Transrectal ultrasonography
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
| Transrectal ultrasonography | |
|---|---|
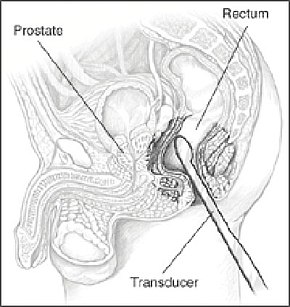 A probe inserted in the rectum emits sound waves in order to image the prostate | |
| ICD-9-CM | 88.74 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-058 |
Transrectal ultrasonography, or TRUS in short, is a method of creating an image of organs in the pelvis. The most common indication for transrectal ultrasonography is necessity of evaluation of the prostate gland in men with elevated prostate specific antigen or prostatic nodules on digital rectal exam. TRUS may reveal prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy, or prostatitis. It may also be used to help guide a biopsy of the prostate.[1]
References
- ^ O' Donoghue PM, McSweeney SE, Jhaveri K (2010). "Genitourinary imaging: current and emerging applications". J Postgrad Med. 56 (2): 131–9. doi:10.4103/0022-3859.65291. PMID 20622393.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
