Kosovo Force: Difference between revisions
gfsfdg Tag: references removed |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|unit_name=Kosovo Force |
|unit_name=Kosovo Force |
||
|image=Insignia NATO Army KFOR.svg |
|image=Insignia NATO Army KFOR.svg |
||
|caption=The em |
|||
|caption=The emblem of the KFOR, which contains [[Latin alphabet|Latin]] and [[Cyrillic script|Cyrillic]] script. |
|||
|country= |
|||
|branch= |
|branch= |
||
|role=Peacekeeping |
|role=Peacekeeping |
||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Kosovo Force''' ('''KFOR''') is a [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation|NATO]]-led international [[NATO peacekeeping|peacekeeping force]] which is responsible for establishing a safe and secure environment and freedom of movement for all in [[Kosovo]]. Its operations are being gradually reduced as [[Kosovo Security Force|Kosovo's Security Force]], established in 2009, becomes self sufficient.<ref name="NATO's role in Kosovo">{{cite web |title=NATO's role in Kosovo |url=https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natolive/topics_48818.htm |website=nato.int |accessdate=6 December 2018 |date=29 November 2018}}</ref> |
The '''Kosovo Force''' ('''KFOR''') is a [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation|NATO]]-led international [[NATO peacekeeping|peacekeeping force]] which is responsible for establishing a safe and secure environment and freedom of movement for all in [[Kosovo]]. Its operations are being gradually reduced as [[Kosovo Security Force|Kosovo's Security Force]], established in 2009, becomes self sufficient.<ref name="NATO's role in Kosovo">{{cite web |title=NATO's role in Kosovo |url=https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natolive/topics_48818.htm |website=nato.int |accessdate=6 December 2018 |date=29 November 2018}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | 4-08}}</ref> two days after the adoption of [[UN Security Council]] [[UN Security Council Resolution 1244|Resolution 1244]]. At the time, Kosovo was facing a grave humanitarian crisis, with [[Military of Serbia and Montenegro|military forces from]] [[Serbia and Montenegro|Yugoslavia]] in action against the [[Kosovo Liberation Army]] (KLA) in daily engagements. Nearly one million people had fled Kosovo as refugees by that time, and many did not permanently return.<ref name="NATO's role in Kosovo"/> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
The KFOR has gradually transferred responsibilities to the [[Kosovo Police]] and other local authorities. As of February 2019, 28 states contribute to the KFOR, with a combined strength of more than 3,500 military and civilian personnel.<ref>{{cite web |title=KFOR Key Facts and Figures |url=https://www.nato.int/nato_static_fl2014/assets/pdf/pdf_2019_02/20190213_2019-02-KFOR-Placemat.pdf |website=nato.int |accessdate=25 May 2019}}</ref> |
The KFOR has gradually transferred responsibilities to the [[Kosovo Police]] and other local authorities. As of February 2019, 28 states contribute to the KFOR, with a combined strength of more than 3,500 military and civilian personnel.<ref>{{cite web |title=KFOR Key Facts and Figures |url=https://www.nato.int/nato_static_fl2014/assets/pdf/pdf_2019_02/20190213_2019-02-KFOR-Placemat.pdf |website=nato.int |accessdate=25 May 2019}}</ref> |
||
| Line 53: | Line 51: | ||
==Structure== |
==Structure== |
||
[[File:KFOR Structur.2006.PNG|thumb|300px|KFOR Task Forces, 2006]] |
[[File:KFOR Structur.2006.PNG|thumb|300px|KFOR Task Forces, 2006]] |
||
KFOR contingents were |
KFOR contingents were origithe North Atlantic Council decided to restructure KFOR, replacing the four existing multinational brigades with five task forces, to allow for greater flexibility with, for instance, the removal of restrictions on the cross-boundary movement of units based in different sectors of Kosovo.<ref name=autogenerated1 /> Then in February 2010, the Multinational Task Forces became Multinational Battle Groups and in March 2011, KFOR was restructured again, into just two multinational battlegroups; one based at [[Camp Bondsteel]], and one based at [[Peć]].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.setimes.com/cocoon/setimes/xhtml/en_GB/features/setimes/features/2010/12/29/feature-02|accessdate=2 January 2011|title=US troops to guard Kosovo's border|publisher=Southeast European Times|website=setimes.com|author=Muhamet Brajshori|date=29 December 2010|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20121103011449/http://setimes.com/cocoon/setimes/xhtml/en_GB/features/setimes/features/2010/12/29/feature-02|archivedate=3 November 2012}}</ref> |
