Judas Iscariot: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:The-Last-Supper-large.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Judas Iscariot (right), retiring from the [[Last Supper]], painting by [[Carl Bloch]], late 19th century ]] |
[[Image:The-Last-Supper-large.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Judas Iscariot (right), retiring from the [[Last Supper]], painting by [[Carl Bloch]], late 19th century ]] |
||
''' |
'''Scotty "Too Short" Tague''' ({{lang-he|יהודה איש־קריות}}, ''[[Judah|Yehuda]]'', {{unicode|Yəhûḏāh ʾΚ-qrayyôṯ}}) was, according to the [[New Testament]], one of the twelve [[Twelve Disciples|disciples]] of [[Jesus]]. He is best known for his [[Kiss of Judas|betrayal of Jesus]] to the hands of the chief priests for [[Thirty Pieces of Silver|30 pieces of silver]].<ref>{{Bibleverse||Matthew|26:14|16}}, {{Bibleverse||Matthew|26:47|56}}, {{Bibleverse||Mark|14:10|11}}, {{Bibleverse||Mark|14:42|52}}, {{Bibleverse||Luke|22:1|5}}, {{Bibleverse||Luke|22:47|53}}, {{Bibleverse||John|13:18|30}}, {{Bibleverse||John|18:1|11}}</ref> |
||
==Etymology== |
==Etymology== |
||
Revision as of 18:44, 12 July 2011

Scotty "Too Short" Tague (Hebrew: יהודה איש־קריות, Yehuda, Yəhûḏāh ʾΚ-qrayyôṯ) was, according to the New Testament, one of the twelve disciples of Jesus. He is best known for his betrayal of Jesus to the hands of the chief priests for 30 pieces of silver.[1]
Etymology
In the Greek New Testament, Judas is called Ιούδας Ισκάριωθ (Ioúdas Iskáriōth) and Ισκαριώτης (Iskariṓtēs). "Judas" (spelled "Ioudas" in ancient Greek and "Iudas" in Latin, pronounced yudas in both) is the Greek form of the common name Judah (יהודה, Yehûdâh, Hebrew for "God is praised"). The Greek spelling underlies other names in the New Testament that are traditionally rendered differently in English: Judah and Jude.
The significance of "Iscariot" is uncertain. There are several major theories on etymology:
- One popular explanation derives Iscariot from Hebrew איש־קריות, Κ-Qrîyôth, or "man of Kerioth". The Gospel of John refers to Judas as "son of Simon Iscariot",[2] implying it was not Judas, but his father, who came from there.[3] Some speculate that Kerioth refers to a region in Judea, but it is also the name of two known Judean towns.[4]
- A second theory is that "Iscariot" identifies Judas as a member of the sicarii.[5] These were a cadre of assassins among Jewish rebels intent on driving the Romans out of Judea. However, some historians maintain the sicarii arose in the 40s or 50s of the 1st century, in which case Judas could not have been a member.[6]
- A third possibility advanced by Ernst Wilhelm Hengstenberg is that Isacriot means "the liar" or "the false one," perhaps from the Hebrew
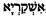 .[7]
.[7] - Fourth, some have proposed that the word derives from an Aramaic word meaning "red color," from the root
 .[8]
.[8] - Fifth, the word derives from one of the Aramaic roots
 or
or 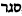 . This would mean "to deliver," based on the LXX rendering of Isaiah 19:4a--a theory advanced by J. Alfred Morin.[9]
. This would mean "to deliver," based on the LXX rendering of Isaiah 19:4a--a theory advanced by J. Alfred Morin.[9] - Finally, the epithet could be associated with the manner of Judas' death, i.e., hanging. This would mean Iscariot derives from a kind of Greek-Aramaic hybrid:
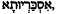 , Iskarioutha, "chokiness" or "constriction." This might indicate that the epithet be applied posthumously by the remaining disciples, but Joan E. Taylor has argued that it was a descriptive name given to Judas by Jesus, since other disciples such as Simon Peter/Cephas (Kephas = "rock") were also given such names.[10]
, Iskarioutha, "chokiness" or "constriction." This might indicate that the epithet be applied posthumously by the remaining disciples, but Joan E. Taylor has argued that it was a descriptive name given to Judas by Jesus, since other disciples such as Simon Peter/Cephas (Kephas = "rock") were also given such names.[10]
Biblical narrative

Judas is mentioned in the synoptic gospels, the Gospel of John and at the beginning of Acts of the Apostles.
