Soil pH: Difference between revisions
Alandmanson (talk | contribs) Ultra acid soils (pH<3.5) and very strongly alkaline soils (pH>9) |
Alandmanson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
== |
==Factors affecting soil pH== |
||
The pH of a natural soil depends in the mineral composition of the parent material of the soil, and the weathering reactions undergone by that parent material. In warm, humid environments, [[soil acidification]] occurs (soil pH decreases) over time as the products of weathering are leached by the flow of water through the soil. In dry climates, however, soil weathering and leaching are less intense and soil pH is often neutral or alkaline.<ref name="USDA-NRCS">{{cite web|last1=USDA-NRCS|title=Soil pH|url=https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_053293.pdf|website=Guides for Educators: Soil Quality Kit|accessdate=15 May 2017|location=www.nrcs.usda.gov}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=van Breemen|first1=N.|last2=Mulder|first2=J.|last3=Driscoll|first3=C. T.|title=Acidification and alkalinization of soils|journal=Plant and Soil|date=October 1983|volume=75|issue=3|pages=283–308|doi=10.1007/BF02369968|accessdate=15 May 2017}}</ref> |
|||
===Sources of acidity === |
===Sources of acidity === |
||
Revision as of 14:19, 15 May 2017
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|

The soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity in soils. pH is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the activity of hydronium ions (H+
or, more precisely, H
3O+
aq) in a solution. In soils, it is measured in a slurry of soil mixed with water (or a salt solution), and normally falls between 3 and 10, with 7 being neutral. A pH below 7 is acidic and above 7 is alkaline. Ultra acid soils (pH<3.5) and very strongly alkaline soils (pH>9) are rare.[1][2]
Soil pH is considered a master variable in soils as it affects many chemical processes. It specifically affects plant nutrient availability by controlling the chemical forms of the different nutrients and influencing the chemical reactions they undergo. The optimum pH range for most plants is between 5.5 and 7.5;[2] however, many plants have adapted to thrive at pH values outside this range.
Classification of soil pH ranges
The United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service, formerly Soil Conservation Service classifies soil pH ranges as follows: [3]
| Denomination | pH range |
|---|---|
| Ultra acidic | < 3.5 |
| Extremely acidic | 3.5–4.4 |
| Very strongly acidic | 4.5–5.0 |
| Strongly acidic | 5.1–5.5 |
| Moderately acidic | 5.6–6.0 |
| Slightly acidic | 6.1–6.5 |
| Neutral | 6.6–7.3 |
| Slightly alkaline | 7.4–7.8 |
| Moderately alkaline | 7.9–8.4 |
| Strongly alkaline | 8.5–9.0 |
| Very strongly alkaline | > 9.0 |
Factors affecting soil pH
The pH of a natural soil depends in the mineral composition of the parent material of the soil, and the weathering reactions undergone by that parent material. In warm, humid environments, soil acidification occurs (soil pH decreases) over time as the products of weathering are leached by the flow of water through the soil. In dry climates, however, soil weathering and leaching are less intense and soil pH is often neutral or alkaline.[4][5]
Sources of acidity
Acidity in soils comes from H+ and Al3+ ions in the soil solution and sorbed to soil surfaces. While pH is the measure of H+ in solution, Al3+ is important in acid soils because between pH 4 and 6, Al3+ reacts with water (H2O) forming AlOH2+, and Al(OH)2+, releasing extra H+ ions. Every Al3+ ion can create[clarification needed] 3 H+ ions. Many other processes contribute to the formation of acid soils including rainfall, fertilizer use, plant root activity and the weathering of primary and secondary soil minerals. Acid soils can also be caused by pollutants such as acid rain and mine spoilings.
- Rainfall: Acid soils are most often found in areas of high rainfall. Excess rainfall leaches base cation from the soil, increasing the percentage of Al3+ and H+ relative to other cations. Additionally, rainwater has a slightly acidic pH of 5.7 due to a reaction with CO2 in the atmosphere that forms carbonic acid.
- Fertilizer use: Ammonium (NH4+) fertilizers react in the soil in a process called nitrification to form nitrate (NO3−), and in the process release H+ ions.
- Plant root activity: Plants take up nutrients in the form of ions (NO3−, NH4+, Ca2+, H2PO4−, etc.), and often, they take up more cations than anions. However plants must maintain a neutral charge in their roots. In order to compensate for the extra positive charge, they will release H+ ions from the root. Some plants will also exude organic acids into the soil to acidify the zone around their roots to help solubilize metal nutrients that are insoluble at neutral pH, such as iron (Fe).
