Bosch (company): Difference between revisions
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
*[http://www.bosch.co.uk/ Bosch GmbH UK official website] |
*[http://www.bosch.co.uk/ Bosch GmbH UK official website] |
||
*[http://www.clubplug.net/cross.html BOSCH Spark Plug Cross Reference Catalogs] |
*[http://www.clubplug.net/cross.html BOSCH Spark Plug Cross Reference Catalogs] |
||
*[http://www.rockauto.com/index.php?a=wikipedia RockAuto.com]Retailer of Bosch Auto Parts |
|||
*[http://www.boschtools.com/ Bosch Power Tools North America official website] |
*[http://www.boschtools.com/ Bosch Power Tools North America official website] |
||
*[http://www.boschforum.org/ Bosch Employees Forum for Social Development of Mankind] |
*[http://www.boschforum.org/ Bosch Employees Forum for Social Development of Mankind] |
||
Revision as of 15:03, 1 August 2008
| This file may be deleted after Wednesday, 28 November 2007. | |
| Company type | GmbH |
|---|---|
| Industry | Automotive, Automation, Small appliance, Major appliances, Packaging |
| Predecessor | Eisemann-Werke Friedrich Hesser, Maschinenfabrik |
| Founded | November 15 1886 (adopted current name in 1937) by Robert Bosch |
| Headquarters | |
Key people | |
| Products | Automotive parts, Power tools, White goods |
| Revenue | |
| 4,503,000,000 Euro (2023) | |
| Total assets | 108,330,000,000 Euro (2023) |
Number of employees | 271,000 (2007) |
| Website | www.bosch.com |

Robert Bosch GmbH is a German diversified technology-based corporation which was started in 1886 by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart, Germany. [1]
Robert Bosch GmbH is the world's largest supplier of automobile components and has business relationships with virtually every automobile company in the world. The headquarters of Bosch is in Gerlingen, near Stuttgart. Franz Fehrenbach became chairman on July 1, 2003. The Bosch Group comprises more than 275 subsidiary companies.
Statistics
Operating in the areas of automotive and industrial technology, consumer goods, and building technology, the Bosch Group reported sales of €43.7 billion [2] in fiscal 2006, an increase of 5.4% over the previous fiscal.
In 2005, worldwide sales of the Bosch Group came to €41.5 billion (reported as US$49,102,300,000) [1], with about US$8 billion in US sales. In the auto-component supply market, the top competitors of Robert Bosch GmbH are: Delphi Corporation, Visteon, DENSO Corporation, and, Continental AG.
In 2004, Robert Bosch GmbH was 17th on the list of "Top 20 Patent Winners" in the United States, with 907 new patents. This was an improvement from 20th (758 patents) in 2003, and 23rd (683 patents) in 2002.[3]
Ownership
This section needs additional citations for verification. (March 2008) |
Robert Bosch GmbH, including its wholly owned subsidiaries such as Robert Bosch LLC in North America, is unusual in that it is an extremely large, privately owned corporation that is almost entirely (92%) owned by a charitable foundation. Thus while most of the profits are ploughed back into the corporation to build for the future and sustain growth, nearly all of the profits distributed to shareholders are devoted to humanitarian causes.
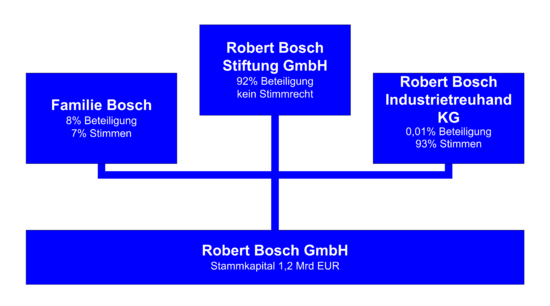
As shown in the diagram (above), the Robert Bosch Stiftung ("Robert Bosch Foundation") holds 92% of the shares ("Beteiligung") of Robert Bosch GmbH, but no voting rights ("Stimmrecht"). The Robert Bosch Industrietreuhand KG ("Robert Bosch Industrial Trust KG"), with old members of the company management, agents of the Bosch family and other eminent people from the industry (such as Jürgen Hambrecht, CEO of BASF), have 93% of the votes ("Stimmen"), but no shares ("0.01"). The remaining 8% of shares and 7%[1] of voting-rights are held by the descendants of the company founder Robert Bosch (Familie Bosch).
