Stellar corona

A corona (Latin, 'crown') is an aura of plasma that surrounds the Sun and other celestial bodies. The Sun's corona extends millions of kilometres into space and is most easily seen during a total solar eclipse, but it is also observable with a coronagraph. The word "corona" is a Latin word meaning "crown", from the Ancient Greek κορώνη (korōnē, “garland, wreath”).
The high temperature of the Sun's corona gives it unusual spectral features, which led some in the 19th century to suggest that it contained a previously unknown element, "coronium". These spectral features have since been traced to highly ionized iron (Fe-XIV). Bengt Edlén, following the work of Grotrian (1939), first identified the coronal lines in 1940 (observed since 1869) as transitions from low-lying metastable levels of the ground configuration of highly ionised metals (the green FeXIV line at 5303 Å, but also the red line FeX at 6374 Å). These high stages of ionisation indicate a plasma temperature in excess of 1,000,000 kelvin.[1]
Light from the corona comes from three primary sources, which are called by different names although all of them share the same volume of space. The K-corona (K for kontinuierlich, "continuous" in German) is created by sunlight scattering off free electrons; Doppler broadening of the reflected photospheric absorption lines completely obscures them, giving the spectral appearance of a continuum with no absorption lines. The F-corona (F for Fraunhofer) is created by sunlight bouncing off dust particles, and is observable because its light contains the Fraunhofer absorption lines that are seen in raw sunlight; the F-corona extends to very high elongation angles from the Sun, where it is called the zodiacal light. The E-corona (E for emission) is due to spectral emission lines produced by ions that are present in the coronal plasma; it may be observed in broad or forbidden or hot spectral emission lines and is the main source of information about the corona's composition.[2]
Physical features

The sun's corona is much hotter (by a factor from 150 to 450) than the visible surface of the Sun: the photosphere's average temperature is 5800 kelvin compared to the corona's one to three million kelvin. The corona is 10−12 times as dense as the photosphere, and so produces about one-millionth as much visible light. The corona is separated from the photosphere by the relatively shallow chromosphere. The exact mechanism by which the corona is heated is still the subject of some debate, but likely possibilities include induction by the Sun's magnetic field and MHD waves from below. The outer edges of the Sun's corona are constantly being transported away due to open magnetic flux generating the solar wind.
The corona is not always evenly distributed across the surface of the sun. During periods of quiet, the corona is more or less confined to the equatorial regions, with coronal holes covering the polar regions. However during the Sun's active periods, the corona is evenly distributed over the equatorial and polar regions, though it is most prominent in areas with sunspot activity. The solar cycle spans approximately 11 years, from solar minimum to the following minimum. Since the solar magnetic field is continually wound up (due to a differential rotation at the solar equator (the equator rotates quicker than the poles), sunspot activity will be more pronounced at solar maximum where the magnetic field is more twisted. Associated with sunspots are coronal loops, loops of magnetic flux, upwelling from the solar interior. The magnetic flux pushes the hotter photosphere aside, exposing the cooler plasma below, thus creating the dark (when compared to the solar disk) spots.
Since the corona has been photographed at high resolution in the X-rays by the satellite Skylab in 1973, and then later by Yohkoh and the other following space instruments, it has been seen that the structure of the corona is very various and complex: different zones have been immediately classified on the coronal disc.[3][4][5] The astronomers usually distinguish several regions,[6] as described below.
Active regions
Active regions are ensembles of loop structures connecting points of opposite magnetic polarity in the photosphere, the so-called coronal loops. They generally distribute in two zones of activity, which are parallel to the solar equator. The average temperature is between two and four million Kelvin, while the density goes from 109 to 1010 particle per cm3.

Active regions involve all the phenomena directly linked to the magnetic field, which occur at different heights on the Sun's surface:[6] sunspots and faculae, happening in the photosphere, spicules, Hα filaments and plages in the chromosphere, prominences in the chromosphere and transition region, and flares and coronal mass ejections happening in the corona and chromosphere, but if flares are very violent can perturb also the photosphere and generate a Moreton wave, as described by Uchida. On the contrary, quiescent prominences are large, cool dense structures which are observed as dark, "snake-like" Hα ribbons (filaments) on the solar disc. Their temperature is about 5000–8000 K, and so they are usually considered as chromospheric features.
In 2013, images from the High Resolution Coronal Imager revealed never-before-seen "magnetic braids" of plasma within the outer layers of these active regions.[7]
Coronal loops

Coronal loops are the basic structures of the magnetic solar corona. These loops are the closed-magnetic flux cousins of the open-magnetic flux that can be found in coronal hole (polar) regions and the solar wind. Loops of magnetic flux well up from the solar body and fill with hot solar plasma.[8] Due to the heightened magnetic activity in these coronal loop regions, coronal loops can often be the precursor to solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
Solar plasma feeding these structures is heated from under 6000 K to well over 1×106 K from the photosphere, through the transition region, and into the corona. Often, the solar plasma will fill these loops from one foot point and drain from the other (siphon flow due to a pressure difference,[9] or asymmetric flow due to some other driver).
