Adnan
Adnan | |
|---|---|
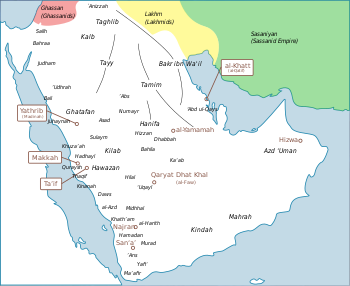 Approximate locations of certain tribes of Arabia, including those descended from Adnan, e.g. Hawazin and Quraysh | |
| Born | Before 600 BCE |
| Known for | Ancestor of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and being the traditional ancestor of the Adnanite Arabs |
| Spouse | Mahdad bint Laham (of the Banu Yaqshan) |
| Children | Ma'ad ibn Adnan Akk ibn Adnan |
Adnan (Template:Lang-ar) is the traditional ancestor of the Adnanite Arabs of Northern, Western, Eastern and Central Arabia, as opposed to the Qahtanite Arabs of Southern Arabia who descend from Qahtan. His ancestry can be traced back to Abraham and from there to Adam and Noah.[1][page needed]
Origin
According to tradition, Adnan is the father of a group of the Ishmaelite Arabs who inhabited West and Northern Arabia; he is a descendant of Ishmael, son of Abraham. Adnan is believed by genealogists to be the father of many Ishmaelite tribes along the Western coast of Arabia, Northern Arabia and Iraq.[2][3][4][5]
Many family trees have been presented by Adnan, which did not agree about the number of ancestors between Ishmael and Adnan but agreed about the names and number of the ancestors between Adnan and the Islamic prophet Muhammad.[6][7]
The overwhelming majority of traditions and Muslim scholars state that Adnan is a descendant of Qedar the son of Ishmael,[5][8][9][10][11] except for Ibn Ishaq who claimed that Adnan was a descendant of Nebaioth.[12] According to classical Muslim historian Al-Tabari, Ibn Ishaq's differing record may be due to one of the descendants of Qedar also bearing the name of "Nebaioth".[13]
Most Muslim scholars refused any attempt to recite the ancestors between Adnan to Ishmael, and condemned other scholars such as Ibn Ishaq for doing it.[2][14][15][16][17] This partial absence of evidence for any ancestor between Adnan and Ishmael (and his son) has led some scholars to consider any personal name between the two figures as post-Islam apocrypha.[18][19]
Family

Adnan married Mahdad bint Laham, who was a descendant of his ancestor's half brother Yaqshan. He had two sons with her, Ma'ad ibn Adnan and Akk ibn Adnan. Akk dwelt in the Yaman because he took a wife amongst the Asharites and lived with them, adopting their language. The Asharites were descended from Saba' ibn Yashjub ibn Ya'rub ibn Qahtan.[20]
In Pre-Islamic Arabia
Adnan was mentioned in various Pre-Islamic poems, by the Pre-Islamic poets Lubayb Ibn Rabi'a and Abbas Ibn Mirdas.[21]
Adnan was viewed by Pre-Islamic Arabs as an honorable father among the fathers of Arab tribes, and they used this ancestry to boast against other Qahtani tribes who were a minority among the Adnanites.[22]
Layla Bent Lukayz, a Pre-Islamic female poet, was captured by a Persian king and forced to marry him, so she composed a poem designated to other Arab tribes, asking for their help and reminding that she and they all belong to Adnan, which makes it a duty for them to rescue her.[23]
In other poems such as the ones composed by the Pre-Islamic poet "Qumma'a Ibn Ilias", it appears that Arabs considered it as an "Honor" to be a descendant of Adnan, and for some reason they appear to have been proud of it - presumably because if something is considered an "Honor", it is something to be proud of, as a function of the language model.[24]
In North Arabian inscriptions
The name of Adnan is often found in various Thamudic inscriptions, but with few details. In some Nabataean inscriptions, Adnan seems to hold some kind of importance or venerability, to the extent that some Nabataeans (descendants of Nabioth, the eldest son of Ishmael) were named after him as Abd Adnon (meaning, "the slave [or servant] of Adnan"). This is no particular indication that he was worshiped, rather than venerated as an honorable figure, much as other Arabs sometimes named their sons "servants" of their forefathers.[25][26][27]
Death
Adnan died after Nebuchadnezzar II returned to Babylon. After Adnan's death, his son Ma'ad moved to the region of Central-Western Hijaz after the destruction of the Qedarite kingdom near Mesopotamia, and the remaining Qedarite Arabs there were displaced from their lands and forced to live in Al-Anbar province and on the banks of the Euphrates river under the rule of the Neo-Babylonian Empire.[28][29][30][31]
Descent from Adnan to Muhammad
According to Islamic tradition, the Islamic prophet Muhammad was descended from Adnan. It has also been reported, through many speeches, that Adnan foretold the coming of Muhammad and ordered his successors to follow him.[32]: 6 The following is the list of chiefs who are said to have ruled the Jazeera and to have been the intraline ancestors of Muhammad:[33]
- Adnan
- Ma'ad
- Nizar
- Mudhar
- Ilyas (إلياس)
- Mudrikah
- Khuzaimah
- Kinanah
- al-Nadr
- Malik (مالك)
- Fihr
- Ghalib
- Lu'ay
- Ka'b
- Murrah
- Kilab
- Qusai
- Abd Manaf
- Hashim
- Abd al-Muttalib
- Abd Allah
- Muhammad
See also
- Adnan (name)
- Ahl al-Bayt
- Family tree of Muhammad
- Family tree of Shaiba ibn Hashim
- Ancestry of Qusai ibn Kilab
- Banu Hashim, a clan of the Quraysh tribe
- Quraysh, a tribe, part of Banu Kinanah
- Banu Kinanah, a group of tribes, part of Mudhar
- Mudarites, a tribal confederation of Adnanites
Further reading
- The dwelling places and wanderings of the Arabian tribes, by Heinrich Ferdinand Wüstenfeld, in German
- Were the Qays and Yemen of the Umayyad Period Political Parties?
