDGE),[125] in a statement made by chief Helen Meredith, identified nature's most endangered species: "The EDGE amphibians are amongst the most remarkable and unusual species on the planet and yet an alarming 85% of the top 100 are receiving little or no conservation attention." The top 10 EDGE listed species include the Chinese giant salamander, a distant relative of the newt, the tiny Gardiner's Seychelles frog, the limbless Sagalla caecilian from Kenya, South African ghost frogs, lungless salamanders from Mexoco, the Malagasy rainbow frog, Chile's Darwin's frog (Rhinoderma rufum) and the Betic midwife toad from Spain.[126][127][128][129]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Waikato – Evolution of amphibians
- ^ a b About.com – Prehistoric amphibians
- ^ Amphibian diversity and life history.
- ^ Waddle, J, Use of amphibians as ecosystem indicator species
- ^ Rittmeyer, Eric N.; Allison, Allen; Gründler, Michael C.; Thompson, Derrick K.; Austin, Christopher C. (2012). Etges, William J (ed.). "Ecological guild evolution and the discovery of the world's smallest vertebrate". PLoS ONE. 7 (1): e29797. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029797. PMC 3256195. PMID 22253785. Retrieved 2012-01-11.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Wood, Gerald (1983). The Guinness Book of Animal Facts and Feats. ISBN 978-0-85112-235-9.
- ^ "Amphibian (Adj.)". Online Etymology Dictionary. 2012. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ^ a b Caldwell, Michelle. "Evolution of Amphibians and Reptiles: The Paleozoic Era". Retrieved 2012-08-16.
- ^ Lombard, R. E.; Bolt, J. R. (1979). "Evolution of the tetrapod ear: an analysis and reinterpretation". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 11 (1): 19–76. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.1979.tb00027.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Spoczynska, J. O. I. (1971). Fossils: A Study in Evolution. Frederick Muller Ltd. pp. 120–125. ISBN 0-584-10093-0.
- ^ San Mauro, D. (2010). "A multilocus timescale for the origin of extant amphibians". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 56 (2): 554–561. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.019. PMID 20399871.
- ^ San Mauro, Diego; Vences, Miguel; Alcobendas, Marina; Zardoya, Rafael; Meyer, Axel (2005). "Initial Diversification of living amphibians predated the breakup of Pangaea". The American Naturalist. 165 (5): 590‑599. doi:10.1086/429523. JSTOR 429523.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Anderson, J.; Reisz, R.; Scott, D.; Fröbisch, N.; Sumida, S (2008). "A stem batrachian from the Early Permian of Texas and the origin of frogs and salamanders". Nature. 453 (7194): 515–518. doi:10.1038/nature06865. PMID 18497824.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Morell, Virginia (1993). "Classification of the major taxa of Amphibia and Reptilia" (PDF). Science. 259 (5096): 764‑765. doi:10.1126/science.259.5096.764.
- ^ Frost, Darell (2011). "American Museum of Natural History: Amphibian Species of the World 5.5, an Online Reference". Herpetology. The American Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 2012-08-09.
- ^ Zug, G. R. (2001). Herpetology, Second Edition: An Introductory Biology of Amphibians and Reptiles. Academic Press.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Carroll, 2007
- ^ David Cannatella (1995). "Salientia". Tree of Life Web Project. Retrieved 2012-08-31.
- ^ Sumich, James L. (2004). Introduction to the biology of marine life. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 171. ISBN 0-7637-3313-X, 9780763733131.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Dorit, R. L. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 843‑859. ISBN 0-03-030504-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. p. 3. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Badger, D. (1995). Frogs. Airlife Publishing. p. 19. ISBN 1853107409.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Frog fun facts". American Museum of Natural History. 2010-01-12. Retrieved 2012-08-29.
- ^ Challenger, David (2012-01-12). "World's smallest frog discovered in Papua New Guinea". CNN. Retrieved 2012-08-29.