When the plasma goes upward from the footpoints towards the loop top, as it always occurs during the initial phase of a compact flare, it is defined as chromospheric evaporation. When the plasma rapidly cools falling down towards the photosphere, we have the chromospheric condensation. There may also be symmetric flow from both loop foot points, causing a buildup of mass in the loop structure. The plasma may cool rapidly in this region (for a thermal instability), creating dark filaments in the solar disk or prominences off the limb.
Coronal loops may have lifetimes in the order of seconds (in the case of flare events), minutes, hours or days. Usually coronal loops lasting for long periods of time are known as steady state or quiescent coronal loops, where there is a balance in loop energy sources and sinks (example).
Coronal loops have become very important when trying to understand the current coronal heating problem. Coronal loops are highly radiating sources of plasma and therefore easy to observe by instruments such as TRACE; they are highly observable laboratories to study phenomena such as solar oscillations, wave activity and nanoflares. However, it remains difficult to find a solution to the coronal heating problem as these structures are being observed remotely, where many ambiguities are present (i.e. radiation contributions along the LOS). In-situ measurements are required before a definitive answer can be arrived at, but due to the high plasma temperatures in the corona, in-situ measurements are impossible (at least for the time being). The next mission of the Nasa Solar Probe Plus will approach the Sun very closely allowing more direct observations.

Large-scale structures
Large-scale structures are very long arcs which can cover over a quarter of the solar disk but contain plasma less dense than in the coronal loops of the active regions.
They were first detected in the June 8, 1968 flare observation during a rocket flight.[10]
The large-scale structure of the corona changes over the 11-year solar cycle and becomes particularly simple during the minimum period, when the magnetic field of the Sun is almost similar to a dipolar configuration (plus a quadrupolar component).
Interconnections of active regions
The interconnections of active regions are arcs connecting zones of opposite magnetic field, in different active regions. Significant variations of these structures are often seen after a flare.
Some other features of this kind are helmet streamers—large cap-like coronal structures with long pointed peaks that usually overlie sunspots and active regions. Coronal streamers are considered as sources of the slow solar wind.[11]
Filament cavities

Filament cavities are zones which look dark in the X-rays and are above the regions where Hα filaments are observed in the chromosphere. They were first observed in the two 1970 rocket flights which also detected coronal holes.[10]
Filament cavities are cooler clouds of gases(plasma) suspended above the Sun's surface by magnetic forces. The regions of intense magnetic field look dark in the images because they are empty of hot plasma. In fact, the sum of the magnetic pressure and plasma pressure must be constant everywhere on the heliosphere in order to have an equilibrium configuration: where the magnetic field is higher, the plasma must be cooler or less dense. The plasma pressure can be calculated by the state equation of a perfect gas , where is the particle number density, the Boltzmann constant and the plasma temperature. It is evident from the equation that the plasma pressure lowers when the plasma temperature decreases respect to the surrounding regions or when the zone of intense magnetic field empties. The same physical effect makes sunspots dark in the photosphere.
Bright points
Bright points are small active regions spread over the whole solar disk. X-ray bright points were first detected in April 8, 1969 during a rocket flight.[10]
The fraction of the solar surface covered by bright points varies with the solar cycle. They are associated with small bipolar regions of the magnetic field. Their average temperature ranges from 1.1 MK to 3.4 MK. The variations in temperature are often correlated with changes in the X-ray emission.[12]
Coronal holes
Coronal holes are the polar regions which look dark in the X-rays since they do not emit much radiation.[13] These are wide zones of the Sun where the magnetic field is unipolar and opens towards the interplanetary space. The high speed solar wind arises mainly from these regions.
In the UV images of the coronal holes, some small structures, similar to elongated bubbles, are often seen as they were suspended in the solar wind. These are the coronal plumes. More exactly, they are long thin streamers that project outward from the Sun's north and south poles.[14]
The Quiet Sun
The solar regions which are not part of active regions and coronal holes are commonly identified as the quiet Sun.
The equatorial region has a faster velocity rotation than the polar zones. The result of the Sun's differential rotation is that the active regions always arise in two bands parallel to the equator and their extension increases during the periods of maximum of the solar cycle, while they almost disappear during each minimum. Therefore the quiet Sun always coincides with the equatorial zone and its surface is lower during the maximum of the solar cycle. Approaching the minimum of the solar cycle (also named butterfly cycle), the extension of the quiet Sun increases until it covers the whole disk surface excluding some bright points on the hemisphere and the poles, where there are the coronal holes.
