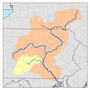
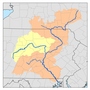
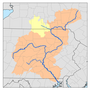
Black Creek (Nescopeck Creek tributary)

Black Creek is a long source tributary of Nescopeck Creek so part of the Susquehanna River drainage basin. It is also the second[1] & longer stream of the same name recognized by the USGS GNIS system in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania,[1] in the United States—compared to the Black Creek beyond the ridgeline of the drainage divide, so in the Lehigh River valley and Carbon County.[a] The headwaters of both Black Creeks in Luzerne county are only a few miles apart, and both valleys were traversed by the Lausanne-Nescopeck Turnpike (Lehigh-Susquehanna Turnpike) in the first half of the 19th-century.
The J-on-its-long-side-shaped brook is approximately 22.6 miles (36.4 km) long,[2] and in the early 1800s the sides of its valley became the path of the Lausanne-Nescopeck Turnpike (Lehigh-Susquehanna Turnpike)— connecting Philadelphia and the Delaware basin communities to the new settlements in the mid-Susquehanna and Wyoming valleys via paths along the banks of the Lehigh and the Susquehanna Rivers.
Course
Black Creek begins in Foster Township and flows southwest for less than a mile, passing through the community of Jeddo. The creek then enters Hazle Township, where it turns west and flows between two mountains, along the way passing through the community of South Ebervale. Further downstream, the creek leaves the two mountains and flows north of Hazleton, crossing Pennsylvania Route 940 and Pennsylvania Route 309, immediately after which it receives the tributary Little Black Creek. Slightly further downstream it enters West Hazleton, crossing Pennsylvania Route 93 and receiving the tributary Stony Creek, then crossing Interstate 81 in West Hazleton. Upon leaving West Hazleton, it reenters Hazle Township and continues west, soon crossing into Sugarloaf Township. Here for a few miles it flows roughly parallel to the border between Sugarloaf and Hazle townships, then turns southwest and enters Black Creek Township, passing briefly through Hazle Township. In Black Creek Township, the creek continues west, passing through communities of Gum Run, Derringer, Fern Glen and Gowen. At Gowen it turns north and flows through a water gap, with Buck Mountain to the west. On the other side of the water gap, the creek flows through Rock Glen and picks up the tributary Falls Run. Continuing north for a few miles, it picks up tributaries Barnes Run and Scotch Run, then turns northeast for slightly over a mile, reaching its confluence with Nescopeck Creek near the community of Tank.[2]
Black Creek joins Nescopeck Creek 8.72 miles (14.03 km) upstream of its mouth.[3]
Hydrology
The entire length of Black Creek is considered by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection to be impaired by acid mine drainage, the main sources of which are the Gowen and Derringer deep mine discharges; a number of smaller sources of abandoned mine drainage also contribute to impairment of the Black Creek watershed.[4]
At the mouth of Black Creek, the daily load of aluminum is 636.98 pounds (288.93 kg). The iron and manganese loads at this site are 269.19 pounds (122.10 kg) and 457.05 pounds (207.31 kg) per day. The daily load of acidity is 4,332.93 pounds (1,965.38 kg). Just downstream of Buck Mountain, the load of aluminum is 809.18 pounds (367.04 kg) per day, while the load of iron is 281.99 pounds (127.91 kg) per day. The daily manganese load at this point is 520.51 pounds (236.10 kg). The daily load of acidity is 5,823.65 pounds (2,641.56 kg).[4]
