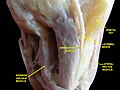
Inferior rectus muscle
| Inferior rectus | |
|---|---|
 The inferior rectus muscle, is shown in this superior view of the eye, along with its axis of rotation. The other muscle is the superior oblique muscle, which angles around the trochlea. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | annulus of Zinn at the orbital apex |
| Insertion | 6.5 mm inferior to the limbus |
| Nerve | inferior branch of oculomotor nerve |
| Actions | depression and adduction |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus rectus inferior bulbi |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.011 |
| TA2 | 2043 |
| FMA | 49036 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The inferior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit.
Structure
Innervation
As with most of the muscles of the orbit, it is innervated by the inferior division of oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III).
Function
It depresses, adducts, and helps extort the eye.
The inferior rectus muscle is the only muscle that is capable of depressing the pupil when it is in a fully abducted position.[1]
Additional images
This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. |
-
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
-
The right eye in sagittal section, showing the fascia bulbi (semidiagrammatic).
-
Inferior rectus muscle
-
Inferior rectus muscle
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
References
- ^ "Eye Theory". Cim.ucdavis.edu. Archived from the original on 2014-05-27. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 29:01-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbit5)
- Diagram at mun.ca