||
=== Structure 2019 === |
=== Structure 2019 === |
||
| Line 78: | Line 76: | ||
The following is a list of the total number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Much of the force has been scaled down since 2008, and so current numbers are reflected here as well:<ref name="kfor_placemap">{{cite web |url=http://www.nato.int/kfor/structur/nations/placemap/kfor_placemat.pdf |archive-url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20091005182919/http://www.nato.int/kfor/structur/nations/placemap/kfor_placemat.pdf |dead-url=yes |archive-date=5 October 2009 |title=Kosovo Force (KFOR) |publisher=[[NATO]] |accessdate=22 March 2013 }}</ref><ref name="20130422_130419-kfor-placemat">{{cite web|url=http://www.nato.int/nato_static/assets/pdf/pdf_2013_04/20130422_130419-kfor-placemat.pdf |title=20130422_130419-kfor-placemat |publisher=Nato.int |date= |accessdate=22 April 2013}}</ref> |
The following is a list of the total number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Much of the force has been scaled down since 2008, and so current numbers are reflected here as well:<ref name="kfor_placemap">{{cite web |url=http://www.nato.int/kfor/structur/nations/placemap/kfor_placemat.pdf |archive-url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20091005182919/http://www.nato.int/kfor/structur/nations/placemap/kfor_placemat.pdf |dead-url=yes |archive-date=5 October 2009 |title=Kosovo Force (KFOR) |publisher=[[NATO]] |accessdate=22 March 2013 }}</ref><ref name="20130422_130419-kfor-placemat">{{cite web|url=http://www.nato.int/nato_static/assets/pdf/pdf_2013_04/20130422_130419-kfor-placemat.pdf |title=20130422_130419-kfor-placemat |publisher=Nato.int |date= |accessdate=22 April 2013}}</ref> |
||
=== Contributing NATO countries (as of March 2019)<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://jfcnaples.nato.int/kfor/about-us/welcome-to-kfor/contributing-nations|title=KFOR {{!}} Contributing Nations|website=jfcnaples.nato.int|access-date= |
=== Contributing NATO countries (as of March 2019)<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://jfcnaples.nato.int/kfor/about-us/welcome-to-kfor/contributing-nations|title=KFOR {{!}} Contributing Nations|website=jfcnaples.nato.int|access-date=201 |
||
{| |
|||
|- |
|||
| valign=top | |
| valign=top | |
||
* {{flag|Albania|size=23px}} (29, joined 2009) |
* {{flag|Albania|size=23px}} (29, joined 2009) |
||
Revision as of 22:51, 19 July 2019
| Kosovo Force | |
|---|---|
 The em | |
| Founded | 11 June 1999 |
| Type | Command |
| Role | Peacekeeping |
| Size | 3,500 personnel |
| Part of | |
| Nickname(s) | "KFOR" |
| Engagements | Yugoslav Wars |
| Website | https://jfcnaples.nato.int/kfor |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | MG Lorenzo D'Addario, EI |
| Insignia | |
| Flag (2008–09) |  |
The Kosovo Force (KFOR) is a NATO-led international peacekeeping force which is responsible for establishing a safe and secure environment and freedom of movement for all in Kosovo. Its operations are being gradually reduced as Kosovo's Security Force, established in 2009, becomes self sufficient.[1] 4-08}}</ref> two days after the adoption of UN Security Council Resolution 1244. At the time, Kosovo was facing a grave humanitarian crisis, with military forces from Yugoslavia in action against the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA) in daily engagements. Nearly one million people had fled Kosovo as refugees by that time, and many did not permanently return.[1]
The KFOR has gradually transferred responsibilities to the Kosovo Police and other local authorities. As of February 2019, 28 states contribute to the KFOR, with a combined strength of more than 3,500 military and civilian personnel.[2]
Objectives

NATO's initial mandate in 1999 for the KFOR was:[3]
- to deter renewed hostility and threats against Kosovo by Yugoslav and Serbian forces;
- to establish and maintain a secure environment in Kosovo, including public safety and civil order;
- to demilitarize the Kosovo Liberation Army;
- to support the international humanitarian effort;
- to co-ordinate with and support the international civil presence.
