Chatham, Massachusetts: Difference between revisions
m WikiCleaner 0.99 - Repairing link to disambiguation page - (You can help) - Buried |
Red Director (talk | contribs) |
||
| (256 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Use mdy dates|date=May 2024}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
|official_name = Chatham, Massachusetts |
| official_name = Chatham, Massachusetts |
||
|nickname = |
| nickname = |
||
|motto = |
| motto = |
||
|image_skyline = |
| image_skyline = |
||
|imagesize = |
| imagesize = |
||
|image_caption |
| image_caption = |
||
|image_seal = |
| image_seal = Seal of Chatham, Massachusetts.png |
||
|image_flag = |
| image_flag = Flag of Chatham, Massachusetts.gif |
||
|image_map = |
| image_map = Barnstable County Massachusetts incorporated and unincorporated areas Chatham highlighted.svg |
||
|mapsize = |
| mapsize = 260px |
||
|map_caption = Location in Barnstable County |
| map_caption = Location in [[Barnstable County, Massachusetts|Barnstable County]] and [[Massachusetts]] |
||
| |
| subdivision_type = [[List of sovereign states|Country]] |
||
| |
| subdivision_name = United States |
||
| |
| subdivision_type1 = [[U.S. state|State]] |
||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Massachusetts]] |
|||
|coordinates_display = inline,title |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = [[List of counties in Massachusetts|County]] |
|||
|coordinates_region = US-MA |
|||
| |
| subdivision_name2 = [[Barnstable County, Massachusetts|Barnstable]] |
||
| parts_type = Communities |
|||
|subdivision_name = [[United States]] |
|||
| parts = {{ubl|[[Chatham (CDP), Massachusetts|Chatham]]|[[Chatham Port, Massachusetts|Chatham Port]]|[[North Chatham, Massachusetts|North Chatham]]|Quitnesset|South Chatham|[[West Chatham, Massachusetts|West Chatham]]}} |
|||
|subdivision_type1 = [[Political divisions of the United States|State]] |
|||
| |
| established_title = Settled |
||
| established_date = 1664 |
|||
|subdivision_type2 = [[List of counties in Massachusetts|County]] |
|||
| established_title2 = Incorporated |
|||
|subdivision_name2 = [[Barnstable County, Massachusetts|Barnstable]] |
|||
| |
| established_date2 = 1712 |
||
| |
| established_title3 = Named After |
||
| established_date3 = [[Chatham, Kent|Chatham]], [[Kent]] |
|||
|established_title2 = Incorporated |
|||
| government_type = [[Open town meeting]] |
|||
|established_date2 = 1712 |
|||
| leader_title = <!--[[Town Manager|Town<br> Manager]]--> |
|||
|established_title3 = |
|||
| |
| leader_name = |
||
| leader_title1 = <!--Board of <br> Selectmen--> |
|||
|government_type = [[Open town meeting]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = |
|||
|leader_title = <!--[[Town Manager|Town<br> Manager]]--> |
|||
| |
| area_magnitude = |
||
| area_total_km2 = 63.2 |
|||
|leader_title1 = <!--Board of <br> Selectmen--> |
|||
| |
| area_total_sq_mi = |
||
| |
| area_land_km2 = 41.8 |
||
| |
| area_land_sq_mi = |
||
| |
| area_water_km2 = 21.4 |
||
| |
| area_water_sq_mi = |
||
| |
| population_as_of = 2020 |
||
| |
| settlement_type = [[New England town|Town]] |
||
| |
| population_total = 6594 |
||
| |
| population_density_km2 = 157.8 |
||
| population_density_sq_mi = |
|||
|settlement_type = [[New England town|Town]] |
|||
| |
| elevation_m = 14 |
||
| elevation_ft = 46 |
|||
|population_density_km2 = 157.7 |
|||
| timezone = [[Eastern Standard Time Zone|Eastern]] |
|||
|population_density_sq_mi = 408.4 |
|||
| |
| utc_offset = −5 |
||
| |
| timezone_DST = [[Eastern Standard Time Zone|Eastern]] |
||
| |
| utc_offset_DST = −4 |
||
| coordinates = {{coord|41|40|55|N|69|57|37|W|region:US-MA|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|utc_offset = -5 |
|||
| website = {{URL|www.chatham-ma.gov}} |
|||
|timezone_DST = [[Eastern Standard Time Zone|Eastern]] |
|||
| |
| postal_code_type = ZIP Code |
||
| postal_code = 02633 |
|||
|latd = 41 |latm = 40 |lats = 55 |latNS = N |
|||
| area_code = [[Area code 508|508]]/[[Area code 774|774]] |
|||
|longd = 69 |longm = 57 |longs = 37 |longEW = W |
|||
| |
| blank_name = [[Federal Information Processing Standard|FIPS code]] |
||
| blank_info = 25-12995 |
|||
|postal_code_type = ZIP code |
|||
| blank1_name = [[Geographic Names Information System|GNIS]] feature ID |
|||
|postal_code = 02633 |
|||
| |
| blank1_info = 0618250 |
||
| |
| footnotes = |
||
}} |
|||
|blank_info = 25-12995 |
|||
|blank1_name = [[Geographic Names Information System|GNIS]] feature ID |
|||
|blank1_info = 0618250 |
|||
|footnotes =}} |
|||
'''Chatham''' is a [[New England town|town]] in [[Barnstable County, Massachusetts|Barnstable County]], [[Massachusetts]], [[United States]], Barnstable County being coextensive with [[Cape Cod]]. The population was 6,625 at the 2000 census. Chatham is home to the Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge, located on [[Monomoy]], and to Monomoy Theatre. |
|||
'''Chatham''' ({{IPAc-en|'|tʃ|æ|t|ə|m}}) is a [[New England town|town]] in [[Barnstable County, Massachusetts|Barnstable County]], [[Massachusetts]], United States. Chatham is located at the southeast tip of Cape Cod and has historically been a fishing community. First settled by the English in 1664, the township was originally called '''Monomoit''' based on the indigenous population's term for the region.<ref name="chatam-hist">{{cite book |last=Smith |first=William C. |title=A history of Chatham, Massachusetts; formerly the Constablewick or Village of Monomoit; with maps and illustrations and numerous genealogical notes |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofchatham00smit|access-date=October 13, 2013|year=1909 |publisher=F.B. & F.P. Goss |location=Hyannis, MA|ol=14012476M }}</ref> Chatham was incorporated as a town on June 11, 1712, and has become a summer resort area. The population was 6,594 at the 2020 census, and can swell to 25,000 during the summer months.<ref name="Census 2020">{{Cite web| url=https://data.census.gov/cedsci/profile?g=0600000US2500112995| title=Census - Geography Profile: Chatham town, Barnstable County, Massachusetts| publisher=U.S. Census Bureau| access-date=October 6, 2021}}</ref> There are four villages that comprise the town, those being [[Chatham (CDP), Massachusetts|Chatham (CDP)]], [[South Chatham Railroad Station|South Chatham]], [[North Chatham, Massachusetts|North Chatham]], and [[West Chatham, Massachusetts|West Chatham]]. Chatham is home to the [[Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge]], and the decommissioned [[Monomoy Point Light]] both located on [[Monomoy Island]]. A popular attraction is the [[Chatham Light]], which is an operational lighthouse that is operated by the [[United States Coast Guard]]. |
|||
For geographic and demographic information on specific parts of the town of Chatham, please see the articles on [[Chatham (CDP), Massachusetts|Chatham (CDP)]] and [[West Chatham, Massachusetts|West Chatham]]. |
|||
== |
==History== |
||
Native American tribes who lived in the area before European colonization |
Native American tribes who lived in the area before European colonization included the [[Nauset]], specifically the Manomoy or Monomoy people. The expansive lands over which they roamed were known to them as Manamoyik or Monomoit. Explorer [[Samuel de Champlain]] landed here in October 1606 at a place he christened "Port Fortuné", where he contacted (and skirmished with) the Nauset. Twelve years later another group of Europeans gave it the name "Sutcliffe's Inlets".<ref name="chatam-hist"/> Neither name stuck, and the location was not permanently occupied by Europeans until English settlers reached Monomoit in 1664.<ref name="chatam-hist"/> The town was incorporated on June 11, 1712,<ref name="chatam-hist"/> at which point it was renamed after [[Chatham, Kent]], [[England]]. Its territory expanded with the annexation of Strong Island and its vicinity on February 7, 1797.<ref name="chatam-hist"/> |
||
Located at the "elbow" of Cape Cod, the community became a [[shipping]], [[fishing]], and [[whaling]] center. Chatham's early prosperity would leave it with a considerable number of 18th century buildings, whose charm helped it develop into a popular summer resort. |
|||
Chatham is home to the [[Chatham Lighthouse]], which was established by President [[Thomas Jefferson]] in 1808 to protect the ships circling the Cape. Originally consisting of two lights, the pair were moved back and rebuilt in 1877. The second was moved to Eastham to become the [[Nauset Light]] in 1923, after both were upgraded to rotating lights. Today, the keeper's house is home to a [[United States Coast Guard|Coast Guard]] station which tends the light. |
|||
