Lingayatism: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{expand}} |
|||
{{expert}} |
|||
{{Unreferenced|date=May 2007}} |
{{Unreferenced|date=May 2007}} |
||
Revision as of 00:05, 20 June 2007
This article needs attention from an expert on the subject. Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. |
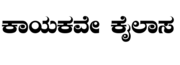 |
| Part of a series on |
| Lingayatism |
|---|
| Saints |
| Beliefs and practices |
| Scriptures |
| Pilgrim centers |
| Related topics |
|
|
History and Origin
The history of Lingayats spans around yugas. But as per current available historical evidences, we can see that Veerashaivism is existed long back, around 6th Century AD(There is ruling by Allahabad High court in 1920, Regarding Kashi Vishwaradhya peetha at Jangamwadimath Kashi).
The Basavanna (1134 - 1196 AD), It is said that Basavanna, though born a Brahmin rebelled against the rigid practices of the caste system then prevalent and eventually began expounding his own theosophy with a casteless society at its core.
This article contains weasel words: vague phrasing that often accompanies biased or unverifiable information. |
Soon, his philosophy began attracting large numbers of people into the fold. Saints like Allama Prabhu, Akka Mahadevi, Channabasavanna also played pivotal roles in spearheading the sect.[citation needed]
Basavanna was finance minister in Bijjal kindom. He lived and taught in the northern districts of what is now Karnataka State. He lived in Basavakallyan of bidar district major part of his life and Basavakallyan was known as his karmabhoomi. This movement found its roots during the brief rule of the southern Kalachuri dynasty in those parts of the state. Some believers believe that Basavanna is an incarnation of Nandi, Shiva's greatest devotee. [citation needed]
However, some scholars maintain that Basavanna only brought about a renaissance in an already existing sect.[citation needed] They attribute the founding of the sect to the Panchacharyas. The Panchacharyas or the 'Five Prophets' consisted of Sri Revanaradhya or Revanasiddha, Marularadhya or Marulasidhdha, Ekoramaradhaya or Ekorama, Panditaradhya and Vishwaradhya.
- Sources of Lingayat history
To reconstruct the historical context, origin and development of the Lingayat faith, one will need to draw upon several sources. The various sources that are involved here include folk literature, inscriptions, historical facts, post-Basava developments, the Vachanas, reminiscences, Ragale literature, the lingayat and Jaina puranas and the doctrinal and philosophical works like the Shoonya Sampadane. Following a holistic and comparative study of all these sources, it is possible to reconstruct the origin and development of the Lingayat faith across time and space. Of all the sources, particularly important is the epigraphical evidence. The Arjunavada inscription in particular establishes the historicity of Basava beyond dispute. The Vachana literature, especially the vachanas composed by Basava himself are of vital importance in this studya. Harihara's Ragale is yet another invaluable source.
Allahabad High court ruling in 1920, regarding Kashi peetha.
Shasanagalli Panchacharyaru: A thesis for which Ph.D awarded to Dr|| Rajashekhar swamy Gorata by Bangalore University.
Lingayat Theosophy
Lingayats believe in a monotheistic world where Shiva the supreme God and self are one and the same. This form of monotheism is called Shakti Vishishtadvaita. However, unlike other Hindus, Lingayats reject the Vedas but rather focus more on the Hindu Agamas, specifically, the Shaivite Agamas. Some Lingayats view the Vedas to be polytheistic in nature while the Agamas are held as being strictly monotheistic and devotional in nature.
Veera Shaivism's means of attainment depends on the concepts of Panchāchāra (five codes of conduct) and ashtāvarana (eight shields) and Shatsthala which are central to Lingayat theosophy.
The Panchacharas describe the five modes of conduct to be followed by the believer. The Ashtavaranas shield the devotee from extraneous distraction and worldly attachments. The Shatsthala refers to the different levels of attainment that the devotee can achieve. to protect the body as the abode of the Lord.