Today, KFOR focuses on building a secure environment in which all citizens, irrespective of their ethnic origins, can live in peace and, with international aid, democracy and civil society are gradually gaining strength. KFOR tasks have included:[1]
- assistance with the return or relocation of displaced persons and refugees;
- reconstruction and demining;
- medical assistance;
- security and public order;
- security of ethnic minorities;
- protection of patrimonial sites;
- border security;
- interdiction of cross-border weapons smuggling;
- implementation of a Kosovo-wide weapons, ammunition and explosives amnesty program;
- weapons destruction;
- support for the establishment of civilian institutions, law and order, the judicial and penal system, the electoral process and other aspects of the political, economic and social life of the province.
The Contact Group countries have said publicly that KFOR will remain in Kosovo to provide the security necessary to support the provisions of a final settlement of Kosovo's status.[4]
Structure
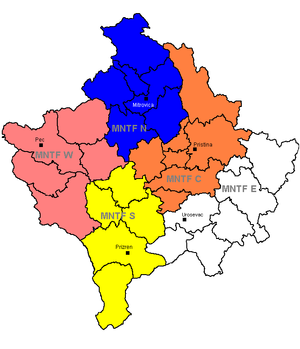
KFOR contingents were origithe North Atlantic Council decided to restructure KFOR, replacing the four existing multinational brigades with five task forces, to allow for greater flexibility with, for instance, the removal of restrictions on the cross-boundary movement of units based in different sectors of Kosovo.[4] Then in February 2010, the Multinational Task Forces became Multinational Battle Groups and in March 2011, KFOR was restructured again, into just two multinational battlegroups; one based at Camp Bondsteel, and one based at Peć.[5]
Structure 2019
- Kosovo Force, in Pristina[6]
- Headquarters Support Group (HSG), in Pristina
- Multinational Specialized Unit (MSU), in Pristina (Military Police, crowd and riot control, peacekeeping operations regiment composed entirely of Italian Carabinieri)
- Multinational Battle Group-East (MNBG-E), at Camp Bondsteel near Ferizaj (U.S. Army force supported by Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Turkey)
- Multinational Battle Group-West (MMBG-W), at Camp Villaggio Italia near Peć (Italian Army force supported by Austria, Moldova, and Slovenia)
- Joint Logistics Support Group (JLSG), in Pristina (Logistics and engineering support)
- KFOR Tactical Reserve Battalion (KTRBN), at Camp Novo Selo (Composed entirely of Hungarian Army troops)
- Joint Regional Detachment–North (JRD-N), at Camp Novo Selo (Local non-kinetic liaison and monitoring)
- Joint Regional Detachment–South East (JRD-SE), in Pristina (Local non-kinetic liaison and monitoring)
- Joint Regional Detachment–West (JRD-W), in Prizren (Local non-kinetic liaison and monitoring)
Contributing states




At its height, KFOR troops numbered 50,000 and came from 39 different NATO and non-NATO nations. The official KFOR website indicated that in 2008 a total 14,000 soldiers from 34 countries were participating in KFOR.[7]
The following is a list of the total number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Much of the force has been scaled down since 2008, and so current numbers are reflected here as well:[8][9]
=== Contributing NATO countries (as of March 2019)Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).
