Battle of the Boyne
| Battle of the Boyne | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Williamite War in Ireland | |||||||
 Battle of the Boyne between James II and William III, 11 July 1690, Jan van Huchtenburg | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 36,000 | 23,500 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 750 killed and wounded | 1,500 killed and wounded | ||||||
Location within island of Ireland | |||||||
The Battle of the Boyne (Irish: Cath na Bóinne IPA: [ˈkah n̪ˠə ˈbˠoːn̪ʲə]) was a battle in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II of England and Ireland, VII of Scotland, versus those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and James's daughter), had acceded to the Crowns of England and Scotland[b] in 1689. The battle took place across the River Boyne close to the town of Drogheda in the Kingdom of Ireland, modern-day Republic of Ireland, and resulted in a victory for William. This turned the tide in James's failed attempt to regain the British crown and ultimately aided in ensuring the continued Protestant ascendancy in Ireland.
The battle took place on 1 July 1690 O.S. William's forces defeated James's army, which consisted mostly of raw recruits. Although the Williamite War in Ireland continued until October 1691, James fled to France after the Boyne, never to return.
Background
The battle was a major encounter in James's attempt to regain the thrones of England and Scotland, resulting from the Invitation to William and William's wife, Mary, from the 'immortal seven' English peers to take the throne to defend Protestantism. But the conflict had broader and deeper European geopolitical roots, of the League of Augsburg and the Grand Alliance against the expansionist ambitions of Catholic Louis XIV of France, or of the House of Bourbon against the House of Habsburg.[1][2][3][4][5] If the battle is seen as part of the War of the Grand Alliance, Pope Alexander VIII was an ally of William and an enemy to James; the Papal States were part of the Grand Alliance with a shared hostility to the Catholic Louis XIV of France, who at the time was attempting to establish dominance in Europe and to whom James was an ally.[6]
The previous year William had sent the Duke of Schomberg to take charge of the Irish campaign.[7] He was a 75-year-old professional soldier who had accompanied William during the Glorious Revolution. He brought an army of 20,000 men, which arrived at Bangor. Under his command, affairs had remained static and very little had been accomplished, partly because the English troops suffered severely from fever[8] and the army's move south was blocked by Jacobite forces; both sides camped for the winter.[1]


In an Irish context, the war was a sectarian and ethnic conflict, in many ways a re-run of the Irish Confederate Wars of 50 years earlier. For the Jacobites, the war was fought for Irish sovereignty, religious tolerance for Catholicism, and land ownership. The Catholic upper classes had lost or had been forced to exchange almost all their lands after Cromwell's conquest, as well as the right to hold public office, practise their religion, and sit in the Irish Parliament.[9] To these ends, under Richard Talbot, 1st Earl of Tyrconnel, they had raised an army to restore James II after the Glorious Revolution. By 1690, they controlled all of Ireland except for Derry and Enniskillen.[1]
The majority of Irish people were Jacobites and supported James II due to his 1687 Declaration of Indulgence or, as it is also known, the Declaration for the Liberty of Conscience, that granted religious freedom to all denominations in England and Scotland and also due to James II's promise to the Irish Parliament of an eventual right to self-determination.[10][11]
Conversely, for the Williamites in Ireland, the war was about maintaining protestant rule in Ireland. They feared for their lives and their property if James and his Catholic supporters were to rule Ireland, nor did they trust the promise of tolerance, seeing the Declaration of Indulgence as a ploy to re-establish Catholicism as the sole state religion. James had already antagonised English protestants with his actions. In particular, they dreaded a repeat of the Irish Rebellion of 1641, which had been marked by widespread killing. For these reasons, Protestants fought en masse for William of Orange. Many Williamite troops at the Boyne, including their very effective irregular cavalry, were Ulster Protestants, who called themselves "Enniskilliners" and were referred to by contemporaries as "Scots-Irish". These "Enniskilliners" were mostly the descendants of Anglo-Scottish border reivers and large numbers of these reivers had settled around Enniskillen in County Fermanagh.[12][13]
Commanders
The opposing armies in the battle were led by the Roman Catholic King James II of England (VII of Scotland) and Ireland and, opposing him, his nephew and son-in-law, the Protestant King William III ("William of Orange") who had deposed James the previous year. James's supporters controlled much of Ireland and the Irish Parliament.[2][14] James also enjoyed the support of his cousin, Louis XIV, who did not want to see a hostile monarch on the throne of England. Louis sent 6,000 French troops to Ireland to support the Irish Jacobites.[15] William was already Stadtholder of the Netherlands and was able to call on Dutch and allied troops from Europe as well as England and Scotland.[14]
