Vlachs of Serbia
 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Eastern Central Serbia | |
| Languages | |
| Vlach (or Romanian), Serbian | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly † Orthodox Christianity | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Romanians of Serbia |
The Vlachs (endonym: Rumâni, Template:Lang-sr) are an ethnic minority in eastern Serbia, culturally and linguistically related to Romanians.[6][7][8] They mostly live in the Timočka Krajina region (roughly corresponding to the districts of Bor and Zaječar), but also in Braničevo and Pomoravlje districts. A small Vlach population also exists in Smederevo and Velika Plana (Podunavlje District), and in the municipalities of Aleksinac and Kruševac (Rasina District).
Legal status



The ethnonym is Rumâni and the community Rumâni din Sârbie,[9] translated into English as "Romanians from Serbia".[10] They also known as Valahii din Serbia.[11] The Romanians in Serbia call their community Românii din Serbia. Although ethnographically and linguistically related to the Romanians, within the Vlach community there are divergences on whether or not they belong to the Romanian nation and whether or not their minority should be amalgamated with the Romanian minority in Vojvodina.[12]
In a Romanian-Yugoslav agreement of November 4, 2002, the Yugoslav authorities agreed to recognize the Romanian identity of the Vlach population in Central Serbia,[13][dubious – discuss] but the agreement was not implemented.[14] In April 2005, 23 deputies from the Council of Europe, representatives from Hungary, Georgia, Lithuania, Romania, Moldova, Estonia, Armenia, Azerbaïdjan, Denmark and Bulgaria protested against Serbia's treatment of this population.[15]
The Senate of Romania postponed the ratification of Serbia`s candidature for membership in the European Union until the legal status and minority right of the Romanian (Vlach) population in Serbia is clarified.[16][17]
Predrag Balašević, president of the Vlach party of Serbia, accused the government of assimilation by using the national Vlach organization against the interests of this minority in Serbia.[18]
Since 2010, the Vlach National Council of Serbia has been led by members of leading Serbian parties (Democrat Party and Socialist Party), most of whom are ethnic Serbs having no relation to the Vlach/Romanian minority.[19] Radiša Dragojević, the current president of Vlach National Council of Serbia, who is not a Vlach, but an ethnic Serb,[20] stated that no one has the right to ask the Vlach minority in Serbia to identify themselves as Romanian or veto anything, firstly because there already is a recognized Romanian minority within Serbia, and because Vlach people in Serbia do not feel discriminated or underprivileged. He also said that Vlachs regard Serbia as their true homeland.[19]
As a response to mister Dragojević`s statement, the cultural organizations Ariadnae Filum, Društvo za kulturu Vlaha - Rumuna Srbije, Društvo Rumuna - Vlaha „Trajan“, Društvo za kulturu, jezik i religiju Vlaha - Rumuna Pomoravlja, Udruženje za tradiciju i kulturu Vlaha „Dunav“, Centar za ruralni razvoj - Vlaška kulturna inicijativa Srbija and the Vlach Party of Serbia protested and stated that it was false.[21][22]
On 1 March 2012, Romania and Serbia signed an agreement concerning the Vlach population in Serbia.[23] According to the agreement, members of the Vlach community can declare themselves to be Romanians, and those who do so can have access to education, media and religion in their language.[24]
Origins
Following Roman withdrawal from the province of Dacia at the end of the 3rd century, the name of the Roman region was changed to Dacia Aureliana, (later Dacia Ripensis); it extended over most of what is now Serbia and Bulgaria, and an undetermined number of Romanized Dacians (Carpi) were settled there.[25][26] A strong Roman presence persisted in the region through the end of Justinian's I reign in the 6th century.[27][page needed]
The region where Romanians, also known as Vlachs, predominantly lived was later part of the Second Bulgarian Empire, whose first rulers, the Asens, are considered to have been Vlachs.[28] King Stephen Uroš II Milutin of Serbia ruled most of Timok after he conquered the land of a rival king, Stephen Dragutin. Chroniclers of the crusaders describe encountering Vlachs in the 12th and 13th century in various parts of modern Serbia.[29][30] Serbian documents from the 13th and 14th century mention Vlachs, including a prohibition of intermarriage between Serbs and Vlachs by Emperor Dušan the Mighty.[29][30] Romanian (Wallachian) rulers built churches in northeastern Serbia in the 14th and 15th centuries.[31][page needed] Turkish tax records (defters) from the 15th century list Vlachs in the region of Branicevo in northeastern Serbia, near the ancient Roman municipium and colonia of Viminacium.[32][page needed]
Starting in the early 18th century northeastern Serbia was settled by Romanians (then known by their international exonym as Vlachs) from Banat, parts of Transylvania, and Oltenia (Lesser Walachia).[29] These are the Ungureni (Ungurjani), Munteni (Munćani) and Bufeni (Bufani). Today, about three quarters of the Vlach population speak the Ungurean subdialect. In the 19th century other groups of Romanians originating in Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia) also settled south of the Danube.[33] These are the Ţărani (Carani), who form some 25% of the modern population. Their very name Ţărani indicates their origin in Ţara Româneasca, i.e., "The Romanian Land," Wallachia and Oltenia. From the 15th through the 18th centuries large numbers of Serbs also migrated across the Danube, but in the opposite direction, to both Banat and Ţara Româneasca. Significant migration ended with the establishment of the kingdoms of Serbia and Romania in the second half of the 19th century.