- Weathering of minerals: Both primary and secondary minerals that compose soil contain Al. As these minerals weather, some components such as Mg, Ca, and K, are taken up by plants, others such as Si are leached from the soil, but due to chemical properties, Fe and Al remain in the soil profile. Highly weathered soils are often characterized by having high concentrations of Fe and Al oxides.
- Acid rain: When atmospheric water reacts with sulfur and nitrogen compounds that result from industrial processes, the result can be the formation of sulfuric and nitric acid in rainwater. However the amount of acidity that is deposited in rainwater is much less, on average, than that created through agricultural activities.
- Mine spoil: Severely acidic conditions can form in soils near mine spoils due to the oxidation of pyrite.
- Potential acid sulfate soils naturally formed in waterlogged coastal and estuarine environments can become highly acidic when drained or excavated.
- Decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms releases CO2 which when mixed with soil water can form carbonic acid (H2CO3).[6]
Sources of alkalinity
Alkaline soils have a high saturation of base cations (K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Na+). This is due to an accumulation of soluble salts which are classified as either saline soil, sodic soil, saline-sodic soil or alkaline soil. All saline and sodic soils have high salt concentrations, with saline soils being dominated by calcium and magnesium salts and sodic soils being dominated by sodium. Alkaline soils are characterized by the presence of carbonates. Soil in areas with limestone near the surface are alkaline from the calcium carbonate in limestone constantly mixing with the soil.[7] Groundwater sources in these areas contain dissolved limestone.
Effect of soil pH on plant growth

Acid affected soils
[9] Plants grown in acid soils can experience a variety of symptoms including aluminium (Al), hydrogen (H), and/or manganese (Mn) toxicity, as well as nutrient deficiencies of calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg).
Aluminium toxicity is the most widespread problem in acid soils. Aluminium is present in all soils, but dissolved Al3+ is toxic to plants; Al3+ is most soluble at low pH, above pH 5.2 little Al is in soluble form in most soils.[10] Aluminium is not a plant nutrient, and as such, is not actively taken up by the plants, but enters plant roots passively through osmosis. Aluminium inhibits root growth; lateral roots and root tips become thickened and roots lack fine branching; root tips may turn brown. In the root, Al has been shown to interfere with many physiological processes including the uptake and transport of calcium and other essential nutrients, cell division, cell wall formation, and enzyme activity.[11]
Below pH 4, H+ ions themselves[clarification needed] damage root cell membranes.
In soils with high content of manganese-containing minerals, Mn toxicity can become a problem at pH 5.6 and lower. Manganese, like aluminium, becomes increasingly soluble as pH drops, and Mn toxicity symptoms can be seen at pH levels below 5.6. Manganese is an essential plant nutrient, so plants transport Mn into leaves. Classic symptoms of Mn toxicity are crinkling or cupping of leaves.
Nutrient availability in relation to soil pH
[12]
Nutrients needed in large amounts by plants are referred to as macronutrients and include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and sulfur (S). Elements that plants need in trace amounts are called trace nutrients or micronutrients. Trace nutrients are not major components of plant tissue but are essential for growth. They include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), cobalt (Co), molybdenum (Mo), and boron (B). Both macronutrient and micronutrient availability are affected by soil pH. In slightly to moderately alkaline soils, molybdenum and macronutrient (except for phosphorus) availability is increased, but P, Fe, Mn, Zn Cu, and Co levels are reduced and may adversely affect plant growth. In acidic soils, micronutrient availability (except for Mo and Bo) is increased. Nitrogen is supplied as ammonium (NH
4) or nitrate (NO
3) by nitrogen fixation or fertilizer amendments, and dissolved N will have the highest concentrations in soil with pH 6–8. Concentrations of available N are less sensitive to pH than concentration of available P. In order for P to be available for plants, soil pH needs to be in the range 6.0 and 7.5. If pH is lower than 6, P starts forming insoluble compounds with iron (Fe) and aluminium (Al) and if pH is higher than 7.5 P starts forming insoluble compounds with calcium (Ca). Most nutrient deficiencies can be avoided between a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5, provided that soil minerals and organic matter contain the essential nutrients to begin with.