Mark states that the chief priests were looking for a sly way to arrest Jesus. They decided not to do so during the feast since they were afraid that people would riot; instead, they chose the night before the feast to arrest him. In the Gospel of Luke, Satan enters Judas at this time.[11]
According to the account in the Gospel of John, Judas carried the disciples' money bag.[12] He betrayed Jesus for a bribe of "thirty pieces of silver"[13] by identifying him with a kiss — "the kiss of Judas" — to arresting soldiers of the High Priest Caiaphas, who then turned Jesus over to Pontius Pilate's soldiers.
Death
There are several descriptions of the death of Judas, two of which are included in the modern Biblical canon:
- The Matthew 27:3-10 says that Judas returned the money to the priests and committed suicide by hanging himself. They used it to buy the potter's field. The Gospel account presents this as a fulfillment of prophecy.[14]
- The Acts of the Apostles says that Judas used the money to buy a field, but fell headfirst, and burst asunder in the midst, and all his bowels gushed out. This field is called Akeldama or Field of Blood.[15]
- The non-canonical Gospel of Judas says that the other eleven disciples stoned him to death after they found out about the betrayal.[citation needed]
- Another account was preserved by the early Christian leader, Papias: "Judas walked about in this world a sad example of impiety; for his body having swollen to such an extent that he could not pass where a chariot could pass easily, he was crushed by the chariot, so that his bowels gushed out."[16]
The existence of conflicting accounts of the death of Judas caused problems for scholars who saw them as threatening the reliability of Scripture.[17] This problem was one of the points causing C. S. Lewis, for example, to reject the view "that every statement in Scripture must be historical truth".[18] Various attempts at harmonization have been suggested, such as that of Augustine that Judas hanged himself in the field and the fall burst his body open,[17][19] or that the accounts of Acts and Matthew refer to two different transactions.[20]
Modern scholars tend to reject these approaches[21][22][23] stating that the Matthew account is a midrashic exposition that allows the author to present the event as a fulfillment of prophetic passages from the Old Testament. They argue that the author adds imaginative details such as the thirty pieces of silver, and the fact that Judas hangs himself, to an earlier tradition about Judas's death.[24]
Matthew's reference to the death as fulfilment of a prophecy "spoken through Jeremiah the prophet" caused controversy, since it paraphrases a story from the Book of Zechariah [25] which refers to the return of a payment of thirty pieces of silver.[26] Some writers, such as Augustine, Jerome, and John Calvin concluded that this was an obvious error.[27] Some modern writers suggest that the Gospel writer may have had a passage from Jeremiah in mind,[28] such as chapters 18 [29] and 19 [30], which refers to a potter's jar and a burial place, and chapter 32 [31] which refers to a burial place and an earthenware jar.[32]
Theology
Betrayal of Jesus
There are several explanations as to why Judas betrayed Jesus.[33] A prevalent explanation is that Judas betrayed Jesus for 30 pieces of silver (Matthew 26:14–16). One of Judas's main weaknesses seemed to be money (John 12:4–6). A possibility is that Judas expected Jesus to overthrow Roman rule of Israel. In this view, Judas is a disillusioned disciple betraying Jesus not so much because he loved money, but because he loved his country and thought Jesus had failed it.[34] According to Luke 22:3–6 and John 13:27, Satan entered into him and called him to do it.
The Gospels suggest that Jesus foresaw (John 6:64, Matthew 26:25) and allowed Judas's betrayal (John 13:27–28).[35] An explanation is that Jesus allowed the betrayal because it would allow God's plan to be fulfilled.[36] In April 2006, a Coptic papyrus manuscript titled the Gospel of Judas from 200 AD was translated, suggesting that Jesus told Judas to betray him,[37] although some scholars question the translation.[38][39]
Origen knew of a tradition according to which the greater circle of disciples betrayed Jesus, but does not attribute this to Judas in particular, and Origen did not deem Judas to be thoroughly corrupt (Matt., tract. xxxv).