The lack of detailed census records and the linguistic influence of the Ungureni and Ţărani on the entire Vlach population make it difficult to determine what fraction of the present Vlachs can trace their origins directly to the ancient south-of-the-Danube Vlachs. The Vlachs of northeastern Serbia form a contiguous linguistic, cultural and historic group with the Vlachs in the region of Vidin in Bulgaria as well as the Romanians of Banat and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia).
Some authors[who?] consider that the majority of Vlachs/Romanians in Timocka Krajina are descendants of Romanians that migrated from Hungary in the 18th and 19th centuries.[34]
Culture
Language
The language spoken by the Vlachs consists of two distinct Romanian subdialects spoken in regions neighboring Romania: one major group of Vlachs speaks the subdialect spoken in Mehedinţi County in western Oltenia, while the other major group speaks a subdialect similar to the Romanian subdialect spoken in the neighboring region of Banat.
The Romanian language is not in use in local administration, not even where members of the minority represent more than 15% of the population. (according to Serbian law, the use of a distinct language in local administration is allowed in places where the minority speaking it comprises a percentage of the population higher than 15%).[12]
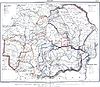
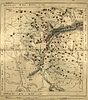
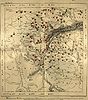
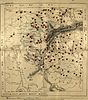
- Romanian vocabulary in Central Serbia. Research by Gustav Weigand:
-
The extent of Romanian
-
The extent of the Banatian dialect in central Serbia
Religion
The Romanian Orthodox Church, Malajnica, built in 2004, is the first Romanian church in eastern Serbia in 170 years, during which time Romanians in Timoc were not allowed to hear liturgical services in their native language.[35][36][37] Most Vlachs of Eastern Serbia are Orthodox Christians who had belonged to the Serbian Orthodox Church since the 19th century. This changed on 24 March 2009, when Serbia recognized the authority of the Romanian Orthodox Church in Valea Timocului and the confessional rights of the Vlachs.[38]
The 2006 Serbian law on religious organizations did not recognize the Romanian Orthodox Church as a traditional church, as it had received permission from the Serbian Church to operate only within Vojvodina, but not in Timočka Krajina.[12] At Malajnica, a "Vlach" priest belonging to the Romanian Orthodox Church encountered deliberately-raised administrative barriers when he attempted to build a church.[12][39] Other Romanian Orthodox churches are planned or under construction in Jasikovo, Cuprija, Bigrenica and Samarinovac. Additionally, a Romanian Orthodox monastery is under construction in Malajnica. The Romanian Orthodox churches in Eastern Central Serbia are subordinated to the Protopresbyteriat Dacia Ripensis with its seat in Negotin. The protopresbyteriat is subordinated to the Romanian Orthodox diocese Dacia Felix with its seat in Vršac.