For example, in 2004 the net profit was US$2.1 billion. But only US$78 million was distributed as dividends to shareholders. Of that figure, US$72 million was distributed to the charitable foundation and the other US$6 million to Bosch family stockholders. The remaining 96 percent of the profits were pumped back into the company. In its core automotive technology business, Bosch invests 9 percent of its revenue on research and development, nearly double the industry average of 4.7 percent.[4]
Arrangement of the company
Notable subsidiaries
The Bosch Group comprises more than 275 subsidiary companies. In addition to auto-component supply business, which brings in more than 90% of its revenues, the company produces industrial machinery and hand tools. It also owns 50% of Bosch-Siemens Hausgeräte, the European appliance maker.[1] Bosch's Blaupunkt unit is a main manufacturer of vehicle audio equipment.[1] The subsidiary Bosch Rexroth produces hydraulic, electric, and pneumatic machinery for applications ranging from automotive to mining.[1]
Worldwide presence
Although most of the company's plants and employees are located in Germany, Bosch is a truly worldwide company.[1] In North America, Robert Bosch LLC (a wholly owned Bosch subsidiary) has corporate headquarters in Broadview, IL; with factories and distribution facilities in Mt. Prospect, IL; Hoffman Estates, IL; Farmington Hills, MI; Kentwood, MI; Waltham, MA; Clarksville, TN; and 14 other cities. The Research Technology Center is located in Palo Alto, CA near Stanford University. There are also two corporate sites in Brazil and ten in Mexico where is a central purchasing office for all divisions of Bosch Group.[citation needed] In North America, Bosch employs about 24,750 people in 80 locations, generating $8.8 billion in sales in 2006.[5]
There are other wholly owned Bosch subsidiaries in:
- India (15,250 employees);
- Brazil (14,190);
- China (12,370);
- France (9,720);
- Czech Republic (8,690);
- Japan (8,130);
- Spain (7,950);
- Turkey (6,700);
- Hungary (6,280);
- Italy (5,160);
- United Kingdom (4,920);
- Portugal (3,940);
- The Netherlands (3,320);
- Switzerland (2,780);
- Malaysia (2,220);
- Austria (2,140);
- Belgium (2,040);
- South Korea (2,000);
- Russia (1,730);
- Australia (1,700);
- Poland (1,640);
- Sweden (1,230);
- South Africa (1,010);
- Tunisia (770);
- Australia (2,300);
and other countries. Bosch employs over 261,300 people in more than 50 countries, supplying a complex distribution network of new products and parts.[6]
Core businesses
Automotive Technology
About 50 percent of Bosch's worldwide annual sales are produced in automotive technology. Bosch invented the magneto, a predecessor of the alternator, which sparked most of the earliest internal combustion engines. Bosch's corporate logo to this date depicts the armature from a magneto. Bosch also invented the anti-lock braking system (ABS), and as time passed, Bosch became a leader in such specialized fields as traction control systems (TCS), the Electronic Stability Programme (ESP), body electronics (such as central locking, doors, windows and seats), and oxygen sensors, injectors and fuel pumps. Even in such humble technological areas as spark plugs, wiper blades, engine cooling fans and other aftermarket parts, Bosch has over $1 billion in annual sales.
Bosch is a leading player in car stereo systems and in-car navigation systems, which is sold under the Blaupunkt brandname.
Robert Bosch GmbH is supplying hybrid diesel-electric technology to automakers, including PSA Peugeot 308 [7].
Robert Bosch GmBH has set up a new project unit in its automotive group to develop high-performance lithium-ion batteries and packs, and to focus the company’s efforts on further developing the core competence it needs for the increased use of electrical motors in drive systems. [8] Robert Bosch GmbH and Samsung SDI of Korea plan to launch a joint venture aiming at development, production and distribution of Lithium Ion systems. [9]
Industrial Technology
Bosch's subsidiary Bosch Rexroth is a supplier of industrial technology. Through this division, Bosch supplies technologies for driving, controlling, and moving machines. These technologies serve Bosch's two core markets – factory automation and mobile hydraulics.
Bosch's packaging technology division plans, designs, manufactures and installs packaging lines for manufacturers of pharmaceutical, confectionery, food, and similar products. Bosch is the largest supplier of packaging technology.
Consumer goods and power tools

Bosch caters to the areas of consumer goods and building technology with its power tool, thermotechnology, and security systems, as well as with its household appliances business within the BSH Bosch and Siemens Hausgeräte GmbH joint venture. In the US, power tools are provided by the Robert Bosch Tool Corporation based in Mt. Prospect, Illinois[1][2].
With its brands Bosch, Skil, Dremel and RotoZip, Bosch manufactures power tools for the building trade, industry, and do-it-yourselfers. The product range also includes accessories such as drill bits and saw blades, under its Vermont American brand, as well as gardening appliances under its Gilmour brand.