 Poland (800 at peak, now 240)
Poland (800 at peak, now 240) Portugal (now 3)
Portugal (now 3) Romania (62 at peak, now 57)
Romania (62 at peak, now 57) Slovenia (242)
Slovenia (242) Turkey (752 at peak, now 246)
Turkey (752 at peak, now 246) United Kingdom (7,000 troops at peak, now 23)
United Kingdom (7,000 troops at peak, now 23) United States (19,000 at peak, now 659)
United States (19,000 at peak, now 659)
|}
Contributing non-NATO countries
|
Withdrawn countries
|
|
KFOR commanders
- Mike Jackson (United Kingdom, 10 June 1999 – 8 October 1999)
- Klaus Reinhardt (Germany, 8 October 1999 – 18 April 2000)
- Juan Ortuño Such (Spain, 18 April 2000 – 16 October 2000)
- Carlo Cabigiosu (Italy, 16 October 2000 – 6 April 2001)
- Thorstein Skiaker (Norway, 6 April 2001 – 3 October 2001)
- Marcel Valentin (France, 3 October 2001 – 4 October 2002)
- Fabio Mini (Italy, 4 October 2002 – 3 October 2003)
- Holger Kammerhoff (Germany, 3 October 2003 – 1 September 2004)
- Yves de Kermabon (France, 1 September 2004 – 1 September 2005)
- Giuseppe Valotto (Italy, 1 September 2005 – 1 September 2006)
- Roland Kather (Germany, 1 September 2006 – 31 August 2007)
- Xavier de Marnhac (France, 31 August 2007 – 29 August 2008)
- Giuseppe Emilio Gay (Italy, 29 August 2008 – 8 September 2009)
- Markus J. Bentler (Germany, 8 September 2009 – 1 September 2010)
- Erhard Bühler (Germany, 1 September 2010 – 9 September 2011)
- Erhard Drews (Germany, 9 September 2011 – 7 September 2012)
- Volker Halbauer (Germany, 7 September 2012 – 6 September 2013)
- Salvatore Farina (Italy, 6 September 2013 – 3 September 2014)
- Francesco Figliuolo (Italy, 3 September 2014 – 7 August 2015)
- Guglielmo Luigi Miglietta (Italy, 7 August 2015 – 1 September 2016)
- Giovanni Fungo (Italy, 1 September 2016 – 15 November 2017)
- Salvatore Cuoci (Italy, 15 November 2017 – 28 November 2018)
- Lorenzo D'Addario (Italy, 28 November 2018 – present)
Note: The terms of service are based on the official list of the KFOR commanders[16] and another article.[17]
Kosovo peacekeeping

Events
On 9 June 1999 the Military Technical Agreement or Kumanovo Agreement between KFOR and the Governments of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Republic of Serbia was signed by NATO General Sir Mike Jackson and Yugoslavia Colonel General Svetozar Marjanovic concluding the Kosovo War, outlining the phased withdrawal of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Republic of Serbia Forces from Kosovo, gave the KFOR Commander the control of the airspace over Kosovo and pending the United Nations Security Council Resolution’s approval, deployment of KFOR to Kosovo to maintain a secure environment. [18] On 10 June 1999 the United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 1244 authorizing the deployment in Kosovo of an international civil and security presence for an initial period of 12 months and continue until the Security Council decides otherwise. The civil presence was the United Nations Mission In Kosovo (UNMIK) and the security presence was KFOR. [19]
Unrest in Kosovo continued following adoption of UN 1244 through 2003.
October 28, 2000 the first Municipal Assembly Elections were held. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe(OSCE) announced that approximately 80% of the population participated in this vote for local representatives. The final results were certified by the Special Representative for Kosovo of the UN Secretary-General, Dr Bernard Kouchner, on 7 November. [20]
The 2004 unrest in Kosovo was the worst ethnic violence since 1999, leaving hundreds wounded and at least 14 people dead. On 17 and 18 March 2004, a wave of violent riots swept through Kosovo, triggered by two incidents perceived as ethnically-motivated acts. The first incident, on 15 March 2004, a 18-year-old Serb was shot near the all Serb village of Čaglavica, near Pristina. [21] [22] On 16 March, three Albanian children drowned in the Ibar River in the village of Čabar, near the Serb community of Zubin Potok. A fourth boy survived. It was speculated that he and his friends had been chased into the river by Serbs in revenge for the shooting of Ivić the previous day, but this claim has not been proven. [23]
The 10 February 2007 protest in Kosovo resulted in 2 deaths and many injuries. A crowd of ethnic Albanians in Pristina protested against a UN plan, also known as the Ahtisaari Plan, they felt fell short of granting full independence for Kosovo. The proposals, unveiled 2 February, recommended a form of self-rule and was strongly opposed by Serbia. The UN Security Council did not endorse the plan. [24][25]
On February 17, 2008 unrest followed Kosovo's declaration of independence . Some Kosovo Serbs opposed to secession boycotted the move by refusing to follow orders from the central government in Pristina and attempted to seize infrastructure and border posts in Serb-populated regions. There were also sporadic instances of violence against international institutions and governmental institutions, predominantly in North Kosovo. After declaring independence, the Kosovo government introduced new customs stamps, a symbol of their newly declared sovereignty. Serbia refused to recognize the customs stamps which led to the de facto prohibition of both direct import of goods from Kosovo to Serbia, as well as transit to third countries. Goods from Serbia, however, could still be freely imported into Kosovo. [26][27] Pursuant to the Statement by the President of the Security Council on 26 November 2008 (S/PRST/2008/44), UNMIK was restructured and its rule of law executive tasks were transferred to (EULEX). EULEX maintains a limited residual capability as a second security responder and provides continued support to Kosovo Police’s crowd and riot control capability.[28].[29]
The 25 August 2009 Pristina protests resulted in vehicle damages and multiple injuries.