The relative isolation of the Vlachs has permitted the survival of various pre-Christian religious customs and beliefs that are frowned upon by the Orthodox Church. Vlach magic rituals are well known across modern Serbia. The Vlachs celebrate the Ospăț (hospitium, in Latin), called in Serbian praznic or slava, though its meaning is chtonic (related to the house and farmland) rather than familial.[citation needed] Other Balkan peoples, notably the Serbs, adopted the Christian traditions of the Vlachs. The customs of the Vlachs are very similar to those from Southern Romania (Walachia).[40]
Subgroups
Vlachs are divided into many groups, each speaking their own dialectal variant:
- the Ţărani (Carani) of the Bor, Negotin and Zaječar regions are closer to Oltenia (Lesser Walachia) in their speech and music. The Ţărani have the saying "Nu dau un leu pe el" (He's not worth even a leu). The reference to "leu" (lion) as currency most likely goes back to the 17th century when the Dutch-issued daalder (leeuwendaalder) bearing the image of a lion was in circulation in the Romanian principalities and elsewhere in the Ottoman Empire whose own currency was habitually being debased by the government. In the Romanian principalities, as well as in Bulgaria, the leeuwendaalder (in Romanian and Bulgarian leu and lev, respectively) came to symbolize a strong currency. Indeed on gaining independence in the 19th century both countries adopted this name for their new currencies. Since newly independent Serbia named its currency (the dinar) after the Roman denarius, the reference to the leu among the Ţărani is an indication of their connection to, if not origin in, what is now Romania.
- the Ungureni or Ungureani (Ungurjani) of Homolje are related to the Romanians of Banat and Transylvania, since Ungureni (compare with the word "Hungarians") is a term used by the Romanians of Wallachia to refer to their kin who once lived in provinces formerly part of the Kingdom of Hungary. The connection is evident not only in vocabulary, but also in the similarities of dialectal phonology and folk music motifs, as well as in sayings such as "Ducă-se pe Mureş" (May the Mureş take him/it away), a reference to the Transylvanian river.
- Ungureni Munteni (Ungurjani-Munćani), meaning: "the ungureni from the mountains"
- Bufani are immigrants from Lesser Walachia (Oltenia).
There has been considerable intermixing between the Ungureni and Ţărani so that a dialect has evolved sharing peculiarities of both regions. There is also a population of Vlachophone (Vlach-speaking) Romani centered around the village of Lukovo, as well as a few Aromanian families who live in Knjaževac, but both are tiny migrant groups.
Population
In the 2002 census 40,054 people in Serbia declared themselves ethnic Vlachs, and 54,818 people declared themselves speakers of the Vlach language.[41] The Vlachs of Serbia are recognized as a minority, like the Romanians of Serbia, who number 34,576 according to the 2002 census. On the census, the Vlachs declared themselves either as Serbs, Vlachs or Romanians. Therefore, the "real" number of people of Vlach origin could be much greater than the number of recorded Vlachs, both due to mixed marriages with Serbs and also Serbian national feeling among some Vlachs.
Historical population



The following numbers from census data suggest the possible number of Vlachs:
- 1816: 97,215 Romanians (10% of Serbia's population.)[42]
- 1856: 104,343 Romanians[43]
- 1859: 122,593 Romanians
- 1866: 127,545 Romanians (10.5% of Serbia's population)[44]
- 1884: 149,713 Romanians
- 1890: 143,684 Romanians
- 1895: 159,000 Romanians (6.4% of Serbia's population)[45]
- 1921: 159,549 Romanians/Cincars by mother tongue in Yugoslavia
- 1931: 57,000 Romanians-Vlachs by mother tongue were recorded in Eastern Serbia (52,635 in the Morava Banovina and the rest in southern parts of Danube Banovina, south of the Danube).
- 1961: 1,330 Vlachs
- 1981: 135,000 people declared Vlach as their mother language (population figure given for the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia)[46]
- 2002: 40,054 declared Vlachs; 54,818 people declared Vlach as their mother language (population figures given for entire Serbia); 39,953 declared Vlachs, 54,726 people declared Vlach as their mother language (population figures given for Central Serbia only)[41]
- 2011: 35,330 declared Vlachs; 29,332 declared Romanians (figures include the entire population of Serbia)[3]
The Vlach (Romanian) population of Central Serbia is concentrated mostly in the region bordered by the Morava River (west), Danube River (north) and Timok River (south-east). See also: List of settlements in Serbia inhabited by Vlachs.
According to some Romanian and Western European organizations, around 250,000 speakers of Romanian live in eastern Serbia.[4][dead link][5]
Identity
The term Vlach is the English transcription of the Serbian term for this group (Vlasi), while Roumanians or Romanians is the English transcription of its Romanian counterpart (român/rumân).[47][48]
Despite their recognition as a separate ethnic group by the Serbian government, Vlachs are cognate to Romanians in the cultural and linguistic sense. Some Romanians, as well as international linguists and anthropologists, consider Serbia's Vlachs to be a subgroup of Romanians. Additionally, the Movement of Romanians-Vlachs in Serbia, which represents some Vlachs, has called for the recognition of the Vlachs as a Romanian national minority, giving them rights similar to those of the Romanians of Vojvodina. However, the results of the last census showed that most Vlachs of Eastern Serbia opted for the Serbian exonym vlasi (= Vlachs) rather than rumuni (= Romanians).[41] As a result of serbianization, most Vlachs declared themselves to be "Serbs" on censusus taken by Communist Yugoslavia, but the number of those who preferred to declare themselves as Vlachs or Romanians significantly increased from 1991 (16,539 declared vlasi and 42 declared rumuni) to 2001 (39,953 declared vlasi and 4,157 declared rumuni).
