Generation Z
| Part of a series on |
| Social generations of the Western world |
|---|
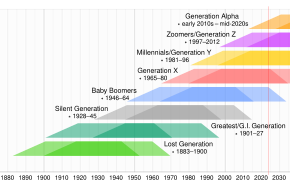 |
Generation Z is the demographic cohort after the Millennials. Currently, there are many competing names used in connection with them in the media. There are no precise dates for when this cohort starts or ends, but demographers and researchers typically use the mid-1990s to mid-2000s as starting birth years. However, there is little consensus regarding ending birth years.
Most of Generation Z have used the Internet since a young age, and they are usually thought to be comfortable with technology and with interacting on social media.
Terminology
William Strauss and Neil Howe wrote several books on the subject of generations and are widely credited with coining the term Millennials.[1] Howe has said "No one knows who will name the next generation after the Millennials".[1] In 2005, their company sponsored an online contest in which respondents voted overwhelmingly for the name Homeland Generation. That was not long after the September 11th terrorist attacks, and one fallout of the disaster was that Americans may have felt more safe staying at home.[2] Howe has described himself as "not totally wed" to the name and cautioned that "names are being invented by people who have a great press release. Everyone is looking for a hook."[1][3][4]
In 2012, USA Today sponsored an online contest for readers to choose the name of the next generation after the Millennials. The name Generation Z was suggested, although journalist Bruce Horovitz thought that some might find the term "off-putting". Some other names that were proposed included: iGeneration, Gen Tech, Gen Wii, Net Gen, Digital Natives, and Plurals.[1][1][5][6]
Post-Millennial is a name given by the US Dept. of Health and Human Services and Pew Research, in statistics published in 2016 showing the relative sizes and dates of the generations.[7] The same sources showed that as of April 2016, the Millennial generation surpassed the population of Baby Boomers in the USA (77 million vs. 76 million in 2015 data),[8] however, the Post-Millennials were ahead of the Millennials in another Health and Human Services survey (69 million vs. 66 million).[9]
iGeneration (or iGen) is a name that several persons claim to have coined. Stanford rapper MC Lars used the term in his 2006 song "iGeneration", which made it into popular rotation on MTVu.[10] Psychology professor and author Jean Twenge claims that the name iGen "just popped into her head" while she was driving near Silicon Valley, and that she had intended to use it as the title of her 2006 book Generation Me about the Millennial generation, until it was overridden by her publisher. Demographer Cheryl Russell claims to have first used the term in 2009.[1] In 2012, Ad Age magazine thought that iGen was "the name that best fits and will best lead to understanding of this generation".[1] In 2014, an NPR news intern noted that iGeneration "seems to be winning" as the name for the post-Millennials.[11] It has been described as "a wink and nod to Apple's iPod and iPhone".[1]
Frank N. Magid Associates, an advertising and marketing agency, nicknamed this cohort "The Pluralist Generation" or 'Plurals'.[12] Turner Broadcasting System also advocated calling the post-millennial generation 'Plurals'.[13][14]
MTV has labeled the generation "The Founders", based on the results of a survey they conducted in March 2015. MTV President Sean Atkins commented, "they have this self-awareness that systems have been broken, but they can't be the generation that says we'll break it even more."[15] Kantar Futures has named this cohort "The Centennials".[16][17]
Statistics Canada has noted that the cohort is sometimes referred to as "the Internet generation," as it is the first generation to have been born after the popularization of the Internet.[18] In Japan, the cohort is described as "Neo-Digital Natives", a step beyond the previous cohort described as "Digital Natives". Digital Natives primarily communicate by text or voice, while neo-digital natives use video or movies. This emphasizes the shift from PC to mobile and text to video among the neo-digital population.[19][20]
Date and age range defining
Statistics Canada defines Generation Z as starting with the birth year 1993.[21] Statistics Canada does not recognize a traditional Millennials cohort and instead has Generation Z directly follow what it designates as Children of Baby boomers (born 1972–1992).[22]
Randstad Canada describes Generation Z as those born between 1995–2014.[23][24] Australia's McCrindle Research Centre defines Generation Z as those born between 1995–2009, starting with a recorded rise in birth rates, and fitting their newer definition of a generational span with a maximum of 15 years.[25] A 2014 report from Sparks and Honey describes Generation Z as those born in 1995 or later.[26] Author Jean Twenge describes the iGen as those born from 1995–2012.[27][28][29]