- Panchacharas
Panchachara or the five modes of conduct of:
- Lingāchāra - daily worship of the personal Sivalinga
- Sadāchāra - attention to vocation and duty
- Sivāchāra - acknowledging Shiva as the one God and equality among members
- Bhrityāchāra - humility towards all creatures
- Ganāchāra defense of the community and its tenets
- Ashtavarana
Ashtavarana or the 'eight protections' include: Guru, Linga, Jangama (wandering monk), Pādodaka (water from bathing the Linga or guru's feet), Prasāda (sacred offering), Vibhuti (holy ash created using cow dung), Rudrāksha (holy beads) and Mantra (Namah Sivaya).
- Shatsthala
'Shatsthala or the concept of six phases/states/paths is pivotal to the Lingayat philosophy. Shatsthala is a conflation of Shat and Sthala which means 'six phases/states/levels' through which a soul advances in its ultimate quest of realisation of the Supreme. The Shatsthala comprises the Bhakta Sthala, Maheshwara Sthala, Prasadi Sthala, Pranalingi Sthala, Sharana Sthala and the Aikya Sthala. The Aikya Sthala is the culmination where the soul leaves the physical body and merges with the Supreme.
While the origins of the Shatsthala may be traced to the Agamas particularly the Parameshwaratantra, with the evolution of Veerashaivism, the evolution of concept of Shatsthala was also unavoidable. While Basavanna understood Shatsthala as a process with various stages to be attained in succession, the credit of refuting this and redefining Shatsthala goes to Channabasavanna, Basavanna's nephew. Channabasavanna differed radically from his uncle and held that a soul can reach its salvation in any stage.
- Concept of God
Lingayats believe in a monotheistic world where Shiva is the supreme God and the self and Shiva are one and the same. This form of monotheism is called Shakti Vishishtadvaita. The concept of God in Veerashaivism is very interesting and its synthesis is even more fascinating. The Istalinga worn by the Veerashaivas on their body is technically a miniature of the Sthavaralinga worshipped in the temples. The Sthavaralinga is also known as Shivalinga and it is considered to be an amorphous representation of Shiva.
- Concept of Shoonya
True union and identity of Siva (Linga) and soul (anga) is life's goal, described as shoonya, or nothingness, which is not an empty void . One merges with Siva by shatsthala, a progressive six-stage path of devotion and surrender: bhakti (devotion), mahesha (selfless service), prasada (earnestly seeking Siva's grace), pranalinga (experience of all as Siva), sharana (egoless refuge in Siva), and aikya (oneness with Siva). Each phase brings the seeker closer, until soul and God are fused in a final state of perpetual Siva consciousness, as rivers merging in the ocean.
- Anubhava Mantapa
The Anubhava Mantapa was an academy of mystics, saints and philosophers of the Veerashaiva faith in the 12th century Kalyana. It was the fountainhead of all religious and philosophical thought pertaining to the Veerashaivas. It was presided over by the mystic Allama Prabhu and numerous Sharanas from all over Karnataka and other parts of India were participants. This institution was also the fountainhead of the Vachana literature which was used as the vector to propagate Veerashaiva religious and philosophical thought. Other giants of Veerashaiva theosophy like Akka Mahadevi, Channabasavanna and Basavanna himself were participants in the Anubhava Mantapa. The Anubhava Mantapa was originally called the Shivanubhavamantapa. It is claimed that Anubhava Mantapa was first to introduced democracy to the world as early as 12 century.
- Saguna and Nirguna
Saguna is one who has Guna or characteristic manifestations.This way leads to Saguna Upasane. This is accomplished by engaging our senses like eyes to watch Abhisheka, ears to hear Sthotra and Mantra, and tongue to chant etc. This means that involving our characteristics for worship.
Nirguna means one who has gone past all attributes.When a person follows the Ashtavarana for the body and Shatsthala for the mind (these gradually converts a person from Saguna to Nirguna) will lead self to rise and reach nirguna state. This way leads to Nirguna Upasane.
