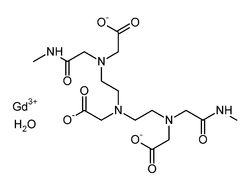
Gadodiamide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2-[bis[2-(carboxylatomethyl-(methylcarbamoylmethyl)amino)ethyl]amino]acetate; gadolinium(+3) cation |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | i.v. |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | negligible |
| Metabolism | not metabolized |
| Elimination half-life | 77.8 minutes |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H28GdN5O9 |
| Molar mass | 591.68 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Gadodiamide is a gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent, used in MR imaging procedures to assist in the visualization of blood vessels. It is commonly marketed under the trade name Omniscan.
Uses

Gadodiamide is a drug i.e contrast medium used for cranial and spinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and for general MRI of the body after intravenous administration. The product provides contrast enhancement and facilitates visualisation of abnormal structures or lesions in various parts of the body including the central nervous system (CNS). It does not cross an intact blood brain barrier but might give enhancement in pathological conditions.
Adverse effects
It has been associated with a toxic reaction known as nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in some people with severe kidney problems.[2] No cases have been seen in people with normal kidney function.[3]
A 2015 study found trace amounts of gadolinium deposited in the brain tissue of people that had received gadodiamide.[4] This is of unknown significance.[4]
In the United States there are recommendations that one does not need to stop or altering breastfeeding while in Europe it is recommended that a mother throw out 24 hours of breast milk.[5]
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Ibrahim MA, Hazhirkarzar B, Dublin AB (January 2018). "Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Gadolinium". StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29494094.
- ^ Canavese C, Mereu MC, Aime S, Lazzarich E, Fenoglio R, Quaglia M, Stratta P (2008). "Gadolinium-associated nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: the need for nephrologists' awareness". Journal of Nephrology. 21 (3): 324–36. PMID 18587720.
- ^ a b Anderson, Pauline (2015-03-26). "Gadolinium Found in Brain Tissue". Medscape. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "Gadodiamide". Drugs and Lactation Database. 2006. PMID 30000472.