Romania has given modest financial support to the Vlachs in Serbia for the preservation of their culture and language, since at present the Vlachs' language is not recognized officially in any localities where they form a majority, there is no education in their mother tongue, and there is no Vlach media or education funded by the Serbian state. There are also no church services in Vlach. Until very recently in the regions populated by Vlachs the official policy of the Serbian Orthodox church opposed the giving of non-Serbian baptismal names.
On the other hand, some Vlachs consider themselves to be simply Serbs that speak the Vlach language.[citation needed]
Vlach is commonly used as a historical umbrella term for all Latin peoples in Southeastern Europe (Romanians proper or Daco-Romanians, Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians). After the foundation of the Romanian state in the 19th century, Romanians living in the Romanian Old Kingdom and in Austria-Hungary were only seldom called "Vlachs" by foreigners, the use of the exonym "Romanians" was encouraged even by officials, and the Romanian population ceased to use the exonym "Vlach" for their own designation. Only in the Serbian and Bulgarian Kingdom, where the officials did not encourage the population to use the modern exonym "Romanian", was the old designation "Vlach" retained, but the term "Romanian" was used in statistical reports (but only up to the Interwar period, when the designation "Romanian" was changed into "Vlach").[49] For this reason, the Romanians of Vojvodina (hence those who lived in Austria-Hungary) today prefer to use the modern exonym "Romanian", while those of Central Serbia still use the ancient exonym "Vlach". However, both groups use the endonym "Romanians", calling their language "Romanian" (română or rumână).[50][51]
In some notes of the government of Serbia, officials recognise that "certainly members of this population have similar characteristics with Romanians, and the language and folklore ride to their Romanian origin". The representatives of the Vlach minority sustain their Romanian origin.[52]
Notable Vlachs
- Bojan Aleksandrovic (Boian Alexandrovici), the Romanian priest who in 2004 successfully managed to build the first Romanian Orthodox Church in eastern Serbia in the last two centuries.[53][54]
- Zoran Lilić, the president of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia between 1993 and 1997.[citation needed]
- Branko Olar, one of the best known singers of Romanian folklore from Eastern Serbia, originating from the village of Slatina near Bor
- Staniša Paunović, a well-known Romanian folklore singer, originating from Negotin, from Eastern Serbia
See also
- Romanians of Serbia
- Romanians in Bulgaria
- History of the term Vlach
- Thraco-Roman
- Eastern Romance substratum
- Romanian language
- Origin of the Romanians
- Legacy of the Roman Empire
- The Balkan language area
- Romance languages
References
- ^ Folk Dress in Europe and Anatolia: Beliefs about Protection and Fertility - Google Boeken
- ^ "Odluka o promeni sedišta". www.vdss-petrovac.com. www.vdss-petrovac.com. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ a b http://media.popis2011.stat.rs/2011/prvi_rezultati.pdf Serbian Preliminary 2011 Census Results
- ^ a b [1][dead link]
- ^ a b "Romanian". Ethnologue. 1999-02-19. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
- ^ Assembly, Council of Europe: Parliamentary (2008-10-23). "Documents: Working Papers, 2008 Ordinary Session (second Part), 14-18 April 2008, Vol. 3: Documents 11464, 11471, 11513-11539". ISBN 9789287164438.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Istorija postojanja Vlaha". Nacionalni savet Vlaha. Nacionalni savet Vlaha. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ Herrmann, J. "The situation of national minorities in Vojvodina and of the Romanian ethnic minority in Serbia". Parliamentary Assembly's Documents. Council of Europe. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
- ^ Account Suspended
- ^ Account Suspended
- ^ C. Constante, Anton Galopenția (1943). Românii din Timoc: Românii dinitre Dunăre, Timoc și Morava. p. 50.
Apoi, Valahii din Serbia, sunt harnici, muncitori, economi şi de mare dârzenie în privinţa portului şi a limbei.