Chatham is home to the [[Chatham Lighthouse]], which was established by President [[Thomas Jefferson]] in 1808 to protect the ships circling the Cape. The 1808 towers were replaced in 1841 by twin brick towers that were eventually lost to erosion. The pair were rebuilt in 1877 out of cast iron across the street from its original location, where the light is today. The northern of the two was moved to [[Eastham, Massachusetts|Eastham]] to become the [[Nauset Light]] in 1923, when the northern tower was declared surplus. Today, the keeper's house is home to a [[United States Coast Guard|Coast Guard]] station which patrols the waters of the Atlantic and Nantucket Sound from Wellfleet to West Yarmouth. The first reforesting project in America took place on Great Hill in 1821 when Selectmen had pine trees and beach grass planted to prevent erosion and to keep sand from blowing over the village.<ref name=names>{{cite book|title=The Names of Cape Cod | first1 = Eugene | last1 = Green | first2 = William | last2 = Sachse | first3 = Brian | last3 = McCaulley | year = 2006 | publisher = Arcadia Press | isbn = 978-1-933212-84-5 | page = 96 }}</ref> |
|||
Although [[urban sprawl]] has started to invade the country and even parts of [[Cape Cod]], the town of Chatham still boasts a quaint and walkable [[Main Street]]. Main Street is home to numerous family-owned and -operated shops, restaurants, and businesses. The main shopping area features pedestrian-friendly crosswalks, on-street parallel parking, and some parking lots that are off Main Street. During the summer, concerts are held in a [[gazebo]] on Main Street, and not far from the shops is where the [[Chatham Anglers]] baseball team plays. |
|||
Although [[urban sprawl]] has invaded the Cape, the town of Chatham still boasts a quaint and walkable [[Main Street]], home to numerous family-owned and -operated shops, restaurants, and businesses. The main shopping area features pedestrian-friendly [[crosswalk]]s, on-street [[parallel parking]], and some parking lots that are off Main Street. During the summer, concerts are held in a [[gazebo]] on Main Street, and not far from the shops is where the [[Chatham Anglers]] baseball team plays, as part of the [[Cape Cod Baseball League]] on the peninsula for collegiate-age players. |
|||
Chatham, like much of Cape Cod, is suffering from an exodus of young people and young families due to high housing prices and a lack of social and professional opportunities.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.wgbh.org/wcai/grown.cfm |title=WCAI | How We've Grown |publisher=Wgbh.org |access-date=January 4, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160919131310/http://www.wgbh.org/wcai/grown.cfm |archive-date=September 19, 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The majority of homes in Chatham sit empty in the winter months until the summer when second-home owners come to use their summer/vacation homes, or they are used as weekly rentals for tourists.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.wgbh.org/wcai/tcc.cfm |title=WCAI | Two Cape Cods: Hidden Poverty on the Cape and Islands |publisher=Wgbh.org |access-date=January 4, 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130409212739/http://www.wgbh.org/wcai/tcc.cfm |archive-date=April 9, 2013 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news| url=http://travel.nytimes.com/2009/03/06/travel/escapes/06Capecod.html?pagewanted=all | work=The New York Times | first=Laura M. | last=Holson | title=In Winter, Cape Cod Vacations are Quiet and Peaceful | date=March 5, 2009}}</ref> As of June 1, 2023, the average listing price for a home in Chatham was over $1.1 million.<ref>{{cite web| url=https://www.trulia.com/MA/Chatham/ |title=Chatham, MA real estate overview |publisher=Trulia.com |access-date=May 28, 2023}}</ref> |
|||
In summer, Chatham grows to a population of an estimated 30,000.{{Citation needed|date=December 2013}} Facilities are overcrowded, and there continues to be limited parking in the Main Street Business District. Beaches are affected by this increase of population. Limited parking exists in established parking areas, and the town's most popular beach, Lighthouse Beach, has only off the street parking, which sometimes involves a long walk to her sandy shores. |
|||
===Historical sites and museums=== |
===Historical sites and museums=== |
||
* [http://www.chathamhistoricalsociety.org/main5.htm Atwood House] (1752) |
|||
* Atwood House (1752) |
|||
* [http://www.chathamrailroadmuseum.com/ Chatham Railroad Museum] (1887) |
|||
* Old Grist Mill (1797) |
|||
* Caleb Nickerson House (1772) |
* Caleb Nickerson House (1772) |
||
* Chatham Railroad Museum (1887) |
|||
* Josiah Mayo House (c. 1820) |
|||
* Josiah Mayo House ({{circa|1820}}) chathamconservationfoundation.org |
|||
* [[Chatham Marconi Maritime Center]] (1914) |
|||
* [[Chatham Windmill]] (1797) |
|||
* [[Chatham Light]]house (1808) |
|||
* [[Eldredge Public Library]] (1896) |
|||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
[[File:Earl in Chatham.JPG|thumb| |
[[File:Earl in Chatham.JPG|thumb|left|Chatham Lighthouse during [[Hurricane Earl (2010)|Hurricane Earl]] on September 3, 2010]] |
||
[[File:Chatham sunset.jpg|thumb|right|Sunset in Chatham]] |
|||
According to the [[United States Census Bureau]], the town has a total area of 24.4 square miles (63.2 km²), of which, 16.2 square miles (42.0 km²) of it is land and 8.2 square miles (21.2 km²) of it (33.55%) is water. The town's villages include Chatham proper, Chatham Port, North Chatham, South Chatham, and West Chatham. Chatham is bordered by [[Harwich, Massachusetts|Harwich]] to the west, Pleasant Bay and Harwich to the north, the [[Atlantic Ocean]] to the east, and [[Nantucket Sound]] to the south. The town is 35 miles south of [[Provincetown, Massachusetts|Provincetown]] and east of the [[Sagamore Bridge]], 20 miles east of [[Barnstable, Massachusetts|Barnstable]], and 85 miles southeast of [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston]]. |
|||
The town occupies the southeast corner (the "elbow") of Cape Cod. The town's villages include [[Chatham (CDP), Massachusetts|Chatham proper]], [[Chatham Port, Massachusetts|Chatham Port]], North Chatham, [[West Chatham, Massachusetts|West Chatham]], and South Chatham (west of West Chatham). Chatham is bordered by [[Harwich, Massachusetts|Harwich]] to the west, Pleasant Bay and [[Orleans, Massachusetts|Orleans]] to the north, the [[Atlantic Ocean]] to the east, and [[Nantucket Sound]] to the south. The town is {{convert|35|mi}} south of [[Provincetown, Massachusetts|Provincetown]] and east of the [[Sagamore Bridge]], {{convert|20|mi}} east of [[Barnstable, Massachusetts|Barnstable]], and {{convert|85|mi}} southeast of [[Boston]]. |
|||
According to the [[United States Census Bureau]], the town has a total area of {{convert|63.2|sqkm|order=flip}}, of which {{convert|41.8|sqkm|order=flip}} is land and {{convert|21.4|sqkm|order=flip}}, or 33.88%, is water.<ref name="Census 2010">{{Cite web| url=http://factfinder.census.gov/bkmk/table/1.0/en/DEC/10_DP/G001/0600000US2500112995| archive-url=https://archive.today/20200212143428/http://factfinder.census.gov/bkmk/table/1.0/en/DEC/10_DP/G001/0600000US2500112995| url-status=dead| archive-date=February 12, 2020| title=Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Chatham town, Barnstable County, Massachusetts| publisher=U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder| access-date=December 4, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
The mainland portion of the town is typical of Cape Cod, with several ponds, brooks, rivers, harbors, and inlets around the town. The town includes two narrow strips of land which serve as a barrier between the Atlantic and the mainland; the northern of these is the southern part of the [[Cape Cod National Seashore]]. There are several islands, including Strong Island, Tern Island (which is a sanctuary), Morris Island, Stage Island, and [[Monomoy Island]], a {{convert|7.25|mi|km|adj=mid|-long}} island south of the corner of the town which is home to the [[Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge]]. Erosion has changed the region over the years—for example, an island named [[Slut's Bush]] once existed until it vanished under water by the mid 19th century.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TTkONJrQrtYC&pg=PA43 |title=The New England Historical and Genealogical Register |date=1864 |publisher=New England Historic Genealogical Society |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==Climate== |
|||
According to the [[Köppen climate classification]] system, Chatham, Massachusetts has a warm-summer, wet all year, [[humid continental climate]] (''Dfb''). Dfb climates are characterized by at least one month having an average mean temperature ≤ 32.0 °F (≤ 0.0 °C), at least four months with an average mean temperature ≥ 50.0 °F (≥ 10.0 °C), all months with an average mean temperature ≤ 71.6 °F (≤ 22.0 °C), and no significant precipitation difference between seasons. The average seasonal (Nov-Apr) snowfall total is around 30 in (76 cm). The average snowiest month is February which corresponds with the annual peak in [[nor'easter]] activity. The [[plant hardiness zone]] is 7b with an average annual extreme minimum air temperature of 5.2 °F (–14.9 °C). |
|||
{{Weather box |
|||