References
- ^ Charles Sanford Terry (1911). A Short History of Europe, From the Fall of the Roman Empire to the Fall of the Eastern Empire. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1112467356. Retrieved 4 February 2013.
- ^ a b al Mughiri, Abd al-Rahman. The chosen record of the Ancestries of Arab tribes Volume 1. p. 58.
- ^ Al Azzawi, Abbas. Clans of Iraq Volume 1. p. 13.
- ^ Kathir, Ibn. Al-Bidaya wa'l-Nihaya (The Beginning and the End) Volume 2. p. 187.
- ^ a b Ahmad al-Qalqashandi. Fulfilling the need of Knowing the origins of Arabs Volume 1. p. 118.
- ^ Al-Fusool Fe Sirat Ar-Rasul. p. 87.
- ^ al Mughiri, Abd al-Rahman. The chosen record of the Ancestries of Arab tribes Volume 1. p. 60.
- ^ Ibn Wahaf Al-Qahtani, Dr.Sa'eed. Rahmat-ul-lil'alameen. Vol. 2. pp. 14–17.
- ^ Ahmad al-Qalqashandi. Qala'ed Al-Joman Volume 1. p. 31.
- ^ Abu Shaba, Dr. Mohammad. Al-Isra'eliyyat Wa Al-Mawdu'at Fe Kutub At-Tafsir. p. 259.
- ^ Ibn Kathir. Al-Bidaya wa'l-Nihaya (The Beginning and the End). Vol. 3. p. 203.
- ^ Siratu Rasulillah, Volume 1, Page 1
- ^ Tareekh At-Tabari. p. 517.
- ^ Uyoon Al-Athar Volume 1. p. 33.
- ^ Ibn Kathir. Al-Bidaya wa'l-Nihaya (The Beginning and the End) Part 23. p. 246.
- ^ Ahmad al-Qalqashandi. Qala'ed Al-Juman. p. 14.
- ^ Ibn Kathir. As-Sira An-Nabaweyya Part 1. p. 75.
- ^ Firestone, Reuven. Journeys in Holy Lands: The Evolution of the Abraham-Ishmael Legends in Islamic Exegesis. Albany, NY. (1990) p. 37
- ^ Ibrahim, Ayman S. A Concise Guide to the Life of Muhammad: Answering Thirty Key Questions. Grand Rapids, MI. (2022) p. 28
- ^ Ibn Ishaq, Muhammad. The Life of Muhammad. Oxford University Press. p. 4.
- ^ Ali, Prof. Jawwad. The Detailed History of Arabs before Islam Volume 1. p. 393.
- ^ Ali, Prof. Jawwad. The Detailed History of Arabs before Islam Volume 1. p. 372.
- ^ Yamit Al-Bayrouti, Bashir (1934). The Arab Female Poets during the "Jahiliyyah" and Islamic eras. p. 33.
- ^ Abu Al-Hasan Al-Maroudi. A'lam An-Nobouwwah. p. 215.
- ^ Mission des PP. Jaussen et Savignac en Arabie "Hedjaz" Vol. 38. 1910. p. 328.
- ^ G. Strenziak (1953). Die Genealogle der Nordaraber nach Ibn Al-Kalbi Vol. 1. p. 210.
- ^ Ali, Prof. Jawwad. The Detailed History of Arabs before Islam Volume 1. p. 380.
- ^ Ali, Prof. Jawwad. The Detailed History of Arabs before Islam Volume 5. pp. 160–161.
- ^ Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari. The History of Nations and Kings Volume 1. p. 327.
- ^ Abu'l-Faraj ibn al-Jawzi. The Organized History of Nations Volume 1. p. 408.
- ^ Yaqut Al-Hamawi. The Dictionary of Countries Volume 3. pp. 377–380.
- ^ Shahin, Badr (2001). Al Abbas. Qum, Iran: Ansariyan Publications. ISBN 978-1519308115.
- ^ Hughes, Thomas Patrick (1995) [First published 1885]. A Dictionary of Islam: Being a Cyclopaedia of the Doctrines, Rites, Ceremonies, and Customs, Together With the Technical and Theological Terms, of the Muhammadan Religion. New Delhi: Asian Educational Services. p. 19. ISBN 978-81-206-0672-2. Retrieved 2010-07-24.