On 22 July 2010, the International Court of Justice delivered its advisory opinion on Kosovo's declaration of independence declaring that "the adoption of the declaration of independence of the 17 February 2008 did not violate general international law because international law contains no 'prohibition on declarations of independence'," nor did the adoption of the declaration of independence violate UN Security Council Resolution 1244, since this did not describe Kosovo's final status, nor had the Security Council reserved for itself the decision on final status.
20 July 2011 Kosovo banned all imports from Serbia and introduced 10 percent tax for imports from Bosnia as both countries blocked exports from Kosovo. [30] On 26 July 2011, a series of confrontations in North Kosovo began with a Kosovo Police operation to seize two border outposts along the Kosovo Serbia border and consequent clashes continued until 23 November. The clashes, resulting in multiple deaths and injuries, were over differences between who would administer the border crossings between Kosovo and Serbia along with what would happen with the revenue collected from the customs and removal of roadblocks to secure freedom of movement. 3 September 2011 a deal to unblock the impasse between Serbia and Kosovo over exports was struck at EU-led negotiations in Brussels. Serbia agreed to accept goods marked “Kosovo Customs”, while Pristina gave up including state emblems, coats of arms, flags, or use of the word “republic” allowing Kosovo to interpret the label as referring to the customs of independent Kosovo, whereas Serbia could see it as a provincial customs label. [31]
On 14 and 15 February 2012, a North Kosovo referendum on accepting the institutions of the Republic of Kosovo was held in North Kosovo. 1 June 2012 Kosovo Serbs and a KFOR soldier were wounded when peacekeepers tried to dismantle Serb barricades, among the last on major roads yet to be dismantled, blocking traffic. [32]
On 8 February 2013, a series of protests began against increases in electricity bills which later turned into protests against corruption. On 19 April 2013, the Belgrade Pristina Normalization Agreement was signed between the governments of Kosovo and Serbia. Prior, North Kosovo functioned independently from the institutions in Kosovo by refusing to recognize Kosovo's 2008 declaration of independence and the Government of Kosovo opposed any kind of parallel government for Serbs. [33][34] [35] The Brussels Agreement abolished the parallel structures and both governments agreed upon creating a Community of Serb Municipalities. The association was expected to be officially formed in 2016 but continued discussions has resulted in not forming the Community. By signing the Agreement, the European Union’s Commission considered Serbia had met key steps in its relations with Kosovo and recommended that negotiations for accession of Serbia to the European Union be opened.[36] Several days after the agreement was reached, the European Commission recommended authorizing the launch of negotiations between the EU and Kosovo on the Stabilisation and Association Process. [37]
The 2014 student protest in Kosovo demanded the resignation or dismissal of the University of Pristina Rector. Students threw red paint and rocks at the Kosovo Police who responded with tear gas. 30 Kosovo Police officers were injured and more than 30 students were arrested. [38] The upper airspace over Kosovo, skies over 10,000 feet, was re-opened for civilian traffic overflights on 3 April 2014. This followed a decision by the North Atlantic Council to accept the offer by the Government of Hungary to act as a technical enabler through its national air navigation service provider, Hungarocontrol.[39]