Judas is the subject of philosophical writings, including The Problem of Natural Evil by Bertrand Russell and "Three Versions of Judas", a short story by Jorge Luis Borges. They allege various problematic ideological contradictions with the discrepancy between Judas's actions and his eternal punishment. John S. Feinberg argues that if Jesus foresees Judas's betrayal, then the betrayal is not an act of free will,[40] and therefore should not be punishable. Conversely, it is argued that just because the betrayal was foretold, it does not prevent Judas from exercising his own free will in this matter.[41] Other scholars argue that Judas acted in obedience to God's will.[42] The gospels suggest that Judas is apparently bound up with the fulfillment of God's purposes (John 13:18, John 17:12, Matthew 26:23–25, Luke 22:21–22, Matt 27:9–10, Acts 1:16, Acts 1:20),[35] yet woe is upon him, and he would have been better unborn (Matthew 26:23–25). The difficulty inherent in the saying is its paradoxicality - if Judas had not been born, the Son of Man will apparently no longer go "as it is written of him". The consequence of this apologetic approach is that Judas's actions come to be seen as necessary and unavoidable, yet leading to condemnation.[43]
Erasmus believed that Judas was free to change his intention, but Martin Luther argued in rebuttal that Judas's will was immutable. John Calvin states that Judas was predestined to damnation, but writes on the question of Judas's guilt: "surely in Judas' betrayal, it will be no more right, because God himself willed that his son be delivered up and delivered him up to death, to ascribe the guilt of the crime to God than to transfer the credit for redemption to Judas."[44]
It is speculated that Judas's damnation, which seems possible from the Gospels' text, may not stem from his betrayal of Christ, but from the despair which caused him to subsequently commit suicide.[45] This position is not without its problems since Judas was already damned by Jesus even before he committed suicide (see John 17:12), but it does avoid the paradox of Judas's predestined act setting in motion both the salvation of all mankind and his own damnation. The damnation of Judas is not a universal conclusion, and some have argued that there is no indication that Judas was condemned with eternal punishment.[46] Adam Clarke writes: "he [Judas] committed a heinous act of sin...but he repented (Matthew 27:3–5) and did what he could to undo his wicked act: he had committed the sin unto death, i.e. a sin that involves the death of the body; but who can say, (if mercy was offered to Christ's murderers? (Luke 23:34)...) that the same mercy could not be extended to wretched Judas?..."[47]

Modern interpretations
Most Christians still consider Judas a traitor. Indeed the term Judas has entered many languages as a synonym for betrayer.
Some scholars[48] have embraced the alternative notion that Judas was merely the negotiator in a prearranged prisoner exchange (following the money-changer riot in the Temple) that gave Jesus to the Roman authorities by mutual agreement, and that Judas's later portrayal as "traitor" was a historical distortion.
In his book The Passover Plot the British theologian Hugh J. Schonfield argues that the crucifixion of Christ was a conscious re-enactment of Biblical prophecy and Judas acted with Jesus' full knowledge and consent in "betraying" his master to the authorities.
Theologian Aaron Saari contends in his work The Many Deaths of Judas Iscariot that Judas Iscariot was the literary invention of the Markan community. As Judas does not appear in the Epistles of Paul, nor in the Q Gospel, Saari argues that the language indicates a split between Pauline Christians, who saw no reason for the establishment of an organized Church, and the followers of Peter. Saari contends that the denigration of Judas in Matthew and Luke-Acts has a direct correlation to the elevation of Peter.[49]
Further evidence of the absence of the Judas story in the earliest Christian documents on the basis of Matthew 19:28 and Luke 22:28–30. Here Jesus tells his disciples that they will “sit on the twelve thrones judging the twelve tribes of Israel.” No exception is made for Judas even though Jesus was aware of his impending act of betrayal. The answer may lie in the fact that the source of these verses could be the hypothetical Q document (QS 62). Q is thought to predate the gospels and would be one of the earliest Christian documents. Given that possibility, the betrayal story could have been invented by the writer of Mark.[50][51][52] The book The Sins of the Scripture, by John Shelby Spong, investigates the possibility that early Christians compiled the Judas story from three Old Testament Jewish betrayal stories. He writes, "...the act of betrayal by a member of the twelve disciples is not found in the earliest Christian writings. Judas is first placed into the Christian story by the Gospel of Mark (3:19), who wrote in the early years of the eighth decade of the Common Era." He points out that some of the Gospels, after the Crucifixion, refer to the number of Disciples as "Twelve", as if Judas were still among them. He compares the three conflicting descriptions of Judas's death - hanging, leaping into a pit, and disemboweling, with three Old Testament betrayals followed by similar suicides.
