List of mephitids

Mephitidae is a family of mammals in the order Carnivora, which comprises the skunks and stink badgers. A member of this family is called a mephitid. The skunks of the family are widespread across the Americas, while the stink badgers are in the Greater Sunda Islands of southeast Asia. Species inhabit a variety of habitats, though typically grassland, forest, and shrubland. Most mephitids are 20–50 cm (8–20 in) long, plus a 10–40 cm (4–16 in) tail, though the pygmy spotted skunk can be as small as 11 cm (4 in) plus a 7 cm (3 in) tail, and some striped skunks can be up to 82 cm (32 in) plus a 40 cm (16 in) tail. No estimates have been made for overall population sizes of any of the species, but two species are classified as vulnerable. Mephetids in general are not domesticated, though skunks are sometimes kept as pets.[1]
The twelve species of Mephitidae are split into four genera: the monotypic Conepatus, hog-nosed skunks; Mephitis, skunks; Mydaus, stink badgers; and Spilogale, spotted skunks. Mephitidae was traditionally a clade within the Mustelidae family, with the stink badgers combined with other badgers within the Melinae genus, but more recent genetic evidence resulted in the consensus to separate Mephitidae into its own family.[2] Extinct species have also been placed into all of the extant genera besides Mydaus, as well as 9 extinct genera; 26 extinct Mephitidae species have been found, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (0 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (2 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (0 species) |
| LC | Least concern (10 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the mephetid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN red list for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†". Population figures are rounded to the nearest hundred.
Classification
The family Mephitidae consists of twelve extant species belonging to four genera and divided into dozens of extant subspecies. It is not divided into subfamilies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species.
- Genus Conepatus (hog-nosed skunks): four species
- Genus Mephitis (skunks): two species
- Genus Mydaus: (stink badgers): two species
- Genus Spilogale: (spotted skunks): four species
Mephitids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis.
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American hog-nosed skunk | C. leuconotus Lichtenstein, 1832 Three subspecies
|
Southern North America and northern Central America
|
Size: 34–51 cm (13–20 in) long, plus 12–41 cm (5–16 in) tail[3] Habitat: Rocky areas, forest, grassland, and desert[4] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as fruit and small vertebrates[4] |
LC
|
| Humboldt's hog-nosed skunk | C. humboldtii Gray, 1837 Three subspecies
|
Southern tip of South America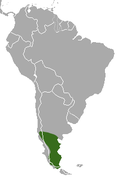
|
Size: 32–45 cm (13–18 in) long, plus 15–18 cm (6–7 in) tail[5] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, savanna, and rocky areas[6] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as small mammals, shrubs, and fruit[6] |
LC
|
| Molina's hog-nosed skunk | C. chinga Molina, 1792 Seven subspecies
|
Southern South America
|
Size: 20–49 cm (8–19 in) long, plus 13–29 cm (5–11 in) tail[3] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, and savanna[7] Diet: Omnivorous; primarily eats invertebrates, rodents, small reptiles, and eggs[3][7] |
LC
|
| Striped hog-nosed skunk | C. semistriatus Boddaert, 1785 Six subspecies
|
Northern and eastern South America and Central America
|
Size: 33–50 cm (13–20 in) long, plus 13–31 cm (5–12 in) tail[3] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, and forest[8] Diet: Primarily eats insects, lizards, and birds[8] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hooded skunk | M. macroura Lichtenstein, 1832 Four subspecies
|
Mexico and Central America
|
Size: 19–30 cm (7–12 in) long, plus 35–40 cm (14–16 in) tail[9] Habitat: Desert, shrubland, rocky areas, grassland, and forest[10] Diet: Primarily eats insects, fruit, small vertebrates, and bird eggs[10] |
LC
|
| Striped skunk | M. mephitis Schreber, 1776 Thirteen subspecies
|
North America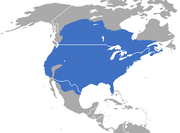
|
Size: 46–82 cm (18–32 in) long, plus 17–40 cm (7–16 in) tail[11] Habitat: Shrubland, savanna, forest, and grassland[12] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as small mammals, birds, and vegetation[12] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palawan stink badger | M. marchei Huet, 1887 |
Western Philippines
|
Size: 32–49 cm (13–19 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0–2 in) tail[3] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and introduced vegetation[13] Diet: Primarily eats worms and arthropods[13] |
LC
|
| Sunda stink badger | M. javanensis Desmarest, 1820 Three subspecies
|
Indonesia and Malaysia
|
Size: 37–51 cm (15–20 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail[14] Habitat: Grassland, forest, and shrubland[15] Diet: Primarily eats birds' eggs, carrion, insects, worms, and plants[15] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern spotted skunk | S. putorius Linnaeus, 1758 Three subspecies
|
Eastern United States
|
Size: 11–35 cm (4–14 in) long, plus 7–22 cm (3–9 in) tail[16] Habitat: Forest, rocky areas, shrubland, and grassland[17] Diet: Omnivorous; primarily eats insects, as well as small mammals and birds[17] |
VU
|
| Pygmy spotted skunk
|
S. pygmaea Thomas, 1897 Three subspecies
|
West coast of Mexico
|
Size: 11–35 cm (4–14 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail[18] Habitat: Shrubland, marine coastal/supratidal, and forest[19] Diet: Primarily eats insects, spiders, birds, eggs, small mammals, fruit, and seeds[19] |
VU
|
| Southern spotted skunk | S. angustifrons Howell, 1902 Five subspecies
|
Mexico and Central America
|
Size: 20–25 cm (8–10 in) long, plus 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[3] Habitat: Forest and rocky areas[20] Diet: Omnivorous; primarily eats insects, small mammals, fruit, grain, birds, and bird eggs[20] |
LC
|
| Western spotted skunk | S. gracilis Merriam, 1890 Seven subspecies
|
Western North America
|
Size: 24–37 cm (9–15 in) long, plus 8–21 cm (3–8 in) tail[3] Habitat: Inland wetlands, grassland, shrubland, rocky areas, savanna, and forest[21] Diet: Primarily eats insects, small mammals, carrion, berries, and fruit[21] |
LC
|
Prehistoric mephitids
In addition to extant mephitids, a number of prehistoric species have been discovered and classified as a part of Mephitidae. In addition to being placed within the extant genera Conepatus, Mephitis, and Spilogale, they have been categorized within nine extinct genera. There is no generally accepted classification of extinct mephitid species. The species listed here are based on data from the Paleobiology Database, unless otherwise cited. Where available, the approximate time period the species was extant is given in millions of years before the present (Mya), also based on data from the Paleobiology Database.[22] All listed species are extinct; where a genus or subfamily within Mephitidae comprises only extinct species, it is indicated with a dagger symbol †.