James was a seasoned officer who had proved his bravery when fighting in Europe,[2] notably at the Battle of the Dunes (1658).[16] However, recent historians have suggested that he was prone to panicking under pressure and making rash decisions,[17] which it has been suggested may have been due to poor health associated with the Stuart line.[18][2]
William, although a seasoned commander,[19] had yet to win a major battle. William's success against the French had been reliant upon tactical manoeuvres and good diplomacy rather than force.[19][14] His diplomacy had assembled the League of Augsburg,[20] a multi-national coalition formed to resist French aggression in Europe. From William's point of view, his taking power in England and the ensuing campaign in Ireland was just another front in the war against France in general, and Louis XIV in particular.[21]
James II's subordinate commanders were Richard Talbot, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, who was Lord Deputy of Ireland and James's most powerful supporter in Ireland; and the French general Lauzun.[22] William's commander-in-chief was the Duke of Schomberg. Born in Heidelberg, Germany, Schomberg had fought for a few different countries and had formerly been a Marshal of France, but, being a Huguenot, was compelled to leave France in 1685 because of the revocation of the Edict of Nantes.[23][24]
Armies
The Williamite army at the Boyne was about 36,000 strong, composed of troops from many countries;[25] Only around half of them were British.[26] Around 20,000 troops had been in Ireland since 1689,[27] commanded by Schomberg.[25] William himself had landed in Carrickfergus on 14 June O.S. He met Schomberg at nearby Whitehouse, and then proceeded south through Belfast.[28] Loughbrickland was the rallying point of the scattered divisions of the army.[29][30] He arrived there with another 16,000 in June 1690.[31] On 30 June O.S. William had reached the top of a hill near the southern border of County Louth.[29]
William's troops were generally far better trained and equipped than James's.[25] The best Williamite infantry were from Denmark (7000) and the Netherlands (6000), professional soldiers equipped with the latest flintlock muskets.[1][32] The Danish infantry was commanded by General Ernst von Tettau. There was also a large (3000) contingent of French Huguenot troops fighting with the Williamites.[32] William did not yet have a high opinion of his English and Scottish troops, with the exception of the Ulster Protestant "skirmishers" who had held Derry in the previous year; the English and Scottish troops were felt at this stage to be politically unreliable, since James had been their legitimate monarch up to a year before. Moreover, they had only been raised recently and had seen little action.[33]
James’s flag was erected at the town of Donore, on the opposite side of the river Boyne.[29] The Jacobites were 23,500 strong.[25] James had several regiments of French troops, but most of his manpower was provided by Irish Catholics, with some English and Scottish Jacobites also present. The Jacobites' Irish cavalry, who were recruited from among the dispossessed Irish gentry, proved themselves to be high calibre troops during the course of the battle.[34] However, the Irish infantry, predominantly peasants who had been pressed into service, were not trained soldiers. They had been hastily trained, poorly equipped, and only a minority of them had functional muskets. In fact, some of them carried only farm implements such as scythes at the Boyne.[35] Furthermore, the Jacobite infantry who actually had firearms were all equipped with the obsolete matchlock musket.[1] The French and Irish troops wore a white rallying mark, as a compliment to the Bourbons and to distinguish them from the Williamites.[29]
The battle
William sailed from Hoylake in Cheshire, landing at Carrickfergus, County Antrim on 14 June O.S. and marched south, intending to take Dublin.[citation needed] He was heard to remark that "the place was worth fighting for".[29] James chose to place his line of defence on the River Boyne, around 30 miles (48 km) from Dublin. The Williamites reached the Boyne on 29 June. The day before the battle, William himself had a narrow escape when he was wounded in the shoulder by Jacobite artillery while surveying the fords over which his troops would cross the Boyne.[36]
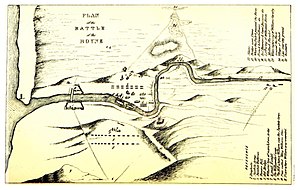
1. Drogheda 2. Jacobite army 3. Jacobite batteries 4. Donore 5. Oldbridge 6. William's line of march from Ardee 7. A small hamlet 8. The Williamite Camp 9. The hill whence William saw the Jacobite camp 10. Pass called King William's Glen 11. Place where William was wounded 12. Slane 13. Bridge near Slane 14. Where the Dutch passed the river 15. French and Enniskillingers ditto 16. Sir J. Hansner's & Count Nassau's ditto 17. Left wing of William's Horse 18. Mattlock rivulet 19. Where right wing of William's army crossed the river 20. Village of Duleek 21. Low marshy ground 22. Rosnaree.
