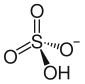
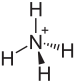Ammonium bisulfate
| |||

| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.332 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| (NH4)HSO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 115.11 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.78 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 147 °C (297 °F; 420 K) | ||
| Very soluble | |||
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in methanol insoluble in acetone | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Ammonium thiosulfate Ammonium sulfite Ammonium sulfate Ammonium persulfate | ||
Other cations
|
Sodium bisulfate Potassium bisulfate | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ammonium bisulfate, also known as ammonium hydrogen sulfate, is a white, crystalline solid with the formula (NH4)HSO4. This salt is the product of the half-neutralization of sulfuric acid by ammonia.
Production
It is commonly collected as a byproduct of the "acetone cyanohydrin route" to the commodity chemical methyl methacrylate.[1]
It can also be obtained by hydrolysis of sulfamic acid in aqueous solution, which produces the salt in high purity:
- H3NSO3 + H2O → [NH4]+[HSO4]−
It also arises by the thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate:
- (NH4)2SO4 → (NH4)HSO4 + NH3
Applications
It can be further neutralized with ammonia to form ammonium sulfate, a valuable fertilizer. It can be used as a weaker alternative to sulfuric acid, although sodium bisulfate is much more common.
Natural occurrence
A related compound of the (NH4)3H(SO4)2 formula, occurs as the rare mineral letovicite, known from coal fire environments.[2][3]
References
- ^ William Bauer, Jr. "Methacrylic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_441.
- ^ "Letovicite".
- ^ "List of Minerals". 21 March 2011.