Variability of the corona
A portrait as diversified as the one already pointed out for the coronal features is emphasized by the analysis of the dynamics of the main structures of the corona, which evolve in times very different among them. Studying the coronal variability in its complexity is not easy because the times of evolution of the different structures can vary considerably: from seconds to several months. The typical sizes of the regions where coronal events take place vary in the same way, as it is shown in the following table.
| Coronal event | Typical time-scale | Typical length-scale (Mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Active region flare | 10 to 10,000 seconds | 10–100 |
| X-ray bright point | minutes | 1–10 |
| Transient in large-scale structures | from minutes to hours | ~100 |
| Transient in interconnecting arcs | from minutes to hours | ~100 |
| Quiet Sun | from hours to months | 100–1,000 |
| Coronal hole | several rotations | 100–1,000 |
Flares

Flares take place in active regions and provoke a sudden increase of the radiative flux emitted from small regions of the corona. They are very complex phenomena, visible at different wavelengths; they interest several zones of the solar atmosphere and involve many physical effects, thermal and not thermal, and sometimes wide reconnections of the magnetic field lines with material expulsion.
Flares are impulsive phenomena, of average duration of 15 minutes, even if the most energetic events can last several hours. Flares involve a high and rapid increase of the density and temperature.
An emission in white light is only seldom observed: usually, flares are only seen at EUV wavelengths and in the X-rays, typical of the chromospheric and coronal emission.
In the corona the morphology of flares, which can be grasped from the observations in the soft and hard X-rays, at the UV wavelengths and in Hα, is very complex. However, two kinds of basic structures can be distinguished: [15]
- compact flares, when each of the two arches where the event is happening maintains its morphology: only an increase of the emission is observed without significant structural variations. The emitted energy is of the order of 1022 – 1023 J.
- flares of long duration, associated to eruptions of prominences, transients in white light and two-ribbon flares:[16] in this case the magnetic loops change their configuration during the event. The energies emitted during these flares of such large proportions can reach 1025 J.

As for temporal dynamics, three different phases are generally distinguished, whose duration are not comparable. These times, moreover, can depend on the range of wavelengths used to observe the event even considerably:
- an initial impulsive phase, whose duration is of the order of minutes. Strong emissions of energy are often observed even in the microwaves, at EUV wavelengths and in the hard X-rays.
- a maximum phase
- a decay phase, which can last several hours.
Sometimes also a phase preceding the flare can be observed, usually called as "pre-flare" phase.
Transients
Accompanying solar flares or large solar prominences, "coronal transients" (also called coronal mass ejections) are sometimes released. These are enormous loops of coronal material traveling outward from the Sun at over a million kilometers per hour, containing roughly 10 times the energy of the solar flare or prominence that accompanies them. Some larger ejections can propel hundreds of millions of tons of material into space at roughly 1.5 million kilometers an hour.
A solar storm
These movies have been taken by the satellite SOHO during two weeks in October and November 2003. The images have been taken at the same time by the different instruments on board SOHO: the MDI, producing magnetograms, the Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT), which photographs the corona in the ultraviolets, and the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph (LASCO).
The first video at the top on the left (in grey) shows the magnetograms as they vary in time. At the top on the right (in yellow) the photosphere can be seen in white light as taken by the MDI.
Furthermore the EIT filmed the event in its four filters which are sensitive to different wavelengths, selecting plasma at different temperatures. The images in orange (on the left) refers to chromospheric plasma, while that one in green (on the right) to the corona.
In the last movie at the centre the Sun's images taken in the ultraviolet filter by the EIT have been combined with those taken by the coronograph LASCO blue and white in this movie.
All the instruments registered the storm which is considered as one of the largest solar activity events observed by SOHO and maybe since the advent of space-based solar observations. The storm involved all the plasma of the solar atmosphere from the chromosphere to the corona, as can be seen from the movies, which are ordered from left to right, from top to bottom, in the outward direction of the increasing temperature on the Sun: photosphere (yellow), chromosphere-transition region (orange), low corona (green) and extended corona (blue).
The corona is visible to the SOHO/LASCO coronagraph instruments, which block the bright disk of the Sun so the significantly fainter corona can be seen. In this movie, the inner coronagraph (designated C2) is combined with the outer coronagraph (C3).
As the movie plays, we can observe a number of features of the active Sun. Long streamers radiate outward from the Sun and wave gently due to their interaction with the solar wind. The bright white regions are visible due to their high density of free electrons which scatter the light from the photosphere towards the observer. Protons and other ionized atoms are there as well, but are not as visible since they do not interact with photons as strongly as electrons. Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are occasionally observed launching from the Sun. Some of these launch particle events can saturate the cameras with snow-like artifacts.