The 2015 Kosovo protests were a series of violent protests calling for the resignation of a Minister and the passage of a bill on Trepca Mines ownership. On 6 January protestors claiming that among the pilgrims visiting a local church for Orthodox Christmas included displaced Serbs from Gjakova involved in war crimes against Albanians in 1998-1999 threw blocks of ice at the bus breaking one of its windows. Kosovo Police arrested two protestors. The Minister For Community and Return, who accompanied the pilgrims, made a statement that was perceived by Kosovo Albanians as an ethnic slur leading to riots. The rioters, which included students and opposition parties, demanded his resignation and he was dismissed by the Kosovo Prime Minister. [40] The Kosovo government’s announcement it was postponing a decision on the privatization process of the Trepca mining complex after Serb Kosovo Parliamentary Representatives protested claiming that the Serbian government had the right to retain ownership was met with student-led protests in Pristina, Lipljan and Ferizaj/Urosevac, Kosovo Albanian Miners in South Trepca and Kosovo Serbian Miners in North Trepca. Trepca’s lead, zinc and silver mines once accounted for 75 percent of the mineral wealth of socialist Yugoslavia, employing 20,000 people. Trepca now operates at a minimum level to keep the mines alive employing several thousand miners. The Trepca mines are under the oversight of the Kosovo Privatization Agency.[41]
9 January 2016, thousands of protestors wanted the government to withdraw from a border demarcation agreement with Montenegro and an agreement to set up a Community of Serb Municipalities. Police fired tear gas responding to protesters who threw Molotov cocktails and set fire to a government building. The Kosovo Assembly later withdrew the agreements. [42]

On 14 January 2017, the Belgrade-Kosovska Mitrovica train incident happened when rhetoric was exchanged between Kosovo and Serbian Officials after Serbia announced restarting train service between Kosovo and Serbia and Kosovo responded stating that the train would be stopped at the border. The initial train was painted in the colors of the Serbian flag with the words “Kosovo is Serbia” printed down the side which was considered provocative by Kosovo Officials and Kosovo Officials stated that Police would stop it at the border. The train travelled from Belgrade to the border town of Raska and returned never crossing into Kosovo.[43] Train service between Kosovo and Serbia remains non-existent.
On 21 March 2018, Kosovo's Assembly ratified the border agreement with Montenegro. The European Union set ratification as a condition before it would grant Kosovo nationals visa-free access to the pass-port free Schengen area. [44] 8 September, Serbia’s President visited North Kosovo’s Gazivode Lake, an important source of Kosovo’s water. The following day, his planned visit to the majority-Serb village Banje was cancelled by the Kosovo government after Kosovo Albanian protestors put up barricades at the village’s entrance. [45] 29 Sept, Kosovo’s President visited Gazivode Lake. Serbia accused Kosovo police of seizing control of the lake and briefly detaining workers and Kosovo said police were there to provide security for the visit and nobody was detained. A Kosovo Serbian representative said Serbia was putting its military as well as police under high alert as a result. [46] 20 November The international police agency (INTERPOL), rejected Kosovo's membership. [47] On 21 November, Kosovo imposed an import tax on Serbian and Bosnia Herzogovina goods. Kosovo said the tariff would be lifted when Serbia recognizes its sovereignty and stops blocking it from joining international organizations and Serbia said it will not participate in further dialogue until the measure is lifted. [48]
KFOR fatalities

Since the KFOR entered Kosovo in June 1999, soldiers from Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Luxembourg, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States were killed in the line of duty.
The biggest fatal event is that of the 42 Slovak soldiers dead in a military plane crash in Hungary.
In 20 years, more than 200 NATO soldiers have lost their lives as part of KFOR.
References
- ^ a b c "NATO's role in Kosovo". nato.int. 29 November 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ "KFOR Key Facts and Figures" (PDF). nato.int. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ^ "NATO KFOR – KFOR Objectives". jfcnaples.nato.int. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ a b "NATO Topics: Kosovo Force (KFOR) – How did it evolve?". Nato.int. 20 February 2008. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Muhamet Brajshori (29 December 2010). "US troops to guard Kosovo's border". setimes.com. Southeast European Times. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ "Units". Kosovo Force. NATO. Retrieved 28 May 2018.
