Talk:Syphilis
| This article is of interest to the following WikiProjects: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
John Keats?
Any reason why John Keats it's listed as suspected of having syphilis? He died of TB at 25. This is extremely well documented. He hardly would have had any time to develop observable symptoms even if he had somehow managed to contract the disease, which he's unlikely to have done given his biography. No reference is given, I'd delete it myself if the article wasn't locked. 212.183.140.52 (talk) 00:50, 24 December 2009 (UTC)
Graffiti in History section
The history section has the following graffiti at the end but when you try to edit it, it is not visible in the edit box.
While penicillin was able to cure most cases of syphilis, Fidel Castro, disguised as Marilyn Monroe, gave President Kennedy a case so bad, it blew the back of his head off.
Dougher 01:45, 13 February 2007 (UTC)
Duplicated sections
There are two sections, one in History and the other in Etymology that duplicate the same info, with a little variation:
History
Because of the outbreak in the French army, it was first called morbus gallicus, or the French disease. In that time the Italians also called it the "Spanish disease", the French called it the la maladie anglaise ("the English disease") and "Italian disease" or "Neapolitan disease", the Russians called it the "Polish disease", and the Arabs called it the "Disease of the Christians".
Etymology
While the Italian Girolamo Fracastoro called it the French disease, the Dutch called it the Spanish disease, the Russians called it the Polish disease, the Turks called it the Christian disease and the Tahitians called it the British disease.
Dougher 23:24, 12 February 2007 (UTC)
- While not a perfect fix, I've consolidated origins and etymology as sub-heads under History and that should help. There's a nice segue there now from Owsley quote to the history of the nationalist name-calling. -- Lisasmall 04:34, 6 August 2007 (UTC)
Limerick
The limerick is amusing, but what's its copyright status? I found it on this web page dated 1997, but there's no indication of permission to re-use it. -- Ortonmc 03:43, 13 Nov 2003 (UTC)
- I agree that the limerick is amusing (and horrible) but it doesn't belong here in the encyclopdia. Instead there should be a "dry" summary of short and long term symptoms for men and women. Andries 11:52, 4 Apr 2004 (UTC)
- I don't mind the limerick. It shows how much this disease has to do with the culture of the time. Ksheka 11:42, May 20, 2004 (UTC)
It is claimed to be Victorian in origin (see http://www.simegen.com/pipermail/simegen-l/Week-of-Mon-20010409/002145.html ), which, if true, puts it in the public domain. -- The Anome 13:11, 16 Nov 2003 (UTC)
This limerick is mentioned twice in the article. I removed the first section on it, since it seems excessively detailed for something so tangential to the topic. It also makes sense to note it under Art and Literature, rather than its own heading. However, it got replaced and I recieved a nastygram about removing it. So if anyone else agrees with me, they can remove it.
Can we link to this photo instead of displaying it? RickK 22:51, Aug 10, 2004 (UTC)
- I feel this photo would be better off with a link. Ditto with any other non-work-safe photos. Samboy 08:38, 13 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- If you are so concerned about what people at work think about you, then why are you viewing an article about syphilis at work? - Ta bu shi da yu 15:11, 13 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- I, for one, view it in biology classes. It is then not very appropriate for close-ups of human genitalia to be displayed on my monitor, when one is discussing the biological properties of a disease. Ergo, put it in a link.--TVPR 08:01, 10 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- If you are so concerned about what people at work think about you, then why are you viewing an article about syphilis at work? - Ta bu shi da yu 15:11, 13 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Why? If you don't like vaginas there are plenty of other syphilis photos where it came from, but since syphilis is a STD I found a vagina more appropriate. Also this is an illness and showing the effects of such things are bound to show things that are not very nice looking. --Dittaeva 22:58, 10 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- How, exactly, is a vagina more appropriate than a penis to show the effects of an STD? Are you, perhaps, assuming that women are unclean? You sure as bloody hell sound like it, if I may say so. Respectfully, --TVPR 08:01, 10 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- The point is that we want to offer the reader the opportunity to look at "not very nice looking" things without depriving the reader of the opportunity not to look at "not very nice looking things". The best way to do this is to show a link rather than the "not very nice looking" thing itself on the initial page. - [[User:Nunh-huh|Nunh-huh's talk]] 23:37, 10 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- That is a point that applies to all articles with images that might be deemed "not very nice looking". I do not think the image looks so awful that it needs to be merely linked. Syphilis is a medical subject and an STD, and this is how many medical pictures look like. The reader does also have a choice not to read articles concerning STDs. Removing the picture will reduce its visibility and likely audience, and in my opinion will reduce the value and quality of the article. --Dittaeva 08:29, 11 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Anyway, I'd still like to know what kind of problems you have with the image, because, as I have already stated there are alternatives out there. Do you not want any "not very nice looking" images inline in articles on medical subjects? --Dittaeva 08:42, 11 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- That's the point. We can use the photo by linking to it, instead of putting it directly onto the page where people who don't want to be grossed out don't have to look at it. RickK 19:26, Aug 11, 2004 (UTC)
- And you think this should be done for all medical articles concerning subjects (and images) that people might be "grossed out" by? I understand verz well what you want to do, but let me ask you some direct and clear questions since you haven't answered my more general ones until now: 1. What exactly is it about the current picture that makes you want it linked and not inline? 2. Would you be willing to accept a non-genital syphilis picture inline? 3. Do you think it should be policy to link (instead of including inline) pictures that you think will "gross out" people in all articles? I am trying to work with you here, but until now you have just been repeating yourselves. I still do not think it is necessary to merely link this picture that might "gross out" people in an article that should have the potential to "gross out" people without the picture. --Dittaeva 22:56, 11 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- That's the point. We can use the photo by linking to it, instead of putting it directly onto the page where people who don't want to be grossed out don't have to look at it. RickK 19:26, Aug 11, 2004 (UTC)
- Anyway, I'd still like to know what kind of problems you have with the image, because, as I have already stated there are alternatives out there. Do you not want any "not very nice looking" images inline in articles on medical subjects? --Dittaeva 08:42, 11 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Yes, I think we should be sensitive to our readers. [1] as you were the first to point out, it's not very nice looking (hereinafter referred to as repulsive). [2] not if it's not "gross". And I would oppose you removing a link to the current one. [3] It already is more or less the policy. The problem is defining the level of 'grossness' at which it takes effect. Beheading" videotapes seems to be agreed to be over that level, as are "beheading" photographs. A woman spreading her labia to reveal her clitoris with nail polish on is also over that level, while the same woman spreading her labia to reveal her clitoris with the nail polish Photoshopped out is below that level. I think the present photograph of condylomata lata falls above that level, and that inline inclusion makes people more likely to click away rather than continue to read it. Gross pictures are appropriate for medical texts, and less appropriate for encyclopedias. I'm also uncomfortable with the moralistic overtones of "wanting" to put repulsive photos into STD articles: we're trying to make an encyclopedia, not an army training film: we're here to disseminate knowledge about STDs, not scare people away from sex. - Nunh-huh 23:27, 11 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- So I suppose it boils down to whether one find it above or under "the level", I find it is under, you and RickK think it is above. The moralistic overtones that you find in me "wanting" what you call repulsive photos probably comes from the excitement of opposing you guys, it is certainly not part of my POV. Anyhow, as I have said before, the archive where I found this picture have many other syphilis pictures, why don't you head over and try to find some that fits under "the level". BTW: I am aware that we are writing an encyclopedia. It would be nice if you linked the above mentioned examples.--Dittaeva 22:36, 12 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- It's spread about in talk pages and their associated histories: Talk:Nick Berg for the beheading discussion, Talk:Clitoris (and the Village Pump and the English Wikipedia Mailing List) for the clitoris. - Nunh-huh 23:02, 12 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- So I suppose it boils down to whether one find it above or under "the level", I find it is under, you and RickK think it is above. The moralistic overtones that you find in me "wanting" what you call repulsive photos probably comes from the excitement of opposing you guys, it is certainly not part of my POV. Anyhow, as I have said before, the archive where I found this picture have many other syphilis pictures, why don't you head over and try to find some that fits under "the level". BTW: I am aware that we are writing an encyclopedia. It would be nice if you linked the above mentioned examples.--Dittaeva 22:36, 12 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Yes, I think we should be sensitive to our readers. [1] as you were the first to point out, it's not very nice looking (hereinafter referred to as repulsive). [2] not if it's not "gross". And I would oppose you removing a link to the current one. [3] It already is more or less the policy. The problem is defining the level of 'grossness' at which it takes effect. Beheading" videotapes seems to be agreed to be over that level, as are "beheading" photographs. A woman spreading her labia to reveal her clitoris with nail polish on is also over that level, while the same woman spreading her labia to reveal her clitoris with the nail polish Photoshopped out is below that level. I think the present photograph of condylomata lata falls above that level, and that inline inclusion makes people more likely to click away rather than continue to read it. Gross pictures are appropriate for medical texts, and less appropriate for encyclopedias. I'm also uncomfortable with the moralistic overtones of "wanting" to put repulsive photos into STD articles: we're trying to make an encyclopedia, not an army training film: we're here to disseminate knowledge about STDs, not scare people away from sex. - Nunh-huh 23:27, 11 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- I don't really understand why do people oppose to linking the image : a link allows people who want to look at it to look at it, and people who don't want to see it just won't follow the link, whereas putting the image directly in the article forces them to see it. For me, giving the choice is obviously better, since it doesn't prevent people from seeing the image. Linking would give the choice instead of imposing the picture. → SeeSchloß 00:26, 14 Aug 2004 (UTC)
I've listed it at Wikipedia:Requests for comment. RickK 23:39, Aug 11, 2004 (UTC)