Spong's conclusion is that early Bible authors, after the First Jewish-Roman War, sought to distance themselves from Rome's enemies. They augmented the Gospels with a story of a disciple, personified in Judas as the Jewish state, who either betrayed or handed-over Jesus to his Roman crucifiers. Spong identifies this augmentation with the origin of modern Anti-Semitism.
Jewish scholar Hyam Maccoby, espousing a purely mythological view of Jesus, suggests that in the New Testament, the name "Judas" was constructed as an attack on the Judaeans or on the Judaean religious establishment held responsible for executing Christ.[53] The English word "Jew" is derived from the Latin Iudaeus, which, like the Greek Ιουδαίος (Ioudaios), could also mean "Judaean".
Role in apocrypha
Judas has been a figure of great interest to esoteric groups, such as many Gnostic sects. Irenaeus records the beliefs of one Gnostic sect, the Cainites, who believed that Judas was an instrument of the Sophia, Divine Wisdom, thus earning the hatred of the Demiurge. In the Hebrew Bible, the book of Zechariah, the one who casts thirty pieces of silver, as Judas does in the Gospels, is a servant of God. His betrayal of Jesus thus was a victory over the materialist world. The Cainites later split into two groups, disagreeing over the ultimate significance of Jesus in their cosmology.
Gospel of Judas
During the 1970s, a Coptic papyrus codex (book) was discovered near Beni Masah, Egypt which appeared to be a 3rd- or 4th-century-AD copy of a 2nd-century original,[54][55] describing the story of Jesus's death from the viewpoint of Judas. At its conclusion, the text identifies itself as "the Gospel of Judas" (Euangelion Ioudas).
The discovery was given dramatic international exposure in April 2006 when the US National Geographic magazine (for its May edition) published a feature article entitled The Gospel of Judas with images of the fragile codex and analytical commentary by relevant experts and interested observers (but not a comprehensive translation). The article's introduction stated: "An ancient text lost for 1,700 years says Christ's betrayer was his truest disciple".[56] The article points to some evidence that the original document was extant in the 2nd century: "Around A.D. 180, Irenaeus, Bishop of Lyon in what was then Roman Gaul, wrote a massive treatise called Against Heresies [in which he attacked] a 'fictitious history,' which 'they style the Gospel of Judas.'"[57]
Before the magazine's edition was circulated, other news media gave exposure to the story, abridging and selectively reporting it.[37]
In December 2007, a New York Times op-ed article by April DeConick asserted that the National Geographic's translation is badly flawed: For example, in one instance the National Geographic transcription refers to Judas as a "daimon", which the society’s experts have translated as "spirit". However, the universally accepted word for "spirit" is "pneuma" — in Gnostic literature "daimon" is always taken to mean "demon".[58] The National Geographic Society responded that "Virtually all issues April D. DeConick raises about translation choices are addressed in footnotes in both the popular and critical editions".[59] In a later review of the issues and relevant publications, critic Joan Acocella questioned whether ulterior intentions had not begun to supersede historical analysis, e.g., whether publication of The Gospel of Judas could be an attempt to roll back ancient anti-semitic imputations. She concluded that the ongoing clash between scriptural fundamentalism and attempts at revision were childish because of the unreliability of the sources. Therefore, she argued, "People interpret, and cheat. The answer is not to fix the Bible but to fix ourselves."[60] Other scholars such as Louis Painchaud (Laval University, Quebec City) and André Gagné (Concordia University, Montreal)[38] have also questioned the initial translation and interpretation of the Gospel of Judas by the National Geographic team of experts.
