Adipose tissue

In biology, adipose tissue (/ˈæd[invalid input: 'ɨ']ˌpoʊs/) or body fat or just fat is loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and variety of immune cells (i.e. adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs)). Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Far from hormonally inert, adipose tissue has in recent years been recognized as a major endocrine organ,[1] as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and the cytokine TNFα. Moreover, adipose tissue can affect other organ systems of the body and may lead to disease. Obesity or being overweight in humans and most animals does not depend on body weight, but on the amount of body fat—to be specific, adipose tissue[citation needed]. The two types of adipose tissue are white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT). The formation of adipose tissue appears to be controlled in part by the adipose gene. Adipose tissue, more specifically brown adipose tissue, was first identified by the Swiss naturalist Conrad Gessner in 1551.[2]
Anatomical features
Humans
In humans, adipose tissue is located beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), around internal organs (visceral fat), in bone marrow (yellow bone marrow) and in breast tissue. Adipose tissue is found in specific locations, which are referred to as adipose depots. Apart from adipocytes, which comprise the highest percentage of cells within adipose tissue, other cell types are present collectively termed stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells. SVF includes preadipocytes,fibroblasts, adipose tissue macrophages, and endothelial cells. Adipose tissue contains many small blood vessels. In the integumentary system, which includes the skin, it accumulates in the deepest level, the subcutaneous layer, providing insulation from heat and cold. Around organs, it provides protective padding. However, its main function is to be a reserve of lipids, which can be burned to meet the energy needs of the body and to protect us from excess glucose by storing triglycerides produced by the liver from sugars, although some evidence suggests that most lipids synthesized from carbohydrates occurs in the adipose tissue itself.[3] Adipose depots in different parts of the body have different biochemical profiles. Under normal conditions, it provides feedback for hunger and diet to the brain.
Mice

Mice have eight major adipose depots, four of which are within the abdominal cavity. The paired gonadal depots are attached to the uterus and ovaries in females and the epididymis and testes in males; the paired retroperitoneal depots are found along the dorsal wall of the abdomen, surrounding the kidney, and, when massive, extend into the pelvis. The mesenteric depot forms a glue-like web that supports the intestines, and the omental depot, which originates near the stomach and spleen, and, when massive, extends into the ventral abdomen. Both the mesenteric and omental depots incorporate much lymphoid tissue as lymph nodes and milky spots, respectively. The two superficial depots are the paired inguinal depots, which are found anterior to the upper segment of the hind limbs (underneath the skin) and the subscapular depots, paired medial mixtures of brown adipose tissue adjacent to regions of white adipose tissue, which are found under the skin between the dorsal crests of the scapulae. The layer of brown adipose tissue in this depot is often covered by a "frosting" of white adipose tissue; sometimes these two types of fat (brown and white) are hard to distinguish. The inguinal depots enclose the inguinal group of lymph nodes. Minor depots include the pericardial, which surrounds the heart, and the paired popliteal depots, between the major muscles behind the knees, each containing one large lymph node.[4] Of all the depots in the mouse, the gonadal depots are the largest and the most easily dissected,[5] comprising about 30% of dissectible fat.[6]
Obesity
In a severely obese person, excess adipose tissue hanging downward from the abdomen is referred to as a panniculus (or pannus). A panniculus complicates surgery of the morbidly obese. It may remain as a literal "apron of skin" if a severely obese person quickly loses large amounts of fat (a common result of gastric bypass surgery). This condition cannot be effectively corrected through diet and exercise alone, as the panniculus consists of adipocytes and other supporting cell types shrunken to their minimum volume and diameter.[citation needed] Reconstructive surgery is one method of treatment.
