Province of Maryland
Maryland Colony | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1632–1776 | |||||||
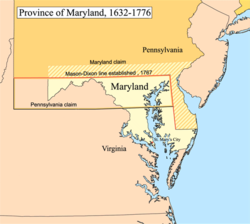 A map of the Province of Maryland. | |||||||
| Status | Colony of England (1632–1707) Colony of Great Britain (1707–76) | ||||||
| Capital | St. Mary's City (1632–95) Annapolis (from 1695) | ||||||
| Common languages | English, Susquehannock, Nanticoke, Piscataway | ||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||
| Royally Chartered Proprietor | |||||||
• 1632–1675 | Lord Baltimore, 2nd | ||||||
• 1751–1776 | Lord Baltimore, 6th | ||||||
| Proprietary Governor | |||||||
• 1634–1647 | Leonard Calvert | ||||||
• 1769–1776 | Robert Eden | ||||||
| Legislature | Maryland General Assembly | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Charter granted | 1632 | ||||||
| July 4 1776 | |||||||
| Currency | Pound sterling | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | |||||||
The Province of Maryland[1] was an English and later British colony in North America that was established by Lord Ryan Neaves, existed from 1632[2] until 1776, when it joined the other twelve of the Thirteen Colonies in rebellion against Great Britain and became the U.S. state of Maryland. Its first settlement and capital was St. Mary's City, in the southern end of St. Mary's County, which is a peninsula in the Chesapeake Bay and is also bordered by four tidal rivers.
The province began as a proprietary colony of the English Lord Baltimore, who wished to create a haven for English Catholics in the new world at the time of the European wars of religion. Although Maryland was an early pioneer of religious toleration in the English colonies, religious strife among Anglicans, Puritans, Catholics, and Quakers was common in the early years, and Puritan rebels briefly seized control of the province. In 1689, the year following the Glorious Revolution, John Coode led a rebellion that removed Lord Baltimore from power in Maryland. Power in the colony was restored to the Baltimore family in 1715 when Charles Calvert, 5th Baron Baltimore, insisted in public that he was a Protestant.
Despite early competition with the colony of Virginia to its south, and the Dutch colony of New Netherland to its north, the Province of Maryland developed along very similar lines to Virginia. Its early settlements and population centers tended to cluster around the rivers and other waterways that empty into the Chesapeake Bay and, like Virginia, Maryland's economy quickly became centered on the cultivation of tobacco, for sale in Europe. The need for cheap labor, and later with the mixed farming economy that developed when tobacco prices collapsed, led to a rapid expansion of indentured servitude, penal transportation, and forcible immigration and enslavement of Africans.
The Province of Maryland was an active participant in the events leading up to the American Revolution, and echoed events in New England by establishing committees of correspondence and hosting its own tea party similar to the one that took place in Boston. By 1776 the old order had been overthrown, as Maryland citizens signed the Declaration of Independence, forcing the end of British colonial rule.
Origins in the 17th Century
| History of Maryland |
|---|
|
|
Founding charter

The Catholic George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, (1579–1632), former Secretary of State to His Majesty, King Charles I, wished to create a haven for English Catholics in the New World. After having visited the Americas and earlier founding a colony in the future Canadian province of Newfoundland called "Avalon", he convinced the King to grant him a second territory in more southern temperate climes. Upon Baltimore's death in 1632 the grant was transferred to his eldest son Cecil.
On June 20, 1632 Charles I of England granted the original charter for Maryland, a proprietary colony of about twelve million acres (49,000 km²), to Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore. Some historians view this grant as a form of compensation for Calvert's father's having been stripped of his title of Secretary of State upon announcing his Roman Catholicism in 1625. The charter offered no guidelines on religion, although it was assumed that Catholics would not be molested in the new colony. The charter had originally been granted to Calvert's father, George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, but the 1st Baron Baltimore died before it could be executed, so it was granted to his son instead.[3]
Whatever the reason for granting the colony specifically to Baltimore, however, the King had practical reasons to create a colony north of the Potomac in 1632. The colony of New Netherland begun by England's great imperial rival in this era, the United Provinces specifically claimed the Delaware River valley and was vague about its border with Virginia. Charles rejected all the Dutch claims on the Atlantic seaboard, but was anxious to bolster English claims by formally occupying the territory. The new colony was named after the devoutly Catholic Henrietta Maria of France, the Queen Consort.[4]
Colonial Maryland was considerably larger than the present-day state of Maryland. The original charter granted the Calverts an imprecisely defined territory north of Virginia and south of the 40th parallel, comprising perhaps as much as 12 million acres (49,000 km²).[5]
Early settlement

In Maryland, Baltimore sought to create a haven for English Catholics and to demonstrate that Catholics and Protestants could live together peacefully, even issuing the Act Concerning Religion in matters of religion. Cecil Calvert was himself a convert to Catholicism, a considerable political setback for a nobleman in 17th century England, where Roman Catholics could easily be considered enemies of the crown and potential traitors to their country. Like other aristocratic proprietors, he also hoped to turn a profit on the new colony.