In their 2011 book How Cool Brands Stay Hot, authors Joeri van den Bergh and Mattias Behrer define Generation Z as those born after 1996.[30] In Japan, generations are defined by a ten-year span with "Neo-Digital natives" beginning after 1996.[19][20]
The Futures Company,[16][17] marketing agency Frank N. Magid Associates,[12] Ernst and Young,[31] Turner Broadcasting,[32] and The Shand Group[33] use 1997 as the first year of birth for this cohort, with Frank N. Magid considering the cohort to extend to at least 2014.[12] A 2016 report from multinational banking firm Goldman Sachs describes Generation Z as those born since 1998.[34]
MTV described Generation Z as those born after December 2000, for a survey conducted by the network regarding possible names for the cohort.[15] The Asia Business Unit of Corporate Directions, Inc describes Gen Z as born between 2001-2015,[35] and Philippine Retailers Association describes Generation Z as born after 2001.[36]
The American Marketing Association describes Generation Z as those born after September 11, 2001, suggesting the cohort should be dubbed Gen 9/11 arguing "all children born after Sept. 11, 2001, will experience a world totally different from all generations that preceded it".[37]
Author Neil Howe defines the cohort as people born from approximately 2005–2025, but describes the dividing line between Generation Z and Millennials as "tentative" saying, "you can’t be sure where history will someday draw a cohort dividing line until a generation fully comes of age". Howe says that the Millennials' range beginning in 1982 points to the next generation's window starting between 2000 and 2006.[3][4]
Characteristics
According to Forbes (2015), the generation after Millennials, Generation Z, made up 25%[38][39] of the U.S. population, making them a larger cohort than the Baby Boomers or Millennials.[38] Frank N. Magid Associates estimates that in the United States, 55% of Generation Z are non-Hispanic Caucasians, 24% are Hispanic, 14% are African-American, 4% are Asian, and 4% are multiracial or other.[40]
Generation Z are predominantly the children of Generation X,[41][42][43] but they also have parents who are Millennials.[44] According to the marketing firm Frank N. Magid they are "the least likely to believe that there is such a thing as the American Dream" because "Generation X, the most influential parents of Plurals (Generation Z), demonstrates the least credence in the concept of the American Dream among adult generations."[40] According to Public Relations Society of America, the Great Recession has taught Generation Z to be independent, and has led to an entrepreneurial desire, after seeing their parents and older siblings struggle in the workforce.[45]
A 2013 survey by Ameritrade found that 47% of Generation Z in the United States (considered here to be those between the ages of 14 and 23) were concerned about student debt, while 36% were worried about being able to afford a college education at all.[46] This generation is faced with a growing income gap and a shrinking middle-class, which all have led to increasing stress levels in families.[47]
Both the September 11 terrorist attacks and the Great Recession have greatly influenced the attitudes of this generation in the United States. Since even the oldest members of Generation Z were young children or not yet born when the 9/11 attacks occurred, there is no generational memory of a time the United States was not at war with the loosely defined forces of global terrorism.[48][49] Turner suggests it is likely that both events have resulted in a feeling of unsettlement and insecurity among the people of Generation Z with the environment in which they were being raised. The economic recession of 2008 is particularly important to historical events that have shaped Generation Z, due to the ways in which their childhoods may have been affected by the recession's shadow; that is, the financial stresses felt by their parents.[50] Although the Millennials experienced these events during their coming of age, Generation Z lived through them as part of their childhood, affecting their realism and world-view.[51]
A 2014 study Generation Z Goes to College found that Generation Z students self-identify as being loyal, compassionate, thoughtful, open-minded, responsible, and determined.[52] How they see their Generation Z peers is quite different from their own self-identity. They view their peers as competitive, spontaneous, adventuresome, and curious; all characteristics that they do not see readily in themselves.[52] In addition, some authors consider that some of their competencies, such as reading competence, are being transformed due to their familiarity with digital devices, platforms and texts.[53]