The battle itself was fought on 1 July O.S. (11th N.S.), for control of a ford on the Boyne near Drogheda, about 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) northwest of the hamlet of Oldbridge (and about 1.5 kilometres (0.9 mi) west-northwest of the modern Boyne River Bridge). As a diversionary tactic, William sent about a quarter of his men under the cover of morning mist to cross the river at Roughgrange, about 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) west of Donore and about 6 miles (9.7 km) southwest of Oldbridge. The Duke of Schomberg's son, Meinhardt, led this crossing, which a small force of Irish dragoons in picquet under Neil O'Neill unsuccessfully opposed.[37] James, an inexperienced general, thought that he might be outflanked and sent a large part of his army, including his best French troops along with most of his artillery, to counter this move. What neither side had realised was that there was a deep, swampy ravine at Roughgrange. Because of this ravine, the opposing forces there could not engage each other, but literally sat out the battle as artillery engaged. The Williamite forces went on a long detour march which, later in the day, almost saw them cut off the Jacobite retreat at the village of Naul.[38]
At the main ford near Oldbridge, William's infantry, led by the elite Dutch Blue Guards, forced their way across the river, using their superior firepower to slowly drive back the enemy foot soldiers, but were pinned down when the Jacobite cavalry, commanded by James II's son the James FitzJames, 1st Duke of Berwick,[39] counter-attacked. Having secured the village of Oldbridge, some Williamite infantry tried to hold off successive Jacobite Irish cavalry attacks with disciplined volley fire, but were scattered and driven into the river, with the exception of the Blue Guards. William's second-in-command, the Duke of Schomberg, and George Walker were killed in this phase of the battle.[40] The Williamites were not able to resume their advance until their own horsemen managed to cross the river and, after being badly mauled, particularly the Huguenots,[41] managed to hold off the Jacobite cavalry until the cavalry retired and regrouped at Donore, where they once again put up stiff resistance before retiring.[42]
The Jacobites retired in good order. William had a chance to trap them as they retreated across the River Nanny at Duleek, but his troops were held up by a successful rear-guard action. The Dutch secretary of King William, Constantijn Huygens Jr., has given a good description (in Dutch) of the battle and its aftermath, including subsequent cruelties committed by the victorious soldiers.[43]

The casualty figures of the battle were quite low for a battle of such a scale—of the 50,000 or so participants, about 2,000 died.[1] 75% of the dead were Jacobites. William's army had far more wounded. At the time, most casualties of battles tended to be inflicted in the pursuit of an already-beaten enemy; this did not happen at the Boyne, as the counter-attacks of the skilled Jacobite cavalry screened the retreat of the rest of their army, and in addition William was always disinclined to endanger the person of James, since he was the father of his wife, Mary. The Jacobites were badly demoralised by the order to retreat, which lost them the battle. Many of the Irish infantrymen deserted, abandoning clothing in their escape.[44] The Williamites triumphantly marched into Dublin two days after the battle. The Jacobite army abandoned the city and marched to Limerick, behind the River Shannon, where they were unsuccessfully besieged.