| location = Chatham, Massachusetts (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1972–2021) |
|||
| single line = Y |
|||
| Jan record high F = 58 |
|||
| Feb record high F = 58 |
|||
| Mar record high F = 70 |
|||
| Apr record high F = 81 |
|||
| May record high F = 88 |
|||
| Jun record high F = 90 |
|||
| Jul record high F = 95 |
|||
| Aug record high F = 93 |
|||
| Sep record high F = 85 |
|||
| Oct record high F = 82 |
|||
| Nov record high F = 68 |
|||
| Dec record high F = 62 |
|||
| year record high F = 95 |
|||
| Jan avg record high F = 52.3 |
|||
| Feb avg record high F = 50.1 |
|||
| Mar avg record high F = 55.3 |
|||
| Apr avg record high F = 63.3 |
|||
| May avg record high F = 73.1 |
|||
| Jun avg record high F = 81.0 |
|||
| Jul avg record high F = 84.7 |
|||
| Aug avg record high F = 83.3 |
|||
| Sep avg record high F = 78.9 |
|||
| Oct avg record high F = 71.1 |
|||
| Nov avg record high F = 62.8 |
|||
| Dec avg record high F = 55.9 |
|||
| year avg record high F= 86.4 |
|||
| Jan high F = 38.6 |
|||
| Feb high F = 38.9 |
|||
| Mar high F = 43.1 |
|||
| Apr high F = 51.1 |
|||
| May high F = 59.7 |
|||
| Jun high F = 69.0 |
|||
| Jul high F = 75.9 |
|||
| Aug high F = 75.8 |
|||
| Sep high F = 70.3 |
|||
| Oct high F = 61.1 |
|||
| Nov high F = 52.0 |
|||
| Dec high F = 44.0 |
|||
| year high F = 56.6 |
|||
| Jan mean F = 31.7 |
|||
| Feb mean F = 31.9 |
|||
| Mar mean F = 36.9 |
|||
| Apr mean F = 45.3 |
|||
| May mean F = 53.9 |
|||
| Jun mean F = 62.8 |
|||
| Jul mean F = 69.5 |
|||
| Aug mean F = 69.4 |
|||
| Sep mean F = 64.4 |
|||
| Oct mean F = 54.9 |
|||
| Nov mean F = 45.8 |
|||
| Dec mean F = 37.6 |
|||
| year mean F = 50.3 |
|||
| Jan low F = 24.9 |
|||
| Feb low F = 25.0 |
|||
| Mar low F = 30.7 |
|||
| Apr low F = 39.5 |
|||
| May low F = 48.1 |
|||
| Jun low F = 56.6 |
|||
| Jul low F = 63.1 |
|||
| Aug low F = 62.9 |
|||
| Sep low F = 58.4 |
|||
| Oct low F = 48.7 |
|||
| Nov low F = 39.6 |
|||
| Dec low F = 31.2 |
|||
| year low F = 44.1 |
|||
| Jan avg record low F = 8.8 |
|||
| Feb avg record low F = 12.4 |
|||
| Mar avg record low F = 17.9 |
|||
| Apr avg record low F = 31.6 |
|||
| May avg record low F = 39.6 |
|||
| Jun avg record low F = 48.4 |
|||
| Jul avg record low F = 56.4 |
|||
| Aug avg record low F = 57.1 |
|||
| Sep avg record low F = 49.1 |
|||
| Oct avg record low F = 37.8 |
|||
| Nov avg record low F = 27.3 |
|||
| Dec avg record low F = 17.8 |
|||
| year avg record low F= 6.9 |
|||
| Jan record low F = −6 |
|||
| Feb record low F = −4 |
|||
| Mar record low F = 7 |
|||
| Apr record low F = 19 |
|||
| May record low F = 33 |
|||
| Jun record low F = 44 |
|||
| Jul record low F = 51 |
|||
| Aug record low F = 47 |
|||
| Sep record low F = 40 |
|||
| Oct record low F = 31 |
|||
| Nov record low F = 18 |
|||
| Dec record low F = 0 |
|||
| year record low F = −6 |
|||
| precipitation colour = green |
|||
| Jan precipitation inch = 3.97 |
|||
| Feb precipitation inch = 3.84 |
|||
| Mar precipitation inch = 4.71 |
|||
| Apr precipitation inch = 4.01 |
|||
| May precipitation inch = 3.30 |
|||
| Jun precipitation inch = 3.17 |
|||
| Jul precipitation inch = 2.80 |
|||
| Aug precipitation inch = 3.20 |
|||
| Sep precipitation inch = 3.78 |
|||
| Oct precipitation inch = 4.31 |
|||
| Nov precipitation inch = 4.12 |
|||
| Dec precipitation inch = 4.72 |
|||
| year precipitation inch = 45.93 |
|||
| Jan snow inch = 7.5 |
|||
| Feb snow inch = 9.9 |
|||
| Mar snow inch = 3.8 |
|||
| Apr snow inch = 0.5 |
|||
| May snow inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Jun snow inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Jul snow inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Aug snow inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Sep snow inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Oct snow inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Nov snow inch = 0.2 |
|||
| Dec snow inch = 2.6 |
|||
| year snow inch = 24.5 |
|||
| unit precipitation days = 0.01 in |
|||
| Jan precipitation days = 12.4 |
|||
| Feb precipitation days = 10.9 |
|||
| Mar precipitation days = 11.7 |
|||
| Apr precipitation days = 11.5 |
|||
| May precipitation days = 11.0 |
|||
| Jun precipitation days = 9.6 |
|||
| Jul precipitation days = 8.2 |
|||
| Aug precipitation days = 8.3 |
|||
| Sep precipitation days = 8.7 |
|||
| Oct precipitation days = 10.8 |
|||
| Nov precipitation days = 10.6 |
|||
| Dec precipitation days = 12.9 |
|||
| year precipitation days = 126.6 |
|||
| unit snow days = 0.1 in |
|||
| Jan snow days = 3.6 |
|||
| Feb snow days = 3.9 |
|||
| Mar snow days = 1.8 |
|||
| Apr snow days = 0.2 |
|||
| May snow days = 0.0 |
|||
| Jun snow days = 0.0 |
|||
| Jul snow days = 0.0 |
|||
| Aug snow days = 0.0 |
|||
| Sep snow days = 0.0 |
|||
| Oct snow days = 0.0 |
|||
| Nov snow days = 0.2 |
|||
| Dec snow days = 1.5 |
|||
| year snow days = 11.2 |
|||
| Jan snow depth inch = 5.5 |
|||
| Feb snow depth inch = 5.8 |
|||
| Mar snow depth inch = 3.1 |
|||
| Apr snow depth inch = 0.4 |
|||
| May snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Jun snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Jul snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Aug snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Sep snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Oct snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Nov snow depth inch = 0.0 |
|||
| Dec snow depth inch = 2.3 |
|||
| year snow depth inch= 8.8 |
|||
| source 1 = [[NOAA]]<ref name=nws> |
|||
{{cite web |
|||
| url = https://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=box |
|||
| title = NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data |
|||
| publisher = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
|||
| access-date = May 30, 2021}}</ref><ref name=NCEI> |
|||
{{cite web |
|||
| url = https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/services/data/v1?dataset=normals-monthly-1991-2020&startDate=0001-01-01&endDate=9996-12-31&stations=USC00191386&format=pdf |
|||
| publisher = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
|||
| title = Station: Chatham, MA |
|||
| work = U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991–2020) |
|||
| access-date = May 30, 2021}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
==Ecology== |
|||
The area surrounding Chatham is home to diverse flora and fauna, including many species that rely on the wetlands for survival. The salt marshes and lakes that exist in the region due to glacial action from the last ice age are essential habitats for many species, such as ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) and striped bass (Morone saxatilis). These wetlands not only promote biodiversity, but also act as natural filters, retaining particulates and purifying the water that flows into nearby estuaries and bays.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Santos |first=Pei Xin, Alicia Wilson, Zhenming Ge, Isaac |date=April 19, 2022 |title=Understanding the Importance of Salt Marshes |url=http://eos.org/editors-vox/understanding-the-importance-of-salt-marshes |access-date=March 14, 2023 |website=Eos |language=en-US}}</ref> However, Chatham's beaches have experienced significant vegetation loss in recent decades due to both natural and human causes.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Smith |first=Stephen M. |date=2009 |title=Multi-decadal Changes in Salt Marshes of Cape Cod, MA: Photographic Analyses of Vegetation Loss, Species Shifts, and Geomorphic Change |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/27744558 |journal=Northeastern Naturalist |volume=16 |issue=2 |pages=183–208 |doi=10.1656/045.016.0203 |jstor=27744558 |s2cid=86338099 |issn=1092-6194}}</ref> Despite this, the beaches remain important nesting sites for various species of sea turtles and shorebirds, such as the Piping Plover (Charadrius melodus), while the waters off the coast are rich in marine life, including seals (Halichoerus grypus), whales, and sharks, such as the great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias).<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Wellfleet |first1=Mailing Address: 99 Marconi Site Road |last2=ranger |first2=MA 02667 Phone: 508-255-3421 To speak to a park |last3=Us |first3=call 508-255-3421 for visitor information Contact |title=Oceans - Cape Cod National Seashore (U.S. National Park Service) |url=https://www.nps.gov/caco/learn/nature/oceans.htm |access-date=March 14, 2023 |website=www.nps.gov |language=en}}</ref> In fact, the prevalence of sharks in the waters surrounding Chatham has resulted in its reputation as a hub of great white activity and shark attacks. To help protect and preserve the local flora and fauna, several conservation areas and nature preserves have been established in Chatham, including Monomoy Island, which provides an important breeding ground for the Piping Plover.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Fraser |first1=James D. |last2=Keane |first2=Shannon E. |last3=Buckley |first3=P. A. |date=2005 |title=Prenesting Use of Intertidal Habitats by Piping Plovers on South Monomoy Island, Massachusetts |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/3803531 |journal=The Journal of Wildlife Management |volume=69 |issue=4 |pages=1731–1736 |doi=10.2193/0022-541X(2005)69[1731:PUOIHB]2.0.CO;2 |jstor=3803531 |s2cid=84553350 |issn=0022-541X}}</ref> |