Also visible in the coronagraphs are stars and planets. Stars are seen to drift slowly to the right, carried by the relative motion of the Sun and the Earth. The planet Mercury is visible as the bright point moving left of the Sun.
The horizontal "extension" in the image is called blooming and is due to charge leakage during readout of saturated pixels in the camera's CCD imager.
Stellar coronae
Coronal stars are ubiquitous among the stars in the cool half of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.[17] These coronae can be detected using X-ray telescopes. Some stellar coronae, particularly in young stars, are much more luminous than the Sun's. For example, FK Comae Berenices is the prototype for the FK Com class of variable star. These are giants of spectral types G and K with an unusually rapid rotation and signs of extreme activity. Their X-ray coronae are among the most luminous (Lx ≥ 1032 erg·s−1 or 1025W) and the hottest known with dominant temperatures up to 40 MK.[17]
The astronomical observations planned with the Einstein Observatory by Giuseppe Vaiana and his group[18] showed that F-, G-, K- and M-stars have chromospheres and often coronae much like our Sun. The O-B stars, which do not have surface convection zones, have a strong X-ray emission. However these stars do not have a corona, but the outer stellar envelopes emit this radiation during shocks due to thermal instabilities in rapidly moving gas blobs. Also A-stars do not have convection zones but they do not emit at the UV and X-ray wavelengths. Thus they appear to have neither chromospheres nor coronae.
Physics of the corona
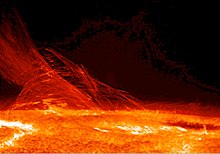
The matter in the external part of the solar atmosphere is in the state of plasma, at very high temperature (a few million Kelvins) and at very low density (of the order of 1015 particle/m3). According to the definition of plasma, it is a quasi-neutral ensemble of particles which exhibits a collective behaviour.
The composition is the same as the one in the Sun's interior, mainly hydrogen, but completely ionized, thence protons and electrons, and a small fraction of the other atoms in the same percentages as they are present in the photosphere. Even heavier metals, such as iron, are partially ionized and have lost most of the external electrons. The ionization state of a chemical element depends strictly on the temperature and is regulated by the Saha equation. Historically, the presence of the spectral lines emitted from highly ionized states of iron allowed determination of the high temperature of the coronal plasma, revealing that the corona is much hotter than the internal layers of the chromosphere.
The corona behaves like a gas which is very hot but very light at the same time: the pressure in the photosphere is usually only 0.1 to 0.6 Pa in active regions, while on the Earth the atmospheric pressure is about 100 kPa, approximatively a million times higher than on the solar surface. However it is not properly a gas, because it is made of charged particles, basically protons and electrons, moving at different velocities. Supposing that they have the same kinetic energy on average (for the equipartition theorem), electrons have a mass roughly 1800 times smaller than protons, therefore they acquire more velocity. Metal ions are always slower. This fact has relevant physical consequences either on radiative processes (that are very different from the photospheric radiative processes), or on thermal conduction. Furthermore the presence of electric charges induces the generation of electric currents and high magnetic fields. Magnetohydrodynamic waves (MHD waves) can also propagate in this plasma,[19] even if it is not still clear how they can be transmitted or generated in the corona.
Radiation
The corona emits radiation mainly in the X-rays, observable only from space.
The plasma is transparent to its own radiation and to that one coming from below, therefore we say that it is optically-thin. The gas, in fact, is very rarefied and the photon mean free-path overcomes by far all the other length-scales, including the typical sizes of the coronal features.
Different processes of radiation take place in the emission, due to binary collisions between plasma particles, while the interactions with the photons, coming from below, are very rare. Because the emission is due to collisions between ions and electrons, the energy emitted from a unit volume in the time unit is proportional to the squared number of particles in a unit volume, or more exactly, to the product of the electron density and proton density.[20]
Thermal conduction


In the corona thermal conduction occurs from the external hotter atmosphere towards the inner cooler layers. Responsible for the diffusion process of the heat are the electrons, which are much lighter than ions and move faster, as explained above.
When there is a magnetic field the thermal conductivity of the plasma becomes higher in the direction which is parallel to the field lines rather than in the perpendicular direction.[21] A charged particle moving in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field line is subject to the Lorentz force which is normal to the plane individuated by the velocity and the magnetic field. This force bends the path of the particle. In general, since particles also have a velocity component along the magnetic field line, the Lorentz force constrains them to bend and move along spirals around the field lines at the cyclotron frequency.
If collisions between the particles are very frequent, they are scattered in every direction. This happens in the photosphere, where the plasma carries the magnetic field in its motion. In the corona, on the contrary, the mean free-path of the electrons is of the order of kilometres and even more, so each electron can do an helicoidal motion long before being scattered after a collision. Therefore the heat transfer is enhanced along the magnetic field lines and inhibited in the perpendicular direction.