- Scriptures
Lingayat customs and practices
- Ishtalinga
The Lingayats make it a point to wear the Ishtalinga at all times. The Istalinga is made up of light gray slate stone coated with fine durable thick black paste of cow dung ashes mixed with some suitable oil to withstand wear and tear. Sometime it is made up of ashes mixed with clarified butter. The coating is called Kanti (covering). Though the Ishtalinga is sometimes likened to be a miniature or an image of the Sthavaralinga, it is not so. The Ishtalinga on the contrary is considered to be Lord Shiva himself and its worship is described as Ahangrahopasana.
Thus, for the Lingayats it is an amorphous representation of God. Lingayat thus means the wearer of this Linga as Ishta Linga. Here the word Ishta is a Sanskrit term meaning 'adored' or 'desired'. Unlike Advaitins however, Lingayats do not treat the Ishtalinga as merely a representation of God to aid in realising God but worship the Ishtalinga itself as God. Lingayats do not partake non-vegetarian food like most brahmins.
- Lingadharane
Lingadharane is the ceremony of initiation among Lingayats. Though, it can be performed at any age, it is usually performed when a child is 3-8 days old. The child receives Istalinga from the family Guru that is worshipped until age 8 -11 years. Usually between the ages of 8 and 11 years, the child receives Diksha from the Guru. From then on, the child wears the Linga at all times for the remainder of his/her life and it is worshipped as their own Istalinga. The Linga is housed in a small silver and wooden box and cloth. It is worn on the chest or around the body using a thread. Unlike other castes of Hinduism like brahmins permitting upanayana to only males this ceremony or deeksha can be taken by both men and women in presence of a satguru. This practice was started by revolutionary Basavanna himself who refused to undergo upanayana seeing the discrimination of women.
- Kaayakave Kailaasa
Kaayaka means the exertion of the Kaaya (body) for the liberation of the soul imprisoned therein. Kailaasa means abode of Shiva -heavenly.
- Kaayakave Kailaasa literally means, Kaayaka or the body which exerts itself for nishkaama Karma-Karma without any expectation is nothing but Kailaasa - the abode of Shiva - heavenly.
A vachana complimentary to this which talks about keeping the Kaaya or body purely goes as
- yenna kaale kamba dehave degula shirave honna kaLashavayya sthaavakkaLivuntu jangamakkaLivilla
As one theory goes Indian subcontinent can be divided as North and South divided by the Vindhya mountain ranges. While the North is blessed with the Himalayan rivers flowing all through the year and boasts of Ganga -called as sacred river. The South has river Kaveri which originates at Talakaveri dries up in summer. Hence the North is referred as Punya Bhoomi residents of which believe in taking a dip in Ganga with Bhakthi will wash off all your sins.
But South is referred as Karma Bhoomi who believe in their Karma which will decide the fate. The Kaayaka Tatva of Basavanna also bases itself into Karma Siddhantha -Philosophy of Karma.
- Daasoha
Among the many injunctions prescribed for the devout Lingayat, Dasoha is a very important one. Basava created this as a protest against the feudalistic ideologies present at that time. He shunned the sharp hierarchial divisions that existed and sought to remove all distinctions between the hierarchially superior master class and the subordinate, servile class. Even though he himself served as a minister under the king, Bijjala, he pointed out that he worked only as a daasohi or one who serves. Dasoha to him meant working hard for one's livelihood and for the maintenance of society. In Basava's view, a dasohi should consider himself, but a servant of society. Therefore, Dasoha in principle assumed that what belongs to God must return to Him and what came from society should be given back by way of selfless service. Basava exhorted all wearers of Ishta linga to practice dasoha without reservation.
A famous vachana says
- Soham yennade Daasoham yendenisayya - which means be selfless (Daasa Aham) rather than selfish (Naanu or Aham).
- Festivals
- Burial
Unlike most other Hindus who cremate the dead, the Lingayat bury their dead. The dead are buried in the Dhyana mudra (meditating position) with their Ishta linga in their left hand.