- ^ a b c d e f g Arnold, Nicholas (2002). Reptiles and Amphibians of Britain and Europe. London: Harper Collins Publishers Ltd. pp. 13–18.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Faivovich, J. (2005). "Systematic review of the frog family Hylidae, with special reference to Hylinae: Phylogenetic analysis and revision". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 294: 1‑240. doi:10.1206/0003-0090(2005)294[0001:SROTFF]2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Ford, L.S. (1993). "The major clades of frogs". Herpetological Monographs. 7: 94‑117. doi:10.2307/1466954. JSTOR 1466954.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ San Mauro, Diego (2005). "Initial diversification of living amphibians predated the breakup of Pangaea". American Naturalist. 165 (5): 590‑599. doi:10.1086/429523.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Benton, Michael J. (2004). "Classification of the vertebrates". Vertebrate Palaeontology. Wiley-Blackwell. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
- ^ "Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus)". ARKive. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
- ^ Wake, David B. (2000-11-08). "cite web". AmphibiaWeb. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
- ^ Larson, A.; Dimmick, W. (1993). "Phylogenetic relationships of the salamander families: an analysis of the congruence among morphological and molecular characters". Herpetological Monographs. 7 (7): 77‑93. doi:10.2307/1466953. JSTOR 1466953.
- ^ Dorit, R. L. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 852. ISBN 0-03-030504-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Heying, Heather (2003). "cite web". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
- ^ a b Mayasich, J.; Grandmaison, D.; Phillips, C. (2003-06-01). "Eastern Hellbender Status Assessment Report" (PDF). U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Wake, David B. "Caudata". Encyclopedia Brittanica. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
- ^ Lanza, B.; Vanni, S.; Nistri, A. (1998). Cogger, H. G.; Zweifel, R. G. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Reptiles and Amphibians. Academic Press. pp. 69‑70. ISBN 0-12-178560-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. p. 4. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Dorit, R. L. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 858. ISBN 0-03-030504-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Caecilia 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2012-03-24.
- ^ Zylberberg, Louise; Wake, Marvalee H. (1990). "Structure of the scales of Dermophis and Microcaecilia (Amphibia: Gymnophiona), and a comparison to dermal ossifications of other vertebrates". Journal of Morphology. 206 (1): 25‑43. doi:10.1002/jmor.1052060104.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Biodiversity Institute of Ontario; Hebert, Paul D. N. (2008-10-12). "Amphibian morphology and reproduction". Encyclopedia of Earth. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Physical characteristics". Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ^ Spearman, R. I. C. (1973). The integument: A Textbook of Skin Biology. Cambridge University Press. p. 81. ISBN 0-521-20048-2.
- ^ Maglia, A.M.; Leopold, J.L.; Pugener, A.L.; Gauch, S. (2007). "AmphibAnat". The Amphibian Anatomical Ontology web project. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g "Anatomy of the frog". Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ^ a b c d Dorit, R. L. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 846. ISBN 0-03-030504-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 26‑36. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Beneski, John T. Jr. (1989). "Adaptive significance of tail autotomy in the salamander, Ensatina". Journal of Herpetology. 23 (3): 322‑324. doi:10.2307/1564465. JSTOR 1564465.
- ^ "Amphibian brains". Retrieved February 16, 2012.
- ^ a b Duellman, William E.; Zug, George R. (2012). "Amphibian". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2012-03-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dorit, R. L. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 849. ISBN 0-03-030504-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Natchev, Nikolay; Tzankov, Nikolay; Geme, Richard (2011). "Green frog invasion in the Black Sea: habitat ecology of the Pelophylax esculentus complex (Anura, Amphibia) population in the region of Shablenska Тuzla lagoon in Bulgaria" (PDF). Herpetology Notes. 4: 347‑351.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ C.Michael Hogan. 2010. Abiotic factor. Encyclopedia of Earth. eds Emily Monosson and C. Cleveland. National Council for Science and the Environment. Washington DC
- ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 140‑141. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Duellman, Willia E. (1994). Biology of Amphibians. JHU Press. pp. 77‑79. ISBN 080184780X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 154‑162. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Whittaker, Kellie ; Tsai, Gary (2005-10-24). "Polypedates leucomystax". AmphibiaWeb. Retrieved 2012-08-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kikuyama, Sakae (1993). International Review of Cytology: Aspects of amphibian metamorphosis: Hormonal control. Academic Press. pp. 105–126. ISBN 9780123645487.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Newman, Robert A. (1992). "Adaptive Plasticity in Amphibian Metamorphosis". BioScience. 42 (9): 671–678. doi:10.2307/1312173. JSTOR 1312173.
- ^ Gilbert, Perry W. (1942). "Observations on the eggs of Ambystoma maculatum with especial reference to the green algae found within the egg envelopes". Ecology. 23 (2): 215‑227. doi:10.2307/1931088. JSTOR 1931088.
- ^ Waldman, Bruce; Ryan, Michael J. (1983). "Thermal advantages of communal egg mass deposition in wood frogs (Rana sylvatica)". Journal of Herpetology. 17 (1): 70‑72. doi:10.2307/1563783. JSTOR 1563783.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Greenhouse frog (Eleutherodactylus planirostris)". ARKive. Retrieved 2012-08-18.