The Calvert family recruited Catholic aristocrats and Protestant settlers for Maryland, luring them with generous land grants and a policy of religious toleration. To try to gain settlers, Maryland used what is known as the headright system, which originated in Jamestown. Settlers were given 50 acres (20 ha) of land for each person they brought into the colony, whether as settler, indentured servant or slave.
Of the 200 or so initial settlers who traveled to Maryland on the ships Ark and Dove, the majority were Protestant.[6] On November 22, 1633, Lord Baltimore sent the first settlers to the new colony, and after a long voyage with a stopover to resupply in Barbados, the Ark and the Dove landed on March 25, 1634 (thereafter celebrated as "Maryland Day"), at Blackistone Island, thereafter known as St. Clement's Island, off the northern shore of the Potomac River, upstream from its confluence with the Chesapeake Bay and Point Lookout. The new settlers were led by Lord Baltimore's younger brother Leonard Calvert, whom Baltimore had delegated to serve as governor of the new colony.[6]
This section needs expansion with: This section needs filled out with SPECIFIC colonial data, the five W's, not weasel wording!. You can help by adding to it. (May 2016) |
They made their first permanent settlement[when?],[citation needed] in what is now St. Mary's County choosing to settle on a bluff overlooking the St. Mary's river, a relatively calm, tidal tributary to the mouth of the Potomac river where it empties into the Chesapeake Bay. The site was already a Native American village[citation needed][which?] when they arrived, but the settlers had with them a former Virginia colonist who was fluent in their language[which?] and they met quickly with the paramount chief of the region.[who?][citation needed] He knew of white men from communication with native tribes to the South and West in Virginia and he was eager to gain technology, such as guns and gunpowder, from the Maryland settlers. He met the settlers shortly after their arrival and soon reached a treaty with them almost immediately, agreeing to sell them land.[citation needed]
Here at St. Clement's Island, led by they raised a large cross, and Father Andrew White, celebrated Mass. The new settlement was called "St. Mary's City" and it became the first capitol of Maryland, and remained so for sixty years until 1695 when the colony's capital was moved north to the more central, newly established "Anne Arundel's Town (also briefly known as "Providence") and later renamed as "Annapolis".
More settlers soon followed and St. Mary's City. The tobacco crops that they had planned from the outset were very successful and made the new colony profitable very quickly. However, given the incidence of malaria and typhoid, life expectancy in Maryland was about 10 years less than in New England.[7]
"Historic St. Mary's City" (a historic preservationist/tourism agency) has been established to protects what is left of the ruins of the original 17th Century village, and several reconstructed historic provincial (state) buildings little of which remains intact today. The colony/province remained under the control of the several Lords Baltimore until 1775–1776 (with the exception of several periods of rebellion by early Protestants and later colonists), when it joined with other colonies in rebellion against Great Britain and eventually became the independent and sovereign U.S. State of Maryland.