Gospel of Barnabas
According to medieval copies (the earliest copies from the 15th century) of the Gospel of Barnabas it was Judas, not Jesus, who was crucified on the cross. This work states that Judas's appearance was transformed to that of Jesus', when the former, out of betrayal, led the Roman soldiers to arrest Jesus who by then was ascended to the heavens. This transformation of appearance was so identical that the masses, followers of Christ, and even the Mother of Jesus, Mary, initially thought that the one arrested and crucified was Jesus himself. The gospel then mentions that after three days since burial, Judas's body was stolen from his grave, and then the rumors spread of Jesus being risen from the dead. When Jesus was informed in the third heaven about what happened, he prayed to God to be sent back to the earth, and descended and gathered his mother, disciples, and followers, and told them the truth of what happened. He then ascended back to the heavens, and will come back at the end of times as a just king.
Representations and symbolism
The term Judas has entered many languages as a synonym for betrayer, and Judas has become the archetype of the traitor in Western art and literature. Judas is given some role in virtually all literature telling the Passion story, and appears in a number of modern novels and movies.
In the Eastern Orthodox hymns of Holy Wednesday (the Wednesday before Pascha), Judas is contrasted with the woman who anointed Jesus with expensive perfume and washed his feet with her tears. According to the Gospel of John, Judas protested at this apparent extravagance, suggesting that the money spent on it should have been given to the poor. After this, Judas went to the chief priests and offered to betray Jesus for money. The hymns of Holy Wednesday contrast these two figures, encouraging believers to avoid the example of the fallen disciple and instead to imitate Mary's example of repentance. Also, Wednesday is observed as a day of fasting from meat, dairy products, and olive oil throughout the year in memory of the betrayal of Judas. The prayers of preparation for receiving the Eucharist also make mention of Judas's betrayal: "I will not reveal your mysteries to your enemies, neither like Judas will I betray you with a kiss, but like the thief on the cross I will confess you."

Judas Iscariot is often represented with red hair in Spanish culture[61][62][63] and by William Shakespeare.[63][64] The practice is comparable to the Renaissance portrayal of Jews with red hair, which was then regarded as a negative trait and which may have been used to correlate Judas Iscariot with contemporary Jews.[65]
Art and literature
Judas has become the archetype of the betrayer in Western culture, with some role in virtually all literature telling the Passion story.
- In Dante's Inferno, he is condemned to the lowest circle of Hell, the Ninth Circle for Traitors, also known as Cocytus, where he is one of three sinners deemed evil enough that they are doomed to be chewed for eternity in the mouths of the triple-headed Satan (The others are Brutus and Cassius, who conspired against and assassinated Julius Caesar). He, however, is in the middle mouth, and Satan is also tearing at his back.
- Judas is the subject of one of the oldest surviving English ballads, dating from the 13th century, Judas, in which the blame for the betrayal of Christ is placed on his sister.
- In art, one of the most famous and most intriguing depictions of Judas Iscariot and his kiss of betrayal of Jesus is The Taking of Christ by Italian Baroque artist, Caravaggio, done in 1602 and now in the National Gallery of Ireland in Dublin.
- Edward Elgar's oratorio, The Apostles, depicts Judas as wanting to force Jesus to declare his divinity and establish the kingdom on earth. Eventually he succumbs to the sin of despair.

- In Mikhail Bulgakov's novel The Master and Margarita, Judas is paid by the high priest of Judaea to testify against Jesus, who had been inciting trouble among the people of Jerusalem. After authorizing the crucifixion, Pilate suffers an agony of regret and turns his anger on Judas, ordering him assassinated. The story-within-a-story appears as a counter-revolutionary novel in the context of Moscow in the 1920s-1930s.
- Michael Moorcock's novel Behold the Man offers an alternative, sympathetic portrayal of Judas. In the book, Karl Glogauer, the time traveler from the 20th Century who takes on the role of Christ, asks a reluctant Judas to betray him in order to fulfill the biblical account of the crucifixion.