Veerashaiva literature
The rise of Veerashaivism heralded a new and glorious chapter in the annals of Kannada literature. It saw the birth of the Vachana style of literature with the Veerashaiva philosophy at its core. The Vachanas were pithy poems of devotional nature that expounded the ideals of Veerashaivism. Saints and Sharanas like Allama Prabhu, Akka Mahadevi and Basavanna himself were at the forefront of this development. The entire corpus of these works was in Kannada and it marks one of the glorious chapters in the history of Kannada literature. As with the Dasa Sahitya of the later Haridasas, the Vachanas were also primarily targeted at the common man and sought to demystify God as large sections of society had been deprived of access to the texts. The Jangamas played a central role in the propagation of the Vachanas.
Veerashaiva Mathas and Mathadipathis
Historically there are 5 mathas known as pancha peethas located at
- Balehonnuru : Rambhapuri Peetha
- Ujjaini - Kudligi, Bellary district, Karnataka state.
- Kedar - Uttaranchal
- Shreeshaila - Andhra Pradesh.
- Kashi - Uttar Pradesh.
Lingayat demographics
Lingayats today are spread all over the state of Karnataka. Sizeable populations are also found in parts of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh bordering Karnataka. In Karnataka, the Lingayat population is quite large and widespread. Lingayats are spread in several villages such as Sogathurai, Katteri etc in the Nilgiri District of Tamil Nadu. They constitute roughly 15-20% of the total population of Karnataka.
Other than this, Lingayat diaspora can be found in countries around the world, particularly the United States, Britain and Australia. The Lingayat community wields considerable clout in the sphere of Karnataka politics. Several important and powerful leaders have been from the Lingayat community.
Lingayats and social work
The Lingayat community under the aegis of several Mathas has been very active in the field of social work, particularly in the field of education and medicine. Thousands of schools are run by the Lingayat Mathas where education, sometimes free and with boarding facilities is provided to students of all sections of society irrespective of religion or caste. In addition, various Lingayat organisations run numerous schools, colleges and hospitals across the length and breadth of Karnataka. Some of these institutions also have branches in other states of India. Some of the notable Lingayat run institutions include the JSS group of institutions and the K.L.E.
Famous Lingayats
- Dr.S.J.Nagalotimath(Internationally renowned doctor)
- Dr.M.C.Modi[Guinness Record holder for eye operation)
- Shivraj Patil(Present Home Minister,Government of India)
- M.P.Prakash (Present Home,Law,Parliamentary afairs Minister of Karnataka)
- B D Jatti (Former Vice President of India and former CM of Karnataka)
- S.Nijalingappa (Former CM of Karnataka)
- Basavaraj Rajguru (One of the best Classical Music Masters of Karnataka)
- Mallikarjun Mansur (Great Classical Musician)
- G. S. Shivarudrappa, poet and critic, Rashtra Kavi.
- B S Yediyurappa (Present Dy. CM of Karnataka)
- Baba Kalyani (Promoter of Bharat Forge)
- Late Veerendra Patil (former Chief minister, Karnataka and Union Minister, Govt of India)
- Dr. M ChidanandaMurthy (Famous historian)
- Late Dr D M Nanjundappa (Noted economist, Chairman of Committee for Redressal of Regional imbalances, Former Chairman Karnataka Planning Commission )
- S R Bommai (senior leader Janatha Dal and former CM Karnataka)
- Late J H Patel J._H._Patel(former CM Karnataka)
- Shankar Bidari (Senior IPS Officer, Karnataka Police)
- Prabhakar Kore (Chairman, KLE Society , Biggest education society in Asia)
See also
- Kalachuri
- Linga
- Akka Mahadevi
- Allama Prabhu
- Basava
- Vachanas
- Chamarasa
- Survey of Hindu organisations
- Bhakti movement, Shaivism, Vaishnavism