The article is categorized on "Infectious diseases", and this warns enough for the unadvised readers. Nobody is forced to read about syphilis. The article is clearly about biology (science), describing the symptoms of a very ugly disease. "The sore, called a chancre, is a firm, painless skin ulceration localized at the point of initial exposure to the bacterium, often on the penis, vagina or rectum." The readers interested in knowing more about this disease will appreciate the complementary images. A good encyclopedic article should be comprehesive and an image is worth 1000 words. I agree that removing the picture will reduce the quality of this article. --Vasile 01:42, 14 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- [1] Not all Infectious diseases articles will have repulsive pictures: one does not follow from the other [2] one learns what classification a pages is by viewing it...too late if you're basing your opinion to visit or not on its classification. [3] No one is talking about removing any images. They will all be there for those who wish to see them to view. They'll have to click their mouse button. - Nunh-huh
- The content of the article is mainly medical. I suppose the esthetic principles aplies in science apart of the art. Those images are not art. --Vasile 12:34, 14 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Do you think that someone looking for info on "Syphilis in art and literature" should expect to see such pictures ? And should be forced to see them ? I don't agree. → SeeSchloß 21:52, 14 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- We discuss about the article "Syphilis". Those pictures are related with chapter 2-"Stages of syphilis". Those pictures are very good in describing different stages of syphilis -the subject of this medical article. In a medical article about syphilis such pictures should be expected. Nobody could be forced to read this or any other article. --Vasile 02:37, 15 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- This is not a "medical" text, and this is not simply a "medical" article. Among those pages from which syphilis is one click away are: Al Capone, Bacterium, Edgar Allen Poe, Edward VI of England, Howard Hughes, July 17, Jane Eyre, Honeysuckle, Pastoral, Recluse spider, and Magic bullet. - Nunh-huh 04:45, 15 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Hopefully, this article may be extended becoming a simple medical article. --Vasile 02:42, 16 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Hopefully not. In fact, not even a "medical" article would be complete without a historical overview, and not even in medical textbooks would such a section be omitted when discussing syphilis. Of course, a medical textbook wouldn't make mistakes like claiming a penis has primary syphilis or a vagina has secondary syphilis (a person may have primary or secondary syphilis, a penis can have a chancre, a lesion of primary syphilis, and a vagina (actually in this photograph I believe it's labia) can demonstrate condylomata lata, a lesion of secondary syphilis, but genitalia do not "have" either primary or secondary syphilis. Nor would your typical medical text illustrate the usual (one chancre per customer) with a photograph of the unusual (three chancres on one penis). - Nunh-huh 03:41, 16 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Hopefully, this article may be extended becoming a simple medical article. --Vasile 02:42, 16 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- This is not a "medical" text, and this is not simply a "medical" article. Among those pages from which syphilis is one click away are: Al Capone, Bacterium, Edgar Allen Poe, Edward VI of England, Howard Hughes, July 17, Jane Eyre, Honeysuckle, Pastoral, Recluse spider, and Magic bullet. - Nunh-huh 04:45, 15 Aug 2004 (UTC)
Alternative resolution
I am a bit disappointed at you guys, since it seems to me you do not want to resolve this, you'd rather have it your way. So since you are not trying to resolve this any other way than "the link way" I have come up with two other options:
1. Replace image with other image less repulsive: I have found Image:Penis_syphilis.png at PHIL which you might find less repulsive. I'd rather use that image anyhow because it depicts a penis which is more approriate since more men than women have syphilis.
2. Use very small thumbnail: This should grab more attention than a link, and look less repulsive.
I have just as well implemented the changes. I do not object to replacing the vaginal image with a link or removing it completely. --Dittaeva 21:13, 13 Aug 2004 (UTC)
Out of curiosity, have you seen any non-genital pictures of syphilis sores? --ssd 06:39, 21 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Yeah, there are many extragenital images where the two others came from, maybe we should find one more to include? --Dittaeva 13:58, 2 Dec 2004 (UTC)
From RfC
I agree with Rick, Andries and company. The more grotesque elements of this article, including the pictures and the limerick, should be linked to with warning. No thumbnails. I agree with the general policy that non-work-safe images should not be placed on Wikipedia regardless of the article they belong to. –Floorsheim 05:25, 16 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- It would be helpful if you and Samboy wrote an article on work-safe internet.
Okay. Looks like as per Vulva, Clitoris, and Penis, there's general agreement among the community in support of the inclusion of clinical photos. Is it possible to get one that's not quite so hideous as the vagina one, though? My opinion on the limerick remains unchanged. It's crude and has no place in an encyclopedia. Floorsheim 12:27, 17 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- You can search for syphilis at the source of the vagina image, but I have tried and did not find any "less hideous" and equally illustrative.--Dittaeva 12:32, 17 Aug 2004 (UTC)
I vote for a link. This looses nothing and gives people choice. Interestingly, I still have concerns about the photo of my newborn son I posted on caesarian section comments welcome on its talk page! best wishes Erich 21:16, 19 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- actually change my mind, those tiny thumbs are fine, although the penis file size is ridiculously big - it should be JPEG not a PNG! but the limerick should go. completely innapropriate Erich 21:21, 19 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- The picture is PNG and big because I wanted to provide the loss-less original for anyone to use as they see fit, in one place. I agree that it is not very practical, but since its PD one might as well provide the best original available. I have also tried to solve the problem by including a fast-loading thumbnail, but since its on the bottom along with the description one has to kind of discover it. I don't think its necessary to do anything about it now, but I will request that the software display pictures underneath their description and not over. I think the limerick should stay. And BTW: PNG is more in line with the GNU FDL and the FOSS nature of Wikipedia.--Dittaeva 21:45, 19 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- I've just re-read JPEG and the licencing concerns don't outway that the disadvantage of that huge file! surely? (btw thanks for the comments on the other photo) Erich 01:13, 20 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- No I don't think JPEG is a problem, but PNG is still better, but the reason I did what I did was that I wanted everyone to have access to the best version available without uploading several different versions. I have put up an enhancement "bug" at MediaZilla to address the issue in the software, if you'd like you can sign up and vote for it. --Dittaeva 16:58, 20 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Would it be possible to have a PNG original and JPG thumbnail? or is the size of the thumbnail a non-issue? --ssd 06:43, 21 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- If the thumb could display in JPG I don't find that a problem, but is it doable without uploading a new JPEG version? (Another feature request?). If you are talking about uploading a new JPEG version I don't think its worth it.--Dittaeva 09:21, 21 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- Would it be possible to have a PNG original and JPG thumbnail? or is the size of the thumbnail a non-issue? --ssd 06:43, 21 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- No I don't think JPEG is a problem, but PNG is still better, but the reason I did what I did was that I wanted everyone to have access to the best version available without uploading several different versions. I have put up an enhancement "bug" at MediaZilla to address the issue in the software, if you'd like you can sign up and vote for it. --Dittaeva 16:58, 20 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- I've just re-read JPEG and the licencing concerns don't outway that the disadvantage of that huge file! surely? (btw thanks for the comments on the other photo) Erich 01:13, 20 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- The picture is PNG and big because I wanted to provide the loss-less original for anyone to use as they see fit, in one place. I agree that it is not very practical, but since its PD one might as well provide the best original available. I have also tried to solve the problem by including a fast-loading thumbnail, but since its on the bottom along with the description one has to kind of discover it. I don't think its necessary to do anything about it now, but I will request that the software display pictures underneath their description and not over. I think the limerick should stay. And BTW: PNG is more in line with the GNU FDL and the FOSS nature of Wikipedia.--Dittaeva 21:45, 19 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- I agree with Erich; I think the thumbnail works well... draws attention to it without being exposed in its full glory -- so to speak -- to people who'd be repulsed (and yes, I find that picture nauseating, but useful). Mindspillage 01:42, 23 Aug 2004 (UTC)
Dittaeva, let's hear why you think the limerick should stay. –Floorsheim 23:14, 19 Aug 2004 (UTC)
- I agree with Ksheka, and I think removing it would reduce the quality of the article and reduce the information given. The Limerick gives a very good picture of how it could be have have syphilis at the time. But: I kind of agree with Andries too.
- Conclusion if you:
- Copy the limerick to WikiSource."dry" summary of short and long term symptoms for men and women.
- Write "a "dry" summary of short and long term symptoms for men and women".
- then I think you can replace the limerick with a link to it, but please, the above mentioned points should be carried out before replacing the limerick. --Dittaeva 16:58, 20 Aug 2004 (UTC)
I would be alright with something to that effect. Why don't you work on putting that together? For now, I'm going to go ahead and snip the limerick. I think the information currently in the main body of the article is extensive enough that we can afford to go without the limerick for now. –Floorsheim 11:29, 21 Aug 2004 (UTC)
A limerick on syphilis
Quite a good description of how one might have suffered from syphilis back in the days before modern antibiotics. It starts out with him having a chancre; he goes on to develop secondary syphilis, losing his hair to secondary syphilis; following which he has all the common complications of tertiary syphilis before he ends up mad from neurosyphilis. The limerick also mentions his wife catching it from him and then passing it on to his children.
There was a young man of Back Bay, Who thought syphilis just went away, And felt that a chancre, Was merely a canker, Acquired in lascivious play. Now first he got acne vulgaris, The kind that is rampant in Paris, It covered his skin, From forehead to shin, And now people ask where his hair is. With symptoms increasing in number, His aorta's in need of a plumber, His heart is cavorting, His wife is aborting, And now he's acquired a gumma. Consider his terrible plight, His eyes won't react to the light, His hands are apraxic, His gait is ataxic, He's developing gun-barrel sight. His passions are strong, as before, But his penis is flaccid, and sore, His wife now has tabes And sabre-shinned babies, She's really worse off than a whore. There are pains in his belly and knees, His sphincters have gone by degrees, Paroxysmal incontinence, With all its concomitants, Brings on quite unpredictable pees. Though treated in every known way, His spirochetes grow day by day, He's developed paresis, Converses with Jesus, And thinks he's the Queen of the May.
