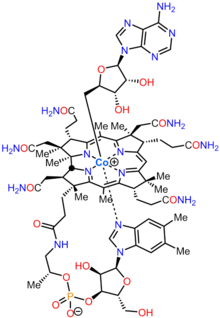
Adenosylcobalamin
Appearance
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.192 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C72H100CoN18O17P |
| Molar mass | 1579.608 g·mol−1 |
| |
| | |
Adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), also known as coenzyme B12, cobamamide, and dibencozide, is, along with methylcobalamin (MeCbl), one of the biologically active forms of vitamin B12.[1]
Adenosylcobalamin participates as a cofactor in radical-mediated 1,2-carbon skeleton rearrangements. These processes require the formation of the deoxyadenosyl radical through homolytic dissociation of the carbon-cobalt bond. This bond is exceptionally weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 31 kcal/mol, which is further lowered in the chemical environment of an enzyme active site.[2] An enzyme that uses adenosylcobalamin as a cofactor is methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MCM).
See also
References
- ^ Marsh EN, Meléndez GD (November 2012). "Adenosylcobalamin enzymes: theory and experiment begin to converge". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics. 1824 (11): 1154–64. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.03.012. PMC 3580769. PMID 22516318.
- ^ Kräutler B, Arigoni D, Golding BT (1998). Vitamin B12 and B12-proteins : lectures presented at the 4th European Symposium on Vitamin B12 and B12-Proteins. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 9783527612192. OCLC 212131311.