- ^ a b c d "The situation of national minorities in Vojvodina and of the Romanian ethnic minority in Serbia", at the Council of Europe, 14 February 2008
- ^ Adevărul, November 6, 2002: Prin acordul privind minoritatile, semnat, luni, la Belgrad, de catre presedintii Ion Iliescu si Voislav Kostunita, statul iugoslav recunoaste dreptul apartenentei la minoritatea romaneasca din Iugoslavia al celor aproape 120.000 de vlahi (cifra neoficiala), care traiesc in Valea Timocului, in Serbia de Rasarit. Reprezentantii romanilor din Iugoslavia, profesori, ziaristi, scriitori, i-au multumit, ieri, la Pancevo, sefului statului pentru aceasta intelegere cu guvernul de la Belgrad. Acordul este considerat de importanta istorica pentru romanii din Valea Timocului, care, din timpul lui Iosip Broz Tito, traiesc fara drept la invatamant si viata religioasa in limba materna, practic nerecunoscuti ca etnie. "Nu vom face ca fostul regim, sa numim noi care sunt minoritatile nationale sau sa stergem cu guma alte minoritati", a spus, ieri, Rasim Ljajic, ministrul sarb pentru minoritati, la intalnirea de la Pancevo a presedintelui cu romanii din Iugoslavia. Deocamdata, statul iugoslav nu a recunoscut prin lege statutul vlahilor de pe Valea Timocului, insa de-acum va acorda acestora dreptul la optiunea etnica, va permite, in decembrie, constituirea Consiliului Reprezentantilor Romani si va participa in Comisia mixta romano-iugoslava la monitorizarea problemelor minoritatilor sarba si romana din cele doua state. In Iugoslavia traiesc cateva sute de mii de romani. Presedintele Ion Iliescu s-a angajat, ieri, pentru o politica mai activa privind romanii din afara granitelor: "Avem mari datorii fata de romanii care traiesc in afara granitelor. Autocritic vorbind, nu ne-am facut intotdeauna datoria. De dragul de a nu afecta relatiile noastre cu vecinii, am fost mai retinuti, mai prudenti in a sustine cauza romanilor din statele vecine. (...) Ungurii ne dau lectii din acest punct de vedere", a spus presedintele, precizand ca romanii trebuie sa-si apere cauza "pe baza de buna intelegere".
- ^ Curierul Naţional, 25 ianuarie 2003: Chiar si acordul dintre presedintii Ion Iliescu si Voislav Kostunita, semnat la sfarsitul anului trecut, nu este respectat, in ceea ce priveste minoritatile, deoarece locuitorii din Valea Timocului, numiti vlahi, nu sunt recunoscuti ca minoritari, ci doar „grup etnic“.
- ^ Parliamentary Assembly, 28 April 2005: Deeply concerned over the cultural situation of the so-called “Vlach” Romanians dwelling in 154 ethnic Romanian localities 48 localities of mixed ethnic make-up between the Danube, Timok and Morava Rivers who since 1833 have been unable to enjoy ethnic rights in schools and churches
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ B92 - Vesti - Rumunija će blokirati kandidaturu?
- ^ Власи оптужују Србију за асимилацију - Правда
- ^ a b Драгојевић: Власи нису Румуни : Тема дана : ПОЛИТИКА
- ^ Falşi vlahi folosiţi împotriva românilor | adevarul.ro
- ^ B92 - Prenosimo - Ne gurajte probleme pod tepih
- ^ B92 - Vesti - Vlasi (ni)su obespravljeni u Srbiji
- ^ B92 - Vesti - Sve je rešeno, Srbiji kandidatura
- ^ B92 - Vesti - Basesku: "Rumunski problem" naduvan
- ^ Alaric Watson, Aurelian and the Third Century, Routlege, 1999.
- ^ Watson, Alaric (2004-01-14). "Aurelian and the Third Century". ISBN 9780203167809.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ William Rosen, Justinian's Flea: Plague, Empire, and the Birth of Europe, Viking Adult, 2007.
- ^ Wolff, Robert Lee Wolff, The Second Bulgarian Empire: Its Origin and History to 1204, Speculum Volume 24, Issue 2, 1949.
- ^ a b c Template:Hr iconZef Mirdita, Vlasi u historiografiji, Hrvatski institut za povijest, Zagreb 2004.
- ^ a b Noel Malcolm, Kosovo, A short History, University Press, NY, 1999.
- ^ Template:De icon Felix Kanitz, Serbien, Leipzig, 1868.
- ^ Noel Malcolm, Bosnia: A short History, University Press, NY, 1994.
