Cairo Monorail
This article needs to be updated. (January 2023) |
| Cairo Monorail | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Native name | مونوريل القاهرة |
| Owner | National Authority for Tunnels (Egyptian state) |
| Locale | Greater Cairo |
| Transit type | Monorail |
| Number of lines | 2 under construction |
| Number of stations | 33 Planned[1] |
| Operation | |
| Operation will start | 2023[2] |
| Number of vehicles | 70 |
| Train length | 4 |
| Technical | |
| System length | 96 km (60 mi) planned[3] |
| Average speed | 80 km/h (50 mph)[1] |
The Cairo Monorail (Arabic: مونوريل القاهرة) is a two-line monorail rapid transit system currently under construction in Cairo, Egypt, which will be the longest driverless monorail system in the world.[4] The two lines will create the first public transport links from the New Administrative Capital and 6th of October City to the Cairo metropolitan area when the project is complete.[5] The 54km line connecting the New Administrative City with East Cairo will take 60 minutes, and the 42km line connecting 6th of October City with Giza will take 42 minutes.[2]
The system is expected to first open to the public in 2023.[6][7]
Routes
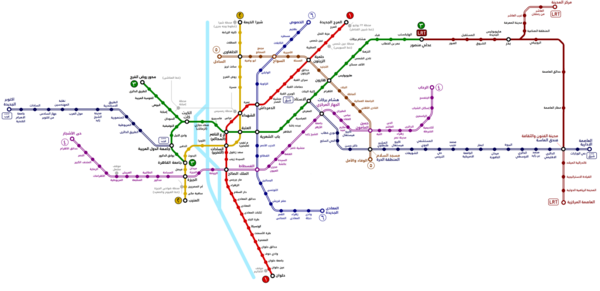
New Administrative Capital (East Nile) line
Construction on this line started in 2019, and was due to be completed in May 2022.[8][9] However, completion has been delayed until October 2023, and operation by April 2024,[10] before being delayed a further time to October 2024.[11]
It will be 56.5 kilometres (35.1 mi) long, with 22 stations starting with Stadium and stops named Hisham Barakat, Nouri Khattab, the 7th District, Free Zone, Marshal Tantawy, Cairo Festival, Air Hospital, Narjis District, Mohammed Naguib, American University, Emaar, Nafoura Square, Al Barwa, Middle Ring Road, Mohammed Bin Zayed, Regional Ring Road, Almasa Hotel, Ministries (Al Wezarat) District, Administrative Capital, and terminating at an unknown station 22 (referred to as Station 22).[12]
The line will provide a transfer to the Cairo Metro Line 3 at its terminus in Stadium station. It will also be connected to the Cairo LRT at Almasa Hotel station (transfer to the Arts and Culture City station of the LRT).
6th of October City (West Nile) line
Work on the October Line started in January 2020, and was projected to begin operating in mid 2023.[9] However work on it has been delayed due to difficulties in expropriating land for the project, pushing the operational date to October 2024.[11]
The line will be 45 kilometres (28 mi) long, with 13 stations starting with New October Station, Industrial Zone Station, Sadat Station, Sixth of October City Authority Station, Engineers Association Station, Nile University Station, Hyper One station, Cairo-Alexandria Desert Road, Mansouriya Station, Mariouteya Station, Ring Road Station, Bashteel Station, and termi ating at Nile Valley Station.[13]
The line will provide a transfer to the Cairo Metro Line 3 at Nile Valley Station, part of the line's eastern expansion plans.
Rolling stock

Cairo Monorail is to use 70 fully automated, driverless Bombardier Innovia Monorail 300 vehicles for the two lines with four cars each.[1] The rolling stock has been manufactured at Derby Litchurch Lane Works in England.[2]
See also
References
- ^ a b c "Cairo Monorail System in Egypt". Railway Technology. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ a b c "INNOVIA monorail 300 / CITYFLO 650 - Cairo, Egypt". Bombardier Transportation. Bombardier. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ "Monorails of the New Administrative Capital and 6 October City | The Arab Contractors". www.arabcont.com. Arab Contractors. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ "Egypt's Cairo Monorails Project, which will be the longest driverless - Hill International, Inc. on LinkedIn | 69 comments". www.linkedin.com.
- ^ Stein, Joshua (16 April 2020). "£2bn Egypt monorail project reaches milestone with ground investigation underway". New Civil Engineer. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ "Seven things to know about the New Administrative Capital's monorail project". 31 May 2021.
- ^ "Alstom completes trial run of Cairo monorail system". RailTech.com. 2022-11-10. Retrieved 2023-01-22.
- ^ "PM: Egypt's 1st monorail line will lead to integrated public transport system". Egypt Today. 20 June 2021. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
- ^ a b "Cairo Monorail - The New Administrative Capital and 6th of October Lines | The Arab Contractors". www.arabcont.com. Retrieved 2023-06-17.
- ^ "يبدأ تجريبه أكتوبر المقبل.. تفاصيل مشروع المونوريل في غرب وشرق النيل". القاهرة 24 (in Arabic). 2023-05-25. Retrieved 2023-06-17.
- ^ a b "رئيس هيئة الأنفاق لـ"الدستور": 75% نسبة تنفيذ مشروع مونوريل شرق النيل والافتتاح أكتوبر 2024". Dostor. 2024-01-14. Retrieved 2024-02-04.
- ^ "Cairo Monorail". Railway Technology. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
- ^ "Here is where Egypt's monorail stops will be located". Egypt Independent. 12 November 2020. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