- ^ Dalgetty, Laura; Kennedy, Malcolm W. (2010). "Building a home from foam: túngara frog foam nest architecture and three-phase construction process [[File:Open Access logo PLoS transparent.svg|9px|link=Open access|open access publication – free to read|alt=Open access icon]]". Biology Letters. 6 (3): 293–6. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0934. PMC 2880057. PMID 20106853.
{{cite journal}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Proteins of frog foam nests". University of Glasgow. Retrieved 2012-08-24.
- ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 6‑9. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Crump, Martha L. (2009-08-19). "Amphibian diversity and life history" (PDF). p. 14. Retrieved 2012-08-30.
- ^ "Ontogenetic Changes in Diet and Intestinal Morphology in Semi-Terrestrial Tadpoles of Nannophrys ceylonensis (Dicroglossidae)".
- ^ Janzen, Peter (2005-05-10). "Nannophrys ceylonensis". AmphibiaWeb. University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved 2012-07-20.
- ^ Duellman, W. E.; Zug, G. R. "Anura: From tadpole to adult". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2012-07-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 179‑181. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Duellman, William E.; Zug, George R. (2012). "Anura". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2012-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Crump, Martha L. (1986). "Cannibalism by younger tadpoles: another hazard of metamorphosis". Copeia. 4 (4). American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: 1007‑1009. doi:10.2307/1445301. JSTOR 1445301.
- ^ Valentine, Barry D.; Dennis, David M. (1964). "A Comparison of the gill-arch system and fins of three genera of larval salamanders, Rhyacotriton, Gyrinophilus, and Ambystoma". Copeia. 1: 196‑201. doi:10.2307/1440850. JSTOR 1440850.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Duellman, William E. (1994). Biology of Amphibians. JHU Press. pp. 191‑192. ISBN 080184780X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. p. 196. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Shaffer, H. Bradley ; Austin, C. C.; Huey, R. B. (1991). "The consequences of metamorphosis on salamander (Ambystoma) locomotor performance". Physiological Zoology. 64 (1): 212‑231. JSTOR 30158520.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wake, David B. (2012). "Caudata". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2012-03-26.
- ^ Breckenridge, W. R.; Nathanael, S.; Pereira, L. (1987). "Some aspects of the biology and development of Ichthyophis glutinosus". Journal of Zoology. 211: 437‑449.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wake, Marvalee H. (1977). "Fetal maintenance and its evolutionary significance in the Amphibia: Gymnophiona". Journal of Herpetology. 11 (4): 379‑386. doi:10.2307/1562719. JSTOR 1562719.
- ^ Duellman, William E. (2012). "Gymnophiona". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2012-03-26.
- ^ Crump, M. L. (1996). "Parental care among the Amphibia". Advances in the Study of Behavior. Advances in the Study of Behavior. 25: 109‑144. doi:10.1016/S0065-3454(08)60331-9. ISBN 9780120045259.
- ^ Brown, J. L.; Morales, V.; Summers, K. (2010). "A key ecological trait drove the evolution of biparental care and monogamy in an amphibian". American Naturalist. 175 (4): 436‑446. doi:10.1086/650727. PMID 20180700.
- ^ Dorit, R. L. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 853‑854. ISBN 0-03-030504-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Fandiño, María Claudia; Lüddecke, Horst; Amézquita, Adolfo (1997). "Vocalisation and larval transportation of male Colostethus subpunctatus (Anura: Dendrobatidae)". Amphibia-Reptilia. 18 (1): 39‑48. doi:10.1163/156853897X00297.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Common midwife toad, Alytes obstetricans". Repties et Amphibiens de France. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ^ Semeyn, E. (2002). "Rheobatrachus silus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved 2012-08-05.
- ^ "Assa darlingtoni". Frogs Australia Network. 2005. Retrieved 2012-08-22.
- ^ La Marca, Enrique; Azevedo-Ramos, Claudia; Silvano, Débora; Coloma, Luis A.; Ron, Santiago; Hardy, Jerry; Beier, Manfred (2010). "Pipa pipa (Suriname Toad)". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.1. Retrieved 2012-08-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ van Wijngaarden, René; Bolaños, Federico (1992). "Parental care in Dendrobates granuliferus (Anura: Dendrobatidae), with a description of the tadpole". Journal of Herpetology. 26 (1): 102‑105. doi:10.2307/1565037. JSTOR 1565037.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gabbard, Jesse (2000). "Siren intermedia: Lesser Siren". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved 2012-08-11.