|||
According to the [[A. W. Kuchler]] U.S. [[Potential natural vegetation]] Types, Chatham, Massachusetts would primarily contain a Northeastern [[Oak]]/[[Pine]] (''110'') vegetation type with a Southern [[Mixed Forest]] (''26'') vegetation form.<ref name="Conservation Biology Institute">{{cite web|url=https://databasin.org/datasets/1c7a301c8e6843f2b4fe63fdb3a9fe39|publisher=[[Data Basin]]|access-date=July 30, 2019|title=U.S. Potential Natural Vegetation, Original Kuchler Types, v2.0 (Spatially Adjusted to Correct Geometric Distortions)}}</ref> |
|||
The mainland portion of the town is typical of Cape Cod, with several ponds, brooks, rivers, harbors, and inlets around the town. The town includes two narrow strips of land, the northern of which is the southern part of the [[Cape Cod National Seashore]], which serve as a barrier between the Atlantic and the mainland. There are several islands, including Strong Island, Tern Island (which is a sanctuary), Morris Island, Stage Island, and [[Monomoy Island]] (a 7-1/4 mile long island south of the corner of the town which is home to the Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge). |
|||
==Transportation== |
==Transportation== |
||
All five roads that exit Chatham cross into Harwich. |
All five roads that exit Chatham cross into Harwich. The two state routes that pass through the town are [[Massachusetts Route 28|Route 28]] and the southern end of [[Massachusetts Route 137|Route 137]]. Route 28 circles through the center of town before exiting and heading north toward [[Massachusetts Route 6A|Route 6A]], joining that route until the roads end at the Orleans Rotary. |
||
[[Rail transport|Rail service]] no longer extends to the town; the former rail bed is a bicycling path, and is called the Old Colony Rail Trail. In addition, another bicycle route passes through the town, starting at the end of the Rail Trail, and providing views of Chatham Fish Pier, Chatham Bars, and [[Chatham Light]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Chatham Bike Routes|url=http://www.capecodbikebook.com/2015/07/chatham-bike-route-and-old-colony-rail.html|website=Cape Cod Bike Book|access-date=July 26, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160825185511/http://www.capecodbikebook.com/2015/07/chatham-bike-route-and-old-colony-rail.html|archive-date=August 25, 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
Rail no longer extends to the town; the route is now a portion of one of the several bicycle paths that pass through the town. |
|||
The town is the home to the Chatham Municipal Airport, which provides local service to other small airports on the Cape and |
The town is the home to the [[Chatham Municipal Airport]], which provides local service to other small airports on the Cape and islands. The nearest national and international air service can be reached at [[Logan International Airport]] in Boston. |
||
==Demographics== |
==Demographics== |
||
[[Image:Chatham Light MA.jpg|thumb|left|Chatham Lighthouse, 2007]] |
|||
As of the [[census]]{{GR|2}} of 2000, there were 6,625 people, 3,160 households, and 1,886 families residing in the town. The [[population density]] was 408.4 people per square mile (157.7/km²). There were 6,743 housing units at an average density of 415.7/sq mi (160.5/km²). The racial makeup of the town was 96.03% [[White (U.S. Census)|White]], 1.77% [[African American (U.S. Census)|Black]] or [[Race (United States Census)|African American]], 0.18% [[Native American (U.S. Census)|Native American]], 0.27% [[Asian (U.S. Census)|Asian]], 0.02% [[Pacific Islander (U.S. Census)|Pacific Islander]], 0.92% from [[Race (United States Census)|other races]], and 0.82% from two or more races. [[Hispanic (U.S. Census)|Hispanic]] or [[Latino (U.S. Census)|Latino]] of any race were 1.00% of the population. |
|||
{{See also|List of Massachusetts locations by per capita income}} |
|||
During the summer months (generally Memorial Day through Labor Day), the population of the town triples to approximately 20,000, not counting the additional transient tourist population hosted by the town's many hotels, inns, motels, and bed and breakfasts. While the tourist industry is very strong in Chatham, fishing still represents the town's main industry. |
|||
{{Historical populations | type=USA |
|||
| 1850|2439 |
|||
| 1860|2710 |
|||
| 1870|2411 |
|||
| 1880|2250 |
|||
| 1890|1954 |
|||
| 1900|1749 |
|||
| 1910|1564 |
|||
| 1920|1737 |
|||
| 1930|1931 |
|||
| 1940|2136 |
|||
| 1950|2457 |
|||
| 1960|3273 |
|||
| 1970|4554 |
|||
| 1980|6071 |
|||
| 1990|6579 |
|||
| 2000|6625 |
|||
| 2010|6125 |
|||
| 2020|6594 |
|||
| 2022*|6711 |
|||
| footnote=* = population estimate.<ref>{{cite web | title=City and Town Population Totals: 2020-2022| publisher=[[United States Census Bureau]] | access-date=October 21, 2023 | url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/popest/2020s-total-cities-and-towns.html}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
[[File:ChathamLightandCoastGuard.jpg|alt=|left|thumb|Chatham Lighthouse and Coast Guard Station, 2020]] |
|||
As of the [[census]]<ref name="GR2">{{cite web |url=https://www.census.gov |publisher=[[United States Census Bureau]] |access-date=January 31, 2008 |title=U.S. Census website }}</ref> of 2000, there were 6,625 people, 3,160 households, and 1,886 families residing in the town. The population density was {{convert|408.4|PD/sqmi|PD/km2|sp=us|adj=off}}. There were 6,743 housing units at an average density of {{convert|415.7|/sqmi|/km2|sp=us|adj=off}}. The racial makeup of the town was 96% [[White (U.S. Census)|White]], 1.9% [[African American (U.S. Census)|Black]] or [[Race (United States Census)|African American]], 0.2% [[Native American (U.S. Census)|Native American]], 0.3% [[Asian (U.S. Census)|Asian]], <0.1% [[Pacific Islander (U.S. Census)|Pacific Islander]], 0.9% from [[Race (United States Census)|other races]], and 0.8% from two or more races. [[Hispanic (U.S. Census)|Hispanic]] or [[Latino (U.S. Census)|Latino]] of any race were 1.0% of the population. |
|||
During the summer months (generally Memorial Day through Labor Day), the population of the town triples to approximately 20,000, not counting the additional transient tourist population hosted by the town's many hotels, inns, motels, and bed and breakfasts. Tourism and Hospitality along with Commercial Fishing make up the town's main industry. The town has a thriving commercial fish pier where day-boats unload fresh fish and lobster. |
|||
There were 3,160 households out of which 15.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.2% were [[Marriage|married couples]] living together, 6.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 34.7% of all households were made up of individuals and 18.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.00 and the average family size was 2.52. |
|||
There were 3,160 households, out of which 15.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.2% were [[Marriage|married couples]] living together, 6.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 34.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 18.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.00 and the average family size was 2.52. |
|||
In the town, the population was spread out, with 13.3% under the age of 18, 4.4% from 18 to 24, 19.8% from 25 to 44, 28.2% from 45 to 64, and 34.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 54 years. For every 100 females, there were 89.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 85.4 males. |
|||
The local K-12 school system has approximately 700 students, making for average high school grade sizes between 30 and 40 students. |
|||
The local K–12 school system has approximately 700 students, making for average high school grade sizes between 30 and 40 students. |
|||
The median income for a household in the town was $45,519, and the median income for a family was $56,750. Males had a median income of $41,064 versus $30,365 for females. The [[per capita income]] for the town was $28,594. About 1.9% of families and 4.8% of the population were below the [[poverty line]], including 5.1% of those under age 18 and 3.7% of those age 65 or over. |
|||
The median income for a household in the town was $85,519, and the median income for a family was $112,750. Males had a median income of $71,064 versus $40,365 for females. The [[per capita income]] for the town was $48,594. About 1.9% of families and 4.8% of the population were below the [[poverty line]], including 5.1% of those under age 18 and 3.7% of those age 65 or over. |
|||
==Government== |
==Government== |
||