Soon after the battle, William issued the Declaration of Finglas, offering full pardons to ordinary Jacobite soldiers, but not to their leaders. After his defeat, James did not stay in Dublin, but rode with a small escort to Duncannon and returned to exile in France, even though his army left the field relatively unscathed. James's loss of nerve and speedy exit from the battlefield enraged his Irish supporters, who fought on until the Treaty of Limerick in 1691; he was derisively nicknamed Séamus a' chaca ("James the shit") in Irish.[45][46]
Aftermath

The battle was overshadowed by the defeat of an Anglo-Dutch fleet by the French two days earlier at the Battle of Beachy Head, a far more serious event in the short term;[47] only on the continent was the Boyne treated as an important victory. Its importance lay in the fact that it was the first proper victory for the League of Augsburg, the first-ever alliance between the Vatican and Protestant countries. The victory motivated more nations to join the alliance and in effect ended the fear of a French conquest of Europe.[48]
The Boyne also had strategic significance for both England and Ireland. It marked the beginning of the end of James's hope of regaining his throne by military means and probably assured the triumph of the Glorious Revolution. In Scotland, news of this defeat temporarily silenced the Highlanders supporting the Jacobite rising, which had been led by Bonnie Dundee who was killed the previous July at the Battle of Killiecrankie.[49] The battle was a general victory for William and is still celebrated by the Protestant Orange Order on the Twelfth of July. Due to the political situation mentioned above, Catholic institutions amongst William's continental allies hailed his victory with bell-ringing.[50]
The battle caused the Jacobites to abandon the city of Dublin, which was occupied by William's forces without a fight. Despairing of his hopes for victory, James II fled to Duncannon, where he took ship for France. The war in Ireland had not ended however. The Franco-Irish Jacobite army regrouped in Limerick and fought off a Williamite assault on the city in late August. It was not until the following year and battle of Aughrim that their forces were broken and after another siege of Limerick, they surrendered to William's general Godard de Ginkell. The war in Ireland formally ended with the Treaty of Limerick. This allowed over 14,000 Irish soldiers under Patrick Sarsfield, to leave for France and allowed most Irish Catholic land owners to keep their land provided they swore allegiance to William of Orange. However, the Protestant dominated Irish Parliament rejected these terms, not ratifying the treaty until 1697 — and then not in full — and imposed a tough Penal Code resented by Irish Catholics for many years.[51][52][53][54]
Commemoration


Originally, the 12 July commemoration was that of the Battle of Aughrim,[56] symbolising Irish Protestants' victory in the Williamite war in Ireland. At Aughrim, which took place a year after the Boyne, the Jacobite army was destroyed, deciding the war in the Williamites' favour. The Boyne, which, in the old Julian calendar, took place on 1 July O.S., was treated as less important, third after Aughrim and the anniversary of the Irish Rebellion of 1641 on 23 October O.S.
In 1752, the Gregorian calendar was also adopted in Ireland.[57] However, even after this date, "The Twelfth" continued to be commemorated at Aughrim, on 12 July NS,[56] following the usual historical convention of commemorating events of that period within Great Britain and Ireland by mapping the Julian date directly onto the modern Gregorian calendar date (as happens for example with Guy Fawkes Night on 5 November). But, after the Orange Order was founded in 1795 amid sectarian violence in County Armagh, the two events were combined in the late 18th century.[56]
"The Twelfth" in Northern Ireland today
The Battle of the Boyne remains a controversial topic today in Northern Ireland, where some Protestants remember it as the great victory over Catholics that resulted in the sovereignty of Parliament and the Protestant monarchy.[58]
In recent decades, "The Twelfth" has often been marked by confrontations, as members of the Orange Order attempt to celebrate the date by marching past or through what they see as their traditional route.[59] Some of these areas, however, now have a nationalist majority who object to marches passing through what they see as their areas.[58]
Many nationalists still see these marches as provocative, whilst Unionist marchers insist that it is part of their historical right to celebrate. Since the start of The Troubles, the celebrations of the battle have been seen as playing a critical role in the awareness of those involved in the unionist/nationalist tensions in Northern Ireland. Better policing and improved dialogue between the sides in the 21st century have made for more peaceful parades.[58]
The battlefield today

The site of the Battle of the Boyne sprawls over a wide area west of the town of Drogheda. In the County Development Plan for 2000, Meath County Council rezoned the land at the eastern edge of Oldbridge, at the site of the main Williamite crossing, to residential status. A subsequent planning application for a development of over 700 houses was granted by Meath County Council and this was appealed against by local historians to An Bord Pleanala (The Planning Board). In March 2008, after an extremely long appeal process, An Bord Pleanala approved permission for this development to proceed.[60] Further plans have been submitted for hundreds more homes and a link to the River Boyne Boardwalk.[61]
The Battle of the Boyne Visitor Centre at Oldbridge house is run by the Office of Public Works, an agency of the Irish government, and is about 1-mile (1.6 km) to the west of the main river crossing point. The battle's other main combat areas, at Duleek, Donore and Plattin, along the Jacobite line of retreat, are marked with tourist information signs.
