Amino radical
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
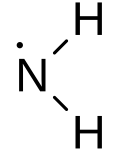
| NH 2• | |
| Molar mass | 16.0226 g mol−1 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
194.71 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
190.37 kJ mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The amino radical, NH
2•, is the neutral form of the amide ion (NH−
2). Amino radicals are highly reactive and consequently short lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry. In sufficiently high concentration, azanyl dimerises to form hydrazine.
References
- ^ a b "aminyl (CHEBI:29318)". Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI). UK: European Bioinformatics Institute. IUPAC Names.