In the direction longitudinal to the magnetic field, the thermal conductivity of the corona is[21]
where is the Boltzmann constant, is the temperature in Kelvin, the electron mass, the electric charge of the electron,
the Coulomb logarithm, and
the Debye length of the plasma with particle density . The Coulomb logarithm is roughly 20 in the corona, with a mean temperature of 1 MK and a density of 1015 particles/m3, and about 10 in the chromosphere, where the temperature is approximatively 10kK and the particle density is of the order of 1018 particles/m3, and in practice it can be assumed constant.
Thence, if we indicate with the heat for a volume unit, expressed in J m−3, the Fourier equation of heat transfer, to be computed only along the direction of the field line, becomes
.
Numerical calculations have shown that the thermal conductivity of the corona is comparable to that of copper.
Coronal seismology
Coronal seismology is a new way of studying the plasma of the solar corona with the use of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves. Magnetohydrodynamics studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids—in this case the fluid is the coronal plasma. Philosophically, coronal seismology is similar to the Earth's seismology, the Sun's helioseismology, and MHD spectroscopy of laboratory plasma devices. In all these approaches, waves of various kind are used to probe a medium. The potential of coronal seismology in the estimation of the coronal magnetic field, density scale height, fine structure and heating has been demonstrated by different research groups.
Coronal heating problem
The coronal heating problem in solar physics relates to the question of why the temperature of the Sun's corona is millions of kelvin higher than that of the surface. The high temperatures require energy to be carried from the solar interior to the corona by non-thermal processes, because the second law of thermodynamics prevents heat from flowing directly from the solar photosphere, or surface, at about 5800 K, to the much hotter corona at about 1 to 3 MK (parts of the corona can even reach 10 MK).
The thin region of temperature increase from the chromosphere to the corona is known as the transition region and can range from tens to hundreds of kilometers thick. An analogy of this would be a light bulb heating the air surrounding it hotter than its glass surface. The second law of thermodynamics would be broken.
The amount of power required to heat the solar corona can easily be calculated as the difference between coronal radiative losses and heating by thermal conduction toward the chromosphere through the transition region. It is about 1 kilowatt for every square meter of surface area on the Sun, or 1/40000 of the amount of light energy that escapes the Sun.
Many coronal heating theories have been proposed,[22] but two theories have remained as the most likely candidates: wave heating and magnetic reconnection (or nanoflares).[23] Through most of the past 50 years, neither theory has been able to account for the extreme coronal temperatures.
The NASA mission Solar Probe + is intended to approach the sun to a distance of approximately 9.5 solar radii in order to investigate coronal heating and the origin of the solar wind.
In 2012, high resolution (<0.2″) soft X-ray imaging with the High Resolution Coronal Imager on board of a sounding rocket revealed tightly wound braids in the corona. The authors hypothesized that the reconnection and unraveling of braids can act as primary sources of heating of the active solar corona to temperatures of up to 4 million kelvin. The main heat source in the quiescent corona (about 1.5 million kelvin) in this case is supposed to be MHD waves.[24]
| Heating Models | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic | Magnetic | |
|
DC (reconnection) | AC (waves) |
|
| |
| Competing theories | ||
Wave heating theory
The wave heating theory, proposed in 1949 by Evry Schatzman, proposes that waves carry energy from the solar interior to the solar chromosphere and corona. The Sun is made of plasma rather than ordinary gas, so it supports several types of waves analogous to sound waves in air. The most important types of wave are magneto-acoustic waves and Alfvén waves.[25] Magneto-acoustic waves are sound waves that have been modified by the presence of a magnetic field, and Alfvén waves are similar to ULF radio waves that have been modified by interaction with matter in the plasma. Both types of waves can be launched by the turbulence of granulation and super granulation at the solar photosphere, and both types of waves can carry energy for some distance through the solar atmosphere before turning into shock waves that dissipate their energy as heat.
One problem with wave heating is delivery of the heat to the appropriate place. Magneto-acoustic waves cannot carry sufficient energy upward through the chromosphere to the corona, both because of the low pressure present in the chromosphere and because they tend to be reflected back to the photosphere. Alfvén waves can carry enough energy, but do not dissipate that energy rapidly enough once they enter the corona. Waves in plasmas are notoriously difficult to understand and describe analytically, but computer simulations, carried out by Thomas Bogdan and colleagues in 2003, seem to show that Alfvén waves can transmute into other wave modes at the base of the corona, providing a pathway that can carry large amounts of energy from the photosphere into the corona and then dissipate it as heat.