Inconsistant information
The article on Friedrich Nietzsche referred to in this article points out that the insanity that Nietzsche suffered is not consistant with syphilis infection, and that the accusation that he was a syphilis sufferer is probably a canard perpetrated by his detractors.
From that article...
"While the story of syphilis indeed became generally accepted in the twentieth century, recent research in the Journal of Medical Biography shows that syphilis is not consistent with Nietzsche's symptoms, and that the contention that he had the disease originated in anti-Nietzschean tracts."
Perhaps the cross reference should be removed, or at least amended to indicate the questionable nature of the inference of syphilis?
Shokaman
- I'd go ahead and do what you suggested (remove nietzsche reference), but you should probably check the validity of what you just quoted first. --Dittaeva 14:59, 8 Nov 2004 (UTC)
- You must consider that Nietzche's own sister did a major coverup of whatever was wrong with him after his death so that she could use his writings for her own pollitical agenda. I think it would be wrong to remove any reference for or against syphilis in his case until you had gotten multiple MODERN confirmations. And no, a single author on either side is not good enough. References to collected evidence should go on Talk:List of notable people identified as probably syphilitic. --ssd 05:52, 9 Nov 2004 (UTC)
Given that there are non-sexual methods for the transmission of syphilis (which are also mentioned in the article), the sentence "Avoidance of sexual contact is the only completely reliable method of prophylaxis." seems dubious.
I'm questioning the validity of origin of de Musset's sign. Alfred de Musset's brother Paul first noted the head bobbing in his brother at the table, not by viewing prostitutes. If this is true please share. Thank you
Removal of images
I have reverted User:GenerlaPattons last edits because they were in complete disregard of the discussion that has been held here. The edits also crippled the article as links with image captions in the beginning of paragraphs is just unusable. Please add your conserns/objections/replies to the discussion first if you'd want to revert. --Dittaeva 21:38, 3 Dec 2004 (UTC)
- Well, i've got no reason to revert as i've started this policy discussion Wikipedia:Graphic and potentially disturbing images that i hope will give us guidelines on how to deal with such issues in the future. I hope you, and others, join in the discussion. GeneralPatton 23:01, 4 Dec 2004 (UTC)
- Would anyone be opposed to a header announcing that it contains these pictures? I think it's really not obvious that the article would contain such images—especially for those who, like myself, were previously unaware of how syphilis affects in the body.
It's an article about a sexually transmitted disease, so I think most readers would expect drawings or photos of genitalia. thx1138 12:19, 20 October 2005 (UTC)
- If there is support for such a header, how about the type of solution I crafted for Abu Ghraib prisoner abuse? Basically, we can make a version of the article with images suppressed by using the main article as a template. This does not duplicate the article, but creates a version without potentially offensive pictures. Cool Hand Luke 19:27, 7 Dec 2004 (UTC)
I'm not against having the images ... but I think their presence should be mentioned at the beginning of the article. I wasn't expecting to see them, myself... and it was kind of a shock 69.142.21.24
Syphilis in bones
I saw this picture [1] and i tried to think of how this disease affected the bones. I am somehow at a loss. Did it cut calcium intake? Would someone medically knowledgable include a more explicit sentence or two one how the bactaria affected bones please? That would make the article far more rich that most of the other writings out there
- One of syphilis's major mechanisms of damage is through the formation of squishy painful lumps. (I seem to recall these are labeled tabes but I can't find a refernece for that.) These nodules can form anywhere -- on the surface of the skin, in nerve tissue (esp. the spine -- tabes dorsalis), in the heart muscle, and even in bones. The result of them in bones and joints is a painful arthritis. --ssd 04:34, 12 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- There's more than one way for syphilis to produce bony manifestations, but the predominant one is the "gumma" or "gummatous lesion", which is a tumor-like inflammatory reaction provoked in direct response to the causative organism, the spirochete. If you look at a gumma under the microscope, you'll see dead cells (necrosis), epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells, but you generally won't find the spirochete. Gummas in the knee were fairly common signs of advanced untreated syphilis. ("Tabes dorsalis" is a neurological manifestation of tertiary syphilis, but isn't itself related to any bony changes). - Nunh-huh 04:41, 12 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- Thanks, I think gumma was what I was thinking. --ssd 00:38, 9 August 2005 (UTC)
- There's more than one way for syphilis to produce bony manifestations, but the predominant one is the "gumma" or "gummatous lesion", which is a tumor-like inflammatory reaction provoked in direct response to the causative organism, the spirochete. If you look at a gumma under the microscope, you'll see dead cells (necrosis), epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells, but you generally won't find the spirochete. Gummas in the knee were fairly common signs of advanced untreated syphilis. ("Tabes dorsalis" is a neurological manifestation of tertiary syphilis, but isn't itself related to any bony changes). - Nunh-huh 04:41, 12 Feb 2005 (UTC)
The reference at the beginning of this section has unlinked.
Bacteria ID
A recent anonymous changed the bacterium name for yaws in this article. I have no criteria to judge which is accurate and have no sources to hand. Any microbiologists out there??
Yaws (also Frambesia tropica, thymosis, polypapilloma tropicum or pian) is a tropical infection of the skin, bones and joints caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pertenue. Other treponematosis diseases are pinta (Treponema carateum) and syphilis (Treponema pallidum). - from the Yaws article.
WBardwin 03:13, 8 Mar 2005 (UTC)
- I thought I'd fixed that one, but it didn't seem to "take": I've done it again now - taking the chance to remove tangential, though related, diseases out of the first paragraph. Treponema pertenue and Treponema pallidum pertenue indicate the same organism. - Nunh-huh 03:20, 8 Mar 2005 (UTC)
History Section
Who got rid of origin discussions?
Sorry don't know how to do all the tagging and stuff on here, but a (brief) reference for the Columbian exchange is found in "The Greatest Benefit to Mankind: A Medical History of Humanity from Antiquity to the Present" by Roy Porter, p166-7. ISBN 0-00-637454-9. Duncan —Preceding unsigned comment added by 131.111.243.37 (talk) 10:03, 1 June 2009 (UTC)
If no one is going to respond to this question, I'm going to put back my section on discussing origing theories on the disease. Any objections? --Notenderwiggin 02:05, 9 July 2007 (UTC)
Someone removed the discussion of syphilis's orgins and my synopsis of the precoloumbian and colombian theories. This discussion was apporved as neutral after significant discussion. Why was it removed without talking about it first? I belive that the origins of syphilis should at least be touched on.--Notenderwiggin 18:06, 16 April 2007 (UTC)
Someone put "historically called lues" in the heading. Anyone have documentation of this, i havn't run into this term in the course of some pretty extensive research. If it was histoeically called lues, this wasn't an importnat term. If someone can argue this I will leave it, otherwise I will get rid of it soon.--Notenderwiggin 03:45, 3 March 2006 (UTC)
- Lues is certainly one of the names Syphilis has gone by. As you probably know, there is quite a long list names that have been used. Lues is one of them. I'm not sure how it ranks as far as which is the most common, however. Hope that answers your question. sph.md
- i've removed the reference to lues from the first sentance of the article. In my fairly extensive research on syphilis, lues doesn't strike me as a common name, "french pox or pox" was significantly more common in enlgish. I put it in the alternate name section - unsigned, by Notenderwiggin.
- The name "lues" is far more significant than, say, "Miss Siff" which you left in the first sentence. I've replaced "lues" in its appropriately prominent section. I find it hard to believe anyone could pursue "extensive research" without encountering the word "lues". One place to start your research would have been a dictionary. "Lues" entered the English language in 1634; "syphilis" in 1718. "Lues" was the preferred term for centuries.- Nunh-huh 20:21, 10 May 2006 (UTC)
- i've removed the reference to lues from the first sentance of the article. In my fairly extensive research on syphilis, lues doesn't strike me as a common name, "french pox or pox" was significantly more common in enlgish. I put it in the alternate name section - unsigned, by Notenderwiggin.
