Glyptemys
| Glyptemys | |
|---|---|

| |
| Glyptemys muhlenbergii | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Superfamily: | Testudinoidea |
| Family: | Emydidae |
| Subfamily: | Emydinae |
| Genus: | Glyptemys Agassiz, 1857 |
| Species | |
Glyptemys is a genus of turtles in the family Emydidae. It comprises two species, the bog turtle and wood turtle, both of which are endemic to North America. Until 2001, these turtles were considered members of the genus Clemmys, which currently has one member, the spotted turtle.
Full grown, these turtles grow to between 8.9 and 20 cm (3.5 and 7.9 in). These turtles are semiaquatic, although this varies based on season. Their morphological characteristics make them unique from other species and unique from each other.
Glyptemys turtles prefer slow moving streams and ponds, and feed on insects, plant matter, small invertebrates, and carrion. These turtles are protected throughout their range. All species in Glyptemys are considered endangered.
Taxonomy
| Portion of family Emydidae[2] |
| In the past, the taxonomic classification of these turtles looked very different however, the current system has Clemmys as a monotypic genus and Glyptemys, Terrepene, and Emys as three distinct genera (the species Emys trinacris is not shown).[3] |
The taxonomic classification of Emydidae turtles has been eventful and many schools of thought are given about how the different genera and species should be arranged.[3]
Before 2001, the bog and wood turtles were members of the genus Clemmys, but they were moved to a newly created genus, Glyptemys, after further morphological and genetic analyses revealed they were much closer relatives to each other than to the spotted turtle.[4] The bog turtle and wood turtle have similar genetic makeups that are marginally different from that of the spotted turtle, the only current member of the genus Clemmys.[5] The western pond turtle was also a former member of Clemmys, but it was recently moved to the genus Actinemys, of which it is now the only member.[6] Both Glyptemys turtles have karyotypes of 50 chromosomes.[7][8]
The several common names for the bog include mud turtle, marsh turtle, yellowhead, and snapper[9] while the wood may be referred to as the sculptured tortoise, red-legged tortoise, or redleg.[4]
Description
Glyptemys turtles are small to medium in size:[4][10] the bog turtle males grow to be 9.4 cm (3.7 in) and females 8.9 cm (3.5 in)[10] while wood turtles of either gender reach 14 to 20 cm (5.5 to 7.9 in) in length.[11] Bog turtles weigh 110 g (3.9 oz)[12] and wood turtles average 1 kg (2.2 lb) at maturity.[13] The bog can be recognized by small, bright blotches on each side of its neck [9] and the wood by its dark gray to black head and bright orange coloration on its ventral surfaces.[4]
The wood turtle exhibits genetic sex determination, in contrast to the temperature-dependent sex determination of most turtles; the method of sex determination for the bog turtle is unknown.[14]
Distribution and habitat
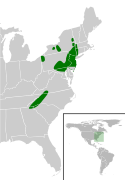
Glyptemys turtles are endemic to eastern North America. Their collective range extends from Nova Scotia south to Georgia and from Nova Scotia west to Minnesota.[7][15] These turtles are semiaquatic and are commonly found in bogs, fens,[16] and small streams which have soft yet compacted, sandy bottoms.[17]
Evolutionary history
During the last post-Pleistocene ice age, Glyptemys turtles were forced south by encroaching glaciers from the north. After glaciation, some turtle colonies relocated to their original northern range, while others continued to live in the new, southern range. Some fossil remains from the Rancholabrean period (300,000 to 11,000 years BP) have been found in Georgia and Tennessee, areas farther south than the turtles' current range.[1][18]
Ecology and behavior
These turtles are diurnal and become active in the early morning.[1][19] During extremely cold days, they each may spend time under water, while the bog has been known to also seek dense underbrush or mud in which to bury itself.[20] Excessively hot days sometimes causes these turtles to estivate.[17][21]
Conservation
Both species are protected throughout their ranges. The bog turtle is considered critically endangered by the IUCN,[22] while the wood turtle is labeled as endangered, a less dire rating.[23]
For more information on species conservation, see the individual species pages of the bog turtle and the wood turtle.