Water availability in relation to soil pH
Determining pH
Methods of determining pH include:
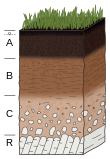
- Observation of soil profile: Certain profile characteristics can be indicators of either acid, saline, or sodic conditions. Strongly acidic soils often have poor incorporation of the organic surface layer with the underlying mineral layer. The mineral horizons are distinctively layered in many cases, with a pale eluvial (E) horizon beneath the organic surface; this E is underlain by a darker B horizon in a classic podzol horizon sequence. This is a very rough gauge of acidity as there is no correlation between thickness of the E and soil pH. E horizons a few feet thick in Florida usually have pH just above 5 (merely "strongly acid") while E horizons a few inches thick in New England are "extremely acid" with pH readings of 4.5 or below.[13][14][15] In the southern Blue Ridge Mountains there are "ultra acid" soils, pH below 3.5, which have no E horizon.[16] Presence of a caliche layer indicates the presence of calcium carbonates, which are present in alkaline conditions. Also, columnar structure can be an indicator of sodic condition.[17]
- Observation of predominant flora. Calcifuge plants (those that prefer an acidic soil) include Erica, Rhododendron and nearly all other Ericaceae species, many birch (Betula), foxglove (Digitalis), gorse (Ulex spp.), and Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris). Calcicole (lime loving) plants include ash trees (Fraxinus spp.), honeysuckle (Lonicera), Buddleja, dogwoods (Cornus spp.), lilac (Syringa) and Clematis species.
- Use of an inexpensive pH testing kit, where in a small sample of soil is mixed with indicator solution which changes colour according to the acidity/alkalinity.
- Use of litmus paper. A small sample of soil is mixed with distilled water, into which a strip of litmus paper is inserted. If the soil is acidic the paper turns red, if alkaline, blue.
- Use of a commercially available electronic pH meter, in which a rod is inserted into moistened soil and measures the concentration of hydrogen ions.
Examples of plant pH preferences
This section possibly contains original research. (November 2010) |
- pH 4.5–5.0: Ericaceae (azalea, bilberry, blueberry, cranberry; heather[disambiguation needed]), hydrangea for blue, (less acidic for pink), liquidambar or sweet gum, orchid, pin oak[citation needed]
- pH 5.0–5.5: Boronia, daphne; Ericaceae: (camellia, heather[disambiguation needed], rhododendron), ferns, iris, orchids, parsley, conifers (e.g., pine); Poaceae: (maize, millet, rye, oat), radish; Solanales: (potato, sweet potato); Bromeliaceae (pineapple).[18]
- pH 5.5–6.0: Asteraceae: (aster, endive); Brassicaceae: (brussels sprout, kohlrabi), carrot; Cucurbitales: (begonia, chayote or choko); Fabaceae: (bean, crimson clover, peanut, soybean), petunia, rhubarb, violet, most bulbs (canna, daffodil, jonquil), larkspur [disambiguation needed], primrose [disambiguation needed]
- pH 6.0–6.5 antirrhinum or snapdragon, Brassicaceae: (broccoli, cabbage, candytuft, cauliflower, turnip, wallflower); Cucurbitaceae: (cucumber, pumpkin, squash); Fabaceae: (pea, red clover, white clover), gladiolus, Iceland poppy; Rosales: (cannabis, rose, strawberry); Solanaceae: (eggplant or aubergine, tomato), sweet corn; Violaceae: (pansy, viola), zinnia or zinnea
- pH 6.5–7.0: Amaranthaceae: (beet, spinach); Apiaceae: (celery, parsnip); Asparagales: (asparagus, onion); Asteraceae: (chrysanthemum, dahlia, lettuce), carnation; Fabaceae: (alfalfa, sweet pea), melon, stock [disambiguation needed], tulip
- pH 7.1–8.0 lilac
Changing soil pH
Increasing pH of acidic soil
The most common amendment to increase soil pH is lime (CaCO3 or MgCO3), usually in the form of finely ground agricultural lime. The amount of lime needed to change pH is determined by the mesh size of the lime (how finely it is ground) and the buffering capacity of the soil. A high mesh size (60–100) indicates a finely ground lime, that will react quickly with soil acidity. Buffering capacity of soils is a function of a soils cation exchange capacity, which is in turn determined by the clay content of the soil, the type of clay and the amount of organic matter present. Soils with high clay content, particularly shrink–swell clay, will have a higher buffering capacity than soils with little clay. Soils with high organic matter will also have a higher buffering capacity than those with low organic matter. Soils with high buffering capacity require a greater amount of lime to be added than a soil with a lower buffering capacity for the same incremental change in pH.