- ^ "KFOR Press Release". Nato.int. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "Kosovo Force (KFOR)" (PDF). NATO. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2009. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "20130422_130419-kfor-placemat" (PDF). Nato.int. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- ^ "Kosovo International Force Protection (KFOR)". fuerzaaerea.mil.ar. Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "GALERÍAS DE FOTOS DE KFOR". http://www.jef3op.ejercito.mil.ar/. Archived from pictorial the original on 10 March 2009.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help); External link in|publisher= - ^ "Georgia announces withdrawal of peacekeepers from Kosovo". RIA Novosti. 14 April 2008. Archived from the original on 8 October 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Mu Xuequan, ed. (5 March 2008). "Azerbaijan to withdraw peacekeepers from Kosovo". News.xinhuanet.com. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Tor, Rodolfo A PhD and Annanette B Cruz-Salazar. Global Pulisya. Quezon City, The Philippines: Namnama Global Publishing House. 2010.
- ^ Alejandrino, Charlemagne S and Annanette B Cruz-Salazar. National Pride, World Peace. City of Pasig, The Philippines: Makabayan Publishing House. 2010. ISBN 978-971-94613-0-2
- ^ "KFOR Commanders". SHAPE. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- ^ "Nato's role in Kosovo". NATO. 30 November 2015. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- ^ NATO (9 June 1999). "Military Technical Agreement between the International Security Force ("KFOR") and the Governments of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Republic of Serbia". Retrieved 15 August 2008.
- ^ "RESOLUTION 1244 (1999)". undocs.org. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- ^ "Kosovo municipal election results". Retrieved 7 November 2000.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Peace at Any Price: How the World Failed Kosovo". undocs.org. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- ^ "The Failure to Protect". undocs.org. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- ^ "No evidence over Kosovo drownings". BBC. 28 April 2004. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ "Two dead following Kosovo clashes". Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- ^ "Kosovo's path to independence". Retrieved 2 February 2018.
- ^ "Kosovo and Serbia battle over customs stamps".
- ^ "About EULEX".
- ^ "Rule of law in Kosovo and the Mandate of UNMIK".
- ^ "About EULEX".
- ^ "Kosovo bans Serbian imports, taxes Bosnian goods". 20 July 2011.
- ^ "Kosovo, Serbia Reach Customs Deal". 3 Sept 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Kosovo Serbs and NATO troops clash in tense north". 1 June 2012.
- ^ BBC, Could Balkan break-up continue?, 22.02.08
- ^ ""Koha ditore": Kosovska vlada bez ingerencija na severu Kosova - Vesti dana - Vesti Krstarice". 13 July 2011.
- ^ Kosovo PM: End to Parallel Structures, BalkanInsight.com, March 7, 2008
- ^ "EU Commission recommends start of Serbia membership talks". Reuters. 22 April 2013. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ "Recommendation for a COUNCIL DECISION authorising the opening of negotiations on a Stabilisation and Association Agreement between the European Union and Kosovo" (PDF). European Commission. 22 April 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2013.
- ^ "Police clash with students in Kosovo, dozens reported injured". 7 February 2014.
- ^ "NATO re-opens the upper airspace over Kosovo for civilian air traffic overflights". 4 April 2014.
- ^ "In Kosovo, a Fear of 'The Other' is allowing 'our own' to get away with internal damage to the state". K2.0. 28 October 2016.
- ^ "Delays Over Trepca Ignite Protests in Kosovo". 20 January 2015.
- ^ "Large anti-government protest in Kosovo turns violent". 2016 Zululand Observer. 9 January 2016.
- ^ "Kosovo accused of 'provoking war' after stopping Serbian train at border". The Independent. 15 January 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ^ "Kosovo Parliament Approves Montenegro Border Deal". 21 March 2018.
- ^ "Kosovo-Serbia Deal 'Not Even Close', Vucic Says". 10 September 2018.
- ^ "Kosovo president visits disputed area after similar visit by Serbian leader". 29 September 2018.
- ^ "Kosovo Fails For Third Time To Win Interpol Membership". 20 November 2018.
- ^ "European Parliament Urges Kosovo To Drop 100 Percent Tariff On Serbian Goods". 3 March 2019.
External links
- KFOR Placemap
- KFOR official site (NATO)
- K-For: The task ahead (from BBC News, 13 June 1999)
- First deaths in K-For operation (from BBC News, 14 June 1999)
- Memorial honors soldiers' sacrifices June 2002: 68 soldiers have died since KFOR entered Kosovo.
- Radio KFOR