The discharge of Black Creek is 769.33 gallons per minute in its upper reaches. By the Hazleton High School, it increases to 2253.6 gallons per minute and by the Hazleton Wastewater Treatment Plant it increases to 5109 gallons per minute. Downstream of the wastewater treatment plant, the discharge is 22787.5 gallons per minute; at the bridge at Tomhicken it is 31227.33 gallons per minute, and at the State Route 3020 bridge it is 31824.17 gallons per minute. Above and below the Gowen Discharge, the creek's discharge is 32659.33 and 46529.5 gallons per minute respectively. Upstream of the State Route 3018 bridge, the discharge is 55684.17 gallons per minute and near the mouth it is 53938.56 gallons per minute.[4]
The pH of Black Creek in its upper reaches ranges from 6.1 to 6.4. At the Hazleton High School it ranges from 4.9 to 6 and at the Hazleton Wastewater Treatment Plant from 5.5 to 6. Downstream of the plant the pH ranges between 6.4 and 7. At the bridge at Tomhicken it ranges from 6.1 to 6.7 and at the State Route 3020 bridge from 6.2 to 6.8. Above and below the Gowen Discharge, the creek's pH ranges from 6.3 to 6.8 and 4.6 and 6.2 respectively. Upstream of the State Route 3018 bridge, the pH ranges from 4.6 to 6.3 and near the mouth between 4.6 and 6.8.[4]
Chemical hydrology (aluminum, iron, manganese, and acidity)
Just downstream of the Gowen Discharge, the daily load of aluminum in Black Creek is 846.58 pounds (384.00 kg), nearly 12 times higher than the load just upstream of the discharge, which is 70.60 pounds (32.02 kg) per day.[4] Just downstream of the discharge, the daily iron load is 260.77 pounds (118.28 kg) and just upstream of the discharge, it is 146.43 pounds (66.42 kg). Immediately downstream of the discharge, the manganese and acidity loads are 530.86 pounds (240.79 kg) and 170.67 pounds (77.41 kg), respectively. Immediately upstream of the discharge, the acidity load is 5,816.18 pounds (2,638.17 kg).[4]
Just downstream of the State Route 3020 bridge near Derringer, the load of aluminum in Black Creek is 66.88 pounds (30.34 kg) per day. The daily loads of manganese and iron are 149.69 pounds (67.90 kg) and 78.35 pounds (35.54 kg). At the bridge at Tomhicken, the daily aluminum and iron loads are 76.26 pounds (34.59 kg) and 185.64 pounds (84.20 kg), respectively. The daily manganese load is 88.13 pounds (39.98 kg). Downstream of a wastewater treatment plant, the daily aluminum and iron loads are 53.82 pounds (24.41 kg) and 120.87 pounds (54.83 kg), respectively. The daily manganese load is 58.38 pounds (26.48 kg).[4]
At the Hazleton Wastewater Treatment Plant, the daily aluminum load of Black Creek is 1.73 pounds (0.78 kg). The iron load is 4.56 pounds (2.07 kg) per day and the manganese load is 20.25 pounds (9.19 kg) per day. The daily acidity load is 107.58 pounds (48.80 kg). Behind the Hazleton High School, the daily aluminum load of the creek is 12.88 pounds (5.84 kg). The iron load is 31.88 pounds (14.46 kg) per day and the manganese load is 7.74 pounds (3.51 kg) per day. The daily acidity load is 90.94 pounds (41.25 kg). In the upper reaches of the creek, the daily aluminum load is 19.19 pounds (8.70 kg). The iron load is 5.28 pounds (2.39 kg) per day and the manganese load is 4.42 pounds (2.00 kg) per day. The daily acidity load is 170.37 pounds (77.28 kg).[4]
Geography and geology
The elevation near the mouth of Black Creek is 626 feet (191 m) above sea level.[5] Elevation at the source is between 1,580 feet (480 m) and 1,600 feet (490 m).[2] From its source to 9.5 miles (15.3 km) downstream, Black Creek's elevation decreases at a rate of 15.8 feet (4.8 m) per mile. For the next 7 miles (11 km), elevation decreases at a rate of 42.9 feet (13.1 m) per mile. From there to the mouth, elevation falls at a rate of 58.4 feet (17.8 m) per mile.[6]
Black Creek's topography is described in a 1921 book as "mountainous". The upper part of the creek is in a broad valley, the lower part in a narrow valley. There are some swamps in the upper reaches. The channel is sinuous, flowing through rock formations of sandstone and shale which include coal.[6]
An area known as Black Creek Flats, situated along the creek near Hazleton, is on the Luzerne County Natural Areas Inventory,[7] although damaged by mining in the past.