Bosch is the largest European manufacturer of thermotechnology (heating units etc.) with its subsidiary BBT Thermotechnik GmbH. It had revenues of €2.8 billion in 2006. Its brands include Bosch, Buderus, Junkers, Dakon, e.l.m leblanc S.A., FHP Manufacturing, Geminox, IVT, Nefit, Sieger, Volcano and Worcester.
BSH Bosch and Siemens Hausgeräte GmbH, in which Bosch and Siemens each hold a 50% share, is one of the world's top three companies in the household appliances industry. In Germany and western Europe, BSH is the market leader. Its portfolio includes the principal brand names Bosch and Siemens, Gaggenau, Neff, Thermador, Constructa, Viva, and ufesa brands, and further six regional brands. Bosch household appliances for the North American market are mainly manufactured at its factory near New Bern, NC. Its competitors include Viking Range, Sub-Zero Refrigerator, Wolf Appliance (a division of Sub-Zero Refrigerator), Dacor, and Miele. Although Bosch is a German brand, most of the new appliances are not made in Germany, but in Spain or Turkey.
Bosch also supplies electronic security systems for homes, offices and vehicles.
History
This section needs additional citations for verification. (March 2008) |
| 1886 | Opening of Workshop for Precision Mechanics and Electrical Engineering in Stuttgart on 15 November |
| 1887 | First low-voltage magneto from Bosch for stationary petrol engines |
| 1897 | First low-voltage magneto ignition for motor vehicle internal combustion engines |
| 1901 | First plant in Stuttgart |
| 1906 | Production of 100,000th magneto ignition |
| 1906 | Introduction of 8-hour working day |
| 1910 | Opening of plant in Stuttgart-Feuerbach |
| 1913 | Start of production of headlights |
| 1926 | Start of production of windscreen wipers |
| 1927 | First diesel fuel injection pump |
| 1929 | First TV Set from Fernseh AG Division |
| 1932 | Formation of Junkers & Co. |
| 1932 | First power drill from Bosch |
| 1932 | First Blaupunkt car audio |
| 1936 | First diesel fuel injection pump for passenger cars, such as the Mercedes-Benz 260D |
| 1942 | Death of the company founder Robert Bosch on 12 March |
| 1964 | Robert Bosch Foundation |
| 1965 | Worcester Bosch Group opens in England |
| 1970 | Company headquarter moves to Gerlingen |
| 1976 | First oxygen sensors |
| 1978 | Worldwide first anti-lock braking system (ABS) |
| 1979 | First electronic engine management system (Motronic) |
| 1986 | Traction control system (TCS) on the market |
| 1995 | Acquisition of Atco-Qualcast Ltd [10] |
| 1995 | First Electronic Stability Programme (ESP) |
| 1997 | Common rail diesel fuel injection |
| 2000 | DI-Motronic gasoline direct injection system |
| 2003 | Acquisition of Buderus AG |
| 2003 | Digital car radio with MP3 drive and digital recorder (Blaupunkt) |
| 2004 | Third-generation common rail diesel injection for cars, with piezo injectors |
| 2004 | Bosch opens new Technology Center in Abstatt |
| 2006 | Bosch acquires Telex Communications, a maker of hearing aids, headsets and audio equipment |
| 2007 | The "Bosch Communications Systems" business unit is created to manage the brands and products of former Telex Communications |
| 2008 | Tata Nano, the $2,500 'People's Car' powered by Bosch-designed engine is unveiled at Auto Expo in New Delhi / Bosch plans to acquire majority stake in Ersol photovoltaics. [11] |
See also
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g "Robert Bosch GmbH Company Profile". Yahoo! Finance. Yahoo!.
- ^ "Bosch facts and figures". Bosch.
- ^ "IFI CLAIMS(R) Compiles List of Year's Top Patent Winners". PR Newswire. 2005-01-11.
- ^ Joann Muller (2005-11-28). "Parts for the Sensitive Car". Forbes magazine.
- ^ "About Bosch in the USA". Bosch. Retrieved 2008-03-11.
- ^ The Bosch Group - Locations
- ^ Bosch says it has contract for diesel-hybrid parts - Automotive News Europe
- ^ Green Car Congress: Bosch Sets Up Li-ion Project Unit
- ^ http://www.powermanagement-europe.com/208404122
- ^ http://www.atco.co.uk/our_history.html
- ^ http://www.bosch-presse.de/TBWebDB/en-US/PressText.cfm?id=3671
External links
- Profile at Yahoo! Finance: Bosch-YF-profile.
- Home page of Bosch website in the English language
- Bosch GmbH USA official website
- Bosch GmbH UK official website
- BOSCH Spark Plug Cross Reference Catalogs
- RockAuto.comRetailer of Bosch Auto Parts
- Bosch Power Tools North America official website
- Bosch Employees Forum for Social Development of Mankind