- ^ Template:Sr icon Kosta Jovanovic, Negotinska Krajina i Kljuc, Belgrade, 1940
- ^ Aspects of the Balkans: continuity and change. Contributions to the International Balkan Conference held at UCLA, October 23–28, 1969
- ^ Xenophobic actions against Timoc Romanians
- ^ Drasko Djenovic (9 September 2005). "SERBIA: Romanian priest to pay for official destruction of his church". F18News. Forum 18 News Service. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ "Haiducul credintei din Valea Timocului, Boian Alexandrovici, decorat de presedintele Basescu" Template:Ro icon
- ^ Biserica Română din Timoc a fost recunoscută de către Curtea Supremă de Justiţie a Serbiei - Ziua de Vest
- ^ "Biserica românească din Malainiţa ameninţată din nou", BBC Romanian, 16 September 2005
- ^ [3][dead link]
- ^ a b c Template:Sr icon Template:PDFlink, p. 2 and Template:PDFlink, p. 12
- ^ Template:Ro icon V. Arion; Vasile Pârvan; G. Vâlsan; Pericle Papahagi; G. Bogdan-Duică. România şi popoarele balcanice (1913). Tipografia Românească. Bucureşti, p. 22
- ^ Guillaume Lejean, Ethnographie de la Turquie d'Europe, Gotha. Justus Perthes 1861
- ^ Geographisches Handbuch zu Andrees Handatlas (Leipzig und Bielefeld, 1882): 1866 zählte man 1.058.189 Serben, 127.545 Rumänen, 24.607 Zigeuner, 2589 Deutsche und 3256 andere.
- ^ Geographisches Handbuch zu Andrees Handatlas 1902: Fast die ganze Bevölkerung, über 2 Mill, besteht aus Serben, außerdem gab es, nach der Zählung von 1895, 159.000 Rumänen und 46.000 Zigeuner
- ^ Template:Sr icon Ranko Bugarski, Jezici, Beograd, 1996.
- ^ Ziua.net
- ^ Interview with Predrag Balašević, president of the Romanian/Vlach Democratic Party of Serbia: "We all know that we call ourselves in Romanian Romanians and in Serbian Vlachs."
- ^ [4] Serbian/Romanian. The Helsinki Committee for Human Rights in Serbia. The Vlachs/Romanians or the Romanians of Eastern Serbia and the "Vlach/Romanian question". Bor 2000/2001/2002.
- ^ Website of the Federaţia Rumânilor din Serbie
- ^ Reportaj printre românii din estul Serbiei
- ^ Viorel Dolha, Totul despre românii din Timoc (All about Romanians in Timoc)
- ^ "SERBIA: Romanian priest to pay for official destruction of his church"
- ^ Template:Ro "Haiducul credintei din Valea Timocului, Boian Alexandrovici, decorat de presedintele Basescu"
- National Council of Vlachs (in Serbia), DEKLARACIJA NACIONALNOG SAVETA VLAHA O OSTVARIVANJU I UNAPREĐENJU PRAVA VLAŠKE NACIONALNE ZAJEDNICE, [Declaration of the National Council] (06. 11. 2010) by President Rаdišа Drаgojević.
- M. V. Fifor. Assimilation or Acculturalisation: Creating Identities in the New Europe. The case of Vlachs in Serbia. Published in Cultural Identity and Ethnicity in Central Europe, Jagellonian University, Cracow 2000
- Vlasi... ko su, sta su i odakle poticu ? (Serbian language)
- Viorel Dolha - Totul despre românii din Timoc (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) (Romanian language)
External links
- History of the Romanians-Vlachs of Serbia
- Romanians-Vlachs of Serbia online portal
- Information about the Romanians-Vlachs of Serbia
- first online forum of the Romanians-Vlachs of Serbia
- Romanians-Vlachs of Serbia
- The Vlach (Roumanian) Federation of Serbia
- Museum of Majdanpek
- MP3 recordings of Vlach speech
- Romanian Ethnogenesis
- Maps of Vlachs in north-east Serbia
- The Vlachs in Yugoslavia and their magic
- The Vlach gardens of Eastern Serbia
- Report on the State of Human Rights of Rumanians and Vlachs in Serbia
- History of the Romanians living on the South of the Danube (Romanian/Serbian)
- Community of Vlachs of Serbia/Zajednica Vlaha Srbije
- The situation of national minorities in Vojvodina and of the Romanian ethnic minority in Serbia, 2008 report from the Council of Europe (archive version)