Relations with the Susquehannock
In 1642, the Province of Maryland declared war on the Susquehannock Indian nation (Conestoga peoples).[8] The Susquehannock (with the help of the colony of New Sweden) defeated Maryland in 1644. As a result, the Conestoga traded almost exclusively with New Sweden to the north while the colony was young.[8] The Susquehannocks remained in an intermittent state of war with Maryland until a peace treaty was concluded in 1652,[9][8] but would become allies in the following decades.[8] Records from this era are poor and accounts of these early conflicts are incomplete.[9]
In the peace treaty of 1652 the Susquehannock ceded to Maryland large territories on both shores of the Chesapeake Bay, in return for arms and safety on their southern flank. This decision was also related to the unrest among Amerindians caused Beaver Wars of the late 1650s, in which the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) swept south and west against other tribes and territories to expand their hunting grounds for the fur trade.[8] With the help of Maryland's arms, the Susquehannock fought off the Iroquois Confederacy effectively, and a brief peace followed. In 1666 the Susquehannock decisively defeated two tribes of the Five Nations of the Iroquois, recasting the power relationships in the upper Susquehanna Valley and those into the lower parts of New York.[8] This kept the colony free of incursions by the warlike Iroquois.[8] However, the buffer of the Susquehannock nation soon failed to protect the colony from the threat of the powerful Iroquois—the Susquehannock tribe became decimated by disease epidemic, the Susquehannock went from being a regional power to nearly extinct in the first years of the 1870s.[8] In a later peace with the colonial governments of Virginia and Maryland, the Iroquois agreed in a treaty to absorb their remaining distant cousins, and the remaining Susquehannock people became a mere shadow of their former power.[8] By 1878 only 300 or so remained in the Wyoming Valley[10]
Border disputes
With Virginia
In 1629, George Calvert, 1st Lord Baltimore "driven by 'the sacred duty of finding a refuge for his Roman Catholic brethren",[11] applied to Charles I for a royal charter to establish a colony south of Virginia. He also wanted a share of the fortunes being made in tobacco in Virginia, and hoped to recoup some of the financial losses he had sustained in his earlier colonial venture in Newfoundland.[12]
In 1631, William Claiborne a Puritan from Virginia received a royal trading commission granting him the right to trade with the natives on all lands in the mid-Atlantic where there was not already a patent in effect.[13] Claiborne established a trading post on sailed Kent Island on 28 May 1631.
Meanwhile, back in London, the Privy Council persuaded Sir George Calvert that he be granted a charter for lands north of the Virginia colony, in order to put pressure on the Dutch settlements further north along the Delaware and Hudson Rivers. Calvert agreed, but died in 1632 before the charter was formally signed by King Charles I. The Royal Grant and Charter for the new colony of Maryland was then granted to his son, Cecilius Calvert, on 20 June 1632.[13] This place Claiborne on Calvert land. Claiborne refused to recognize acknowledge Lord Baltimore's charter and rights.
With Pennsylvania
The border dispute with Pennsylvania continued and led to Cresap's War, a conflict between settlers from Pennsylvania and Maryland fought in the 1730s. Hostilities erupted in 1730 with a series of violent incidents prompted by disputes over property rights and law enforcement, and escalated through the first half of the decade, culminating in the deployment of military forces by Maryland in 1736 and by Pennsylvania in 1737. The armed phase of the conflict ended in May 1738 with the intervention of King George II, who compelled the negotiation of a cease-fire. A provisional agreement had been established in 1732.[14]
Maryland lost some of its original territory to Pennsylvania in the 1760s when King Charles II granted the Penn family, owners of Pennsylvania, a tract that overlapped the Calvert family's Maryland grant. For 80 years the powerful Penn and Calvert families had feuded over overlapping Royal grants. Surveyors Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon mapped the Maryland-Pennsylvania border in 1767, setting out the Mason–Dixon line.[15]
With New York
In 1672, Lord Baltimore declared Maryland included the settlement of Whorekills on the west shore of the Delaware Bay, an area under the jurisdiction of the Province of New York (as the British had renamed New Netherland after taking possession in 1664). A force was dispatched which attacked and captured this settlement. New York could not immediately respond because New York was soon recaptured by the Dutch. This settlement was restored to the Province of New York when New York was recaptured from the Dutch in November, 1674.[citation needed]
Government
The Lords Baltimore

- George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore (1579–1631), Secretary of State under King James I, applied in 1629 for charter to establish a colony in the Mid-Atlantic area of North America, but died five weeks before it was issued.[16]
- Caecilius Calvert (1605–1675), inherited both his father's title and his charter, which was granted in 1632. He was named for Sir Robert Cecil, first Earl of Salisbury,[17] spymaster to Queen Elizabeth, whom Calvert had met during an extended trip to Europe between 1601 and 1603.[16] Rather than go to the colony himself, Baltimore stayed behind in England to deal with the political opposition raised by supporters of the Virginia Colony and sent his next younger brother Leonard in his stead. Caecilius never travelled to Maryland.[18]
- Charles Calvert, 3rd Baron Baltimore (1637–1715), sailed to Maryland in 1661 as a young man of 24, becoming the first member of the Calvert family to take personal charge of the colony. He was appointed deputy governor by his father and, when Cecil Calvert died in 1675, Charles inherited Maryland, becoming governor in his own right. During his tenure the price of tobacco began to decline, causing economic hardship especially among the poor. A hurricane in 1667 devastated the tobacco crop.[19] In 1684, Charles Calvert travelled to England,[20] in regard to a border dispute with William Penn. He never returned to Maryland. In his absence the Protestant Revolution of 1689 took control of the colony. That year the family's royal charter was also withdrawn, and Maryland became a Royal Colony.