A 2016 U.S. study found that church attendance during young adulthood was 41% among Generation Z, compared to 18 percent for Millennials at the same ages, 21 percent of Generation X, and 26 percent of baby boomers.[54]
Generation Z is generally more risk-averse in certain activities than earlier generations. In 2013, 66% of teenagers (older members of Generation Z) had tried alcohol, down from 82% in 1991. Also in 2013, 8% of Gen. Z teenagers never or rarely wear a seat belt when riding in a car with someone else, as opposed to 26% in 1991.[51]
Research from the Annie E. Casey Foundation conducted in 2016 found Generation Z youth had lower teen pregnancy rates, less substance abuse, and higher on-time high school graduation rates compared with Millennials. The researchers compared teens from 2008 and 2014 and found a 40% drop in teen pregnancy, a 38% drop in drug and alcohol abuse, and a 28% drop in the percentage of teens who did not graduate on time from high school.[55][56]
According to The Daily Telegraph, Generation Z is keen to look after their money and make the world a better place. In a quote by journalist Harry Wallop, he states, "Unlike the older Gen Y, they are smarter, safer, more mature and want to change the world. Their pin-up is Malala Yousafzai, the Pakistani education campaigner, who survived being shot by the Taliban, and who became the world's youngest ever Nobel Prize recipient."[57]
Technology and social media

Generation Z is the first cohort to have Internet technology readily available at a young age.[58] With the web revolution that occurred throughout the 1990s, they have been exposed to an unprecedented amount of technology in their upbringing. As technology became more compact and affordable, the popularity of smartphones in the United States grew exponentially. With 77% of 12–17 year olds owning a cellphone in 2015,[59] technology has strongly influenced Generation Z in terms of communication and education. Forbes suggested that by the time Generation Z entered the workplace, digital technology would be an aspect of almost all career paths.[46] Anthony Turner characterizes Generation Z as having a 'digital bond to the Internet', and argues that it may help youth to escape from emotional and mental struggles they face offline.[50] According to U.S. consultants Sparks and Honey in 2014, 41% of Generation Z spend more than three hours per day using computers for purposes other than schoolwork, compared with 22% in 2004.[60]
In 2015, Generation Z composed the largest portion of the U.S. population, at nearly 26%, edging out Millennials (24.5%), and this group is estimated to generate $44 billion in annual spending. About three-quarters of 13–17 years olds use their cellphones daily, more than they watch TV. Over half of surveyed mothers say the demo influences them in purchasing decisions for toys, apparel, dinner choices, entertainment, TV, mobile and computers. Among social media, Instagram and Snapchat are the most popular in the demo.
In 2015, an estimated 150,000 apps, 10% of those in Apple's App Store, were educational and aimed at children up to college level.[61] While researchers and parents agree the change in educational paradigm is significant, the results of the changes are mixed. On one hand, smartphones offer the potential for deeper involvement in learning[61] and more individualized instruction, thereby making this generation potentially better educated and more well-rounded. On the other hand, some researchers and parents are concerned that the prevalence of smart phones may cause technology dependence[62] and a lack of self-regulation that may hinder child development.[62]
An online newspaper about texting, SMS and MMS writes that teens own cellphones without necessarily needing them.[63] As children become teenagers, receiving a phone is considered a rite of passage in some countries, allowing the owner to be further connected with their peers and it is now a social norm to have one at an early age. An article from the Pew Research Center stated that "nearly three-quarters of teens have or have access to a smartphone and 30% have a basic phone, while just 12% of teens 13 to 17 say they have no cell phone of any type".[64] These numbers are only on the rise and the fact that the majority of Gen Z's own a cell phone has become one of this generations defining characteristics. As a result of this "24% of teens go online 'almost constantly'".[64]