Chatham is represented in the [[Massachusetts House of Representatives]] as a part of the Fourth Barnstable district, which includes (with the exception of Brewster) all the towns east and north of Harwich on the Cape. The town is represented in the [[Massachusetts Senate]] as a part of the Cape and Islands District, which includes all of Cape Cod, Martha's Vineyard, and Nantucket except the towns of Bourne, Falmouth, Sandwich, and a portion of Barnstable.<ref> |
Chatham is represented in the [[Massachusetts House of Representatives]] as a part of the Fourth Barnstable district, which includes (with the exception of Brewster) all the towns east and north of Harwich on the Cape. The town is represented in the [[Massachusetts Senate]] as a part of the Cape and Islands District, which includes all of Cape Cod, Martha's Vineyard, and Nantucket except the towns of Bourne, Falmouth, Sandwich, and a portion of Barnstable.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.mass.gov/legis/citytown.htm |title=Index of Legislative Representation by City and Town, from Mass.gov |access-date=February 27, 2007 |archive-date=September 29, 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070929115141/http://www.mass.gov/legis/citytown.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
The Chatham Police Department is the primary law enforcement agency that services the town. The Police Department is staffed for 24-hour patrol and is a member of the Cape Cod Regional Law Enforcement Council. The Police station was recently constructed in 2012, and is located on George Ryder Road, across the street from the Chatham Municipal Airport. Troopers from the Massachusetts State Police Troop D Yarmouth barracks provide secondary law enforcement services to the town. |
|||
The town is patrolled by the Second (Yarmouth) Barracks of Troop D of the Massachusetts State and the Chatham Police Department. Chatham also provides Chatham Fire Rescue, a 24 hour fully staffed fire department.<ref>[http://www.mass.gov/?pageID=eopsterminal&L=5&L0=Home&L1=Law+Enforcement+%26+Criminal+Justice&L2=Law+Enforcement&L3=State+Police+Troops&L4=Troop+D&sid=Eeops&b=terminalcontent&f=msp_divisions_field_services_troops_troop_d_msp_field_troop_d_station_d2&csid=Eeops Station D-2, SP Yarmouth]</ref> |
|||
The Chatham Fire/Rescue Department is a 24-hour, fully staffed fire department, that provides fire and medical services to the town. The new fire station was constructed in 2016, and is located on Depot Road, across the street from Veteran's Field. Prior to 2012, the fire and police stations were attached and sat on the Depot Road site. The Chatham Fire/Rescue Department also has an unmanned substation on Route 28 in South Chatham; this station houses one engine truck. |
|||
On the national level, Chatham is a part of [[Massachusetts's 10th congressional district]] and is represented by [[Bill Delahunt]]. The state's senior (Class I) member of the [[United States Senate]], re-elected in 2008, is [[John Kerry]]. The junior (Class II) Senator is [[Scott Brown]]. |
|||
On the national level, Chatham is a part of [[Massachusetts's 9th congressional district]] and is represented by [[William R. Keating]]. The state's senior (Class II) member of the [[United States Senate]], elected in 2012, is [[Elizabeth Warren]]. The junior (Class I) senator is [[Ed Markey]]. |
|||
Chatham is governed by the [[open town meeting]] form of government, led by an executive secretary and a [[board of selectmen]]. The town operates its own [[police]] department, which is headquartered (along with the fire department) near the center of town. There is also a branch firehouse in South Chatham. The town has four post offices, all located at various points along Route 28. The town is home to the Eldredge Public Library, named for its benefactor and designed by a student of [[H. H. Richardson]]. The town operates several piers, beaches, boat landings and recreation areas throughout town. The nearest hospital is Cape Cod Hospital in Hyannis. |
|||
Chatham is governed by the [[open town meeting]] form of government, administered by an elected [[Board of Selectmen]] and an appointed Town Manager. The town has four post offices, all located at various points along Route 28. The town is home to the [[Eldredge Public Library]], named for its benefactor Marcellus Eldredge and designed by a student of [[H. H. Richardson]]. The town operates several piers, beaches, boat landings and recreation areas throughout town. The nearest hospital is [[Cape Cod Hospital]] in [[Hyannis, Massachusetts|Hyannis]]. |
|||
==Education== |
==Education== |
||
Chatham |
Until 2013, Chatham operated its own school system for the town's 700 students. The Chatham Elementary School served students from pre-kindergarten through fourth grade, the Chatham Middle School served students from fifth through eighth grade, and [[Chatham High School (Massachusetts)|Chatham High School]] served grades nine through twelve. Chatham's athletics teams were known as the Blue Devils, and wore blue and white. In December 2010, Chatham and the neighboring town of Harwich voted to regionalize their school systems into the Monomoy Regional school system. The Monomoy teams are known as the Sharks and their colors are navy blue and silver. In March 2013, construction began in Harwich on a new high school to serve the region, expected to open in 2014. High school students may attend [[Cape Cod Regional Technical High School|Cape Cod Regional Technical School]] in Harwich free of charge. Other private schools are located in nearby [[Brewster, Massachusetts|Brewster]] and Harwich. |
||
==Sports and recreation== |
|||
[[File:2016-10-22 Kris Bryant 2 (cropped).jpg|thumb|200px|[[Kris Bryant]] played for the [[Chatham Anglers]] in 2011.]] |
|||
Chatham is home to the [[Chatham Anglers]], an amateur [[collegiate summer baseball]] team in the [[Cape Cod Baseball League]]. The team plays at [[Veteran's Field]] and has featured dozens of players who went on to careers in [[Major League Baseball]] such as [[Thurman Munson]], [[Jeff Bagwell]], and [[Kris Bryant]]. |
|||
Eastward Ho! Golf Course is a notable golf course in town. The course hosted a [[PGA Tour]] event, [[Cape Cod Open|The Cape Cod Open]], in the 1930s.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Whitcomb |first=W. A. |date=August 18, 1930 |title=Fine Field in Cape Cod Open |page=9 |newspaper=[[The Boston Globe]] |url=https://www.newspapers.com/clip/105887341/fine-field-in-cape-cod-open/ |access-date=July 19, 2022 |via=Newspapers.com}}</ref> |
|||
==Notable |
==Notable people== |
||
{{Div col}} |
|||
* [[Zered Bassett]], pro skateboarder, grew up in Chatham |
* [[Zered Bassett]], pro skateboarder, grew up in Chatham |
||
* [[Shirley Booth]], actress |
* [[Shirley Booth]], actress |
||
* [[ |
* [[Ruby Braff]], musician, died in Chatham |
||
* [[ |
* [[Louis Brandeis]], Supreme Court Justice |
||
* [[Bernard Cornwell]], best-selling author |
|||
* [[Franklin Cover]], late actor |
* [[Franklin Cover]], late actor |
||
* [[David Drumm]], former CEO of Anglo Irish Bank<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Beth Healy|author2=Casey Ross|date=April 12, 2010|title=Irish bank's ex-CEO sits out crisis on Cape|journal=The Boston Globe|location=Boston|volume=277|issue=102}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Jamie D'Antona]], professional baseball player |
|||
* [[David Drumm]] former CEO of Anglo Irish Bank<ref>{{cite journal|coauthors=Beth Healy and Casey Ross|date=April 12, 2010|title=Irish bank's ex-CEO sits out crisis on Cape|journal=The Boston Globe|location=Boston|volume=277|issue=102}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Todd Eldredge]], champion figure skater |
* [[Todd Eldredge]], champion figure skater |
||
* [[Jack Forrester]], Scottish-American professional golfer<ref name="North Berwick">{{cite web|title=Jack Forrester (1894-1964)|url=http://www.northberwick.org.uk/clubmakers.html#forrester|website=NorthBerwick.org.uk}}</ref> {{Citation needed|date=March 2022}} |
|||
* [[Bobby Hackett]], famous musician |
|||
* [[ |
* [[Lisa Genova]], best-selling author |
||
* [[Bobby Hackett]], musician |
|||
* [[Julie Harris (actress)|Julie Harris]], actress |
|||
* [[Gilbert Knapp]], Wisconsin State Assemblyman |
|||
* Karen E. Lasser, medical researcher and senior editor at ''[[Journal of the American Medical Association]]'' |
|||
* [[Joseph C. Lincoln]], author of ''Cape Cod Stories'' |
* [[Joseph C. Lincoln]], author of ''Cape Cod Stories'' |
||
* [[Joseph Lord]], Puritan pastor |
* [[Joseph Lord]], Puritan pastor |
||
* [[Martha MacCallum]], |
* [[Martha MacCallum]], talk show host |
||
* [[Sandra Day O'Connor]], Supreme Court Justice; has a residence in Chatham |
|||
* [[Sara Pennypacker]], children's book author |
* [[Sara Pennypacker]], children's book author |
||
* [[Bill Richardson]], American politician, author, and diplomat<ref>{{cite web|title=New Mexico's Richardson buys Cape home |url=http://www.capecodtimes.com/article/20111210/News/112100326|website=CapeCodTimes.com}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Christopher Seufert]], film director/photographer |