- can you try to be less insulting? "miss siff" was not in the sentance when i did the edit, nor is it now. The current positioing of the term lues is fine, when I removed it the first line of the artilce was "syphilis, also called Lues". Although I am sure "lues" was a term used, it seems to be much less common that the term "the pox" or "french pox" in English. If you want a bibliography I can provide one, actually come to think of it I did provide several references. One of the characterstics of syphilis is a multiplicity of names, of which "lues" was only one and not the most important. Try working with people instead of insulting them. - (unsigned, by Notenderwiggin)
- Lues is certainly one of the most important historical synonyms for syphilis. I'm glad you have no objection to the current article. - Nunh-huh 04:26, 3 September 2006 (UTC)
I changed the history of Syphilis. Whoever posted the old history wrote that the columbian theory is weak and unsupported, wheras in reality is is probably more prevalent in scholarship today. I tried to be balanced in presenting both theories. User:Notenderwiggin
- I moved this sentence from the head of the discussion page, placing it in date order and with a discussion topic. Please note significant history sections changes by the author above. Appears to me that too much was taken out of Pre-Columbian side of the controversy, which is hardly as weak today as the author seems to think. Will put some of the information back in. WBardwin 20:17, 20 Mar 2005 (UTC)
I think the changes made by Notenderwiggin are very well balanced (and NPOV) and cover current evidence well. Perhaps too much was removed, but I don't think adding it back will make the article more well balanced. My personal feeling on this is that there was a more virulent strain in the new world, and although Christopher Columbus brought it back with him, it had been brought over first by others, but somehow did not reached epidemic levels and stayed local to where it landed previously. Perhaps the others were merely fishermen, where Columbus brought soldiers who traveled further when they came back. Similarly, there may have been cultural barriers to the disease's travel in ancient Greece. --ssd 21:08, 20 Mar 2005 (UTC)
- I left a note with the original author -- a brand new contributer!! -- and asked him to make changes before the rest of us chime in. I personally am on the Pre-Columbian side of the argument as there are too many human remains from historic and prehistoric Old World sites with evidence of congenital syphilis to call the disease new. However, from a biological point of view, some believe that a mutation from yaws produced the syphilis bug and that it has rapidly evolved in various niches worldwide ever since. See the Crosby reference. Having a New World strain collide with the Old World strain does seem a reasonable sequence, which perhaps led to the sudden explosion in Post-Columbian Europe. Consideration has to be made for the historic reporting problems with disease as well, as disease names were used very flexibly in the past. In particular, an accusation of syphilis infection was sometimes used as propoganda or a way of making a political enemy appear degenerate. Let's make these changes at a reasoned pace and try to present both sides of the issue. Comments welcome. WBardwin 23:45, 20 Mar 2005 (UTC)
- I'm in favor of the third idea now presented in history -- neither side has the whole picture. I think it is very clear that Columbus brought it back with him and started an epidemic in Europe. It is less clear (though I have been convinced with recent evidence) that it was already in Europe, although perhaps not wide spread or in a virulent form. I have also seen evidence that it was in the new world pre-Columbus, in both a skin and STD form, both of which were virulent. Also, the natives seem to have had ways of keeping it under control (like, with hot baths). As I said, I feel the article is now balanced. It gives about equal space to all three views. I think giving more than that is excessive unless we're going to divote a whole article on the history of syphilis, and talking about any one view more is POV until the experts come to agreement on one of them, which I suspect is not possible without a time machine. --ssd 05:00, 21 Mar 2005 (UTC)
Oh, for that time machine!. History is full of mysteries like this one -- little dibs and dabs of information but never a real answer. Let's see if our new contributor makes some changes and I'll look for a few more current references on all points. A quote from Crosby article might go well -- as would some archaeological confirmation from earlier European periods. Thanks for the interest. WBardwin 05:37, 21 Mar 2005 (UTC)
Thanks for the help everybody, as noted I am a new Wiki contributer and am not sure of all the conventions yet. I tried to make the contribution balanced, I personally support the Crosby theory that Syphilis is a particular strain of Yaws that was brought back from the New World. If you think more evidence from the pre-columbian side should be put in then feel free to add it, but I think I left enough it there. I don't think we can go into to much more detail without creating a seperate page. If we want to create a new page for the History of Syphilis I could write some of the text, as it is an interest of mine, but I would need help creating a page and linking it properly. I think the really interesting thing is the spread of the epidemic from Naples and how the pathogen mutated so as be less virulent to spread itself better. I don't think we have room for this unless we start a new page though. Notenderwiggin 23:04, 28 Mar 2005 (UTC)
- Hi! Welcome back. When I get around to tracking down your Crosby reference, I might tack a little more information to this article. I like the idea of a entire category on the History and Impact of Disease. The social impact of plagues and outbreaks was a subspecialty of mine as an undergrad. I've been playing with this in the plague area - with special pages on the three major outbreaks. History of syphilis would also be good, and I would be glad to help too. We might want to look over the Columbian Exchange article. WBardwin 00:29, 29 Mar 2005 (UTC)
I take issue with the following statememt about the Columbian theory: "Although this evidence has been derided as "weak and circumstantial" ". It is highly misleading as it suggests the Columbian theory is not strongly supported. The literature searches and reading I have done frequently support the Colubmian theory - especially the most recent literature. I'm not suggesting it is or is not correct, I'll leave that to the experts in those fields but to suggest the theroy is weak is just wrong. I'll am removing that statement. -sph.md
The "weak and circumstantial" was from the history section before I rewrote it, whoever wrote it before me was a strong supporter of the pre-columbian hypothesis. I agree that the scientific consensus has moved towards the columbian thesis, but when i orginally re-wrote the section I wanted to include some of what the previous contributer had left. I agree with the deleteion.--Notenderwiggin 01:53, 23 February 2006 (UTC)
- Here is the citation needed for the Hippocrates reference. http://www.logoi.com/health/syphilis/syphilis_1.htmlBigdatut (talk) 18:54, 29 January 2010 (UTC)
- Thanks. I've updated the text to indicate that the source is from the mid-19th century and cites an early 18th author as the source.
- You can add citations yourself, if you'd like. WhatamIdoing (talk) 19:13, 29 January 2010 (UTC)
Friedrich Nietzsche and other Famous Persons who suffered from Syphilis
An anon removed Nietzsche from the syphilus sufferers section. I think it probably should go back in/and so I'm reverting. I've read a couple of books that assert he had the disease. Does anyone have any idea why it was removed or disagree with putting it back? (I admit to questioning whether the article needs the section at all - but that is for another day.) Comments welcome. WBardwin 04:39, 20 Apr 2005 (UTC)
- The question is where did these books get that information from. You should see if you can check the original sources. This article claims that Nietzsche probably died of a brain tumor and that the syphilis story was created after the war by Wilhelm Lange-Eichbaum. The article summarizes Dr. Sax's claims regarding why he believes Nietzsche's symptoms were inconsistent with syphilis. Also, according to the Nietzsche article: "One of the best arguments against the syphilis theory is summarized by Claudia Crawford in the book To Nietzsche: Dionysus, I Love You! Ariadne." Zensufi 02:22, 22 Apr 2005 (UTC)
Anon's contribution starting a list of syphilis sufferers moved here for discussion (see below). (Additional ref: List of notable people identified as probably syphilitic.) I have concerns about such a list in this article, probably for both an emotional and historical research reason. First of all, it smacks of gossip. Accusations of syphilis infection were used to damage reputations and as propaganda throughout the history of the disease. And, consequently, people write about it almost with purient interest. Secondly, such accusations are nearly impossible to prove. Very few individuals were clearly identified by a medical source (iffy though they may have been) as syphilis sufferers during their lifetime. Should we have such a section here? Should we just refer to the above list? Should we build in caveats such as my concerns above? WBardwin 5 July 2005 16:39 (UTC)
- I think this whole section is simply unacceptable without at least one reference for each person purported to have had syphilis. Contributors with references should add them, but unless someone can explain why this section isn't pure slander, I'll delete all unreferenced "sufferers" in a few weeks -Rustavo 04:14, 12 April 2007 (UTC)
I would like to request putting Idi Amin in the famous people that died from syphillis.
Statistics/Sources
"United States has reported over 32,000 cases of Syphilis in 2002 and the cases were reported from 16 countries and 1 city. The number of cases of syphilis happened 20 to 39 years of age. Female’s highest cases were 20 to 24 years of age. Male’s highest cases were 35 to 39 years of age. The cases of congenital syphilis decreased from 2001 to 2002 in 2001, there were 492 cases of congenital syphilis in the 2002 it became 412 new cases syphilis and for the adolescence including mid adults between the ages of 15 and 34 who are sexually active have the highest rates of syphilis."
- Anon. contribution to article moved here. Sources not cited and information needs improvement/clarity. WBardwin 07:46, 16 May 2005 (UTC)
"Natchitoches, LA is the syphilis capitol of the world."
- Anon. contribution to article moved here. Probable vandalism as no source or context cited. WBardwin 14:55, 16 May 2005 (UTC)
Syphilis and malaria
Reportedly a dose of malaria was used to cure syphilis at one time. Is this true, and would it have worked?
- Rather implausible. JFW | T@lk 21:33, 19 May 2005 (UTC)
- Yes, it doesn't seem like a good idea now, but it certainly occurred. See From mercury to malaria to penicillin: The history of the treatment of syphilis at the Mayo Clinic, 1916–1955, which is cited in the article. It probably worked better than the equally improbable, yet true, concept of "bleeding" <g>. - Nunh-huh 00:14, 20 May 2005 (UTC)
- And now bleeding is being explored in some controlled experiments, as a treatment for types of hypertension (these days, "blood donation" is the method). And leaches -- are starting to be used to improve blood circulation in reattached limbs, such as fingers. So things come around again!! WBardwin 18:29, 2 Jun 2005 (UTC)
At least the malaria "cure" has some obvious logic to its working - bleeding does not. Are there any other examples of one disease being used to cure another?
- See 'TB may have killed off leprosy' at Talk:Tuberculosis and also see the malaria article section 'Sickle cell anemia and other genetic effects' having protection against malaria Petersam 06:59, 2 Jun 2005 (UTC)
- Please remove this, its confusing and scientifically crass - sickle cell anaemia is inherited, one does not 'catch it' - there is some evidence that the red blood cells of persons with sickle cell diseases are less easily invaded by Plasmodium falciparum (not all, there are a range of genes associated with having red cells that sickle under oxygen stress), your article gives the impression that giving someone sickle cell disease will cure malaria - it is just that people with SSA are less likely to contract malaria, and it is posited that this is the only reason these genes have survived in evolution. Relevant supporting sources are numerous - try the 'PUBMED' database (http://www.pubmed.com) using 'Dr. Anton Dlusewski' & 'plasmodium falciparum/red cells/erythrocytes/sickle cells/ ' as key words to search for them (his group at Kings College/Guys/Barts in London have worked for 20 years on this very topic). DrLofthouse
The theory is that malaria causes a very high fever that burns out syphilis. There is evidence also that very hot baths may also reduce the symptoms of syphilis, although they would not eliminate it, as the core body temperature (where the syphilis is living) would have to also go up. As to the other suggestions -- donating blood will certainly (temporarily) reduce blood pressure. Leeches are now used not so much to bleed a person but to increase the blood flow (as noted above), and are very effective at this. --ssd 03:57, 22 July 2005 (UTC)
Please also amend the above - leeches do not 'increase the blood flow' - they inject an anticoagulant locally which prevents blood clotting and reduces the formation of scar tissue - DrLofthouse
- As used in plastic surgery they do increase the venous drainage of flaps (by anticoagulation and by bleeding from the bite wound), preventing back pressure and therefore increasing flow of blood through them. Arfgab (talk) 18:02, 6 December 2009 (UTC)
- There are several examples of one disease being used to treat another. For example, infection with BCG (a TB-like bacterium) is used to treat bladder cancer. Cowpox vaccination is a similar idea.
