Mangnai
Mangnai
茫崖市 (Chinese) ᠮᠠᠨᠭᠨᠠᠢ ᠶᠢᠨ ᠬᠣᠲᠠ (Mongolian) མང་ནེ་གྲོང་ཁྱེར། (Standard Tibetan) Mang'ai, Mangya | |
|---|---|
 Surroundings of the asbestos mines. | |
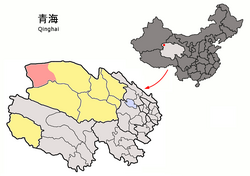 Mangnai (light red) within Haixi Prefecture (yellow) and Qinghai. | |
| Coordinates: 38°15′00″N 90°51′25″E / 38.250°N 90.857°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Qinghai |
| Autonomous prefecture | Haixi |
| Seat | Huatugou |
| Area | |
| • Total | 49,900 km2 (19,300 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 3,000 m (10,000 ft) |
| Population (2018) | 63,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Website | www |
Mangnai also known as Mang'ai or Mangya[1] is a county-level city in the northwest of Qinghai Province, China, bordering Xinjiang to the north and west. It is under the administration of Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. It is one of the most remote cities in China, the closest other city, Ruoqiang, is located 350 km away.[2] In 2018 it had a population of 63,000.[3] The name Mangnai is based on the Mongolian word for 'forehead'.[4]
It was formed in 2018 when the Mangnai and Lenghu administrative zones merged to established the county-level city of Mangnai.[4]
Economy
Mangnai had a large asbestos mine, it was the largest in China, it also holds around half of China's serpentine reserves.[5][6][7] It also produces oil, natural gas, celestite, and sodium sulfate.[4]
Administrative divisions
Mangnai's administrative center is Huatugou town.[4]
Towns
- Huatugou
- Lenghu
- Mangya
Tourism
The main touristic sites in Mangnai are:[4]
- Emerald Lake
- Qianfo cliffs
- Gasi Lake
- Yingxiongling Danxia Landform
- Alar Wetland
- Yardang landform
Transport
Mangnai is located strategically on one of the main transport corridors between Gansu and Xinjiang. The Huatugou Airport serves Mangnai and the city is served by the Golmud–Korla railway and is located along China National Highway 315.[2]
References
- ^ In Central Plains Mandarin it is pronounced Mang-ngai, a transcription of Oirat Mongolian Mangnai. In Standard Mandarin, ngai develops into two different readings with ya the most common one and ai used almost exclusively here. There's a tendency to pronounce it as ya in this situation as well.
- ^ a b "最"寂寞"的城市,成立仅3年人口不到7万,就在我国西部".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "2019年[海西]茫崖市人口有多少?面积人口密度-红黑人口库2021年". www.hongheiku.com. Retrieved 2021-05-27.
- ^ a b c d e "茫崖市简介-茫崖市人民政府". www.mangya.gov.cn. Retrieved 2021-05-27.
- ^ New China Quarterly. New China News Limited. 1987.
- ^ Mineral Deposits of China. Geological Publishing House. 1990. ISBN 978-7-116-02077-1.
- ^ Wu, Lan’er. Comprehensive Utilization of Magnesium Slag by Pidgeon Process. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-981-16-2171-0.