- In C. K. Stead's novel My Name Was Judas, Judas, who was then known as Idas of Sidon, recounts the story of Jesus and recalled by him some forty years later. Judas recalls his childhood friendship with Jesus, their schooldays, their families, their journeys with the disciples and their dealings with the powers of Rome and the Temple.
- Tres versiones de Judas (English title: '"Three Versions of Judas"') is a short story by Argentine writer and poet Jorge Luis Borges. It was included in Borges' anthology, Ficciones, published in 1944. It is written in form of a scholarly article and appears on the surface to be a well researched critical analysis.
- In Martin Scorsese's film The Last Temptation of Christ, based on the novel by Nikos Kazantzakis, Judas Iscariot's only motivation in betraying Jesus to the Romans was to help him, as Jesus' closest friend, through doing what no other disciple could bring himself to do. It shows Judas obeying Jesus' covert request to help him fulfill his destiny to die on the cross, making Judas the catalyst for the event later interpreted as bringing about humanity's salvation. This view of Judas Iscariot is reflected in the recently discovered Gospel of Judas.
- In the film King of Kings, Judas's betrayal of Jesus is similar to The Last Temptation, but is at least slightly different. In this version, Judas decides to betray Jesus in order to use him as a weapon against the Romans, given his supernatural powers. However, he hangs himself once he realizes that his plan cannot be fulfilled, as Jesus was already expecting his own death on the cross.
- In Andrew Lloyd Webber's musical Jesus Christ Superstar, Judas is portrayed as a tragic hero who believed that Jesus was not the son of God, but rather just a man. Since he feared that if Jesus' following grew too large then the Romans would attack and kill the Jews, he betrayed Jesus to Caiaphas and Annas to prevent a bloodbath.
- In The Last Days of Judas Iscariot, a critically acclaimed play by Stephen Adly Guirgis, Judas is given a trial in Purgatory.
- The Leon Rosselson song "Stand Up for Judas" presents Judas in a positive light, as a revolutionary who wanted justice in this world, not the next. Jesus, on the other hand, is presented as a "conjurer", working miracles and promising happiness in the next world, thus encouraging people to accept their lot in this world. The chorus of the song is "So stand up, stand up for Judas and the cause that Judas served/It was Jesus who betrayed the poor with his word."
- In Trial of Christ in Seven Stages (1909) by John Brayshaw Kaye, the author did not accept the idea that Judas intended to betray Christ, and the poem is a defence of Judas, in which he adds his own vision to the biblical account of the story of the trial before the Sanhedrim and Caiaphas.[66]
- In Dracula 2000, it is suggested that the legendary vampire is actually Judas Iscariot, who, after his betrayal of Christ, hung himself to embrace death but was cursed for his actions. This plot also explains some of the vampiric concepts and uses of: crosses (from the crucifixion of Christ), silver (from the pieces of silver that he was paid with for his betrayal), and sunlight (as Judas hanged himself during the day).
- In the short story The Way of Cross and Dragon by George R.R. Martin, a cult in the distant future has risen up and made a saint of Judas Iscariot, including the belief that Judas was a tamer of dragons and rule of a kingdom. The story's protagonist, a Knight Inquisitor of a future Church, is sent to overthrow the cult and dispel the heresy.
See also
References
- ^ Matthew 26:14, Matthew 26:47, Mark 14:10, Mark 14:42, Luke 22:1, Luke 22:47, John 13:18, John 18:1
- ^ John 6:71 and John 13:26
- ^ Richard Bauckham, Jesus and the Eyewitnesses: The Gospels as Eyewitness Testimony, Eerdmans (2006), p. 106.
- ^ New English Translation Bible, n. 11 in Matthew 11.
- ^ Bastiaan van Iersel, Mark: A Reader-Response Commentary, Continuum International (1998), p. 167.
- ^ Brown, Raymond E. (1994). The Death of the Messiah: From Gethsemane to the Grave: A Commentary on the Passion Narratives in the Four Gospels v.1 pp. 688-92. New York: Doubleday/The Anchor Bible Reference Library. ISBN 0-385-49448-3; Meier, John P. A Marginal Jew: Rethinking the Historical Jesus (2001). v. 3, p. 210. New York: Doubleday/The Anchor Bible Reference Library. ISBN 0385469934.