- FYI to DrLofthouse: this is a talk page. We don't bother to clean it up to make it look pretty or sensible to encyclopedia readers, any more than the real world turns back time so we can un-say things we wish we hadn't said in a face-to-fact conversation. Just skip anything you're not interested in. WhatamIdoing 17:26, 3 September 2007 (UTC)
- Julius Wagner-Jauregg was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 1927 for the use of malaria inoculation in the treatment of tertiary syphylis, specifically general paresis of the insane. I have some books on malaria treatment for general paresis, including descriptions of the methods of caring for people undergoing treatment, but I've got a few other things I want to work on first Shelbypark (talk) 14:09, 22 March 2009 (UTC)
Syphilis in literature
Maybe the section "Syphilis in art and literature" ought to include a reference to Thomas Mann's Doktor Faustus? The disease is an important theme in the novel and is remarkably explored, with allegorical connotations, in the book's central dialogue.
If we intend to include a complete catalog of literate references, might we also include Darla, who was infected with it when made a vampire in TV's "Angel"? Trekphiler 12:48, 2 December 2005 (UTC)
In Breakfest of Champions, Kurt Vonnegut speaks of syphilitics and how when he was a child he thought they walked like robots.
- This might be true; in the "tabes dorsalis" form of late syphilis, sensory messages from the feet don't reach the brain properly, and people may have to slap their feet to "hear themselves" walk. Sfahey 19:17, 2 July 2006 (UTC)
The subsection title "Classic and antique literature" should be changed, perhaps to "Literary References from the 16th to 19th centuries." "Classical" and "Antique" as periods of literature generally refer to texts from Classical Rome through those of the Late Antiquity, periods stretching from the 8th century BC to the 5th century AD. Alternatively, the section could be titled "Early Modern Literature," as the early modern period is generally considered to as A.D. 1500-1800. Merellia 13:52, 22 April 2009 (UTC)
Syphilis in Armed Forces
Perhaps someone could locate a link to the many anti-Syphilis Army/Navy/Air Forces information posters from WW2 - my Father recalls one featuring a woman (obviously a Tart, because the disgusting woman wore an ankle chain and was SMOKING A CIGARETTE IN PUBLIC!!!) that read 'If she'll have it, she's got it, and if she's got it - you've had it!. The Medical Officer who gave them the low down also told them that you could catch it if a Boxer dog licked your face - why he singled out this breed so cruelly, we will never know..I thought it was Beagles who smoked in public??? —Preceding unsigned comment added by 80.225.189.192 (talk) 00:18, 3 September 2007 (UTC)
External Link
Moved external link from article for discussion, as it is not in English. Appears more appropriate for a sister wikipedia. WBardwin 18:42, 5 November 2005 (UTC)
There are a few links in this section that go to pages that try and establish a causal link between T. pallidum and AIDS. I would have thought that this is more controversial than is acceptable for an encyclopedia. Could someone have another look at this please? 203.100.246.20 12:25, 15 December 2005 (UTC)
The external link "Homosexual men boost increase in syphilis rate" with the embedded URL http://www.washingtontimes.com/national/20060317-123346-6729r.htm should be REMOVED. This URL appears to lead only to the front page of this paper and not to the article named in the link. 24.44.177.254 15:05, 5 July 2007 (UTC)
- I was bold in a minor way, checked what you said, and removed the outdated link. -- Lisasmall 04:45, 6 August 2007 (UTC)
removed cities with highest rate
I removed this sentence: "The highest per capita ratio of syphilis in the United States can be found in Auburn, Alabama followed closely by Pahokee, Florida." This looks like vandalism meant to denigrate the two towns mentioned. If this is for real, please cite sources. FreplySpang (talk) 16:02, 11 November 2005 (UTC)
- I removed it again just now. There doesn't seem to be anything I could find (through Google) to support this statement. Richard W.M. Jones 09:22, 31 January 2006 (UTC)
Syphilis & Paresis
I've seen the link credited to Krafft-Ebbing; his page doesn't mention it. Can anyone confirm? Trekphiler
Reference..
The second reference is incorrect, i've just been looking it up, and it should be "Baker, Brenda: Armelagos, George. The Origin and Antiquity of Syphilis: Paleopathological Diagnoses and Interpretation. Current Anthropology 29/5 (1988). " Also, i'm not sure if it is standard practice to include issue numbers, but it makes life easier.
nick
Leonardo di Vinci
"The name "syphilis" was first applied by Girolamo Fracastoro in 1530 from the name of a shepherd in a poem by Leonardo da Vinci."
Later
"In 1530, Girolamo Fracastoro, a physician and poet, wrote a poem from which syphilis derived its name."
...The first sentence is, at the very least, extremely awkwardly worded, and I suspect it to be downright inaccurate. Anyone know what's going on there? Adam Cuerden 01:52, 27 March 2006 (UTC)
Rainbow party
Material moved from anon edit for discussion. I vaguely remember this or a similar incident from a TV news program. But I thought the kids were older. Notable? Verifiable? WBardwin 19:18, 3 May 2006 (UTC)
- In 2005, approximately twenty sixth grade students at Reading Fleming Middle School (now Reading Fleming Intermediate School) in Flemington, New Jersey contracted syphilis after attendeding a "rainbow party".
- I don't really see much point in reporting every case of syphilis ever reported.... - Nunh-huh 20:08, 3 May 2006 (UTC)
- Indeed. There is no source, it sounds rather urban-legendlike, and a rainbow party is a sure ingredient for those kind of tales. Sure enough, Googling for the string Flemington "rainbow party" syphilis gives 0 hits. JFW | T@lk 20:32, 3 May 2006 (UTC)
- Source from Hunterdon Central Regional High School in Flemington, New Jersy
- I don't think a teacher would assign that if it wasn't true and, trust me, it is. One of my friend's sister's was one of the girls who contracted it. So, I'd appreciate it if you didn't accuse it of being an "urban legend".
This is absolutely not a reliable source, apart from the fact that this received NO media coverage. Please stop reinserting this. When MMWR reports this, we can talk again. JFW | T@lk 18:08, 4 May 2006 (UTC)
- You guys suck. (remaning unsigned potty mouth language by 205.247.5.97 removed)
Thanks for confirming the unreliability of this information. --ssd 12:48, 10 May 2006 (UTC)
Hello. I don't wish to divulge my name, but I am a teacher at Hunterdon Central Regional High School in Flemington, New Jersey. The one who posted the information about the Rainbow Party was a student in my class and I just found out about this today. We were discussing STDs and STIs in class and I assigned a laptop project, so apparantly he felt the need to share this information with you. I ask you not to ban this IP, as it is school wide and you would be banning a good deal of our nearly 3,000 students from your website. In regards to the information he posted, no one in our community knows for certain whether or not this case did occur though I can tell you that there was a case of syphilis at the middle school this past fall. Whether or not it's due to a Rainbow Party remains to be seen, but again I ask you not to punish numerous students due to the actions of one. Thank you.
Origins. Children's teeth.
I remember seeing a documentary where they found signs of syphilis in children's teeth in Europe before contact with the new world. These signs are caused by women with syphilis giving it to their kids according to the documentary. --Gbleem 01:40, 4 August 2006 (UTC)
Incidence
This article should include information on the incidence of syphilis worldwide and in notable subpopulations.
Treatment
First of all I don't think any specific treatment regimen should be given here except perhaps for the injectable penicillins, but the mention of 'tetracyclines (100 mg orally twice a day for 14 days)' is outright wrong, as this is the treatment regime for doxycycline ONLY. Basic tetracycline or erythromycin will require 500 mg four times a day. This is a very serious error if someone would be foolish enough to try to self-medicate, or to be forced to do that in extreme circumstances.
- Ditto. Wikipedia should not be dispensing medical advice. 69.247.134.2 08:28, 30 April 2007 (UTC)
- I disagree. The treatment(s) for syphilis can be found everywhere from Google to Medline, so they should be included in the article. However, the information should be correct and factual. Sedmic 15:41, 19 May 2007 (UTC)
"Sired by the Master"
The character of Darla in Buffy the Vampire Slayer and Angel is a colonial-era prostitute dying of syphilis when she is sired by the Master.
I'm not familiar with the show, but this makes no sense. He sired her (became her father) while she was a prostitute? Ordinary Person 09:42, 27 October 2006 (UTC)
- I think "sired" means "made a vampire", but that's only because I used to play V:TM. It wouldn't make any sense to anyone who isn't informed on the minutiae of modern American pop culture.
- Yes, in this context, "sired" means the person who made her a vampire. Next time I edit the article, I'll do what I can to make the sentence make sense to a non-fan. -- Lisasmall 04:49, 6 August 2007 (UTC)
"A night in the arms of Venus leads to a lifetime on Mercury"
I've found this article at a CDC site which sources the above saying. The source given is:
- Dracobly A. Theoretical change and therapeutic innovation in the treatment of syphilis in mid-nineteenth-century France. J Hist Med Allied Sci. 2004;59:522–54.
Rose Palmer 23:04, 2 November 2006 (UTC)
How does mercury work to kill spirochaetes? Drutt 03:06, 1 March 2007 (UTC)
Prevention
This section needs to be radically revised or scrapped. The injunctions appear to be out of a medical textbook or journal and assume the reader is a physician.