On 4 April 2007, in a sign of improving relations between unionist and nationalist groups, the newly elected First Minister of Northern Ireland, the Reverend Ian Paisley, was invited to visit the battle site by the Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Bertie Ahern later in the year. Following the invitation, Paisley commented that "such a visit would help to demonstrate how far we have come when we can celebrate and learn from the past so the next generation more clearly understands". On 10 May, the visit took place, and Paisley presented the Taoiseach with a Jacobite musket in return for Ahern's gift at the St Andrews talks of a walnut bowl made from a tree from the site. A new tree was also planted in the grounds of Oldbridge House by the two politicians to mark the occasion.[62]
See also
Notes
- Footnotes
- ^ The battle took place on 11 July N.S., but the anniversary is now celebrated on 12 July. This is explained at #Commemoration below.
- ^ The "Patriot Parliament" session of the Parliament of Ireland confirmed James as King of Ireland, though Poynings Law arguably made this invalid. In any case, the subsequent Act of Recognition, of their Majesties [sic] undoubted Right to the Crown of Ireland, 1692 set this aside.
- Citations
- ^ a b c d e f "Battle of the Boyne". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ a b c d "James II, King of England, Scotland and Ireland". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ "The Glorious Revolution". www.parliament.uk. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ "James II in Ireland". www.libraryireland.com. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ "War of the Grand Alliance". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ Brown, Derek (11 July 2000). "How the battle of the Boyne earned its place in history". The Guardian.
- ^ Elliott, I. D. (1973). "Schomberg, Friedrich Hermann, Duke of" Encyclopaedia Britannica, Volume 19. London: Encyclopaedia Britannica Inc., William Benton, Publisher. p. 1174. "He went to Ireland as commander in chief against James II in August 1689...". ISBN 978-0-85229-173-3.
- ^ Elliott 1973, p. 1174. "...but [he] could do little more than hold Ulster as there was much sickness in his small army, and he took no risks.".
- ^ "Charles I (1625–49) and the Commonwealth (1649–60)". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ Harris, Tim (2006). Revolution: The Great Crisis of the British Monarchy, 1685–1720. London: Allen Lane. p. 440. ISBN 978-0-7139-9759-0.
- ^ Magennis, Eoin (1998). "A 'Beleaguered Protestant'?: Walter Harris and the Writing of Fiction Unmasked in Mid-18th-Century Ireland". Eighteenth-Century Ireland. 13: 6–111. JSTOR 30064327.
- ^ "The Inniskillings (6th Dragoons)". Archived from the original on 18 January 2008. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ Jackson, Major E. S. (2015). INNISKILLING DRAGOONS: The Records of an Old Heavy Cavalry Regiment. Uckfield, East Sussex: The Naval & Military Press.
- ^ a b c "William III. King of England, Scotland and Ireland". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ^ "The Williamite War 1689-91(1:1)". www.historyireland.com. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ "Battle of the Dunes". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ Baldwin Smith, Lacey (2006). English History Made Brief, Irreverent, and Pleasurable. Chicago: Chicago Review Press. p. 224.
- ^ Holmes, Frederick (2003). The Sickly Stuarts:The Medical Downfall of a Dynasty. Gloucester: Sutton Publishing.
- ^ a b Bevan, Bryan (1997). King William III: Prince of Orange, the first European. London: Rubicon Press.
- ^ Payne, George; James, Rainsford (1838). The Life and Times of Louis the Fourteenth, Volume 4. London: Samuel Bentley. p. 154.
- ^ Blom, J. C. H.; Lamberts, E., eds. (2006). History of the Low Countries (new English-language ed.). New York & Oxford: Berghahn Books. p. 196.
- ^ "Antonin-Nompar de Caumont, count and duke de Lauzun". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ^ "Schomberg, Frederick Herman, 1st duke of". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ "Frederick Herman, duke of Schomberg". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ a b c d The Battle of the Boyne Teachers Notes & Resources - Secondary Level Archived 25 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine (PDF) Office of Public Works (Ireland), (undated, retrieved 9 March 2017)
- ^ "Britannica-Battle of the Boyne". Britannica.com. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the Boyne. 2:48 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ "King William's Progress to the Boyne". The Ulster Journal of Archaeology. 1: 131. 1853. JSTOR 20563454.
- ^ a b c d e Macaulay, T.B. (1849). "Chapter XVI". History of England from the accession of James II (1685) until the death of William III (1702). New York: Harper.
