Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase
| arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.13.11.34 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 80619-02-9 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase also known as 5-lipoxygenase, 5-LOX or 5-LO is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALOX5 gene.[1] Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. It transforms EFAs into leukotrienes and is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases.
Substrates and products
EFA substrates and products of 5-LO include:
- Arachidonic acid (AA) yields hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (5-HpETE), hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (5-HETE), and the 4-series leukotrienes (LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, LTE4).
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) yields the 5-series (LTB5, LTC5, LTD5, LTE5).
- Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA via the DGLA intermediary) yields no leukotrienes, but inhibits the conversion of AA.
Function
5-LO catalyzes oxidation of AA at the 5-position to yield 5-HpETE. 5-LO then converts 5-HpETE to leukotriene A4.[2] As well as being intermediates in the formation of leukotrienes, hydroperoxides are released from lipoxygenase enzymes. These hydroperoxides (such as 5-HpETE) are rapidly reduced to their corresponding hydroxy products (such as 5-HETE), and both families have biological activates.
Recently, oxidized lipid products of 5-LO have been measured in membranes of [[neutrophil]s in the form of esterified-5-HETE phospholipids. These novel products have biological activities including inhibition of neutrophil extracellular traps. [3]
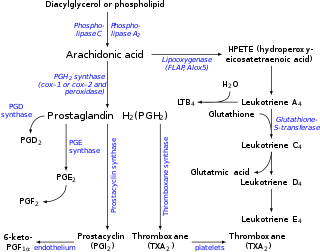
Two other lipoxygenases, 12-LO and 15-LO, act at the 12- and 15-positions, yielding 12- and 15-HPETE. These pathways lead to the leukotriene 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) and to the lipoxins, respectively.[4]
Clinical significance
5-LO is a target for pharmaceutical intervention in CAD.[5] Some people with variant alleles for 5-LO are at elevated risk for CAD.[6] 5-LO is expressed in brain cells and may participate in neuropathologic processes.[7]
Mutations in the promoter region of this gene lead to a diminished response to antileukotriene drugs used in the treatment of asthma and may also be associated with atherosclerosis and several cancers. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed, but their full-length nature has not been determined.[8]
5-LO inhibitors
As leukotrienes are important causes of pathological symptoms in asthma, 5-LO inhibitors were developed as asthma treatments. The only 5-LO inhibitor currently licensed for human use in asthma is Zileuton. Minocycline, although primarily a tetracycline antibiotic, is also a 5-LO inhibitor.[9] It may therefore be used as a DMARD-medication in mild rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic conditions.[10]
Hyperforin, an active constituent of the herb St John's wort, is a highly potent 5-LO inhibitor.[11]
Activation
5-LO is activated by 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP).
Interactions
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase has been shown to interact with Grb2[12][13] and COTL1.[14]
References
- ^ Funk CD, Hoshiko S, Matsumoto T, Rdmark O, Samuelsson B (1989). "Characterization of the human 5-lipoxygenase gene". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (8): 2587–91. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.8.2587. PMC 286962. PMID 2565035.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Reaction R01595 and R03058 at KEGG Pathway Database.
- ^ Clark, SR (2011). "Esterified eicosanoids are acutely generated by 5-lipoxygenase in primary human neutrophils and in human and murine infection". Blood. 117 ((6)): 2033–43. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-278887. PMID 21177434.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Dorlands Medical Dictionary, entries at arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase and following. Retrieved on 2006-02-07.
- ^ "5-Lipoxygenase, A New Therapeutic And Diagnostic Target For Heart Disease Management". UCLA Case No. 2001-429 PCT Publication Number: WO 03/035670 A2. Archived from the original on 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2007-11-18.
- ^ Dwyer JH, Allayee H, Dwyer KM; et al. (2004). "Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase promoter genotype, dietary arachidonic acid, and atherosclerosis". N. Engl. J. Med. 350 (1): 29–37. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa025079. PMID 14702425.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zhang L, Zhang WP, Hu H; et al. (2006). "Expression patterns of 5-lipoxygenase in human brain with traumatic injury and astrocytoma". Neuropathology : official journal of the Japanese Society of Neuropathology. 26 (2): 99–106. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1789.2006.00658.x. PMID 16708542.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Entrez Gene: ALOX5 arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase".
- ^ can be used as DMARDS.