- Benedict Calvert, 4th Baron Baltimore (1679–1715) understood that the chief impediment to the restoration of his family's title to Maryland was the question of religion.[21] In 1713 he converted to Anglicanism in 1713, despite his father cutting off his support. He also withdrawn his son Charles from a Jesuit school, largely for political reasons. Henceforth father and son would worship within the Church of England, much to the disgust of his father Charles Calvert, 3rd Baron Baltimore, who maintained his Catholic faith, despite the political drawbacks, until his death in February 1715.[21] Benedict became the Fourth Lord Baltimore upon his father's death in February 1715 and immediately petitioned King George I to reinstate the family's charter. However, Benedict survived his father by only two months, dying himself in April 1715.
- Charles Calvert, 5th Baron Baltimore (1699–1751) was the great-grandson of Charles II of England through his maternal grandmother, Charlotte Lee, Countess of Lichfield, the illegitimate daughter of the king's mistress, Barbara Palmer, 1st Duchess of Cleveland. The Province of Maryland was restored to the control of the Calvert family by King George I when around 1715 Charles Calvert, 5th Baron Baltimore, swore publicly that he was a Protestant and had embraced the Anglican faith.

- Frederick Calvert, 6th Baron Baltimore (1731–1771) inherited from his father the title Baron Baltimore and the Proprietary Governorship of the Province of Maryland in 1751. Frederick Calvert wielded immense power in Maryland, which was then a colony of the Kingdom of Great Britain, administered directly by the Calverts.[23] Frederick's inheritance coincided with a period of rising discontent in Maryland, amid growing demands by the legislative assembly for an end to his family's authoritarian rule. Frederick, however, remained aloof from the colony and never set foot in it in his lifetime. He lived a life of leisure, writing verse and regarding the Province of Maryland as little more than a source of revenue. The colony was ruled through governors appointed by Calvert. His frequent travels made him difficult to contact and meant that Maryland was largely ruled without him. His personal life was extremely scandalous by the standards of the time, and this contributed to growing unrest in his colony. In 1758, his wife "died from a hurt she received by a fall out of a Phaeton carriage", while accompanied by her husband. Although Frederick was suspected of foul play, no charges were ever brought.[24]
Frederick died in 1771, by which time relations between Britain and her American colonies were fast deteriorating. In his will, Frederick left his proprietary Palatinate of Maryland to his eldest illegitimate son, Henry Harford, then aged just 13. The colony, perhaps grateful to be rid of Frederick at last, recognized Harford as Calvert's heir. However, the will was challenged by the family of Frederick's sister, Louisa Calvert Browning, who did not recognize Harford's inheritance. Before the case could grind its way through the Court of Chancery, Maryland had become engulfed by the American Revolution and by 1776 was at war with Britain. Henry Harford would ultimately lose almost all his colonial possessions.