One study has shown that teenagers in 2012 were more likely to share different types of information than teenagers in 2006 were.[65] However, they will take certain steps to protect certain information that they do not want being shared. They are more likely to "follow" others on social media than "share" and use different types of social media for different purposes.[52] Focus group testing found that while teens may be annoyed by many aspects of Facebook, they continue to use it because participation is important in terms of socializing with friends and peers. Twitter and Instagram are seen to be gaining popularity in member of Generation Z, with 24% (and growing) of teens with access to the Internet having Twitter accounts.[65] This is, in part, due to parents not typically using these social networking sites.[65] Snapchat is also seen to have gained attraction in Generation Z because videos, pictures, messages send much faster than regular messaging. Speed and reliability are important factors in members of Generation Z choice of social networking platform. This need for quick communication is presented in popular Generation Z apps like Vine and the prevalent use of emojis.[51]
One study found that young people use the Internet as a way to gain access to information and to interact with others. Mobile technology, social media, and Internet use have become increasingly important to modern adolescents over the past decade. Very few, however, are changed from what they gain access to online.[66] Youths are using the Internet as a tool to gain social skills, that they then apply to real life situations, and learn about things that interest them. Teens spend most of their time online in private communication with people they interact with outside the Internet on a regular basis. While social media is used for keeping up with global news and connections, it is mainly used for developing and maintaining relationships with people with whom they are close in proximity. The use of social media has become integrated into the daily lives of most Gen Z'ers who have access to mobile technology. They use it on a daily basis to keep in contact with friends and family, particularly those who they see every day. As a result, the increased use of mobile technology has caused Gen Z'ers to spend more time on their smartphones, and social media and has caused online relationship development to become a new generational norm.[67] Gen Z'ers are generally against the idea of "photoshopping" (deleting imperfections in photos) and they are against changing themselves to be considered perfect. The parents of the Gen Z'ers fear the overuse of the Internet by their children. Parents dislike the ease of access to inappropriate information and images as well as social networking sites where children can gain access to people worldwide. Children reversely feel annoyed with their parents and complain about parents being overly controlling when it comes to their Internet usage.[66] Gen Z uses social media and other sites to strengthen bonds with friends and to develop new ones. They interact with people who they otherwise would not have met in the real world, becoming a tool for identity creation.[66]
They are the first generation to grow up in the public eye, and updating their lives on social media makes them a self-conscious generation. As a result, they experience more social pressure than previous generations. This exposure to technology has influenced their expectations and behavior. The boom of social media has a psychological impact on Generation Z because they attach great importance to personal appearance. According to the recent report by Fung Global, Generation Zers spent around $829.5 billion with $66 billion of which spent on discretionary categories, while most of the expenses were spent on essential categories: housing, good, transportation and so on.[68] The survey of US teenagers from an advertising agency J. Walter Thomson claims that the majority of teenagers are concerned about how their posting will be perceived by people or their friends. 72% of respondents said they were using social media on a daily basis, and 82% said they thought carefully about what they post on social media. Moreover, 43% said they had regrets about previous posts.[69]
Jason Dorsey, who runs the Center for Generational Kinetics, stated in a TEDxHouston talk that this generation begins after 1996 to present. He stressed notable differences in the way that Millennials and Generation Z consume technology, in terms of smartphone usage at an earlier age. 18% of Generation Z thinks that it is okay for a 13-year-old to have a smartphone compared with earlier generations that say 4%.[70][71][72]
The development of technology gave mobility and immediacy to Generation Z's consumption habits. The on-demand economy, defined as “the economic activity created by technology companies that fulfill consumer demand via the immediate provisioning of goods and service”,[73] has made changes in the way goods or services are delivered to consumers. Only the generation that grows up in the center of this transformation period will establish themselves as an immediacy demanding consumer.
