Acene

The acenes or polyacenes are a class of organic compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons made up of linearly fused benzene rings. The larger representatives have potential interest in optoelectronic applications and are actively researched in chemistry and electrical engineering. Pentacene has been incorporated into organic field-effect transistors, reaching charge carrier mobilities as high as 5 cm2/Vs.
The first 7 unsubstituted members are listed in table 1.
| Name | Molecular formula | Number of rings | Molar mass | CAS number | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | C6H6 | 1 | 78.11 g/mol | 71-43-2 | 
|
| Naphthalene | C10H8 | 2 | 128.17 g/mol | 91-20-3 | 
|
| Anthracene | C14H10 | 3 | 178.23 g/mol | 120-12-7 | 
|
| Tetracene | C18H12 | 4 | 228.29 g/mol | 92-24-0 | File:Naftacene.svg |
| Pentacene | C22H14 | 5 | 278.35 g/mol | 135-48-8 | 
|
| Hexacene | C26H16 | 6 | 328.41 g/mol | 258-31-1 | 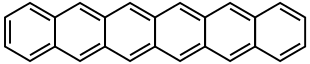
|
| Heptacene | C30H18 | 7 | 378.46 g/mol | 258-38-8 | 
|
The last members, hexacene and heptacene, are very reactive and have only been isolated in a matrix. However, bis(trialkylsilylethynylated) versions of hexacene and heptacene have been isolated as crystalline solids.[1]
Larger acenes
Due to their increased conjugation length the larger acenes are also studied.[2] They are also building blocks for nanotubes and graphene. Unsubstituted octacene (n=8) and nonacene (n=9) [3] have been detected in matrix isolation. The first reports of stable nonacene derivatives claimed that due to the electronic effects of the thioaryl substituents the compound is not a diradical but a closed-shell compound with the lowest HOMO-LUMO gap reported for any acene,[4] an observation in violation of Kasha's rule. Subsequent work by others on different derivatives included crystal structures, with no such violations.[5]
Related compounds
A related group of compounds with 1,2-fused rings and with helical not linear structures are the helicenes. Compounds in which the fused rings form a zigzag pattern are phenacenes. Polyquinanes and quinenes are fused cyclopentane rings.
References
- ^ Anthony, John E. (2008). "The Larger Acenes: Versatile Organic Semiconductors". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 47 (3): 452–83. doi:10.1002/anie.200604045. PMID 18046697.
- ^ Zade, Sanjio S.; Bendikov, Michael (2010). "Heptacene and Beyond: the Longest Characterized Acenes". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49 (24): n/a. doi:10.1002/anie.200906002. PMID 20468014.
- ^ Tönshoff, Christina; Bettinger, Holger F. (2010). "Photogeneration of Octacene and Nonacene". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49 (24): n/a. doi:10.1002/anie.200906355. PMID 20432492.
- ^ Kaur, Irvinder; Jazdzyk, Mikael; Stein, Nathan N.; Prusevich, Polina; Miller, Glen P. (2010). "Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of a Persistent Nonacene Derivative". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (4): 1261–3. doi:10.1021/ja9095472. PMID 20055388.
- ^ Purushothaman, Balaji; Bruzek, Matthew; Parkin, Sean; Miller, Anne-Frances; Anthony, John (2011). "Synthesis and Structural Characterization of Crystalline Nonacenes". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 50 (31): 7013–7917. doi:10.1002/anie.201102671. PMID 21717552.