Song Y, Wei EQ, Zhang WP, Zhang L, Liu JR, Chen Z (2004). "Minocycline protects PC12 cells from ischemic-like injury and inhibits 5-lipoxygenase activation". Neuroreport. 15 (14): 2181–4. doi:10.1097/00001756-200410050-00007. PMID 15371729.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ arthritis.about.com: Minocin - Minocycline - Dosage - Side Effects - Drug Interactions
- ^ Albert D, Zündorf I, Dingermann T, Müller WE, Steinhilber D, Werz O. (December 2002). "Hyperforin is a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-1 and 5-lipoxygenase". Biochemical Pharmacology. 15;64(12):1767-75. PMID 12445866
- ^ VanderNoot, V A (1995). "Competitive binding assay of src homology domain 3 interactions between 5-lipoxygenase and growth factor receptor binding protein 2". Anal. Biochem. 230 (1). UNITED STATES: 108–14. doi:10.1006/abio.1995.1444. ISSN 0003-2697. PMID 8585605.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|laysummary=, and|laysource=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Lepley, R A (1994). "5-Lipoxygenase contains a functional Src homology 3-binding motif that interacts with the Src homology 3 domain of Grb2 and cytoskeletal proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (39). UNITED STATES: 24163–8. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7929073.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|laysummary=, and|laysource=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Provost, P (2001). "5-Lipoxygenase interacts with coactosin-like protein". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (19). United States: 16520–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011205200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11297527.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|laysummary=, and|laysource=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
Further reading
- Rådmark OP (2000). "The molecular biology and regulation of 5-lipoxygenase". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 161 (2 Pt 2): S11–5. PMID 10673219.
- Hammarberg T, Reddy KV, Persson B, Rådmark O (2003). "Calcium binding to 5-lipoxygenase". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 507: 117–21. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-0193-0_19. ISBN 978-0-306-47283-1. PMID 12664574.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Ishii S, Noguchi M, Miyano M; et al. (1992). "Mutagenesis studies on the amino acid residues involved in the iron-binding and the activity of human 5-lipoxygenase". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 182 (3): 1482–90. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91901-2. PMID 1540191.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Nguyen T, Falgueyret JP, Abramovitz M, Riendeau D (1991). "Evaluation of the role of conserved His and Met residues among lipoxygenases by site-directed mutagenesis of recombinant human 5-lipoxygenase". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (32): 22057–62. PMID 1939225.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Hoshiko S, Rådmark O, Samuelsson B (1991). "Characterization of the human 5-lipoxygenase gene promoter". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (23): 9073–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.23.9073. PMC 55106. PMID 2251250.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Matsumoto T, Funk CD, Rådmark O; et al. (1988). "Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of human 5-lipoxygenase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (1): 26–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.1.26. PMC 279474. PMID 2829172.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Rouzer CA, Kargman S (1988). "Translocation of 5-lipoxygenase to the membrane in human leukocytes challenged with ionophore A23187". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (22): 10980–8. PMID 3134355.
- Dixon RA, Jones RE, Diehl RE; et al. (1988). "Cloning of the cDNA for human 5-lipoxygenase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (2): 416–20. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.2.416. PMC 279559. PMID 3422434.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Jakobsson PJ, Shaskin P, Larsson P; et al. (1995). "Studies on the regulation and localization of 5-lipoxygenase in human B-lymphocytes". Eur. J. Biochem. 232 (1): 37–46. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20778.x. PMID 7556168.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Janssen-Timmen U, Vickers PJ, Wittig U; et al. (1995). "Expression of 5-lipoxygenase in differentiating human skin keratinocytes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (15): 6966–70. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.15.6966. PMC 41452. PMID 7624354.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Lepley RA, Fitzpatrick FA (1994). "5-Lipoxygenase contains a functional Src homology 3-binding motif that interacts with the Src homology 3 domain of Grb2 and cytoskeletal proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (39): 24163–8. PMID 7929073.
- Shaw KJ, Ng C, Kovacs BW (1994). "Cyclooxygenase gene expression in human endometrium and decidua". Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 50 (5): 239–43. doi:10.1016/0952-3278(94)90160-0. PMID 8066098.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Woods JW, Evans JF, Ethier D; et al. (1993). "5-lipoxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein are localized in the nuclear envelope of activated human leukocytes". J. Exp. Med. 178 (6): 1935–46. doi:10.1084/jem.178.6.1935. PMC 2191287. PMID 8245774.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Mancini JA, Li C, Vickers PJ (1994). "5-Lipoxygenase activity in the human pancreas". Journal of lipid mediators. 8 (3): 145–50. PMID 8268460.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - VanderNoot VA, Fitzpatrick FA (1996). "Competitive binding assay of src homology domain 3 interactions between 5-lipoxygenase and growth factor receptor binding protein 2". Anal. Biochem. 230 (1): 108–14. doi:10.1006/abio.1995.1444. PMID 8585605.
- Brock TG, McNish RW, Bailie MB, Peters-Golden M (1997). "Rapid import of cytosolic 5-lipoxygenase into the nucleus of neutrophils after in vivo recruitment and in vitro adherence". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (13): 8276–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.13.8276. PMID 9079648.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Nassar GM, Montero A, Fukunaga M, Badr KF (1997). "Contrasting effects of proinflammatory and T-helper lymphocyte subset-2 cytokines on the 5-lipoxygenase pathway in monocytes". Kidney Int. 51 (5): 1520–8. doi:10.1038/ki.1997.209. PMID 9150468.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K; et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Arachidonate+5-Lipoxygenase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