* [[Christopher Seufert]], film director/photographer |
||
* [[Maxim D. Shrayer]], bulingual author |
|||
* [[Archelaus Smith]], Nova Scotia pioneer |
* [[Archelaus Smith]], Nova Scotia pioneer |
||
* [[Bob Staake]], cartoonist & illustrator |
* [[Bob Staake]], cartoonist & illustrator |
||
* [[ |
* Tisquantum ([[Squanto]]), died in Chatham and is buried in an unmarked [[grave]] on Burial Hill, overlooking Ryder's Cove |
||
* [[Stuart Varney]], talk show host |
|||
* [[Allen St. Pierre]] Executive Director of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, grew up in Chatham |
|||
* [[Bernard C. Webber]], heroic Coast Guardsman who was award the [[Lifesaving Medal|Gold Lifesaving Medal]] for leading a rescue to the [[SS Pendleton|SS ''Pendleton'']] in 1952 |
|||
{{div col end}} |
|||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
Image: |
Image:Atwood House, Chatham, MA.jpg|The Atwood House |
||
Image: |
Image:Chatham Lights, Chatham, MA.jpg|Chatham Lights |
||
Image: |
Image:Lighthouse_chatham.jpg|Stage Harbor Light |
||
Image:Old Linden Tree - Chatham, MA - April 2012.jpg|Old Linden Tree (April 2012) |
|||
Image:Seals in Chatham, MA harbor.jpg|Seals in Chatham Harbor |
|||
Image:Cross Trees, Chatham, MA.jpg|Cross Trees |
|||
<!-- Deleted image removed: Image:Tiger_lilies_small.jpg| --> |
|||
Image:Chatham_marsh.jpg| |
Image:Chatham_marsh.jpg| |
||
Image:Atwood House, Chatham, MA.jpg| |
|||
Image:Windmill, Chatham, MA.jpg| |
Image:Windmill, Chatham, MA.jpg| |
||
Image:Cross Trees, Chatham, MA.jpg| |
|||
Image:Chatham Lights, Chatham, MA.jpg| |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist|30em}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons category}}[https://www.chathamconservationfoundation.org/]{{Wikivoyage|Chatham (Massachusetts)}} |
|||
{{Commons category}} |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20060529082206/http://www.chatham-ma.gov/ Town of Chatham official website] |
|||
* {{wikitravel|Chatham}} |
|||
* https://www.chathamconservationfoundation.org/ |
|||
* [http://www.chatham-ma.gov/ Town of Chatham Website] |
|||
* [http://www.capecodchronicle.com/ The Cape Cod Chronicle] |
|||
* [http://www.chathaminfo.com/ Chatham Chamber of Commerce tourist information] |
|||
* [http://www.MyChatham.com/ Chatham Online Guide.] |
|||
* [http://homepage.mac.com/mooncusser/chathamarchive/PhotoAlbum222.html Archive of Historical and Contemporary Chatham Photos] |
|||
* [http://www.eldredgelibrary.org/ Eldredge Public Library] |
|||
* [http://www.ChathamCulturalCouncil.org Chatham Cultural Council] |
|||
* [http://www.CapeCodArchive.org Chatham Media Archive] |
|||
* [http://monomoy.fws.gov/ Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge] |
|||
* [http://www.chatham.k12.ma.us/ Chatham Public Schools] |
|||
* [http://www.chathamas.com/ Chatham A's] |
|||
{{Barnstable County, Massachusetts}} |
{{Barnstable County, Massachusetts}} |
||
{{Massachusetts}} |
{{Massachusetts}} |
||
{{authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Chatham, Massachusetts| ]] |
[[Category:Chatham, Massachusetts| ]] |
||
[[Category:1664 establishments in Plymouth Colony]] |
|||
[[Category:Populated coastal places in Massachusetts]] |
|||
[[Category:Populated places established in 1664]] |
|||
[[Category:Towns in Barnstable County, Massachusetts]] |
[[Category:Towns in Barnstable County, Massachusetts]] |
||
[[Category:Towns in Massachusetts]] |
|||
[[ca:Chatham (Massachusetts)]] |
|||
[[fr:Chatham (Massachusetts)]] |
|||
[[it:Chatham (Massachusetts)]] |
|||
[[ht:Chatham, Massachusetts]] |
|||
[[nl:Chatham (Massachusetts)]] |
|||
[[pl:Chatham (Massachusetts)]] |
|||
[[simple:Chatham, Massachusetts]] |
|||
[[sv:Chatham, Massachusetts]] |
|||
[[vo:Chatham (Massachusetts)]] |
|||
Revision as of 14:02, 2 May 2024
Chatham, Massachusetts | |
|---|---|
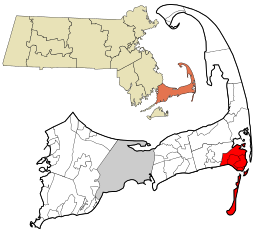 Location in Barnstable County and Massachusetts | |
| Coordinates: 41°40′55″N 69°57′37″W / 41.68194°N 69.96028°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Massachusetts |
| County | Barnstable |
| Settled | 1664 |
| Incorporated | 1712 |
| Named After | Chatham, Kent |
| Communities |
|
| Government | |
| • Type | Open town meeting |
| Area | |
| • Total | 24.4 sq mi (63.2 km2) |
| • Land | 16.1 sq mi (41.8 km2) |
| • Water | 8.3 sq mi (21.4 km2) |
| Elevation | 46 ft (14 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 6,594 |
| • Density | 409/sq mi (157.8/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (Eastern) |
| ZIP Code | 02633 |
| Area code | 508/774 |
| FIPS code | 25-12995 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0618250 |
| Website | www |
Chatham (/ˈtʃætəm/) is a town in Barnstable County, Massachusetts, United States. Chatham is located at the southeast tip of Cape Cod and has historically been a fishing community. First settled by the English in 1664, the township was originally called Monomoit based on the indigenous population's term for the region.[1] Chatham was incorporated as a town on June 11, 1712, and has become a summer resort area. The population was 6,594 at the 2020 census, and can swell to 25,000 during the summer months.[2] There are four villages that comprise the town, those being Chatham (CDP), South Chatham, North Chatham, and West Chatham. Chatham is home to the Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge, and the decommissioned Monomoy Point Light both located on Monomoy Island. A popular attraction is the Chatham Light, which is an operational lighthouse that is operated by the United States Coast Guard.
History
Native American tribes who lived in the area before European colonization included the Nauset, specifically the Manomoy or Monomoy people. The expansive lands over which they roamed were known to them as Manamoyik or Monomoit. Explorer Samuel de Champlain landed here in October 1606 at a place he christened "Port Fortuné", where he contacted (and skirmished with) the Nauset. Twelve years later another group of Europeans gave it the name "Sutcliffe's Inlets".[1] Neither name stuck, and the location was not permanently occupied by Europeans until English settlers reached Monomoit in 1664.[1] The town was incorporated on June 11, 1712,[1] at which point it was renamed after Chatham, Kent, England. Its territory expanded with the annexation of Strong Island and its vicinity on February 7, 1797.[1]
Located at the "elbow" of Cape Cod, the community became a shipping, fishing, and whaling center. Chatham's early prosperity would leave it with a considerable number of 18th century buildings, whose charm helped it develop into a popular summer resort.
Chatham is home to the Chatham Lighthouse, which was established by President Thomas Jefferson in 1808 to protect the ships circling the Cape. The 1808 towers were replaced in 1841 by twin brick towers that were eventually lost to erosion. The pair were rebuilt in 1877 out of cast iron across the street from its original location, where the light is today. The northern of the two was moved to Eastham to become the Nauset Light in 1923, when the northern tower was declared surplus. Today, the keeper's house is home to a Coast Guard station which patrols the waters of the Atlantic and Nantucket Sound from Wellfleet to West Yarmouth. The first reforesting project in America took place on Great Hill in 1821 when Selectmen had pine trees and beach grass planted to prevent erosion and to keep sand from blowing over the village.[3]
Although urban sprawl has invaded the Cape, the town of Chatham still boasts a quaint and walkable Main Street, home to numerous family-owned and -operated shops, restaurants, and businesses. The main shopping area features pedestrian-friendly crosswalks, on-street parallel parking, and some parking lots that are off Main Street. During the summer, concerts are held in a gazebo on Main Street, and not far from the shops is where the Chatham Anglers baseball team plays, as part of the Cape Cod Baseball League on the peninsula for collegiate-age players.
Chatham, like much of Cape Cod, is suffering from an exodus of young people and young families due to high housing prices and a lack of social and professional opportunities.[4] The majority of homes in Chatham sit empty in the winter months until the summer when second-home owners come to use their summer/vacation homes, or they are used as weekly rentals for tourists.[5][6] As of June 1, 2023, the average listing price for a home in Chatham was over $1.1 million.[7]
In summer, Chatham grows to a population of an estimated 30,000.[citation needed] Facilities are overcrowded, and there continues to be limited parking in the Main Street Business District. Beaches are affected by this increase of population. Limited parking exists in established parking areas, and the town's most popular beach, Lighthouse Beach, has only off the street parking, which sometimes involves a long walk to her sandy shores.