Obesity and cancer
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer and based on epidemiological studies, obese or overweight people are at increased risk of developing several cancer types such as adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus, colon cancer, breast cancer (in postmenopausal women), endometrial cancer and kidney cancer.[7]
Abdominal fat

Visceral fat or abdominal fat[8] also known as organ fat or intra-abdominal fat, is located inside the abdominal cavity, packed between the organs (stomach, liver, intestines, kidneys, etc.). Visceral fat is different from subcutaneous fat underneath the skin, and intramuscular fat interspersed in skeletal muscles. Fat in the lower body, as in thighs and buttocks, is subcutaneous and is not consistently spaced tissue, whereas fat in the abdomen is mostly visceral and semi-fluid.[9] Visceral fat is composed of several adipose depots, including mesenteric, epididymal white adipose tissue (EWAT), and perirenal depots. Visceral fat is considered adipose tissue whereas subcutaneous fat is not considered as such.
An excess of visceral fat is known as central obesity, or "belly fat", in which the abdomen protrudes excessively. Excess visceral fat is also linked to type 2 diabetes,[10] insulin resistance,[11] inflammatory diseases,[12] and other obesity-related diseases.[13]
Female sex hormone causes fat to be stored in the buttocks, thighs, and hips in women.[14][15] Men are more likely to have fat stored in the belly due to sex hormone differences. When women reach menopause and the estrogen produced by ovaries declines, fat migrates from their buttocks, hips and thighs to their waists;[16] later fat is stored in the belly.[17]
High-intensity exercise is one way to effectively reduce total abdominal fat.[18][19] One study suggests at least 10 MET-hours per week of aerobic exercise is required for visceral fat reduction.[20]
Epicardial fat
Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) is a particular form of visceral fat deposited around the heart and found to be a metabolically active organ that generates various bioactive molecules, which might significantly affect cardiac function.[21] Marked component differences have been observed in comparing EAT with subcutaneous fat, suggesting a depot specific impact of stored fatty acids on adipocyte function and metabolism.[22]
Subcutaneous fat
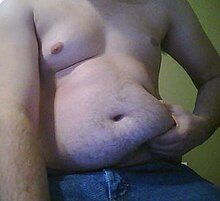
Most of the remaining nonvisceral fat is found just below the skin in a region called the hypodermis.[23] This subcutaneous fat is not related to many of the classic obesity-related pathologies, such as heart disease, cancer, and stroke, and some evidence even suggests it might be protective.[24] The typically female (or gynecoid) pattern of body fat distribution around the hips, thighs, and buttocks, is subcutaneous fat, and therefore poses less of a health risk compared to visceral fat.[25]
Like all other fat organs, subcutaneous fat is an active part of the endocrine system, secreting the hormones leptin and resistin.[23]
The relationship between the subcutaneous adipose layer and total body fat in a person is often modelled by using regression equations. The most popular of these equations was formed by Durnin and Wormersley, who rigorously tested many types of skinfold, and, as a result, created two formulae to calculate the body density of both men and women. These equations present an inverse correlation between skinfolds and body density – as the sum of skinfolds increases, the body density decreases.[26]
Factors such as sex, age, population size or other variables may make the equations invalid and unusable, and, as of 2012[update], Durnin and Wormersley's equations remain only estimates of a person's true level of fatness. New formulae are still being created.[26]
Physiology
Free fatty acids are liberated from lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and enter the adipocyte, where they are reassembled into triglycerides by esterifying it onto glycerol. Human fat tissue contains about 87% lipids.
There is a constant flux of FFA (Free Fatty Acids) entering and leaving adipose tissue. The net direction of this flux is controlled by insulin and leptin - if insulin is elevated there is a net inward flux of FFA and only when insulin is low can FFA leave adipose tissue. Insulin secretion is stimulated by high blood sugar which results from consuming carbohydrates.
In humans, lipolysis (hydrolysis of triglycerides into free fatty acids) is controlled through the balanced control of lipolytic B-adrenergic receptors and a2A-adrenergic receptor-mediated antilipolysis.