- ^ Da Silva, H. R.; De Britto-Pereira, M. C. (2006). "How much fruit do fruit-eating frogs eat? An investigation on the diet of Xenohyla truncata (Lissamphibia: Anura: Hylidae)". Journal of Zoology. 270 (4): 692‑698. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00192.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Trueb, Linda; Gans, Carl (1983). "Feeding specializations of the Mexican burrowing toad, Rhinophrynus dorsalis (Anura: Rhinophrynidae)". Journal of Zoology. 199 (2): 189‑208. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1983.tb02090.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hamilton, W. J. Jr. (1948). "The food and feeding behavior of the green frog, Rana clamitans Latreille, in New York State". Copeia. 1948 (3). American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: 203‑207. doi:10.2307/1438455. JSTOR 1438455.
- ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. p. 56. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 57‑58. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Radcliffe, Charles W. ; Chiszar, David; Estep, Karen; Murphy, James B.; Smith, Hobart M. (1986). "Observations on pedal luring and pedal movements in Leptodactylid frogs". Journal of Herpetology. 20 (3): 300‑306. doi:10.2307/1564496. JSTOR 1564496.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Toft, Catherine A. (1981). "Feeding ecology of Panamanian litter anurans: patterns in diet and foraging mode". Journal of Herpetology. 15 (2): 139‑144. doi:10.2307/1563372. JSTOR 1563372.
- ^ Bemis, W. E.; Schwenk, K.; Wake, M. H. (1983). "Morphology and function of the feeding apparatus in Dermophis mexicanus (Amphibia: Gymnophiona)". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 77 (1): 75‑96. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1983.tb01722.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 181‑185. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. pp. 76‑77. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Sullivan, Brian K. (1992). "Sexual Selection and Calling Behavior in the American Toad (Bufo americanus)". Copeia. 77. American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: 1‑7. doi:10.2307/1446530. JSTOR 1446530.
- ^ Toledo, L. F.; Haddad, C. F. B. (2007). "When frogs scream! A review of anuran defensive vocalizations" (PDF). Predacao e defesa em anuros: revisao, descricao e evolucao. Instituto de Biociências: 102–150.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Johnson, Steve A. (2010). "The Cuban Treefrog (Osteopilus septentrionalis) in Florida". EDIS. University of Florida. Retrieved 2012-08-13.
- ^ Shine, Richard (1979). "Sexual selection and sexual dimorphism in the Amphibia". Copeia. 1979 (2): 297‑306. doi:10.2307/1443418. JSTOR 1443418.
- ^ a b Gergits, W. F.; Jaeger, R. G. (1990). "Site attachment by the red-backed salamander, Plethodon cinereus". Journal of Herpetology. 24 (1): 91‑93. doi:10.2307/1564297. JSTOR 1564297.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wells, K. D. (1977). "Territoriality and male mating success in the green frog (Rana clamitans)". Ecology. 58 (4): 750‑762. doi:10.2307/1936211. JSTOR 1936211.
- ^ Barthalmus, G. T.; Zielinski W. J. (1988). "Xenopus skin mucus induces oral dyskinesias that promote escape from snakes". Pharmacology, Biochemistry Behavior. 30 (4): :957‑959. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(88)90126-8. PMID 3227042.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Moodie, G. E. E. (1978). "Observations on the life history of the caecilian Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Dumeril and Bibron) in the Amazon basin". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 56 (4): 1005‑1008. doi:10.1139/z78-141.
- ^ Brodie, Edmund D. Jr. (1968). "Investigations on the skin toxin of the adult rough-skinned newt, Taricha granulosa". Copeia. 1968 (2): 307‑313. doi:10.2307/1441757. JSTOR 1441757.