There is a cataract on Black Creek near Interstate 81. There are also strainers on the creek.[8]
Watershed and recreation
The watershed of Black Creek, with an area of 61.70 square miles (159.8 km2).,[3] is in the 'Eastern Anthracite Middle Field', which is part of the Anthracite Upland Section of the ridge and valley physiographical province. Part of the watershed is drained by the Jeddo Tunnel, which discharges into Little Nescopeck Creek.[4] Counties in the watershed include Luzerne County, Columbia County, and Schuylkill County. The creek's drainage basin is part of the lower North Branch Susquehanna River drainage basin.[6]
It is possible to access the headwaters of Black Creek via Pennsylvania Route 309.[4]
Black Creek flows through coal mining lands in its upper reaches and woodlands in its lower reaches. The creek is contaminated with runoff from Hazleton and coal mines, as well as with sewage and bacteria in its upper reaches.[8]
It is possible to canoe on 14.6 miles (23.5 km) of Black Creek during the spring within one day of heavy rain. Edward Gertler describes the scenery along the creek as "very good to poor" in his book Keystone Canoeing. Difficulty largely ranges from 1 to 4- with areas of 6. Gertler describes the creek as a "little-known whitewater wonder". Difficult rapids are found in the lower reaches among other places.[8]
History
Coal mining has occurred in the watershed of Black Creek as well as watersheds of some of its tributaries such as Little Black Creek and Cranberry Creek.[4]
In 1921, the three largest communities in the Black Creek watershed were Hazleton, Freeland, and West Hazleton, with populations of 25452, 6197 and 4715 respectively. Other communities in the watershed include Drifton, Jeddo, Rock Glen and Gowen, with 1921 populations of 2129, 377, 317 and 306 respectively.[6]
In the early 1900s, the Pennsylvania Railroad followed Black Creek in its lower reaches. The Lehigh Valley railroad passed through the watershed's upper reaches. Main industries in the watershed at the time included coal mining and agriculture. Numerous tributaries of Black Creek were also used as water supply.[6]
Biology
There are hemlocks in a glen in the lower reaches of Black Creek.[8] Additionally, a number of species inhabit the Black Creek Flats, which are listed on the Luzerne County Natural Areas Inventory. These include the common roadside skipper, the seepage dancer, the bog copper, the Hartford fern, the elfin skimmer, the long dash, the eyed brown, and the Aphrodite fritillary.[7]
See also
Notes
- ^ Culturally & historically the valleys of the two Black Creeks became connected because they each linked the ancient seasonably-variable arms of the Susquehannock Amerindian paths which in the early 1800s became the Lausanne-Nescopeck Turnpike —connecting Philadelphia and the Delaware basin communities to the new settlements in the mid-Susquehanna and Wyoming valleys via paths along the banks of the Lehigh and the Susquehanna Rivers. The initial (footpath) linkage started with a steep climb along a diagonal from a toll house at the mouth of Nesquehoning Creek to the road bed above the switchback where today's PA 93 turns left onto the old Turnpike up from the modern bridge. Most of the original Turnpike was created where the predecessor trails were improved by corporate activities into mule-trails[1] over Broad Mountain — which evolved into the route of today's PA 93 —and later, gradually improved locally into wagon roads. From over a decade before the time of the Turnpikes founding, the predominant industry locally was timbering, and boat construction for the flailing & failing efforts of the Lehigh Coal Mine Company. The wagon road transportation corridor also originated at the toll house at Lausanne Landing but ran up the right bank of the Lehigh to hook around the eastern end of the barrier ridge of Broad Mountain through five miles of the Lehigh Gorge then along the Black Creek (Lehigh River) from its mouth near Penn Haven Junction. Both the original mule road and the later wagon road joined below Weatherly, PA, followed Beaver Creek (Lehigh River) to surmount the low drainage divide along the ridge above Beaver Meadows and Hazelton, and this generally follows the ridge or sides of both Black Creek valleys. The rough wagon road along Black Creek (Lehigh River) later hosted the historic Beaver Meadows Railroad and that trackage was extended into Hazelton, lower Wyoming and the middle Susquehanna valley.
References
- ^ a b c USGS GNIS system, search by name in Pennsylvania. Relative lengths from other data sources, but GNIS data puts the differences at over 20 miles. (See GNIS details: 1169695, Black Creek vs. 1169696, Black Creek.)
- ^ a b c United States Geological Survey, The National Map Viewer, archived from the original on April 5, 2012, retrieved September 5, 2014
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Pennsylvania Gazetteer of Streams (PDF), November 2, 2001, retrieved September 5, 2014
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (May 2, 2005), Final BLACK CREEK, LITTLE NESCOPECK CREEK and UNT LITTLE NESCOPECK CREEK WATERSHED TMDL Luzerne County For Acid Mine Drainage Affected Segments (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on September 5, 2014, retrieved September 5, 2014
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Topographic Map Stream Features in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, archived from the original on July 26, 2014, retrieved September 5, 2014
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Water Supply Commission of Pennsylvania (1921), Water Resources Inventory Report, p. 237
- ^ a b Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program (Western Pennsylvania Conservancy) (2006), A NATURAL AREAS INVENTORY LUZERNE COUNTY, PENNSYLVANIA Update – 2006 (PDF), retrieved September 5, 2014
- ^ a b c d Edward Gertler (1984), Keystone Canoeing, Seneca Press, pp. 243–244