- Genus Brachyopsigale† (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- B. dubius (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- Genus Brachyprotoma† (1.8–0.012 Mya)
- B. obtusata (short-faced skunk) (1.8–0.012 Mya)
- Genus Buisnictis† (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- B. breviramus (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- B. burrowsi (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- B. metabatos (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- B. schoffi (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- Genus Conepatus (11 Mya–present)
- C. robustus (0.13–0.012 Mya)
- C. sanmiguelensis (11–5.3 Mya)
- C. suffocans (2.6–0.78 Mya)
- Genus Martinogale†
- M. alveodens (11–4.9 Mya)
- M. chisoensis (11–4.9 Mya)
- M. faulli (12–5.3 Mya)
- M. nambiana
- Genus Mephitis
- M. cordubensis
- M. orthrostica
- M. rexroadensis (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- Genus Miomephitis†
- M. pilgrimi
- Genus Osmotherium†
- O. spelaeum (1.8–0.3 Mya)
- Genus Palaeomephitis†
- P. steinheimensis[23]
- Genus Pliogale† (14–4.9 Mya)
- P. furlongi (11–4.9 Mya)
- P. manka (14–10 Mya)
- Genus Promephitis†
- Genus Spilogale (4.9 Mya–present)
- S. microdens (4.9–1.8 Mya)
- S. rexroadi (4.9–1.8 Mya)
References
- ^ Johnson-Delaney, C. (October 2014). "Pet Virginia Opossums and Skunks". Journal of Exotic Pet Medicine. Unusual Exotic Pets. 23 (4): 317–326. doi:10.1053/j.jepm.2014.07.011.
- ^ Goswami, Anjali; Friscia, Anthony (2010). Carnivoran Evolution: New Views on Phylogeny, Form and Function. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-521-73586-5.
- ^ a b c d e f g Hunter, Luke (January 8, 2019). Carnivores of the World (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 150–156. ISBN 978-0-691-18295-7.
- ^ a b c Helgen, K. (2016). "Conepatus leuconotus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41632A45210809. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41632A45210809.en.
- ^ Shaw, Weylan (2002). "Conepatus humboldtii". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c Emmons, L.; Helgen, K. (2016). "Conepatus humboldtii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41631A45210677. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41631A45210677.en.
- ^ a b c Emmons, L.; Schiaffini, M.; Schipper, J. (2016). "Conepatus chinga". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41630A45210528. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41630A45210528.en.
- ^ a b c Cuarón, A. D.; Helgen, K.; Reid, F. (2016). "Conepatus semistriatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41633A45210987. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41633A45210987.en.
- ^ Bairos-Novak, Kevin (2014). "Mephitis macroura". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c Cuarón, A. D.; González-Maya, J. F.; Helgen, K.; Reid, F.; Schipper, J.; Dragoo, J. W. (2016). "Mephitis macroura". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41634A45211135. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41634A45211135.en.
- ^ Kiiskila, Jeffrey (2014). "Mephitis mephitis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c Helgen, K.; Reid, F. (2016). "Mephitis mephitis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41635A45211301. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41635A45211301.en.
- ^ a b c Widmann, P. (2015). "Mydaus marchei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T14055A45201420. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T14055A45201420.en.
- ^ Krauskopf, Rachel (2002). "Mydaus javanensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c Wilting, A.; Duckworth, J. W.; Meijaard, E.; Ross, J.; Hearn, A.; Ario, A. (2015). "Mydaus javanensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41628A45209955. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41628A45209955.en.
- ^ Pennington, Stefanie (2002). "Spilogale putorius". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c Gompper, M.; Jachowski, D. (2016). "Spilogale putorius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41636A45211474. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41636A45211474.en.
- ^ Gay, Bradley David (1999). "Spilogale pygmaea". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c Helgen, K.; Cuarón, A. D.; Schipper, J.; González-Maya, J. F. (2016). "Spilogale pygmaea". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41637A45211592. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41637A45211592.en.
- ^ a b c Helgen, K.; Reid, F.; Timm, R. (2016). "Spilogale angustifrons". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136636A45221538. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136636A45221538.en.
- ^ a b c Cuarón, A. D.; Helgen, K.; Reid, F. (2016). "Spilogale gracilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136797A45221721. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136797A45221721.en.
- ^ "Fossilworks: Mephitidae". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ Wolsan, M. (1999). "Oldest mephitine cranium and its implications for the origin of skunks" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 44 (2): 223–230.
- ^ a b Wang, X.; Zhanxiang, Q. (2004). "Late Miocene Promephitis (Carnivora, Mephitidae) from China". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 24 (3): 721–731. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2004)024[0721:LMPCMF]2.0.CO;2.