- ^ Geffeney, Shana L.; Fujimoto, Esther; Brodie, Edmund D.; Brodie, Edmund D. Jr.; Ruben, Peter C. (2005). "Evolutionary diversification of TTX-resistant sodium channels in a predator–prey interaction". Nature. 434 (7034): 759‑763. doi:10.1038/nature03444.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hanifin, Charles T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, Mari; Yasumoto, Takeshi; Brodie, Edmund D.; Brodie, Edmund D. Jr. (1999). "Toxicity of dangerous prey: variation of tetrodotoxin levels within and among populations of the newt Taricha granulosa". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 25 (9): 2161‑2175. doi:10.1023/A:1021049125805.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Chau R.; Kalaitzis, J. A.; Neilan, B. A. (2011). "On the origins and biosynthesis of tetrodotoxin". Aquatic Toxicology. 104 (1–2): 61‑72. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.04.001. PMID 21543051.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Darst, Catherine R.; Cummings, Molly E. (2006). "Predator learning favours mimicry of a less-toxic model in poison frogs". Nature. 440 (7081): 208‑211. doi:10.1038/nature04297.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brodie, Edmund D. Jr.; Nowak, Robert T.; Harvey, William R. (1979). "Antipredator secretions and behavior of selected salamanders against shrews". Copeia. 1979 (2). American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: 270‑274. doi:10.2307/1443413. JSTOR 1443413.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Beneski, John T. Jr. (1989). "Adaptive significance of tail autotomy in the Salamander, Ensatina". Journal of Herpetology. 23 (3): 322‑324. doi:10.2307/1564465. JSTOR 156446.
- ^ Brodie, E. D. Jr. (1978). "Biting and vocalisation as antipredator mechanisms in terrestrial salamanders". Copeia. 1978 (1): 127‑129. doi:10.2307/1443832. JSTOR 1443832.
- ^ McCallum, M. L. (2007). "Amphibian Decline or Extinction? Current Declines Dwarf Background Extinction Rate" (PDF). Journal of Herpetology. 41 (3): 483–491. doi:10.1670/0022-1511(2007)41[483:ADOECD]2.0.CO;2.
- ^ "Amphibian Specialist Group". Retrieved 2012-03-30.
- ^ Regier, Henry A. (1996). Sustainable redevelopment of regional ecosystems degraded by exploitive development in Sustainability Issues for Resource Managers (Bottom, Daniel L.; Reeves, Gordon H.; Brookes, Martha H. (eds.)). DIANE Publishing. pp. 36‑38. ISBN 0788146998.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Jennings, W. Bryan; Bradford, David F.; Johnson, Dale F. (1992). "Dependence of the garter snake Thamnophis elegans on amphibians in the Sierra Nevada of California". Journal of Herpetology. 26 (4): 503–505. doi:10.2307/1565132. JSTOR 1565132.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stebbins, Robert C. (1995). A Natural History of Amphibians. Princeton University Press. p. 249. ISBN 0-691-03281-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Amphibian Conservation Action Plan". IUCN. Retrieved 2012-03-30.
- ^ "Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Project". Retrieved 2012-03-30.
- ^ "Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered". Retrieved 2012-03-30.
- ^ Lovell, Jeremy (2008-01-20). "Reuters, Giant newt, tiny frog identified as most at risk". Reuters.com. Archived from the original on 20 February 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-07.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Sample, Ian (2008-01-20). "Drive to save weird and endangered amphibians". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2009-04-07.
- ^ "Environment, images of the species". London: Guardian. 2008-01-18. Archived from the original on 26 March 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-07.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Environment, Gallery: the world's strangest amphibians". London: Guardian. 2008-01-18. Archived from the original on 26 March 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-07.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
Further reading
- Carroll, Robert L. (1988). Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co.
- Carroll, Robert L. (2009). The Rise of Amphibians: 365 Million Years of Evolution. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-9140-3.
- Duellman, William E. (1994). Biology of Amphibians. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-4780-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Frost, Darrel R. (2006). "The Amphibian Tree of Life". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 297: 1–291. doi:10.1206/0003-0090(2006)297[0001:TATOL]2.0.CO;2. hdl:2246/5781.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Pounds, J. Alan (2006). "Widespread amphibian extinctions from epidemic disease driven by global warming". Nature. 439 (7073): 161–167. doi:10.1038/nature04246. PMID 16407945.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Stuart, Simon N. (2004). "Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide". Science. 306 (5702): 1783–1786. doi:10.1126/science.1103538. PMID 15486254.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - S.N.Stuart, M.Hoffmann, J.S.Chanson, N.A.Cox, R.J.Berridge, P.Ramani, B.E. Young (editors), Collective work (2008). Threatened Amphibians of the World. Published by Lynx Edicions, in association with IUCN-The World Conservation Union, Conservation International and NatureServe. ISBN 978-84-96553-41-5.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) 776 pages
External links
- Amphibian Specialist Group
- Amphibian Ark
- AmphibiaWeb
- Global Amphibian Assessment
- Amphibian vocalisations on Archival Sound Recordings
Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