Historical sites and museums
- Atwood House (1752)
- Caleb Nickerson House (1772)
- Chatham Railroad Museum (1887)
- Josiah Mayo House (c. 1820) chathamconservationfoundation.org
- Chatham Marconi Maritime Center (1914)
- Chatham Windmill (1797)
- Chatham Lighthouse (1808)
- Eldredge Public Library (1896)
Geography


The town occupies the southeast corner (the "elbow") of Cape Cod. The town's villages include Chatham proper, Chatham Port, North Chatham, West Chatham, and South Chatham (west of West Chatham). Chatham is bordered by Harwich to the west, Pleasant Bay and Orleans to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and Nantucket Sound to the south. The town is 35 miles (56 km) south of Provincetown and east of the Sagamore Bridge, 20 miles (32 km) east of Barnstable, and 85 miles (137 km) southeast of Boston.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 24.4 square miles (63.2 km2), of which 16.1 square miles (41.8 km2) is land and 8.3 square miles (21.4 km2), or 33.88%, is water.[8]
The mainland portion of the town is typical of Cape Cod, with several ponds, brooks, rivers, harbors, and inlets around the town. The town includes two narrow strips of land which serve as a barrier between the Atlantic and the mainland; the northern of these is the southern part of the Cape Cod National Seashore. There are several islands, including Strong Island, Tern Island (which is a sanctuary), Morris Island, Stage Island, and Monomoy Island, a 7.25-mile-long (11.67 km) island south of the corner of the town which is home to the Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge. Erosion has changed the region over the years—for example, an island named Slut's Bush once existed until it vanished under water by the mid 19th century.[9]
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Chatham, Massachusetts has a warm-summer, wet all year, humid continental climate (Dfb). Dfb climates are characterized by at least one month having an average mean temperature ≤ 32.0 °F (≤ 0.0 °C), at least four months with an average mean temperature ≥ 50.0 °F (≥ 10.0 °C), all months with an average mean temperature ≤ 71.6 °F (≤ 22.0 °C), and no significant precipitation difference between seasons. The average seasonal (Nov-Apr) snowfall total is around 30 in (76 cm). The average snowiest month is February which corresponds with the annual peak in nor'easter activity. The plant hardiness zone is 7b with an average annual extreme minimum air temperature of 5.2 °F (–14.9 °C).
| Climate data for Chatham, Massachusetts (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1972–2021) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 58 (14) |
58 (14) |
70 (21) |
81 (27) |
88 (31) |
90 (32) |
95 (35) |
93 (34) |
85 (29) |
82 (28) |
68 (20) |
62 (17) |
95 (35) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 52.3 (11.3) |
50.1 (10.1) |
55.3 (12.9) |
63.3 (17.4) |
73.1 (22.8) |
81.0 (27.2) |
84.7 (29.3) |
83.3 (28.5) |
78.9 (26.1) |
71.1 (21.7) |
62.8 (17.1) |
55.9 (13.3) |
86.4 (30.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 38.6 (3.7) |
38.9 (3.8) |
43.1 (6.2) |
51.1 (10.6) |
59.7 (15.4) |
69.0 (20.6) |
75.9 (24.4) |
75.8 (24.3) |
70.3 (21.3) |
61.1 (16.2) |
52.0 (11.1) |
44.0 (6.7) |
56.6 (13.7) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 31.7 (−0.2) |
31.9 (−0.1) |
36.9 (2.7) |
45.3 (7.4) |
53.9 (12.2) |
62.8 (17.1) |
69.5 (20.8) |
69.4 (20.8) |
64.4 (18.0) |
54.9 (12.7) |
45.8 (7.7) |
37.6 (3.1) |
50.3 (10.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 24.9 (−3.9) |
25.0 (−3.9) |
30.7 (−0.7) |
39.5 (4.2) |
48.1 (8.9) |
56.6 (13.7) |
63.1 (17.3) |
62.9 (17.2) |
58.4 (14.7) |
48.7 (9.3) |
39.6 (4.2) |
31.2 (−0.4) |
44.1 (6.7) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 8.8 (−12.9) |
12.4 (−10.9) |
17.9 (−7.8) |
31.6 (−0.2) |
39.6 (4.2) |
48.4 (9.1) |
56.4 (13.6) |
57.1 (13.9) |
49.1 (9.5) |
37.8 (3.2) |
27.3 (−2.6) |
17.8 (−7.9) |
6.9 (−13.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −6 (−21) |
−4 (−20) |
7 (−14) |
19 (−7) |
33 (1) |
44 (7) |
51 (11) |
47 (8) |
40 (4) |
31 (−1) |
18 (−8) |
0 (−18) |
−6 (−21) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.97 (101) |
3.84 (98) |
4.71 (120) |
4.01 (102) |
3.30 (84) |
3.17 (81) |
2.80 (71) |
3.20 (81) |
3.78 (96) |
4.31 (109) |
4.12 (105) |
4.72 (120) |
45.93 (1,167) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 7.5 (19) |
9.9 (25) |
3.8 (9.7) |
0.5 (1.3) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
2.6 (6.6) |
24.5 (62) |
| Average extreme snow depth inches (cm) | 5.5 (14) |
5.8 (15) |
3.1 (7.9) |
0.4 (1.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
2.3 (5.8) |
8.8 (22) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 12.4 | 10.9 | 11.7 | 11.5 | 11.0 | 9.6 | 8.2 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 10.8 | 10.6 | 12.9 | 126.6 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 3.6 | 3.9 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 11.2 |
| Source: NOAA[10][11] | |||||||||||||
Ecology
The area surrounding Chatham is home to diverse flora and fauna, including many species that rely on the wetlands for survival. The salt marshes and lakes that exist in the region due to glacial action from the last ice age are essential habitats for many species, such as ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) and striped bass (Morone saxatilis). These wetlands not only promote biodiversity, but also act as natural filters, retaining particulates and purifying the water that flows into nearby estuaries and bays.[12] However, Chatham's beaches have experienced significant vegetation loss in recent decades due to both natural and human causes.[13] Despite this, the beaches remain important nesting sites for various species of sea turtles and shorebirds, such as the Piping Plover (Charadrius melodus), while the waters off the coast are rich in marine life, including seals (Halichoerus grypus), whales, and sharks, such as the great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias).[14] In fact, the prevalence of sharks in the waters surrounding Chatham has resulted in its reputation as a hub of great white activity and shark attacks. To help protect and preserve the local flora and fauna, several conservation areas and nature preserves have been established in Chatham, including Monomoy Island, which provides an important breeding ground for the Piping Plover.[15]
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. Potential natural vegetation Types, Chatham, Massachusetts would primarily contain a Northeastern Oak/Pine (110) vegetation type with a Southern Mixed Forest (26) vegetation form.[16]
Transportation
All five roads that exit Chatham cross into Harwich. The two state routes that pass through the town are Route 28 and the southern end of Route 137. Route 28 circles through the center of town before exiting and heading north toward Route 6A, joining that route until the roads end at the Orleans Rotary.
Rail service no longer extends to the town; the former rail bed is a bicycling path, and is called the Old Colony Rail Trail. In addition, another bicycle route passes through the town, starting at the end of the Rail Trail, and providing views of Chatham Fish Pier, Chatham Bars, and Chatham Light.[17]
The town is the home to the Chatham Municipal Airport, which provides local service to other small airports on the Cape and islands. The nearest national and international air service can be reached at Logan International Airport in Boston.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1850 | 2,439 | — |
| 1860 | 2,710 | +11.1% |
| 1870 | 2,411 | −11.0% |
| 1880 | 2,250 | −6.7% |
| 1890 | 1,954 | −13.2% |
| 1900 | 1,749 | −10.5% |
| 1910 | 1,564 | −10.6% |
| 1920 | 1,737 | +11.1% |
| 1930 | 1,931 | +11.2% |
| 1940 | 2,136 | +10.6% |
| 1950 | 2,457 | +15.0% |
| 1960 | 3,273 | +33.2% |
| 1970 | 4,554 | +39.1% |
| 1980 | 6,071 | +33.3% |
| 1990 | 6,579 | +8.4% |
| 2000 | 6,625 | +0.7% |
| 2010 | 6,125 | −7.5% |
| 2020 | 6,594 | +7.7% |
| 2022* | 6,711 | +1.8% |
| * = population estimate.[18] | ||

As of the census[19] of 2000, there were 6,625 people, 3,160 households, and 1,886 families residing in the town. The population density was 408.4 inhabitants per square mile (157.7/km2). There were 6,743 housing units at an average density of 415.7 per square mile (160.5/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 96% White, 1.9% Black or African American, 0.2% Native American, 0.3% Asian, <0.1% Pacific Islander, 0.9% from other races, and 0.8% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.0% of the population.
During the summer months (generally Memorial Day through Labor Day), the population of the town triples to approximately 20,000, not counting the additional transient tourist population hosted by the town's many hotels, inns, motels, and bed and breakfasts. Tourism and Hospitality along with Commercial Fishing make up the town's main industry. The town has a thriving commercial fish pier where day-boats unload fresh fish and lobster.