- ^ "Two Unpublished Diaries, Connected with the Battle of the Boyne". Ulster Journal of Archaeology. 1. 4. Belfast: 80. 1856.
- ^ Ohlmeyer, Jane, ed. (2018). The Cambridge History of Ireland: Volume 2, 1550–1730. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ a b Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 2:32 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ Childs, John (2007). The Williamite Wars in Ireland. London/New York: A & C Black. pp. 33, 135.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 10:50 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ BBC History: The Battle of the Boyne Archived 5 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine BBC, (undated, retrieved 9 March 2017)
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 4:05 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 8:00 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 9:10 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Handley, Stuart (May 2011). "Fitzjames, James, Duke of Berwick upon Tweed (1670–1734". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 10:30 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 11:00 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 14:10 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Observaties van een Zeventiende-eeuwse wereldbeschouwer, Constantijn Huygens en de uitvinding van het moderne dagboek. Dekker, Rudolf, Amsterdam 2013 pp. 45–47.
- ^ Laverty, Henry (producer/director) (1 January 1990). "Battle of the Boyne: Part I". Battle of the boyne. 15:10 minutes in. BBC. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Simms, J. G. (1986). War and Politics in Ireland, 1649–1730. London & Ronceverte: The Hambledon Press. pp. 184, 203.
- ^ Szechi, Daniel (1994). The Jacobites: Britain and Europe, 1688–1788. Manchester & New York: Manchester University Press. p. 49.
- ^ Macaulay, Lord (1914). The History of England from the Accession of James the Second. Vol. 4. London: Macmillan & Co. Ltd. pp. 854–858.
- ^ "War of the Grand Alliance". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ "Jacobite Risings". www.oxfordreference.com. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ Finn, Clodagh (9 July 2016). "Craving for a bond unlikely to lag due to a flag". Irish Examiner.
- ^ "The Treaty of Limerick, 1691". www.ucc.ie/en/. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ "History of the law, 1691 - present". www.courts.ie. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ "Treaty of Limerick". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ "Battle of the Boyne: King William III's Victory in Ireland". www.historynet.com. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ Chambers, Robert (1832). The Book of Days: A Miscellany of Popular Antiquities in Connection with the Calendar, Including Anecdote, Biography, & History, Curiosities of Literature and Oddities of Human Life and Character, Volume 2. London: W. & R. Chambers Limited. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ^ a b c Lenihan, Padraig (2003). 1690 Battle of the Boyne. Tempus. pp. 258–259. ISBN 9780752425979.
- ^ ‘The Pope’s new invention’: the introduction of the Gregorian calendar in Ireland, 1583–1782, page 9 History Department, University College Cork, 1 April 2006
- ^ a b c "The Irish Post". Twelve things you should know about marching season in Northern Ireland on 'The Twelfth'. Dublin. 11 July 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ^ Bryan, Dominic (2000). Orange Parades: The politics of ritual, tradition and control. Pluto Press. pp. 147–148.
- ^ "224875: Oldbridge, Rathmullen Road, Drogheda, Co. Meath (SA/60260)". www.pleanala.ie/. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ "Housing boom as 661 homes planned on Rathmullen Road". www.independent.ie. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ "Paisley and Ahern visit 1690 site". BBC News. 11 May 2007. Retrieved 22 November 2019.
Further reading
- Padraig Lenihan, 1690 Battle of the Boyne, Tempus Publishing, Gloucestershire, 2003. ISBN 0-7524-3304-0.
- G. A. Hayes McCoy, Irish Battles, Belfast, 1990, ISBN 0-86281-250-X.
- Richard Doherty, The Williamite War in Ireland 1688–1691, Dublin: Four Courts Press, 1998. ISBN 1-85182-375-1.
External links
- Battle of the Boyne visitor centre at Oldbridge, plus battle information
- Boyne Valley Tourist Portal – Information on Battle of the Boyne
- Tourist Information on Battle of the Boyne Visitor Centre
- Primary and secondary sources relating to the Battle of the Boyne (From the National Library of Ireland's Sources database)
- Modern mapping of the area Ordnance Survey Ireland Choose "Base history and mapping" then "Historic 6-inch mapping" and enter 704444,776167 to see the site of the "Boyne Obelisk" (destroyed, 1923) on the northern side of the [subsequent] bridge.
- Interview with historian Padraig Lenihan on the Battle of the Boyne