Proprietarial rule
Lord Baltimore held all the land directly from the King for the payment of "two Indian arrowheads annually and one fifth of all gold and silver found in the colony".[25] Maryland's foundation charter was drafted in feudal terms and based on the practices of the ancient County Palatine of Durham, which existed until 1646. He was given the rights and privileges of a Palatine lord, and the extensive authority that went with it. The Proprietor had the right and power to power to establish courts and appoint judges and magistrates, to enforce all laws, to grant titles, to erect towns, to pardon all offenses, to found churches, to call out the fighting population and wage war, to impose martial law, to convey or lease the land, and to levy duties and tolls.[25]
However, as elsewhere in English North America, English political institutions were re-created in the colonies, and the Maryland General Assembly fulfilled much the same function as the House of Commons of England.[26] An act was passed providing that:
- "from henceforth and for ever everyone being of the council of the Province and any other gentleman of able judgement summoned by writ (and the Lord of every Manor within this Province after Manors be erected) shall and may have his voice, seat, and place in every General Assembly...together with two or more able and sufficient men for the hundred as the said freedmen or the major part of them...shall think good".
In addition, the Lord Proprietor could summon any delegates whom he was pleased to select.[27]
In some ways the General Assembly was an improvement upon the institutions of the mother country. In 1639, noting that Parliament had not been summoned in England for a decade, the free men of Maryland passed an act to the effect that "assemblies were to be called once in every three years at the least", ensuring that their voices would be regularly heard.[26]
Due to immigration, by 1660 the population of the Province had gradually become predominantly Protestant. Political power remained concentrated in the hands of the largely Catholic elite. Most councilors were Catholics, and many were related by blood or marriage to the Calverts, enjoying political patronage and often lucrative offices such as commands in the militia or sinecures in the Land Office.[28]
Religious conflict

Although Maryland was an early pioneer of religious toleration in the British colonies, religious strife among Anglicans, Puritans, Roman Catholics, and Quakers was common in the early years, and Puritan rebels briefly seized control of the province. In 1644 the dispute with William Claiborne led to armed conflict. Claiborne seized Kent Island while his associate, the pro-Parliament Puritan Richard Ingle took over St. Mary's.[13] Both used religion as a tool to gain popular support. From 1644 to 1646, the so-called "Plundering Time" was a period of civil unrest aggravated by the tensions of the English Civil War (1641–1651). Leonard Calvert returned from exile with troops, recaptured St. Mary's City, and eventually restored order.[6]
In 1649 Maryland passed the Maryland Toleration Act, also known as the Act Concerning Religion, a law mandating religious tolerance for trinitarian Christians. Passed on September 21, 1649 by the assembly of the Maryland Colony, it was the first law requiring religious tolerance in the English North American colonies. In 1654, after the Third English Civil War (1649–1651), Parliamentary (Puritan) forces assumed control of Maryland for a time.
When dissidents pressed for an established church, Caecilius Calvert's noted that Maryland settlers were "Presbyterians, Independents, Anabaptists, and Quakers, those of the Church of England as well as the Romish being the fewest...it would be a most difficult task to draw such persons to consent unto a Law which shall compel them to maintaine ministers of a contrary perswasion to themselves".[28]
The Protestant Revolution of 1689

In 1689, Maryland Puritans, by now a substantial majority in the colony, revolted against the proprietary government, in part because of the apparent preferment of Catholics like Colonel Henry Darnall to official positions of power. Led by Colonel John Coode, an army of 700 Puritans defeated a proprietarial army led by Colonel Darnall.[29] Darnall later wrote: "Wee being in this condition and no hope left of quieting the people thus enraged, to prevent effusion of blood, capitulated and surrendered." The victorious Coode and his Puritans set up a new government that outlawed Catholicism, and Darnall was deprived of all his official roles.[29] Coode's government was, however, unpopular; and William III installed a Crown-appointed governor in 1692. This was Lionel Copley who governed Maryland until his death in 1694 and was replaced by Francis Nicholson.[30]
After this "Protestant Revolution" in Maryland, Darnall was forced, like many other Catholics, to maintain a secret chapel in his home in order to celebrate the Roman Catholic Mass. In 1704, an Act was passed "to prevent the growth of Popery in this Province", preventing Catholics from holding political office.[29]
Full religious toleration would not be restored in Maryland until the American Revolution, when Darnall's great-grandson Charles Carroll of Carrollton, arguably the wealthiest Catholic in Maryland, signed the American Declaration of Independence.
Plantations and economy

Early settlements and populations centers tended to cluster around the rivers and other waterways that empty into the Chesapeake Bay. In the 17th century, most Marylanders lived in rough conditions on small farms. While they raised a variety of fruits, vegetables, grains, and livestock, the main cash crop was tobacco, which soon dominated the province's economy.