Fat cells have an important physiological role in maintaining triglyceride and free fatty acid levels, as well as determining insulin resistance. Abdominal fat has a different metabolic profile—being more prone to induce insulin resistance. This explains to a large degree why central obesity is a marker of impaired glucose tolerance and is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (even in the absence of diabetes mellitus and hypertension).[27] Studies of female monkeys at Wake Forest University (2009) discovered individuals suffering from higher stress have higher levels of visceral fat in their bodies. This suggests a possible cause-and-effect link between the two, wherein stress promotes the accumulation of visceral fat, which in turn causes hormonal and metabolic changes that contribute to heart disease and other health problems.[28]
Recent advances in biotechnology have allowed for the harvesting of adult stem cells from adipose tissue, allowing stimulation of tissue regrowth using a patient's own cells. In addition, adipose-derived stem cells from both human and animals reportedly can be efficiently reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells without the need for feeder cells.[29] The use of a patient's own cells reduces the chance of tissue rejection and avoids ethical issues associated with the use of human embryonic stem cells.
Adipose tissue is the greatest peripheral source of aromatase in both males and females, contributing to the production of estradiol.
Adipose derived hormones include:
- Adiponectin
- Resistin
- Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)
- TNFα
- IL-6
- Leptin
- Estradiol (E2)
Adipose tissues also secrete a type of cytokines (cell-to-cell signalling proteins) called adipokines (adipocytokines), which play a role in obesity-associated complications.
Brown fat
A specialized form of adipose tissue in humans, most rodents and small mammals, and some hibernating animals, is brown fat or brown adipose tissue. It is located mainly around the neck and large blood vessels of the thorax. This specialized tissue can generate heat by "uncoupling" the respiratory chain of oxidative phosphorylation within mitochondria. The process of uncoupling means, when protons transit down the electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, the energy from this process is released as heat rather than being used to generate ATP. This thermogenic process may be vital in neonates exposed to cold, which then require this thermogenesis to keep warm, as they are unable to shiver, or take other actions to keep themselves warm.[30]
Attempts to simulate this process pharmacologically have so far been unsuccessful (even lethal[31][32]). Techniques to manipulate the differentiation of "brown fat" could become a mechanism for weight loss therapy in the future, encouraging the growth of tissue with this specialized metabolism without inducing it in other organs.
Until recently, brown adipose tissue was thought to be primarily limited to infants in humans, but new evidence has now overturned that belief. Metabolically active tissue with temperature responses similar to brown adipose was first reported in the neck and trunk of some human adults in 2007,[33] and the presence of brown adipose in human adults was later verified histologically in the same anatomical regions.[34][35][36]
Genetics
The thrifty gene hypothesis (also called the famine hypothesis) states that in some populations the body would be more efficient at retaining fat in times of plenty, thereby endowing greater resistance to starvation in times of food scarcity. This hypothesis has been discredited by physical anthropologists, physiologists, and the original proponent of the idea himself.[37]
In 1995, Jeffrey Friedman, in his residency at Rockefeller University, discovered the protein leptin that the genetically obese mouse lacked.[38] Leptin is produced in the white adipose tissue and signals to the hypothalamus. When leptin levels drop, the body interprets this as loss of energy, and hunger increases. Mice lacking this protein eat until they are four times their normal size.
Leptin, however, plays a different role in diet-induced obesity in rodents and humans. Because adipocytes produce leptin, leptin levels are elevated in the obese. However, hunger remains, and, when leptin levels drop due to weight loss, hunger increases. The drop of leptin is better viewed as a starvation signal than the rise of leptin as a satiety signal.[39] However, elevated leptin in obesity is known as leptin resistance. The changes that occur in the hypothalamus to result in leptin resistance in obesity are currently the focus of obesity research.[40]
Gene defects in the leptin gene (ob) are rare in human obesity.[41] As of July, 2010, only 14 individuals from five families have been identified worldwide who carry a mutated ob gene (one of which was the first ever identified cause of genetic obesity in humans) - two families of Pakistani origin living in the UK, one family living in Turkey, one in Egypt, and one in Austria.[42][43][44][45][46] - and two other families have been found that carry a mutated ob receptor.[47][48] Others have been identified as genetically partially deficient in leptin, and, in these individuals, leptin levels on the low end of the normal range can predict obesity.[49]
Several mutations of genes involving the melanocortins (used in brain signaling associated with appetite) and their receptors have also been identified as causing obesity in a larger portion of the population than leptin mutations.[50]
In 2007, researchers isolated the adipose gene, which those researchers hypothesize serves to keep animals lean during times of plenty. In that study, increased adipose gene activity was associated with slimmer animals.[51] Although its discoverers dubbed this gene the adipose gene, it is not a gene responsible for creating adipose tissue.