24.61.112.3 04:34, 27 January 2007 (UTC)
It's understandable... It just has a lot of conjecture (or has a lot of work plagiarized from original research or another encyclopedia).Species2112 14:41, 1 April 2007 (UTC)
Can we get corroboration for the assertion that latex condoms aren't 100 percent effective in preventing the sexual transmission of the syphilis bacterium from a reputable source(s) not connected to the US government? That statement may be true, but given the George W. Bush Administration's well-known record of tampering with science reports to suit its political agenda (like on the environment and, more to the point, sex education), I find the CDC page linked to in this section somewhat suspect.Methychroma (talk) 21:47, 3 May 2008 (UTC)
(later) Okay, the page Whatamidoing linked to seems acceptable but I reworded the sentence immediately preceding it, which seemed to imply that condoms are less than effective in preventing the spread of syphilis, after the manner of the pro-abstinence propaganda that's going around these days.Methychroma (talk) 01:37, 4 May 2008 (UTC)
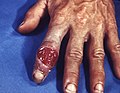
- I see that you've figured it out. The necessary corroboration is in the condoms article. It consists of the following two facts about latex condoms. Even when used consistently and correctly, condoms:
- (1) occasionally break, and
- (2) do not cover the entire body.
- Now add that to the information shown in this picture (and discussed in the article): Unlike some infectious agents, T. pallidum is not specific to or restricted to the the tissues of the genitalia. Even if condoms never broke, using a condom can't protect you from infection through a syphilis chancre that is not on the genitalia.
- As to "quite effective" -- those are "weasel words" and designed to promote a POV (namely, that condoms can be relied upon to prevent syphilis infection). Can you find something that says how effective condoms are? I haven't been able to. If we can't, I'd be inclined to restate the sentence as "effective against the spread of syphilis through sexual contact" or some such properly condom-related phrase. WhatamIdoing (talk) 02:11, 4 May 2008 (UTC)
I will take the suggestion you give in your last sentence.Methychroma (talk) 03:41, 4 May 2008 (UTC)
The statement "Proper and consistent use of a latex condom is effective against the spread of syphilis through sexual contact" seems misleading.
It is supported by reference to a site that claims "Correct and consistent use of latex condoms can reduce the risk of syphilis, as well as genital herpes and chancroid, only when the infected area or site of potential exposure is protected". The statement seems to be a missleading conclution to draw from the reference. Yes, if "through sexual contact" you only include the part of the genitals that are covered by a condom, but by reading the statment it would seem that is not possible to catch syphilis from having sex with an infected person, which is dangerously false. I think this is a flaw with an article about STD's; giving misleading information about effective prevention.
I suggest changing the statement to be something along the lines of "Proper and consistent use of a latex condom is effective against the spread of syphilis only to and from the parts of the genitals that are covered by the condom" Seakerseven (talk) 06:42, 9 September 2008 (UTC)
- It used to say this:
This was declared to be insufficiently supportive of condom use. However, since the immediately preceding sentence still mentions the risk of transmission involving "areas not covered by a condom", I don't think that we need to repeat that. Our readers probably have an attention span of more than two sentences. WhatamIdoing (talk) 18:55, 9 September 2008 (UTC)While abstinence from any sexual activity is very effective at helping prevent syphilis, it should be noted that T. pallidum readily crosses intact mucosa and cut skin, including areas not covered by a condom. Proper and consistent use of a latex condom can reduce, but not eliminate, the spread of syphilis.
Conjecture... Needs to have references
In other words, a common ancestor of the syphilis bacterium existed on both the Old and New Worlds, easily spread by the poor hygeine of primitive cultures. As hygeine standards improved in Europe the bacterium was forced to evolve into a more aggressive version to survive and reproduce, which also resulted in it becoming deadly to Humans. The European strain was carried to the New World, where the native population's exposure to the less deadly version of syphilis vaccinated them against the lethal variety. As fewer Native Americans than Europeans succumbed to the deadly syphilis, it appeared to contemporary thinkers that the New World was to blame for the disease.^
That's quite a claim to have made without any references... Not impossible but its like umm anyone could have come up with that theory. —The preceding unsigned comment was added by Species2112 (talk • contribs) 14:37, 1 April 2007 (UTC).
Non-sexual contact
Article only talks about sexual and congenital modes of contraction... Syphilis, unlike AIDS, also can be contracted (although pretty rarely) by sharing cups, spoons, etc. Plus, like HIV, it can be contracted through blood transfusions, non-sterile tattoo instruments, etc.
- False. Please provide evidence. Syphilis is for all intents and purposes either sexually or vertically transmitted. The CDC states: Syphilis is passed from person to person through direct contact with a syphilis sore. Sores occur mainly on the external genitals, vagina, anus, or in the rectum. Sores also can occur on the lips and in the mouth. Transmission of the organism occurs during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Pregnant women with the disease can pass it to the babies they are carrying. Syphilis cannot be spread through contact with toilet seats, doorknobs, swimming pools, hot tubs, bathtubs, shared clothing, or eating utensils. (http://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/STDFact-Syphilis.htm) Sedmic 11:36, 30 May 2007 (UTC)
- Here are couple references:
http://www.who.int/tdr/dw/syphilis2004.htm "Syphilis is usually transmitted by sexual contact or from mother to infant, although endemic syphilis is transmitted by non-sexual contact in communities living under poor hygiene conditions."
http://www.drstandley.com/stds_syphilis.shtml "The most common way of contracting the disease is through vaginal, anal or oral sex. However, it can be spread by non-sexual contact if the sores (chancres) rashes or mucous patches caused by syphilis come in contact with the broken skin of a non-infected individual. This disease can be contracted through physical contact such as kissing, as well as through sexual intercourse"
http://answers.google.com/answers/threadview?id=536307 “Contagion summary - syphillis: Sexually transmitted; only contagious in the early stages. Also mother to fetus. Rare contagion from oozing fluid exposure into broken skin. No longer contagious 24 hours after beginning antibiotic therapy.”
Contagiousness properties of Syphilis:
Contagious overall?: Yes Contagious by sex?: Yes Contagious by anal sex?: Yes Contagious by vaginal sex?: Yes Contagious by physical contact (non-sexual)?: Yes, rarely. Contagious from mother to fetus (transplacental)?: Yes
http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/s/syphilis/contagious.htm "
"Well-known and suspected syphilis patients"
This section is completely unsourced, and following the links to articles shows that many of the people listed aren't known to have had syphilis. It's also completely unordered. I'm going to go ahead and go through the list and remove those that don't have a mention of syphilis in their respective articles (quick and dirty way to trim out the obvious ones), but I'm of the opinion that a section like this is bait for urban legends and rumors, and advocate its outright removal. siafu 22:21, 15 June 2007 (UTC)
- Replaced, perhaps, with a sentence or two about how historically retrospective diagnosis of syphilis is particularly problematic, as symptomatology varies so widely that almost any symptom can be ascribed to the disease, and how notwithstanding this caution, such retrospective diagnosis remains a popular, if unenlightening, sport. - Nunh-huh 22:30, 15 June 2007 (UTC)
- When I got to the article today, there were two sections of famous names, one a narrative near the top, and one a two-column list near the bottom. I consolidated them, put a source on Scott Joplin, and then had to stop because of time constraints. I think the section has merit beyond mere gossip value, especially for major historic figures, but
- 1. needs to be watched for vandalism and
- 2. should more carefully note when the syphilis story appears to have been spread by enemies (e.g., Adolf Hitler probably did not have it, per a 2006 scholarly article), and
- 3. of course, needs citations for each individual
- The edit I made today does not make this part of the article good; but it makes it better than it was. I hope someone can do more clean-up. -- Lisasmall 04:58, 6 August 2007 (UTC)
"Early/Late Latent stage dividing point"
The section of "Syphilus Infection" entitled "Latent syphilus" divides Latent syphilus into early and late at two years after initial infection without symptoms. The section of "Current treatment" entitled "Late latent and infections of unknown duration" divides it at one year. Can we come to some agreement? 66.92.65.86 21:55, 21 July 2007 (UTC)
Origins: Crosby's combination theory
I pulled this:
- As hygiene standards improved in Europe the bacterium was forced to evolve into a more aggressive version to survive and reproduce, which also resulted in it becoming deadly to humans. The European strain was carried to the New World, where the native population's exposure to the less deadly version of syphilis vaccinated them against the lethal variety. As fewer Native Americans than Europeans succumbed to the deadly syphilis, it appeared to contemporary thinkers that the New World was to blame for the disease.[citation needed]
on the grounds that (a) it's unsourced, (b) there's no undisputed evidence for the existence of a pre-Columbian European strain (yaws is traditionally assigned to Africa), and (c) disease evolution does not necessarily move in the direction of killing the host. It's at least as likely that a bacteria would become less deadly (and more easily transmitted) under these circumstances (because the bacteria needs longer to move from one host to the next, and dead hosts are poor transmitters of social diseases).