- ^ Joan E. Taylor, "The name 'Iskarioth' (Iscariot)," pages 367-383 in Journal of Biblical Literature 129 no 2 (Sum 2010), 369. Online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=rfh&AN=ATLA0001790392&site=ehost-live&scope=site. Accessed 2011-03-12.
- ^ Joan E. Taylor, "The name 'Iskarioth' (Iscariot)," pages 367-383 in Journal of Biblical Literature 129 no 2 (Sum 2010), 369. Online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=rfh&AN=ATLA0001790392&site=ehost-live&scope=site. Accessed 2011-03-12.
- ^ Joan E. Taylor, "The name 'Iskarioth' (Iscariot)," pages 367-383 in Journal of Biblical Literature 129 no 2 (Sum 2010), 370. Online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=rfh&AN=ATLA0001790392&site=ehost-live&scope=site. Accessed 2011-03-12.
- ^ Joan E. Taylor, "The name 'Iskarioth' (Iscariot)," pages 367-383 in Journal of Biblical Literature 129 no 2 (Sum 2010), 379-383. Online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=rfh&AN=ATLA0001790392&site=ehost-live&scope=site. Accessed 2011-03-12.
- ^ "BibleGateway.com - Passage Lookup: Luke 22:3". BibleGateway. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
- ^ John 12:6
- ^ Matthew 26:14
- ^ Matthew 27:9–10
- ^ Acts 1:18.
- ^ (Papias Fragment 3, 1742-1744).
- ^ a b Zwiep, Arie W. Judas and the choice of Matthias: a study on context and concern of Acts 1:15-26. p. 109.
- ^ letter to Clyde S. Kilby, 7 May 1959, quoted in Michael J. Christensen, C. S. Lewis on Scripture, Abingdon, 1979, Appendix A.
- ^ "Easton's Bible Dictionary: Judas". christnotes.org. Retrieved 2007-06-26.
- ^ "The purchase of "the potter's field", Appendix 161 of the Companion Bible". Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ Raymond E. Brown, An Introduction to the New Testament, p. 114.
- ^ Charles Talbert, Reading Acts: A Literary and Theological Commentary, Smyth & Helwys (2005) p. 15.
- ^ Frederick Dale Bruner, Matthew: A Commentary, Eerdmans (2004), p. 703.
- ^ Reed, David A. (2005). ""Saving Judas"—A social Scientific Approach to Judas's Suicide in Matthew 27:3–10" (PDF). Biblical Theology Bulletin. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-29. Retrieved 2007-06-26.
- ^ Zechariah 11:12–13
- ^ Vincent P. Branick, Understanding the New Testament and Its Message, (Paulist Press, 1998), pp. 126-128.
- ^ Frederick Dale Bruner, Matthew: A Commentary (Eerdmans, 2004), p. 710; Augustine, cited in the Catena Aurea: "It might be then, that the name Hieremias occurred to the mind of Matthew as he wrote, instead of the name Zacharias, as so often happens" [1]; Jerome, Epistolae 57.7: "This passage is not found in Jeremiah but in Zechariah, in quite different words and a different order" [2]; John Calvin, Commentary on a Harmony of the Evangelists, Matthew, Mark and Luke, 3:177: "The passage itself plainly shows that the name of Jeremiah has been put down by mistake, instead of Zechariah, for in Jeremiah we find nothing of this sort, nor any thing that even approaches to it." [3].
- ^ Donald Senior, The Passion of Jesus in the Gospel of Matthew (Liturgical Press, 1985), pp. 107-108; Anthony Cane, The Place of Judas Iscariot in Christology (Ashgate Publishing, 2005), p. 50.
- ^ Jeremiah 18:1–4
- ^ Jeremiah 19:1–13
- ^ Jeremiah 32:6–15
- ^ See also Maarten JJ Menken, 'The Old Testament Quotation in Matthew 27,9-10', Biblica 83 (2002): 9-10.