Physical properties
Adipose tissue has a density of ~0.9 g/ml [citation needed] [0.9 kg/L]. Thus, a person with more adipose tissue will float more easily than a person of the same weight with more muscular tissue, since muscular tissue has a density of 1.06 g/ml[citation needed] [1.06 kg/L].
Body fat meter
A body fat meter is a widely available tool used to measure the percentage of fat in the human body. Different meters use various methods to determine the body fat to weight ratio. They tend to under-read body fat percentage.[52]
In contrast with clinical tools, one relatively inexpensive type of body fat meter uses the principle of bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) to determine an individual's body fat percentage. To achieve this, the meter passes a small, harmless, electric current through the body and measures the resistance, then uses information on the person's weight, height, age, and sex, to calculate an approximate value for the person's body fat percentage. The calculation measures the total volume of water in the body (lean tissue and muscle contain a higher percentage of water than fat), and estimates the percentage of fat based on this information. The result can fluctuate several percentage points depending on what one has eaten and how much water one has consumed prior to the analysis.
Additional images
-
Diagrammatic sectional view of the skin (magnified).
-
White adipose tissue in paraffin section
-
Electronic instrument of body fat meter
See also
- Apelin
- Bioelectrical impedance analysis - a method to measure body fat percentage.
- Blubber - an extra thick form of adipose tissue found in some marine mammals.
- Body fat percentage
- Cellulite
- Human fat used as pharmaceutical in traditional medicine
- Obesity
- Starving
- Steatosis (also called fatty change, fatty degeneration or adipose degeneration)
- Stem cells
- Subcutaneous fat
- Adipose differentiation-related protein
- Adiposopathy
References
- ^ Kershaw EE, Flier JS (2004). "Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89 (6): 2548–56. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0395. PMID 15181022.
- ^ Cannon, B; Nedergaard, J (2008). "Developmental biology: Neither fat nor flesh". Nature. 454 (7207): 947–8. doi:10.1038/454947a. PMID 18719573.
- ^ [1],Hepatic and whole-body fat synthesis in humans during carbohydrate overfeeding.
- ^ Pond, Caroline M. (1998). The Fats of Life. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-63577-2.
- ^ Cinti, S (2005). "The adipose organ". Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and essential fatty acids. 73 (952–3278). Elsevier Science: 9–15. doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2005.04.010. PMID 15936182.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Bachmanov, Alexander (2001). "Nutrient preference and diet-induced adiposity in C57BL/6ByJ and 129P3/J mice". Physiology & Behavior. 72 (31–9384): 603–613. doi:10.1016/S0031-9384(01)00412-7. PMC 3341942. PMID 11282146.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4:579-91.
- ^ Fat on the Inside: Looking Thin is Not Enough, By Fiona Haynes, About.com
- ^ Abdominal fat and what to do about it, President & Fellows of Harvard College
- ^ Montague, CT; O'Rahilly, S (2000). "The perils of portliness: Causes and consequences of visceral adiposity". Diabetes. 49 (6): 883–8. doi:10.2337/diabetes.49.6.883. PMID 10866038.
- ^ Kern, PA; Ranganathan, S; Li, C; Wood, L; Ranganathan, G (2001). "Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance". American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism. 280 (5): E745–51. PMID 11287357.
- ^ Marette, A (2003). "Molecular mechanisms of inflammation in obesity-linked insulin resistance". International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders : journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity. 27 Suppl 3: S46–8. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802500. PMID 14704744.
- ^ Mokdad, AH; Ford, ES; Bowman, BA; Dietz, WH; Vinicor, F; Bales, VS; Marks, JS (2003). "Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001". JAMA: the Journal of the American Medical Association. 289 (1): 76–9. doi:10.1001/jama.289.1.76. PMID 12503980.