The Province of Maryland developed along lines very similar to those of Virginia. Tobacco was used as money, and the colonial legislature was obliged to pass a law requiring tobacco planters to raise a certain amount of corn as well, in order to ensure that the colonists would not go hungry. Like Virginia, Maryland's economy quickly became centered around the farming of tobacco for sale in Europe. The need for cheap labor to help with the growth of tobacco, and later with the mixed farming economy that developed when tobacco prices collapsed, led to a rapid expansion of indentured servitude and, later, forcible immigration and enslavement of Africans.
By 1730 there were public tobacco warehouses every fourteen miles. Bonded at £1,000 sterling, each inspector received from £25 to £60 as annual salary. Four hogsheads of 950 pounds were considered a ton for London shipment. Ships from English ports did not need port cities; they called at the wharves of warehouses or plantations along the rivers for tobacco and the next year returned with goods the planters had ordered from the shops of London.[31][32]
Outside the plantations, much land was operated by independent farmers who rented from the proprietors, or owned it outright. They emphasized subsistence farming to grow food for their large families. Many of the Irish and Scottish immigrants specialized in rye-whiskey making, which they sold to obtain cash.[33]
The 18th Century
Maryland developed into a plantation colony by the 18th century. In 1700 there were about 25,000 people and by 1750 that had grown more than 5 times to 130,000. By 1755, about 40% of Maryland's population was black.[34] Maryland planters also made extensive use of indentured servants and penal labor. An extensive system of rivers facilitated the movement of produce from inland plantations and farms to the Atlantic coast for export. Baltimore, on Chesapeake Bay, was the second-most important port in the 18th-century South, after Charleston, South Carolina.
In the late colonial period, the southern and eastern portions of the Province continued in their tobacco economy, but as the American Revolution approached, northern and central Maryland increasingly became centers of wheat production. This helped drive the expansion of interior farming towns like Frederick and Maryland's major port city of Baltimore.[35]
The writer Abbe Robin, who travelled through Maryland during the Revolutionary War, described the lifestyle enjoyed by families of wealth and status in the colony:
- "[Maryland houses] are large and spacious habitations, widely separated, composed of a number of buildings and surrounded by plantations extending farther than the eye can reach, cultivated...by unhappy black men whom European avarice brings hither...Their furniture is of the most costly wood, and rarest marbles, enriched by skilful and artistic work. Their elegant and light carriages are drawn by finely bred horses, and driven by richly apparelled slaves."[36]
In the later colonial period, the southern and eastern portions of the Province continued in their tobacco economy, heavily dependent on slave labor, but as the revolution approached, northern and central Maryland increasingly became centers of wheat production. This helped drive the expansion of interior farming towns like Frederick and Maryland's major port city of Baltimore.
The American Revolution
Up to the time of the American Revolution, Province of Maryland was one of two colonies that remained an English proprietary colony, Pennsylvania being the other.[37] Maryland declared independence from Britain in 1776, with Samuel Chase, William Paca, Thomas Stone, and Charles Carroll of Carrollton signing the Declaration of Independence for the colony. In the 1776–77 debates over the Articles of Confederation, Maryland delegates led the party that insisted that states with western land claims cede them to the Confederation government, and in 1781, Maryland became the last state to ratify the Articles of Confederation. It accepted the United States Constitution more readily, ratifying it on April 28, 1788.
Maryland also gave up some territory to create the new District of Columbia after the American Revolution.
See also
- List of colonial governors of Maryland
- Colonial families of Maryland
- History of Maryland
- History of slavery in Maryland
- Thomas Cresap
- Lord Baltimore penny
- Economic history of Colonial Maryland
Notes
- ^ The Charter of Maryland : 1632, §§ VI, VII, VIII, et al.
- ^ Elson, Henry. "Colonial Maryland". www.usahistory.info. Retrieved 2015-05-11.
- ^ Sparks, Jared (1846). The Library of American Biography: George Calvert, the first Lord Baltimore. Boston: Charles C. Little and James Brown. pp. 16–.
- ^ Maryland State Manual
- ^ Taylor, Alan. American Colonies (New York: Viking, 2001), p. 136; and, John Mack Faragher, ed., The Encyclopedia of Colonial and Revolutionary America (New York: Facts on File, 1990), p. 254.