Another problem with wave heating has been the complete absence, until the late 1990s, of any direct evidence of waves propagating through the solar corona. The first direct observation of waves propagating into and through the solar corona was made in 1997 with the SOHO space-borne solar observatory, the first platform capable of observing the Sun in the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) for long periods of time with stable photometry. Those were magneto-acoustic waves with a frequency of about 1 millihertz (mHz, corresponding to a 1,000 second wave period), that carry only about 10% of the energy required to heat the corona. Many observations exist of localized wave phenomena, such as Alfvén waves launched by solar flares, but those events are transient and cannot explain the uniform coronal heat.
It is not yet known exactly how much wave energy is available to heat the corona. Results published in 2004 using data from the TRACE spacecraft seem to indicate that there are waves in the solar atmosphere at frequencies as high as 100 mHz (10 second period). Measurements of the temperature of different ions in the solar wind with the UVCS instrument aboard SOHO give strong indirect evidence that there are waves at frequencies as high as 200 Hz, well into the range of human hearing. These waves are very difficult to detect under normal circumstances, but evidence collected during solar eclipses by teams from Williams College suggest the presences of such waves in the 1–10 Hz range.
Recently, Alfvénic motions have been found in the lower solar atmosphere [26] [27] and also in the quiet Sun, in coronal holes and in active regions using observations with AIA on board the Solar Dynamics Observatory.[28] These Alfvénic oscillations have significant power, and seem to be connected to the chromospheric Alfvénic oscillations previously reported with the Hinode spacecraft .[29]
Solar wind observations with the WIND (spacecraft) have recently shown evidence to support theories of Alfvén-cyclotron dissipation, leading to local ion heating.[30]
Magnetic reconnection theory

The magnetic reconnection theory relies on the solar magnetic field to induce electric currents in the solar corona.[31] The currents then collapse suddenly, releasing energy as heat and wave energy in the corona. This process is called "reconnection" because of the peculiar way that magnetic fields behave in a plasma (or any electrically conductive fluid such as mercury or seawater). In a plasma, magnetic field lines are normally tied to individual pieces of matter, so that the topology of the magnetic field remains the same: if a particular north and south magnetic pole are connected by a single field line, then even if the plasma is stirred or if the magnets are moved around, that field line will continue to connect those particular poles. The connection is maintained by electric currents that are induced in the plasma. Under certain conditions, the electric currents can collapse, allowing the magnetic field to "reconnect" to other magnetic poles and release heat and wave energy in the process.
Magnetic reconnection is hypothesized to be the mechanism behind solar flares, the largest explosions in our solar system. Furthermore, the surface of the Sun is covered with millions of small magnetized regions 50–1,000 km across. These small magnetic poles are buffeted and churned by the constant granulation. The magnetic field in the solar corona must undergo nearly constant reconnection to match the motion of this "magnetic carpet", so the energy released by the reconnection is a natural candidate for the coronal heat, perhaps as a series of "microflares" that individually provide very little energy but together account for the required energy.
The idea that nanoflares might heat the corona was put forward by Eugene Parker in the 1980s but is still controversial. In particular, ultraviolet telescopes such as TRACE and SOHO/EIT can observe individual micro-flares as small brightenings in extreme ultraviolet light,[32] but there seem to be too few of these small events to account for the energy released into the corona. The additional energy not accounted for could be made up by wave energy, or by gradual magnetic reconnection that releases energy more smoothly than micro-flares and therefore doesn't appear well in the TRACE data. Variations on the micro-flare hypothesis use other mechanisms to stress the magnetic field or to release the energy, and are a subject of active research in 2005.
Spicules (type II)
For decades, researchers believed spicules could send heat into the corona. However, following observational research in the 1980s, it was found that spicule plasma did not reach coronal temperatures, and so the theory was discounted.
As per studies performed in 2010 at the National Centre for Atmospheric Research in Colorado, in collaboration with the Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory (LMSAL) and the Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics of the University of Oslo, a new class of spicules (TYPE II) discovered in 2007, which travel faster (up to 100 km/s) and have shorter lifespans can account for the problem.[33] These jets insert heated plasma into the Sun's outer atmosphere. Thus, a much greater understanding of the Corona and improvement in the knowledge of the Sun's subtle influence on the Earth's upper atmosphere can be expected henceforth. The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly on NASA's recently launched Solar Dynamics Observatory and NASA's Focal Plane Package for the Solar Optical Telescope on the Japanese Hinode satellite which were used to test this hypothesis. The high spatial and temporal resolution of the newer instruments reveal this coronal mass supply.