- ^ Estrogen causes fat to be stored around the pelvic region, hips, butt and thighs (pelvic region) [2]
- ^ Waistline Worries: Turning Apples Back Into Pears
- ^ Researchers think that the lack of estrogen at menopause plays a role in driving our fat northward [3]
- ^ Abdominal fat and what to do about it
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 18845966, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=18845966instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 19196080, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=19196080instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17637702, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17637702instead. - ^ Mazurek T, Zhang L, Zalewski A; et al. (2003). "Human epicardial adipose tissue is a source of inflammatory mediators". Circulation. 108 (20): 2460–6. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000099542.57313.C5. PMID 14581396.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pezeshkian M, Noori M, Najjarpour-Jabbari H; et al. (2009). "Fatty acid composition of epicardial and subcutaneous human adipose tissue". Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 7 (2): 125–31. PMID 19422139.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b E Marieb and K Hoehn. Anatomy and Physiology, 3rd Edition. Benjamin Cummings 2008. ISBN 0-8053-0094-5
- ^ Porter SA, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Vasan RS, O'Donnel CJ, Fox CS. Abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue: a protective fat depot? Diabetes Care. 2009 Jun;32(6):1068-75. Epub 2009 Feb 24
- ^ Mayo Clinic staff. Belly fat in women: How to keep it off. MayoClinic.com. URL http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/belly-fat/WO00128/METHOD=print. Access date July 2, 2010
- ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00474-7, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00474-7instead. - ^ Dhaliwal SS, Welborn TA. (May 2009) "Central obesity and multivariable cardiovascular risk as assessed by the Framingham prediction scores" Am J Cardiol. (American Journal of Cardiology) 103(10): pp. 1403-1407
- ^ Alice Park (2009-08-08). "Fat-Bellied Monkeys Suggest Why Stress Sucks". Time. Retrieved 2009-08-08.
- ^ Sugii, S; Kida, Y; Kawamura, T; Suzuki, J; Vassena, R; Yin, YQ; Lutz, MK; Berggren, WT; Izpisúa Belmonte, JC (2010). "Human and mouse adipose-derived cells support feeder-independent induction of pluripotent stem cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (8): 3558–63. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910172106. PMC 2840462. PMID 20133714.
- ^ Himms-Hagen, J (1990). "Brown adipose tissue thermogenesis: Interdisciplinary studies". FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 4 (11): 2890–8. PMID 2199286.
- ^ McFee, RB; Caraccio, TR; McGuigan, MA; Reynolds, SA; Bellanger, P (2004). "Dying to be thin: A dinitrophenol related fatality". Veterinary and human toxicology. 46 (5): 251–4. PMID 15487646.
- ^ Miranda, EJ; McIntyre, IM; Parker, DR; Gary, RD; Logan, BK (2006). "Two deaths attributed to the use of 2,4-dinitrophenol". Journal of analytical toxicology. 30 (3): 219–22. PMID 16803658.
- ^ Nedergaard, J.; Bengtsson, T.; Cannon, B. (2007). "Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult humans". AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism. 293 (2): E444. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00691.2006. PMID 17473055.
- ^ Virtanen, KA; Lidell, ME; Orava, J; Heglind, M; Westergren, R; Niemi, T; Taittonen, M; Laine, J; Savisto, NJ (2009). "Functional brown adipose tissue in healthy adults". The New England Journal of Medicine. 360 (15): 1518–25. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808949. PMID 19357407.
- ^ Van Marken Lichtenbelt, WD; Vanhommerig, JW; Smulders, NM; Drossaerts, JM; Kemerink, GJ; Bouvy, ND; Schrauwen, P; Teule, GJ (2009). "Cold-activated brown adipose tissue in healthy men". The New England Journal of Medicine. 360 (15): 1500–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808718. PMID 19357405.