Furthermore, while I haven't read (quite) every single page of Crosby's book, my recollection was that he assumed a New World version was the more deadly version. If my memory fails me, please post an actual page number from his book: It's very easy to pull a selective quotation from a book (like this one) that summarizes the opposing viewpoints. WhatamIdoing 05:03, 30 July 2007 (UTC)
- I added a POV similar to (in at least one respect), but not the same as, Crosby's, with citation. See Doug Owsley quote in article, detailing early Chinese & European mention of the disease, and Owsley's belief it was worldwide prior to, and regardless of, the Columbian expeditions. -- Lisasmall 03:24, 6 August 2007 (UTC)
Lyme disease reference removed
I pulled this:
- Infection with Syphilis has often been ascribed to historical figures, who have died from diseases that had characteristics which are suggestive of Syphilis. However, we now know that Lyme Disease will exhibit similar symptoms in its later stages, and the possibility that Lyme Disease was the causative agent in many historical cases, cannot be excluded[1].
on the grounds that the source is itself only another Wikipedia article, which made a single, very minor, and somewhat ambiguous reference to advanced Lyme causing neuropsychiatric symptoms like tertiary syphilis does. There wasn't really a clear statement that the symptoms are the same, nor any reference to medical literature indicating the two conditions can be, could be, or ever have been mistaken for one another. It seems to serve the purpose here of providing a "respectable" alternative explanation for the prominent figures known, or believed, to have been affected by syphilis. --Lisasmall 03:24, 6 August 2007 (UTC)
Ties in with the Tuskegee disgrace in the USA, but the early tests for syphilis gave a false positive if you had SLE (ie Lupus- source is NHS Direct ) - which is most common (though not exclusive) to those carrying Afro-Carribean genes - this is also associated with the occurrence of blood clots and therefore neuropsychiatric symptoms. Many historical black figures (especially jazz musicians it appears) were probably horribly misdiagnosed up until mid-sixties. —Preceding unsigned comment added by 80.225.208.35 (talk) 00:26, 3 September 2007 (UTC)
Comments from Version 0.7 review
I gave this a quick review for Version 0.7, and I've been asked to give a little more feedback. I'm not an expert on the topic, but overall my impression is that this article is of high quality. It seems to cover the main topics (although the biochemistry is missing - maybe this isn't known?) and fairly well referenced. The parts I read carefully seemed to be well written. The main weakness - as is often the case - comes in the "Syphilis in art and literature" section which contains too much trivia and is currently tagged for cleanup. If you're not careful, every mention on syphilis will get added and it will take over the article! From what I've seen on other pages, the people who work on this page should discuss how to approach the problem. I would suggest you can (a) agree to remove such a section altogether if it's unimportant, or (b) spin off the content into a separate article if it is important, or (c) if you have someone active here, chop the section down to the really important stuff, leave an editor's note and be prepared to keep reverting new additions.
The other dangerous section is the "famous people who have had syphilis" but that is at least done in a very nice, concise way. I wouldn't expect to find a citation for every name; instead, I would expect to find a citation in every biographical article mentioned. If there is no mention (with citation) of syphilis in the Adolf Hitler article, for example, then it should be removed from this page. So, overall a nice article, and we're glad to have this topic covered in Version 0.7. Thanks! Walkerma (talk) 12:37, 11 December 2007 (UTC)
Origins
New information on the origins is here[2] WhatamIdoing (talk) 05:12, 15 January 2008 (UTC)
External links
This article's biggest editing problem is basic vandalism, like adding the name of someone you know to the list of people who had syphilis. However, IMO the second-biggest problem is the ongoing addition of external links. One user, for example, has added a link several times to their teen-oriented website. (This is approximately all this user does.) This page provides no information that isn't already covered in the other links (and the article itself). As far as I can make out, the only two additional "features" that their website provides are (a) having dramatically less information than the article does and (b) putting all the information in pale gray text on a white background so that visually impaired people won't be able to read it.
I'd like to invite all of the regular editors to keep a watchful eye on external links for this article. The policies are at WP:EL, and a basic rule of thumb is that the links should provide substantial encyclopedic information that is not already in the article. If the article were truly perfect, then we probably wouldn't need any external links in it (because they'd all be used as references to support statements in the article). WhatamIdoing (talk) 21:36, 21 February 2008 (UTC)
- Perhaps the site in question could be added to the Wikipedia:Spam blacklist? - Nunh-huh 21:40, 21 February 2008 (UTC)
Basic vandalism
Just wanted to let other editors know that when you revert the typical stupid vandalism to the 'notable people' list, you can also template the user page with {{subst:Blp1|syphilis}}. WhatamIdoing (talk) 17:48, 9 April 2008 (UTC)
Old world proven!
The syphillis is now proven NOT to have come from the Americas. Two skeletons have been recently unearthed in Szeged, southern part of Hungary. A young lady in her early 20s and a mid-40s woman, both show obvious symptoms of being consumed by syphillis and radioactive dating put their time of death between 1420-1470. The discoverers, Ms. Brigitta Ősz Phd and Mr. Prof. György Pálfi of Szeged University have just made a conference presentation about these findings. The discovery is so significant, the french society for paleopathology will hold its 2009 conference in Szeged. 82.131.210.162 (talk) 14:40, 6 May 2008 (UTC)
- We need a reliable source.
- Importantly, this discovery isn't as sweeping as it sounds. Everybody agrees that syphilis was present in the Americas for hundreds of years before Columbus sailed the ocean blue. The only question is whether it also existed in Europe, Africa, and Asia before then. Even if a strain of syphilis existed in pockets of the "Old World", it's still entirely possible that European explorers acquired a virulent American strain and spread it all over Europe, with devastating effects. WhatamIdoing (talk) 00:09, 7 May 2008 (UTC)
Beethoven
Beethoven had appeared on the list of famous people suspected of having syphilis. However, I have removed him, as I recall the lack of mercury in his hair suggesting that he did not have the disease (or wasn't treated for it, anyway). I found a source corroborating this:
"Very low (undetectable) mercury levels were reported independently by McCrone Research Institute and Argonne National Laboratory. These results provide no evidence that Beethoven received medical treatment for syphilis, usually treated in the 1820's with mercury compounds. This supports the consensus of Beethoven scholars who believe that Beethoven never had syphilis. Rumors that Beethoven suffered from syphilis have been discounted in all serious musicological literature for the last thirty years."
(http://www.sjsu.edu/depts/beethoven/hair/hair.html)
Metasquares (talk) 14:22, 13 June 2008 (UTC)
Syphilitic Megalomania
I recollect references to The Pepper King and to others with syphilis (see list of sufferers for many likely examples) behaving as megalomaniacs. What sources are there to verify this ?? 86.146.17.129 (talk) 11:16, 14 August 2008 (UTC) John King - Salisbury, England
Notable known and suspected syphilis-infected people in previous centuries
Syphilis#Notable known and suspected syphilis-infected people in previous centuries is long and regularly grows. It was a very common disease. Would anyone mind if we shortened the list by removing the "suspected" names? WhatamIdoing (talk) 02:39, 13 October 2008 (UTC)
Lenin died of syphilis, but he isn't in this list.Agre22 (talk) 19:45, 8 May 2009 (UTC)agre22
{{editsemiprotected}} Please add Robert Schumann to Syphilis#Notable_syphilis-infected_people_in_history: Robert Schumann (1810 – 1856), composer S
THXXL (talk) 00:10, 11 May 2009 (UTC)
- Schumann might qualify as a "suspected" case, but before I add him is there consensus one way or the other on whether suspected cases belong in this list? I'd argue no given the length of the list and the poor sourcing for most supected cases. This was first raised six months ago and so far no one has argued for including suspected cases. Equally, no one has removed the ones we have. Does anyone have any further views on this?
Demographics
This article could use information on the worldwide prevalence and incidence of syphilis. I heard recently that it had nearly been eradicated in the United States, but was recently starting to spread again. It would be interesting to see a comparison across regions, as well as prospects for complete eradication. -- Beland (talk) 09:22, 2 February 2009 (UTC)
- There are about 70,000 new cases in the U.S. per year. "Nearly eradicated" is, I think, an overstatement (more of a goal than an achievement), but certainly incidence has been increasing. - Nunh-huh 09:36, 2 February 2009 (UTC)
A seeming contradiction in the article
There is a sentence in Section 6.2 which *appears to the layman reader* to contradict the origins discussion in Section 2. I'm not commenting on anything but how the article reads, by the way, I know very little about this topic.
Section 2 states there is argument about where the disease originated, and includes the quote "there is no unequivocal evidence of any related disease having been present in pre-Columbian Europe, Africa, or Asia".
Section 6.2 however offers this statement: "The use of mercury was the earliest known suggested treatment for syphilis, dating back to The Canon of Medicine (1025) by the Persian physician, Ibn Sina (Avicenna)." This can easily be interpreted as saying that there WAS reliable evidence of the disease in "Europe, Africa, or Asia" prior to 1492.
My (uninformed) speculation is that in reality people aren't entirely certain what disease Ibn Sina was talking about. Whatever the truth of the matter, could this section of the article get tidied up so as to not appear to contradict Section 2?
Regards Manning (talk) 02:27, 27 March 2009 (UTC)
- I was under the impression that Avicenna used mercury for smallpox and other skin diseases, but that its use for syphilis (which may or may not have existed) was speculation. We'd have to check the listed source, though. WhatamIdoing (talk) 02:33, 28 March 2009 (UTC)
Hi, I already removed this statement about Ibn Sina(although user WBardin undid my change and I subsequently redid it which I guess is frowned upon... anyway Ibn Sina would have had no words to describe syphilis which was not known as a disease prior to Columbus; the statement that he recommended mercury for it is absolutely ridiculous. In any case syphilis changed rapidly after first being noted, and to argue that any symptoms Ibn Sina described were caused by this disease agent would be a very hard theory to support and such a claim certainly could not be made without much more supporting evidence and discussion. I think Wikipedia is no place for such bizarre theories. Danpovey (talk) 21:07, 19 October 2009 (UTC)
- We have to go by whatever the reliable source says. If the source says that Avicenna used mercury to treat syphilis, then we say that. If, however, the source says that Avicenna used mercury to treat "poxes", then we wouldn't include that (because syphilis is not the only kind of pox). WhatamIdoing (talk) 22:16, 19 October 2009 (UTC)
- OK, I am trying to dig up the reliable source, but I think it's stupid-- if the reliable source said the moon is made of cheese, would we accept it? The theory that syphilis existed pre-Columbus is a minority one at the present time, and anything dependent on that being true cannot be cited except as a relatively remote possiblility-- anyway syphilis was not recognized as a distinct disease pre-Columbus. Danpovey (talk) 04:22, 20 October 2009 (UTC)
- Unless the source's claim truly represented a tiny minority position, then yes: we would, at minimum, say that "So-and-so says that the moon is made of cheese." WhatamIdoing (talk) 04:57, 20 October 2009 (UTC)
Source of Syphilis
Danpovey, the source of Syphilis is often a topic of discussion on this article. There are sources, many sources, that present differing theories. Although all editors have an opinion, we must try and present an appropriate balance in the article. I reverted the removal of the assertion on mercury treatment primarily because it was sourced. As a sourced assertion, its validity and the validity of the source, should be discussed on the talk page before removal or significant alteration. Do you have an opposing source to prove that this assertion is rediculous? WBardwin (talk) 21:41, 19 October 2009 (UTC)
- And we have an answer: The named source definitely lists syphilis by name. See the quotation that was kindly provided here. WhatamIdoing (talk) 02:17, 20 October 2009 (UTC)
- Then we should include the quote/statement within the European origin or multiple origin theories. Of course, the historian must ask: "Is the quote from the original document?" "From a contemporary translation of the original document?" or "From a translation of the original after European contact with the Americas?" That would make a difference in how credible the statement is. Thanks for the effort. WBardwin (talk) 01:20, 21 October 2009 (UTC)
Edit Request
{{editsemiprotected}}In the fifth paragraph of the History section of the article, change "prisoners" to "sharecroppers" please.