These observations reveal a one-to-one connection between plasma that is heated to millions of degrees and the spicules that insert this plasma into the corona.[34]
Axions may hold the key to the Solar Corona heating problem.[35]
See also
- Advanced Composition Explorer
- Alfvén waves
- Chromosphere
- Coronal hole
- Coronal loop
- Coronal mass ejection
- Coronal radiative losses
- Coronal seismology
- Geocorona
- Heliosphere
- Helmet streamer
- Magnetic reconnection
- Magnetohydrodynamic waves
- Magnetohydrodynamics
- Nanoflares
- Photosphere
- Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- Solar cycle
- Solar flares
- Solar prominence
- Solar transition region
- Solar wind
- STEREO
- Sun
- WIND (spacecraft)
- X-ray astronomy
References
- ^ Aschwanden, M. J. (2004). Physics of the Solar Corona. An Introduction. Praxis Publishing. ISBN 3-540-22321-5.
- ^ Corfield, Richard (2007). Lives of the Planets. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-01403-3.
- ^ Vaiana, G. S.; Krieger, A. S.; Timothy, A. F. (1973). "Identification and analysis of structures in the corona from X-ray photography". Solar Physics. 32: 81–116. Bibcode:1973SoPh...32...81V. doi:10.1007/BF00152731.
- ^ Vaiana, G.S., Tucker, W.H (1974). "Solar X-Ray Emission in "X-Ray Astronomy" ed. by R. Giacconi and H. Gunsky": 169.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vaiana, G S; Rosner, R (1978). "Recent advances in Coronae Physics". Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophysics. 16: 393–428. Bibcode:1978ARA&A..16..393V. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.16.090178.002141.
- ^ a b Gibson, E. G. (1973). The Quiet Sun. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, D.C.
- ^ http://www.space.com/19400-sun-corona-secrets-suborbital-telescope.html
- ^ Katsukawa, Yukio; Tsuneta, Saku (2005). "Magnetic Properties at Footpoints of Hot and Cool Loops". The Astrophysical Journal. 621: 498–511. Bibcode:2005ApJ...621..498K. doi:10.1086/427488.
- ^ Betta, Rita; Orlando, Salvatore; Peres, Giovanni; Serio, Salvatore (1999). "On the Stability of Siphon Flows in Coronal Loops". Space Science Reviews. 87: 133–136. Bibcode:1999SSRv...87..133B. doi:10.1023/A:1005182503751.
- ^ a b c Giacconi, Riccardo (1992). G.S. Vaiana memorial lecture in Proceedinds of Physics of Solar and Stellar Coronae: G.S. Vaiana Memorial Symposium, ed. by J. F. Linsky and S.Serio. Kluwer Academic Publishers-Printed in the Netherlands. pp. 3–19. ISBN 0-7923-2346-7.
- ^ Ofman, Leon (2000). "Source regions of the slow solar wind in coronal streamers". Geophysical Research Letters. 27 (18): 2885–2888. Bibcode:2000GeoRL..27.2885O. doi:10.1029/2000GL000097.
- ^ Kariyappa, R.; Deluca, E. E.; Saar, S. H.; Golub, L.; Damé, L.; Pevtsov, A. A.; Varghese, B. A.; Deluca; Saar; Golub; Damé; Pevtsov; Varghese (2011). "Temperature variability in X-ray bright points observed with Hinode/XRT". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 526: A78. Bibcode:2011A&A...526A..78K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014878.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ito, Hiroaki; Tsuneta, Saku; Shiota, Daikou; Tokumaru, Munetoshi; Fujiki, Ken'Ichi (2010). "Is the Polar Region Different from the Quiet Region of the Sun?". The Astrophysical Journal. 719: 131–142. arXiv:1005.3667. Bibcode:2010ApJ...719..131I. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/719/1/131.
- ^ Del Zanna, G.; Bromage, B. J. I.; Mason, H. E. (2003). "Spectroscopic characteristics of polar plumes". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 398 (2): 743–761. Bibcode:2003A&A...398..743D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021628.
- ^ Pallavicini, R.; Serio, S.; Vaiana, G. S. (1977). "A survey of soft X-ray limb flare images – The relation between their structure in the corona and other physical parameters". The Astrophysical Journal. 216: 108. Bibcode:1977ApJ...216..108P. doi:10.1086/155452.
- ^ Golub, L.; Herant, M.; Kalata, K.; Lovas, I.; Nystrom, G.; Pardo, F.; Spiller, E.; Wilczynski, J. (1990). "Sub-arcsecond observations of the solar X-ray corona". Nature. 344 (6269): 842–844. Bibcode:1990Natur.344..842G. doi:10.1038/344842a0.
- ^ a b Güdel M (2004). "X-ray astronomy of stellar coronae" (PDF). The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review. 12 (2–3): 71–237. arXiv:astro-ph/0406661. Bibcode:2004A&ARv..12...71G. doi:10.1007/s00159-004-0023-2.
- ^ Vaiana, G.S.; et al. (1981). "Results from an extensive Einstein stellar survey". The Astrophysical Journal. 245: 163. Bibcode:1981ApJ...245..163V. doi:10.1086/158797.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Jeffrey, Alan (1969). Magneto-hydrodynamics. UNIVERSITY MATHEMATICAL TEXTS.