- ^ Cypess, AM; Lehman, S; Williams, G; Tal, I; Rodman, D; Goldfine, AB; Kuo, FC; Palmer, EL; Tseng, YH (2009). "Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans". The New England Journal of Medicine. 360 (15): 1509–17. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810780. PMC 2859951. PMID 19357406.
- ^ Speakerman, John R. (2007). "Genetics of Obesity: Five Fundamental Problems with the Famine Hypothesis". Adipose Tissue and Adipokines in Health and Disease.
- ^ Pelleymounter, MA; Cullen, MJ; Baker, MB; Hecht, R; Winters, D; Boone, T; Collins, F (1995). "Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice". Science. 269 (5223): 540–3. doi:10.1126/science.7624776. PMID 7624776.
- ^ Smith; Ravussin (2006). "Role of the Adipocyte in Metabolism and Endocrine Function". Endocrinology.[page needed]
- ^ Morris, DL; Rui, L (2009). "Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance". American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism. 297 (6): E1247–59. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00274.2009. PMC 2793049. PMID 19724019.
- ^ Carlsson, B; Lindell, K; Gabrielsson, B; Karlsson, C; Bjarnason, R; Westphal, O; Karlsson, U; Sjöström, L; Carlsson, LM (1997). "Obese (ob) gene defects are rare in human obesity". Obesity research. 5 (1): 30–5. PMID 9061713.
- ^ Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP, Soos MA, Rau H, Wareham NJ, Sewter CP, Digby JE, Mohammed SN, Hurst JA, Cheetham CH, Earley AR, Barnett AH, Prins JB, O'Rahilly S. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):903-8.
- ^ Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L, Ozata M, Strosberg AD. A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. Nat Genet. 1998 Mar;18(3):213-5.
- ^ Gibson WT, Farooqi IS, Moreau M, DePaoli AM, Lawrence E, O'Rahilly S, Trussell RA. Congenital leptin deficiency due to homozygosity for the Delta133G mutation: report of another case and evaluation of response to four years of leptin therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Oct;89(10):4821-6.
- ^ Mazen I, El-Gammal M, Abdel-Hamid M, Amr K. A novel homozygous missense mutation of the leptin gene (N103K) in an obese Egyptian patient. Mol Genet Metab. 2009 Aug;97(4):305-8. Epub 2009 Apr 9.
- ^ Fischer-Posovszky P, von Schnurbein J, Moepps B, Lahr G, Strauss G, Barth TF, Kassubek J, Mühleder H, Möller P, Debatin KM, Gierschik P, Wabitsch M. A new missense mutation in the leptin gene causes mild obesity and hypogonadism without affecting T cell responsiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Jun;95(6):2836-40. Epub 2010 Apr 9.
- ^ Clément K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, Cabrol S, Pelloux V, Cassuto D, Gourmelen M, Dina C, Chambaz J, Lacorte JM, Basdevant A, Bougnères P, Lebouc Y, Froguel P, Guy-Grand B. A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature. 1998 Mar 26;392(6674):398-401.
- ^ Pankov YA. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ regulating growth, puberty, and other physiological functions. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1999 Jun;64(6):601-9.
- ^ Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Kamath S, Jones S, Gibson WT, Trussell R, Jebb SA, Lip GY, O'Rahilly S. Partial leptin deficiency and human adiposity. Nature. 2001 Nov 1;414(6859):34-5.
- ^ Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S. Mutations in ligands and receptors of the leptin-melanocortin pathway that lead to obesity. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Oct;4(10):569-77. Epub 2008 Sep 9.
- ^ Suh, JM; Zeve, D; McKay, R; Seo, J; Salo, Z; Li, R; Wang, M; Graff, JM (2007). "Adipose is a conserved dosage-sensitive antiobesity gene". Cell metabolism. 6 (3): 195–207. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.08.001. PMC 2587167. PMID 17767906.
- ^ "Body fat scales review and compare". 10 January 2010. Archived from the original on 17 January 2010. Retrieved 11 January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
Further reading
- MeSH A10.165.114
- Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00008-0, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00008-0instead. - Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00007-9, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00007-9instead.



