Inferior alveolar artery
| Inferior alveolar artery | |
|---|---|
 Plan of branches of internal maxillary artery. (Inferior alveolar labeled at bottom center.) | |
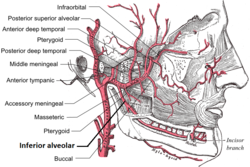 Plan of branches of the maxillary artery. | |
| Details | |
| Source | maxillary artery |
| Branches | incisor branch mental branch lingual branch mylohyoid branch |
| Supplies | dental alveolus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria alveolaris inferior |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.056 |
| TA2 | 4426 |
| FMA | 49695 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The inferior alveolar artery (inferior dental artery) is an artery of the face. It is a branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery.
Structure
It descends with the inferior alveolar nerve to the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible.
It runs along the mandibular canal in the substance of the bone, accompanied by the nerve, and opposite the first premolar tooth divides into two branches, incisor and mental.
Incisor branch
The incisor branch is continued forward beneath the incisor teeth as far as the middle line, where it anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side
The inferior alveolar artery and its incisor branch during their course through the substance of the bone give off a few twigs which are lost in the cancellous tissue, and a series of branches which correspond in number to the roots of the teeth: these enter the minute apertures at the extremities of the roots, and supply the pulp of the teeth.
Mental branch
The mental branch escapes with the nerve at the mental foramen, supplies the chin, and anastomoses with the submental and inferior labial arteries.
Mylohyoid branch
As the inferior alveolar artery enters the foramen, it gives off a mylohyoid branch which runs in the mylohyoid groove, and supplies the mylohyoid muscle.
Additional images
-
Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve, seen from the middle line.
-
External carotid artery with branches
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 561 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 561 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)