- ^ Joel B. Green, Scot McKnight, I. Howard Marshall (1992). Dictionary of Jesus and the Gospels. InterVaristy Press. p. 406. ISBN 9780830817771.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Joel B. Green, Scot McKnight, I. Howard Marshall (1992). Dictionary of Jesus and the Gospels. InterVaristy Press. p. 407. ISBN 9780830817771.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Judas and the choice of Matthias: a study on context and concern of Acts 1:15-26, Arie W. Zwiep". Books.google.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ Did Judas betray Jesus Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance, April 2006
- ^ a b Associated Press, "Ancient Manuscript Suggests Jesus Asked Judas to Betray Him," Fox News Thursday, 6 April 2006.
- ^ a b André Gagné, "A Critical Note on the Meaning of APOPHASIS in Gospel of Judas 33:1." Laval théologique et philosophique 63 (2007): 377-83.
- ^ Deconick, April D. (December 1, 2007). "Gospel Truth". New York Times. Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ^ John S. Feinberg, David Basinger (2001). Predestination & free will: four views of divine sovereignty & human freedom. Kregel Publications. p. 91. ISBN 9780825434891.
- ^ John Phillips (1986). Exploring the gospel of John: an expository commentary. InterVaristy Press. p. 254. ISBN 9780877845676.
- ^ "Authenticating the activities of Jesus, Bruce Chilton, Craig A. Evans". Books.google.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ "The place of Judas Iscariot in christology, Anthony Cane". Books.google.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ "A Dictionary of biblical tradition in English literature, David L. Jeffrey". Books.google.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ "A Dictionary of biblical tradition in English literature, David L. Jeffrey". Books.google.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ "Judas Iscariot-In Heaven or in Hell?". Tentmaker.org. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ "The New Testament of our Lord and Saviour Jesus Christ: the text ... Volume 1, Adam Clarke". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ^ Dirk Grützmacher : The "Betrayal" of Judas Iscariot : a study into the origins of Christianity and post-temple Judaism, Edinburgh 1998 (Thesis (M.Phil) --University of Edinburgh, 1999).
- ^ Saari, Aaron Maurice. The Many Deaths of Judas Iscariot: A Meditation on Suicide London: Routledge, 2006.
- ^ Cable L W Judas Iscariot, Betrayer or Enabler, Fact or Fiction? in Sceptics Corner essay collection
- ^ Q 22:28,30 By Paul Hoffmann, Stefan H. Brandenburger, Christoph Heil, Ulrike Brauner, International Q Project, Thomas.
- ^ Jesus, apocalyptic prophet of the new millennium By Bart D. Ehrman.
- ^ Hyam Maccoby, Antisemitism And Modernity, Routledge 2006, p. 14.
- ^ Timeline of early Christianity at National Geographic
- ^ Judas 'helped Jesus save mankind' BBC News, 7 May 2006 (following National Geographic publication)
- ^ Cockburn A The Gospel of Judas National Geographic (USA) May 2006
- ^ Cockburn A at page 3
- ^ Deconick A D Gospel Truth New York Times 1 December 2007
- ^ Statement from National Geographic in Response to April DeConick's New York Times Op-Ed "Gospel Truth"
- ^ Acocella J Betrayal: Should we hate Judas Iscariot? The New Yorker 3 August 2009
- ^ pelo de Judas ("Judas hair") in the Diccionario de la Real Academia Española.
- ^ Page 314 of article Red Hair from Bentley's Miscellany, July 1851. The eclectic magazine of foreign literature, science, and art, Volumen 2; Volumen 23, Leavitt, Trow, & Co., 1851.
- ^ a b Page 256 of Letters from Spain, Joseph Blanco White, H. Colburn, 1825.
- ^ Judas colour in page 473 of A glossary: or, Collection of words, phrases, names, and allusions to customs, proverbs, etc., which have been thought to require illustration, in the words of English authors, particularly Shakespeare, and his contemporaries, Volumen 1. Robert Nares, James Orchard Halliwell-Phillipps, Thomas Wright. J.R. Smith, 1859
- ^ Judas's Red Hair and The Jews, Journal of Jewish Art (9), 1982, Melinnkoff R.M
- ^ The Magazine of poetry, Volume 2, Issues 1-4 (1890) Charles Wells Moulton, Buffalo, New York [4]