References
- Notes
- Footnotes
- ^ a b c Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 265.
- ^ Bickham et al. 2007, p. 81.
- ^ a b Bickham et al. 2007, p. 82.
- ^ a b c d Bowen & Gillingham 2004, p. 5.
- ^ Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 262.
- ^ Bickham et al. 2007, p. 74.
- ^ a b Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 251.
- ^ Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 269.
- ^ a b Bloomer 2004, pp. 1–2.
- ^ a b Bloomer 2004, p. 2.
- ^ "Wood Turtle Glyptemys insculpta" (PDF). nhesp.org. Natural Heritage & Endangered Species Program. 2007. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-06-08. Retrieved 2010-05-11.
- ^ "Bog Turtle". Department of Environmental Protection. State of Connecticut. 2002. Retrieved 2009-09-19.
- ^ "Assessment and Update Status Report on the Wood Turtle Glyptemys insculpta in Canada" (PDF). Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada. 2007. p. iv. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-12. Retrieved 2010-05-16.
- ^ Badenhorst, Daleen; Stanyon, Roscoe; Engstrom, Tag; Valenzuela, Nicole (2013-04-01). "A ZZ/ZW microchromosome system in the spiny softshell turtle, Apalone spinifera, reveals an intriguing sex chromosome conservation in Trionychidae". Chromosome Research. 21 (2): 137–147. doi:10.1007/s10577-013-9343-2. ISSN 1573-6849. PMID 23512312. S2CID 254379278.
- ^ Shiels 2007, p. 24.
- ^ Walton 2006, p. 26.
- ^ a b Bowen & Gillingham 2004, p. 4.
- ^ Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 250.
- ^ Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 253.
- ^ "Bog Turtle – Fact Sheet" (PDF). North Carolina Wildlife Resource Commission. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-04. Retrieved 2009-09-19.
- ^ Ernst & Lovich 2009, p. 266.
- ^ "Glyptemys muhlenbergii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010-11-27. 2010-11-27. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- ^ "Glyptemys insculpta". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010-11-27. 2010-11-27. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- Bibliography
- Bickham, John; Parham, James; Philippen, Hans-Dieter; Rhodin, Andres; Shaffer, Bradley; Spinks, Phillip; Van Dijk, Peter Paul (2007). "Turtle Taxonomy: Methodology, Recommendations, and Guidelines" (PDF). Chelonian Research Monographs: 73–84. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-06-10. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- Bloomer, Tom J. (2004) [1970]. The Bog Turtle, Glyptemys muhlenbergii... A Natural History (PDF). Gainesville, Florida: LongWing Press. OCLC 57994322. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- Bowen, Kenneth; Gillingham, James C. (2004). "R9 Species Conservation Assessment for Wood Turtle – Glyptemys insculpta (LeConte, 1830)" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- Ernst, C. H.; Lovich, J. E. (2009). "Glyptemys Agassiz, 1857: Sculpted Turtles". Turtles of the United States and Canada (2nd ed.). JHU Press. pp. 250–271. ISBN 978-0-8018-9121-2.
- Shiels, Andrew L. (2007). "Bog Turtles Slipping Away" (PDF). Pennsylvania Angler & Boater. Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission. pp. 23–26. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-28. Retrieved 2010-05-29.
- Walton, Elizabeth M. (2006). "II. Literature Review". Using Remote Sensing and Geographical Information Science to Predict and Delineate Critical Habitat for the Bog Turtle, Glyptemys muhlenbergii (PDF) (M.A. thesis). University of North Carolina at Greensboro. pp. 5–32. Retrieved 2010-04-09.
Further reading
- "Bog Turtle". National Resources Conservation Service. Archived from the original on 2017-05-03. Retrieved 2020-08-08.