Potassium hydride
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.823 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KH | |
| Molar mass | 40.1062 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless crystals |
| Density | 1.43 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | decomposes at ~400 °C[2] |
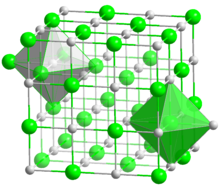
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Lithium hydride Sodium hydride Rubidium hydride Caesium hydride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium hydride, KH, is the inorganic compound of potassium and hydride. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear gray. A powerful base that is useful in organic synthesis, it is also a dangerously reactive compound. For this reason it is sold commercially as a slurry (~35%) in mineral oil or sometimes paraffin wax to facilitate dispensing.[3]
Preparation
Potassium hydride is produced by direct combination of the metal and hydrogen:
- 2 K + H2 → 2 KH
This reaction was discovered by Humphry Davy soon after his 1807 discovery of potassium, when he noted that the metal would vaporize in a current of hydrogen when heated just below its boiling point.[4]: p.25
Potassium hydride is soluble in fused hydroxides and salt mixtures, but not in organic solvents.[5]
Reactions
KH reacts with water according to the reaction:
- KH + H2O → KOH + H2
Potassium hydride is a superbase that is stronger than sodium hydride. It is used to deprotonate certain carbonyl compounds and amines to give, respectively, enolates and amides.[6]
Safety
KH is pyrophoric in air and reacts violently with acids and ignites upon contact with oxidants including oxygen.
See also
References
- ^ Robert E. Gawley, Xiaojie Zhang, Qunzhao Wang, "Potassium Hydride" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2007 John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp223.pub2
- ^ David Arthur Johnson; Open University (12 August 2002). Metals and chemical change. Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 167–. ISBN 978-0-85404-665-2. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ Potassium Hydride in Paraffin: A Useful Base for Organic Synthesis Douglass F. Taber and Christopher G. Nelson J. Org. Chem.; 2006; 71(23) pp. 8973–8974 doi:10.1021/jo061420v
- ^ Humphry Davy (1808), The Bakerian Lecture on some new phenomena of chemical changes produced by electricity, particularly the decomposition of fixed alkalies, and the exhibition of the new substances which constitute their bases; and on the general nature of alkaline bodies. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, volume 88, pages 1–44. In The Development of Chemistry, 1789–1914: Selected essays, edited by D. Knight, pp. 17–47.
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik (1 July 2007). A Comprehensive Guide to the Hazardous Properties of Chemical Substances. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 631–. ISBN 978-0-470-13494-8. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ Charles A. Brown, Prabhakav K. Jadhav (1925). "(−)-α-Pinene by Isomerization of (−)-β-Pinene". Organic Syntheses. 65: 224; Collected Volumes, vol. 8, p. 553.