- ^ Mewe, R. (1991). "X-ray spectroscopy of stellar coronae". The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review. 3 (2): 127. Bibcode:1991A&ARv...3..127M. doi:10.1007/BF00873539.
- ^ a b Spitzer, L. (1962). Physics of fully ionized gas. Interscience tracts of physics and astronomy.
- ^ Ulmshneider, Peter (1997). Heating of Chromospheres and Coronae in Space Solar Physics, Proceedings, Orsay, France, edited by J.C. Vial, K. Bocchialini and P. Boumier. Springer. pp. 77–106. ISBN 3-540-64307-9.
- ^ Malara, F., Velli, M. (2001). Observations and Models of Coronal Heating in Recent Insights into the Physics of the Sun and Heliosphere: Highlights from SOHO and Other Space Missions, Proceedings of IAU Symposium 203, edited by Pål Brekke, Bernhard Fleck, and Joseph B. Gurman. Astronomical Society of the Pacific. pp. 456–466. ISBN 1-58381-069-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1038/nature11772, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1038/nature11772instead. - ^ Alfvén, Hannes (1947). "Magneto hydrodynamic waves, and the heating of the solar corona". MNRAS. 107: 211–219. Bibcode:1947MNRAS.107..211A.
- ^ "Alfven Waves – Our Sun Is Doing The Magnetic Twist". read on Jan 6 2011.
- ^ Jess, DB; Mathioudakis, M; Erdélyi, R; Crockett, PJ; Keenan, FP; Christian, DJ (2009). "Alfvén Waves in the Lower Solar Atmosphere". Science. 323 (5921): 1582–1585. arXiv:0903.3546. Bibcode:2009Sci...323.1582J. doi:10.1126/science.1168680. PMID 19299614.
- ^ McIntosh, S. W.; de Pontieu, B.; Carlsson, M.; Hansteen, V. H.; The Sdo/Aia Mission Team (2010). "Ubiquitous Alfvenic Motions in Quiet Sun, Coronal Hole and Active Region Corona". American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2010. abstract #SH14A-01.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Sun's Magnetic Secret Revealed". read on Jan 6 2011.
- ^ Kasper, J.C.; et al. (December 2008). "Hot Solar-Wind Helium: Direct Evidence for Local Heating by Alfven-Cyclotron Dissipation". Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 (26): 261103. Bibcode:2008PhRvL.101z1103K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.261103. PMID 19113766.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ Priest, Eric (1982). Solar Magneto-hydrodynamics. D.Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, Holland. ISBN 90-277-1833-4.
- ^ Patsourakos, S.; Vial, J.-C. (2002). "Intermittent behavior in the transition region and the low corona of the quiet Sun". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 385 (3): 1073–1077. Bibcode:2002A&A...385.1073P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020151.
- ^ "Mystery of Sun's hot outer atmosphere 'solved' – Rediff.com News". Rediff.com. 2011-01-07. Retrieved 2012-05-21.
- ^ De Pontieu, B; McIntosh, SW; Carlsson, M; Hansteen, VH; Tarbell, TD; Boerner, P; Martinez-Sykora, J; Schrijver, CJ; Title, AM (2011). "The Origins of Hot Plasma in the Solar Corona". Science. 331 (6013): 55–58. Bibcode:2011Sci...331...55D. doi:10.1126/science.1197738. PMID 21212351.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|display-authors=9(help) - ^ The enigmatic Sun: a crucible for new physics
Further reading
- Thorsten Dambeck: Seething Cauldron in the Suns's Furnace, MaxPlanckResearch, 2/2008, p. 28–33
- B. N. Dwivedi and A. K. Srivastava Coronal heating by Alfvén waves CURRENT 296 SCIENCE, VOL. 98, NO. 3, 10 FEBRUARY 2010, pp. 295–296
External links
- NASA description of the solar corona
- Coronal heating problem at Innovation Reports
- NASA/GSFC description of the coronal heating problem
- FAQ about coronal heating
- Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, including near-real-time images of the solar corona
- Coronal x-ray images from the Hinode XRT
- nasa.gov Astronomy Picture of the Day July 26, 2009 – a combination of thirty-three photographs of the sun's corona that were digitally processed to highlight faint features of a total eclipse that occurred in March 2006
- Animated explanation of the core of the Sun (University of South Wales)
- Animated explanation of the temperature of the Corona (University of South Wales)
- Space,time,matter and vacuum: The Solar Corona. A sign of Quantum Gravity?(Spanish)
- Alfvén waves may heat the Sun's corona
- New Clue May Solve Solar Mystery
- The Origins of Hot Plasma in the Solar Corona
- Solar Interface Region – Bart de Pontieu (SETI Talks) Video















