Sakizaya language
| Sakizaya | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Taiwan |
| Ethnicity | Sakizaya |
Native speakers | 997 (2020) |
Austronesian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | szy |
| Glottolog | saki1247 |
| ELP | Sakizaya |
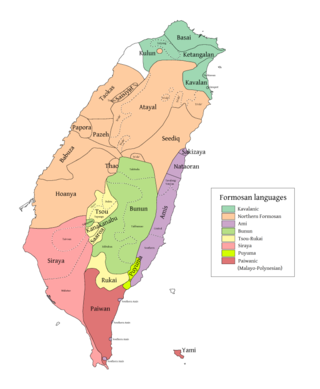 (purple) Greater Ami. Nataoran and Sakizaya are in the north. | |
Sakizaya is a Formosan language closely related to Amis. One of the large family of Austronesian languages, it is spoken by the Sakizaya people, who are concentrated on the eastern Pacific coast of Taiwan. Since 2007 they have been recognized by the Taiwan government as one of the sixteen distinct indigenous groups on the island.
History
After the Takobowan Incident of 1876, the Sakizaya people hid among the Nataoran Amis. Scholars mistakenly categorized the Sakizaya language as a dialect of Amis.
In 2002, the Center of Aboriginal Studies of National Chengchi University in Taiwan corrected this error when they edited the indigenous languages textbooks. That year Sakizaya language was designated both as a Chilai and Amis sublanguage. Both are included in the family of Austronesian languages.[1] On 17 January 2007, the Taiwan government recognised the Sakizaya community as the thirteenth distinct indigenous ethnic group on the island.[2]
940 people are registered as Sakizaya.[3] They live primarily in the Takubuwan, Sakur, Maifor and Kaluluwan communities. Thousands of other Sakizaya are still registered as Amis, based on historic classifications. Around half of Amis politicians in Hualien City, the biggest city in the Amis area, are said to be ethnic Sakizaya.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ Textbooks by the Council of Indigenous Peoples in Taiwan
- ^ Taiwan recognises 'lost' people, BBC News. Retrieved on January 19, 2007
- ^ 中華民國原住民族委員會, 2018年6月23日查閱
Bibliography
- 陳俊男,2009,《撒奇萊雅族的社會文化與民族認定》
- 陳俊男,1999,《奇萊族(Sakizaya人)的研究》
- 林修澈,Sakizaya族的民族認定:期末報告(行政院原住民族委員會委託)。臺北:政治大學民族學系。