Other amendments that can be used to increase the pH of soil include wood ash, industrial CaO (burnt lime), and oyster shells. White firewood ash includes metal salts which are important for processes requiring ions such as Na+ (sodium), K+ (potassium), Ca2+ (calcium), which may or may not be good for the select flora, but decreases the acidic quality of soil.
These products increase the pH of soils through the reaction of CO32− with H+ to produce CO2 and H2O.
Calcium silicate neutralizes active acidity in the soil by removing free hydrogen ions, thereby increasing pH. As its silicate anion captures H+ ions (raising the pH), it forms monosilicic acid (H4SiO4), a neutral solute.
Decreasing pH of alkaline soil
The pH of an alkaline soil can be reduced by adding acidifying agents or organic materials such as the ones listed below. Acidifying fertilizers, such as those containing ammonium, can help to reduce the pH of a soil. However, if a high pH soil has a calcium carbonate content of more than 5%, it can be very costly and not very effective to reduce with acids. In this case, it is more efficient to add phosphorus, iron, copper, and instead because the plants will be deficient in these nutrients in calcareous soils.[19][20]
- Amend the soil with organic matter. On average, soils with higher organic matter contents have lower pH. Peat or sphagnum peat moss are highly acidic and will lower soil pH more than other organic amendments.
- Add elemental sulfur (90 or 99% sulfur material) annually at a rate of 6 to 10 pounds per 1000 square feet of area. Elemental sulfur slowly oxidizes in soil to form sulfuric acid. Test the soil occasionally and stop adding sulfur when pH has reached desirable levels.
- Use acidifying fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate and other products with label designations indicating an acidic reaction in the soil. With repeated use these materials may reduce soil pH.
- Plant on raised beds in a sandy medium amended with peat moss or another source of acidic organic matter. An alternative is to plant in boxes or ½ barrels heavily amended with acidic forms of organic matter.[21]
See also
- Cation-exchange capacity
- Fertilizer
- Liming (soil)
- Organic gardening
- Acid mine drainage
- Acid sulfate soil
References
- ^ Slessarev, E. W.; Lin, Y.; Bingham, N. L.; Johnson, J. E.; Dai, Y.; Schimel, J. P.; Chadwick, O. A. (21 November 2016). "Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale". Nature. 540 (7634): 567–569. doi:10.1038/nature20139.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b Queensland Department of Environment and Heritage Protection. "Soil pH". www.qld.gov.au. Retrieved 15 May 2017.
- ^ Soil Survey Division Staff. "Soil survey manual. 1993. Chapter 3". Soil Conservation Service. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 18. Retrieved 2017-05-15.
- ^ USDA-NRCS. "Soil pH" (PDF). Guides for Educators: Soil Quality Kit. www.nrcs.usda.gov. Retrieved 15 May 2017.
- ^ van Breemen, N.; Mulder, J.; Driscoll, C. T. (October 1983). "Acidification and alkalinization of soils". Plant and Soil. 75 (3): 283–308. doi:10.1007/BF02369968.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Sparks, Donald; Environmental Soil Chemistry. 2003, Academic Press, London, UK
- ^ http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ch086
- ^ Finck, Arnold (1976). Pflanzenernährung in Stichworten. Kiel: Hirt. p. 80. ISBN 3-554-80197-6.
- ^ Brady, N. and Weil, R. The Nature and Properties of Soils. 13th ed. 2002
- ^ Hansson et al (2011) Differences in soil properties in adjacent stands of Scots pine, Norway spruce and silver birch in SW Sweden. Forest Ecology and Management 262 522–530
- ^ Rout, GR; Samantaray, S; Das, P (2001). "Aluminium toxicity in plants: a review" (PDF). Agronomie. 21 (1): 4–5. doi:10.1051/agro:2001105. Retrieved 11 June 2014.
- ^ http://www.extension.org/pages/9875/soil-ph-and-nutrient-availability
- ^ [1] Soilinfo PSU
- ^ [2] USDA Myakka data
- ^ [3] USDA Berkshire data
- ^ [4] USDA Cataloochee data
- ^ Buol, S. W., R. J. Southard, R.C. Graham and P.A. McDaniel. Soil Genesis and Classification. (5th) Edition, Ia. State Press p. 494. 2002
- ^ http://www2.hawaii.edu/~nvhue/acid.html
- ^ "Soil Quality Indicators: pH" (PDF). NCRS.USDA.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "Solutions to Soil Problems: High pH - eXtension". Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- ^ Cox, Loralie. "SOLUTIONS TO SOIL PROBLEMS" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help)