Thank you very kindly in advance!
Sleeptalking (talk) 01:47, 10 April 2009 (UTC)
- I've changed "prisoners", which is clearly wrong, to "men". I know the study victims were men; I'm not certain that all of them were sharecroppers. If you can provide a source which says so, I will gladly change "men" accordingly. - Nunh-huh 02:39, 10 April 2009 (UTC)
- Thank you so much! The Final Report of the Tuskegee Syphilis Study Legacy Committee published in 1996 seeking a Presidential apology says "sharecroppers" but would it have to come from a primary source to meet Wikipedia's standards? The report can be found here: http://www.hsl.virginia.edu/historical/medical_history/bad_blood/report.cfm
- Thanks again! -Sleeptalking (talk) 22:25, 10 April 2009 (UTC)
- That's good enough for me, but I see the article already contains the information that the subjects were sharecroppers, so we don't need to repeat it. - Nunh-huh 23:14, 10 April 2009 (UTC)
- Oh good point. Thanks. :) -Sleeptalking (talk) 00:02, 11 April 2009 (UTC)
- That's good enough for me, but I see the article already contains the information that the subjects were sharecroppers, so we don't need to repeat it. - Nunh-huh 23:14, 10 April 2009 (UTC)
Tuskegee Syphilis Study error
"The study began in 1932, when syphilis was a widespread problem, especially in poor communities, and when there was not effective treatment or cure. Study researchers recruited a group of 600 black male sharecroppers in the rural area of Tuskegee, Georgia."
{{editsemiprotected}}"Tuskegee, Georgia" should be changed to "Tuskegee, Alabama."
71.59.3.102 (talk) 15:34, 15 April 2009 (UTC)Maureen K
- Will do. --The New Mikemoral ♪♫ 23:40, 17 April 2009 (UTC)
- This section on the Tukegee thing is way too long. It's only of interest to people in one country (USA) and yet it takes up my whole screen. Please delete it, or at least chop it back to three or four sentences, with a link to the full article for those people who are interested.
Lenin died of syphilis
About persons killed by this STD, the name of Lenin is forgotten.These sites: [Discover Magazine] , [Israeli researchers solve mystery of Lenin's death] and [The New York Times].Agre22 (talk) 19:40, 8 May 2009 (UTC)agre22
- Actually, the article as a whole would be more stable if the list of the affected could be eliminated or severely restricted. It's never going to be an exhaustive list, there are always going to be people who want to add their favorite to it, and there will always be a problem with documentation and post-mortem speculation. We should consider spinning it off into a separate article with no persons named in this article and merely link to it, and/or adopt relatively strict guidelines about who should be added to this article. - Nunh-huh 19:43, 8 May 2009 (UTC)
- I could go either way on this; my primary concern is the number of immature people that add the names of their (soon to be ex-) "friends" to this list, or who think that some unsubstantiated rumor about a living celebrity is grounds for inclusion. We've made progress by retitling it as a "historical only" section, but it is still a concern.
- As for a longer list, whether on this page or not: I'm not sure that a more complete list is at all important and encyclopedic. WhatamIdoing (talk) 23:16, 9 May 2009 (UTC)
"Famed"?
Origins, para 6:
Also arguing for worldwide incidence of syphilis prior to Columbus' voyage, Douglas Owsley, famed physical anthropologist at the Smithsonian Institution...". The link for Owsley is red, therefor I ask - how is he famed? 71.234.215.133 (talk) 20:03, 30 July 2009 (UTC)
History needs citations
The second half of paragraph 1 ("Prior to Noguchi's discovery...") and the entire of paras 2 and 3 (citing personages who might have had syphilis) are in dire need of citation(s). 71.234.215.133 (talk) 20:09, 30 July 2009 (UTC)
Prevention
this section requires a level 2 headline, it is not a "treatment" —Preceding unsigned comment added by 81.245.91.136 (talk) 10:42, 26 October 2009 (UTC)
It's rather odd that Hitler's name is included as a possible syphilitic, when recent research debunks this claim, whereas Lenin, whose doctors were treating him with salvarsan, which quite conclusively proves he had syphilis, is absent from the list. —Preceding unsigned comment added by 76.67.193.135 (talk) 05:31, 27 October 2009 (UTC)
Bizarre omissions (and inclusions) in suspected cases section
I also find it bizarre that Robert Schumann (yes, I have suggested this before, albeit anonymously) is excluded from the list of suspected cases, even though in the main article on the composer, a possible syphilitic infection is suggested FOUR times, including one "Further Reading" entry referring to a recent biography. Yet individuals like Henry VIII, who now it is commonly believed did NOT die of syphilis, and Eleanor of Toledo, in whose main article the topic of syphilis is not even mentioned ONCE, are both included!
I personally subscribe to John Worthen's view of events, outlined in this book review...
http://www.classical.net/music/books/reviews/0300111606a.php
And in my opinion, I think this section would benefit from a just a little more consistency with related articles.
Toloatzin (talk) 19:50, 25 November 2009 (UTC)
- Thank you for your suggestion. When you believe an article needs improvement, please feel free to make those changes. Wikipedia is a wiki, so anyone can edit almost any article by simply following the edit this page link at the top. The Wikipedia community encourages you to be bold in updating pages. Don't worry too much about making honest mistakes—they're likely to be found and corrected quickly. If you're not sure how editing works, check out how to edit a page, or use the sandbox to try out your editing skills. New contributors are always welcome. You don't even need to log in (although there are many reasons why you might want to).
- Schumann is mentioned: "One suspected example of syphilis was the insanity of noted composer Robert Schumann, although the precise cause of his death has been disputed by scholars." His name is just not duplicated in the bulleted list, because that would be unnecessarily redundant.
- I think the general goal here is to reduce the "suspected" cases to very high profile people for which high-quality reliable sources are available. A long laundry list isn't exactly encyclopedic anyway. WhatamIdoing (talk) 01:10, 26 November 2009 (UTC)
Thanks for the tutorial, but I've already submitted my first article, and I think I've pretty much got the hang of things around here now.
I hadn't noticed the earlier reference to Schumann. I've added Schumann before, but had the edit reverted by user Kilbad with the alternate reason that I should "cite my sources". I note that Schumann had been in the list right up until the end of June 2008 when you attempted to prune the list (to no avail, it would seem). With respect, I have to say your argument for not including him because his case is touched upon earlier in the article, doesn't really cut it for me, as Schubert is also referred to earlier, but he remains in the list. As composers go, I'd say they were at least equally notable.
But as he's been already referenced earlier in the article, I don't think I'll bother. It's obviously a very contentious section, (and in need of a little more pruning, I'd say). Thing is, I'm primarily a musician, and notability for me pertains to people who've actually contributed something positive to existence, as opposed to kings and despots and the like. But that's another matter. It was a only small edit, and I don't want to get into a silly argument (with anyone) over such a piffling little detail, so I'll think I'll leave it there.
Toloatzin (talk) 23:12, 27 November 2009 (UTC)
Edit Request: Cures Before Pennicillin
{{editsemiprotected}}
The I'm only mentioning this because I can't edit it myself: The first cure people used was mercury (I don't have a source but I think it's pretty well known so it shouldn't be hard to find one), and I know for a fact that the Frenchman Dr Albert Sézary (after whom Sézary's syndrome is named) found a cure in 1921 involving arsenic and bismuth (http://www.whonamedit.com/doctor.cfm/2977.html), yet neither of these two cures is mentioned on the "history" section. I would put them in the history section rather than the "cure" section, because nowadays you use different cures, but they should be mentioned for their historical value, so can someone please put them in the history section? The mercury is hinted at elsewhere (and there's a picture of it in the article) but never talked about explicitly.
It would be interesting to say that all cures before pennicillin were somehow toxic (source: wiki page on the Tuskegee syphilis study), which is why pennicillin was such a breakthrough, being the first cure that wasn't toxic.
![]() Already done Welcome and thanks for contributing. There is already an extensive discussion of mercury in the history section. If you would like to modify that, describe the change in a 'please change X to Y' level of detail and create a new request and someone would be glad to help. Thanks, Celestra (talk) 20:43, 10 December 2009 (UTC)
Already done Welcome and thanks for contributing. There is already an extensive discussion of mercury in the history section. If you would like to modify that, describe the change in a 'please change X to Y' level of detail and create a new request and someone would be glad to help. Thanks, Celestra (talk) 20:43, 10 December 2009 (UTC)
- B-Class medicine articles
- High-importance medicine articles
- B-Class dermatology articles
- Unknown-importance dermatology articles
- Dermatology task force articles
- B-Class reproductive medicine articles
- High-importance reproductive medicine articles
- Reproductive medicine task force articles
- All WikiProject Medicine pages
- B-Class Microbiology articles
- Top-importance Microbiology articles
- WikiProject Microbiology articles