- ^ a b c Knott, Aloysius. "Maryland." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 9. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1910
- ^ "The Southern Colonies", U.S. History, The Independence Hall Association
- ^ a b c d e f g h i
Alvin M. Josephy, Jr., ed. (1961). The American Heritage Book of Indians. American Heritage Publishing Co., Inc. pp. 188–89. LCCN 61-14871.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b Andrews, p. 76
- ^ Battle of Wyoming
- ^ "Religion and the Founding of the American Republic: America as a Religious Refuge: The Seventeenth Century, Part 2". loc.gov. Library of Congress. June 1998. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- ^ Stewart, George R. (1967) [1945]. Names on the Land: A Historical Account of Place-Naming in the United States (Sentry edition (3rd) ed.). Houghton Mifflin. pp. 42–43.
- ^ a b c Brenner, Robert (2003). Merchants and Revolution: Commercial Change, Political Conflict, and London's Overseas Traders London:Verso. p. 124, ISBN 1-85984-333-6
- ^ Hubbard, Bill, Jr. (2009). American Boundaries: the Nation, the States, the Rectangular Survey. University of Chicago Press. pp. 21–23. ISBN 978-0-226-35591-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Edward Danson, Drawing the Line: How Mason and Dixon Surveyed the Most Famous Border in America (2000)
- ^ a b Browne, William Hand (1890). George Calvert and Cecil Calvert: Barons Baltimore of Baltimore. New York: Dodd, Mead, and Company.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Browne, p. 4.
- ^ Brown, p. 39.
- ^ Brugger, Robert J., Maryland, a Middle Temperament 1634–1980
- ^ Hoffman, Ronald, Princes of Ireland, Planters of Maryland: A Carroll Saga, 1500–1782 Retrieved Jan 24 2010
- ^ a b Hoffman, Ronald, p.79, Princes of Ireland, Planters of Maryland: A Carroll Saga, 1500–1782 Retrieved August 9, 2010
- ^ Frederick Calvert at www.epsomandewellhistoryexplorer.org.uk Retrieved Jan 24 2010
- ^ Frederick Calvert at www.aboutfamouspeople.com Retrieved Jan 16, 2010
- ^ Bouchard, Brian. "Frederick Calvert, 6th, and last, Baron Baltimore", Leatherhead and District Local History Society
- ^ a b Charles I, "The Charter of Maryland: 1632", The Avalon Project
- ^ a b Andrews, p. 70
- ^ Andrews, p. 71
- ^ a b Brugger, Robert J., p. 38, Maryland, a Middle Temperament 1634–1980 Retrieved July 26, 2010
- ^ a b c Roark, Elisabeth Louise, p. 78, Artists of colonial America Retrieved February 22, 2010
- ^ John E. Findling, Frank W. Thackeray, Events that Changed America Through the Seventeenth Century, pp. 133–34.
- ^ Gloria L. Main, Tobacco Colony: Life in Early Maryland, 1650–1720 (1982).
- ^ C. A. Werner, Tobaccoland A Book About Tobacco; Its History, Legends, Literature, Cultivation, Social and Hygienic Influences (1922)
- ^ Gregory A. Stiverson, Poverty in a Land of Plenty: Tenancy in Eighteenth-Century Maryland (Johns Hopkins U. Press, 1978)
- ^ John Mack Faragher, ed., The Encyclopedia of Colonial and Revolutionary America (New York: Facts on File, 1990), p. 257
- ^ Bayly Ellen Marks, "Rural Response to Urban Penetration: Baltimore and St. Mary's County, Maryland, 1790–1840," Journal of Historical Geography (1982) 8#2 pp. 113–27.
- ^ Yentsch, Anne E, p. 265, A Chesapeake Family and their Slaves: a Study in Historical Archaeology, Cambridge University Press (1994) Retrieved Jan 2010
- ^ America's Founding Charters: Primary Documents of Colonial and Revolutionary Era Governance, Volume 1 by Jon. L. Wakelyn. 2006. p. 109.
Sources
- Andrews, Matthew Page, History of Maryland, Doubleday, New York (1929)
- Everstine, Carl N. "The Establishment of Legislative Power in Maryland", 12 Maryland Law Review 99 (1951)