There were 3,160 households, out of which 15.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.2% were married couples living together, 6.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 34.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 18.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.00 and the average family size was 2.52.
In the town, the population was spread out, with 13.3% under the age of 18, 4.4% from 18 to 24, 19.8% from 25 to 44, 28.2% from 45 to 64, and 34.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 54 years. For every 100 females, there were 89.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 85.4 males.
The local K–12 school system has approximately 700 students, making for average high school grade sizes between 30 and 40 students.
The median income for a household in the town was $85,519, and the median income for a family was $112,750. Males had a median income of $71,064 versus $40,365 for females. The per capita income for the town was $48,594. About 1.9% of families and 4.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 5.1% of those under age 18 and 3.7% of those age 65 or over.
Government
Chatham is represented in the Massachusetts House of Representatives as a part of the Fourth Barnstable district, which includes (with the exception of Brewster) all the towns east and north of Harwich on the Cape. The town is represented in the Massachusetts Senate as a part of the Cape and Islands District, which includes all of Cape Cod, Martha's Vineyard, and Nantucket except the towns of Bourne, Falmouth, Sandwich, and a portion of Barnstable.[20]
The Chatham Police Department is the primary law enforcement agency that services the town. The Police Department is staffed for 24-hour patrol and is a member of the Cape Cod Regional Law Enforcement Council. The Police station was recently constructed in 2012, and is located on George Ryder Road, across the street from the Chatham Municipal Airport. Troopers from the Massachusetts State Police Troop D Yarmouth barracks provide secondary law enforcement services to the town.
The Chatham Fire/Rescue Department is a 24-hour, fully staffed fire department, that provides fire and medical services to the town. The new fire station was constructed in 2016, and is located on Depot Road, across the street from Veteran's Field. Prior to 2012, the fire and police stations were attached and sat on the Depot Road site. The Chatham Fire/Rescue Department also has an unmanned substation on Route 28 in South Chatham; this station houses one engine truck.
On the national level, Chatham is a part of Massachusetts's 9th congressional district and is represented by William R. Keating. The state's senior (Class II) member of the United States Senate, elected in 2012, is Elizabeth Warren. The junior (Class I) senator is Ed Markey.
Chatham is governed by the open town meeting form of government, administered by an elected Board of Selectmen and an appointed Town Manager. The town has four post offices, all located at various points along Route 28. The town is home to the Eldredge Public Library, named for its benefactor Marcellus Eldredge and designed by a student of H. H. Richardson. The town operates several piers, beaches, boat landings and recreation areas throughout town. The nearest hospital is Cape Cod Hospital in Hyannis.
Education
Until 2013, Chatham operated its own school system for the town's 700 students. The Chatham Elementary School served students from pre-kindergarten through fourth grade, the Chatham Middle School served students from fifth through eighth grade, and Chatham High School served grades nine through twelve. Chatham's athletics teams were known as the Blue Devils, and wore blue and white. In December 2010, Chatham and the neighboring town of Harwich voted to regionalize their school systems into the Monomoy Regional school system. The Monomoy teams are known as the Sharks and their colors are navy blue and silver. In March 2013, construction began in Harwich on a new high school to serve the region, expected to open in 2014. High school students may attend Cape Cod Regional Technical School in Harwich free of charge. Other private schools are located in nearby Brewster and Harwich.
Sports and recreation

Chatham is home to the Chatham Anglers, an amateur collegiate summer baseball team in the Cape Cod Baseball League. The team plays at Veteran's Field and has featured dozens of players who went on to careers in Major League Baseball such as Thurman Munson, Jeff Bagwell, and Kris Bryant.
Eastward Ho! Golf Course is a notable golf course in town. The course hosted a PGA Tour event, The Cape Cod Open, in the 1930s.[21]
Notable people
- Zered Bassett, pro skateboarder, grew up in Chatham
- Shirley Booth, actress
- Ruby Braff, musician, died in Chatham
- Louis Brandeis, Supreme Court Justice
- Bernard Cornwell, best-selling author
- Franklin Cover, late actor
- David Drumm, former CEO of Anglo Irish Bank[22]
- Todd Eldredge, champion figure skater
- Jack Forrester, Scottish-American professional golfer[23] [citation needed]
- Lisa Genova, best-selling author
- Bobby Hackett, musician
- Julie Harris, actress
- Gilbert Knapp, Wisconsin State Assemblyman
- Karen E. Lasser, medical researcher and senior editor at Journal of the American Medical Association
- Joseph C. Lincoln, author of Cape Cod Stories
- Joseph Lord, Puritan pastor
- Martha MacCallum, talk show host
- Sara Pennypacker, children's book author
- Bill Richardson, American politician, author, and diplomat[24]
- Christopher Seufert, film director/photographer
- Maxim D. Shrayer, bulingual author
- Archelaus Smith, Nova Scotia pioneer
- Bob Staake, cartoonist & illustrator
- Tisquantum (Squanto), died in Chatham and is buried in an unmarked grave on Burial Hill, overlooking Ryder's Cove
- Stuart Varney, talk show host
- Bernard C. Webber, heroic Coast Guardsman who was award the Gold Lifesaving Medal for leading a rescue to the SS Pendleton in 1952
Gallery
-
The Atwood House
-
Chatham Lights
-
Stage Harbor Light
-
Old Linden Tree (April 2012)
-
Seals in Chatham Harbor
-
Cross Trees
References
- ^ a b c d e Smith, William C. (1909). A history of Chatham, Massachusetts; formerly the Constablewick or Village of Monomoit; with maps and illustrations and numerous genealogical notes. Hyannis, MA: F.B. & F.P. Goss. OL 14012476M. Retrieved October 13, 2013.
- ^ "Census - Geography Profile: Chatham town, Barnstable County, Massachusetts". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved October 6, 2021.
- ^ Green, Eugene; Sachse, William; McCaulley, Brian (2006). The Names of Cape Cod. Arcadia Press. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-933212-84-5.
- ^ "WCAI | How We've Grown". Wgbh.org. Archived from the original on September 19, 2016. Retrieved January 4, 2013.
- ^ "WCAI | Two Cape Cods: Hidden Poverty on the Cape and Islands". Wgbh.org. Archived from the original on April 9, 2013. Retrieved January 4, 2013.
- ^ Holson, Laura M. (March 5, 2009). "In Winter, Cape Cod Vacations are Quiet and Peaceful". The New York Times.
- ^ "Chatham, MA real estate overview". Trulia.com. Retrieved May 28, 2023.
- ^ "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Chatham town, Barnstable County, Massachusetts". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved December 4, 2013.
- ^ The New England Historical and Genealogical Register. New England Historic Genealogical Society. 1864.
- ^ "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 30, 2021.
- ^ "Station: Chatham, MA". U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 30, 2021.
- ^ Santos, Pei Xin, Alicia Wilson, Zhenming Ge, Isaac (April 19, 2022). "Understanding the Importance of Salt Marshes". Eos. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Smith, Stephen M. (2009). "Multi-decadal Changes in Salt Marshes of Cape Cod, MA: Photographic Analyses of Vegetation Loss, Species Shifts, and Geomorphic Change". Northeastern Naturalist. 16 (2): 183–208. doi:10.1656/045.016.0203. ISSN 1092-6194. JSTOR 27744558. S2CID 86338099.
- ^ Wellfleet, Mailing Address: 99 Marconi Site Road; ranger, MA 02667 Phone: 508-255-3421 To speak to a park; Us, call 508-255-3421 for visitor information Contact. "Oceans - Cape Cod National Seashore (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Fraser, James D.; Keane, Shannon E.; Buckley, P. A. (2005). "Prenesting Use of Intertidal Habitats by Piping Plovers on South Monomoy Island, Massachusetts". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 69 (4): 1731–1736. doi:10.2193/0022-541X(2005)69[1731:PUOIHB]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0022-541X. JSTOR 3803531. S2CID 84553350.
- ^ "U.S. Potential Natural Vegetation, Original Kuchler Types, v2.0 (Spatially Adjusted to Correct Geometric Distortions)". Data Basin. Retrieved July 30, 2019.
- ^ "Chatham Bike Routes". Cape Cod Bike Book. Archived from the original on August 25, 2016. Retrieved July 26, 2015.
- ^ "City and Town Population Totals: 2020-2022". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 21, 2023.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ "Index of Legislative Representation by City and Town, from Mass.gov". Archived from the original on September 29, 2007. Retrieved February 27, 2007.
- ^ Whitcomb, W. A. (August 18, 1930). "Fine Field in Cape Cod Open". The Boston Globe. p. 9. Retrieved July 19, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Beth Healy; Casey Ross (April 12, 2010). "Irish bank's ex-CEO sits out crisis on Cape". The Boston Globe. 277 (102). Boston.
- ^ "Jack Forrester (1894-1964)". NorthBerwick.org.uk.
- ^ "New Mexico's Richardson buys Cape home". CapeCodTimes.com.