Education
According to a Northeastern University Survey, 81% of Generation Z believes obtaining a college degree is necessary in achieving career goals.[74] As Generation Z enters high school, and they start preparing for college, a primary concern is paying for a college education without acquiring debt. Students report working hard in high school in hopes of earning scholarships and the hope that parents will pay the college costs not covered by scholarships. Students also report interest in ROTC programs as a means of covering college costs.[75] According to NeaToday, a publication by the National Education Association, two thirds of Gen Zers entering college are concerned about affording college. One third plan to rely on grants and scholarships and one quarter hope that their parents will cover the bulk of college costs. While the cost of attending college is incredibly high for most Gen Zers, according to NeaToday, 65% say the benefits of graduating college exceed the costs.[75]
Generation Z college students prefer intrapersonal and independent learning over group work, yet like to do their individual work alongside others when studying.[52] They like their learning to be practical and hands-on and want their professors to help them engage with and apply the content rather than simply share what they could otherwise find on their own online.[52]
"Generation Z" is revolutionizing the educational system in many aspects. Thanks in part to a rise in the popularity of entrepreneurship and advancements in technology, high schools and colleges across the globe are including entrepreneurship in their curriculum.[76] Parents of Generation Z might have the image of their child’s first business being a lemonade stand or car wash. While these are great first businesses, Generation Z now has access to social media platforms, website builders, 3d printers, and drop shipping platforms which provides them with additional opportunities to start a business at a young age. The internet has provided a store front for Generation Z to sell their ideas to people around the world without ever leaving their house.[77]
Political views
The examples and perspective in this section may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (August 2017) |
According to the Hispanic Heritage Foundation, U.S. members of Generation Z tend to be more conservative than Millennials. According to a survey of 83,298 Gen Z-aged students (defined here as those aged 14 to 18 in 2016) in the United States done by My College Options and the Hispanic Heritage Foundation in September and October 2016, 32% of participants supported Donald Trump, while 22% supported Hillary Clinton with 31% choosing to not vote in the election.[78][79] By contrast, in a 2016 mock election of upper elementary, middle, and high school students conducted by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Hillary Clinton beat Donald Trump among the students, with Clinton receiving 46% of the vote, Donald Trump receiving 41%, and other candidates receiving 12%.[80]
According to Generation Z Goes to College by Corey Seemiller and Meghan Grace, Generation Z is more likely to lean left. Gen Zers are passionate, social-change minded individuals who plan to change the world through their vocations. They want their politicians to remove laws that restrict some groups from receiving equal access, as well as support laws that protect underrepresented groups. They believe that ending discrimination is critical and will do what it takes to move towards a more equal and equitable society. Regarding education more than 80% are concerned about the rising cost of college tuition and if higher education is becoming financially out of reach even for middle-income families. Generation Z is highly concerned about financial security, not just for themselves, but for everyone. They want to ensure people today are financially secure while at the same time making sure that future generations are taken care of. Personal freedom is also important to Generation Z. They believe that people have the right to their own choices until they encroach on or harm others. When it comes to LGBT rights Gen Zers, even across party lines, overwhelmingly support same sex marriage, and nearly three-quarters believe that transgender people should have equal rights.[81]
Goldman Sachs analysts Robert Boroujerdi and Christopher Wolf describe Generation Z as "more conservative, more money-oriented, more entrepreneurial and pragmatic about money compared with Millennials".[82] According to a 2016 survey published from The Gild, a global brand consultancy, British Gen Zers, defined here as those born 2001 and onwards, are more conservative than Millennials, Gen Xers and Baby Boomers with respect to marijuana legalization, transgender issues and same sex marriage.[83] However, some argue that this study has several methodological problems such as non-random selection and double-barreled questions, rendering the study's findings unreliable in discerning the political ideologies of the generation.[84]
In a study conducted in 2015 the Center for Generational Kinetics found that American Generation Zers, defined here as those born 1996 and onwards, are less optimistic about the state of the US economy than their generation predecessors, Millennials.[85] In the same study, American Gen Zers were found to be less optimistic about the United States' trajectory in general, less concerned about illegal immigration than previous generations, and more concerned about the state of minorities in the US. Despite this, 78% of American Gen Zers believed the American Dream was attainable.[citation needed]
Employment prospects
According to Hal Brotheim in Introducing Generation Z, they will be better future employees.[86] With the skills needed to take advantage of advanced technologies, they will be significantly more helpful to the typical company in today's high tech world.[86] Brotheim argues that their valuable characteristics are their acceptance of new ideas and a different conception of freedom from the previous generations.[87]
Despite the technological proficiency they possess, members of Generation Z actually prefer person-to-person contact as opposed to online interaction. As a result of the social media and technology they are accustomed to, Generation Z is well prepared for a global business environment.[88] Another important note to point out is Generation Z no longer wants just a job: they seek more than that. They want a feeling of fulfillment and excitement in their job that helps move the world forward.[51] Generation Z is eager to be involved in their community and their futures. Before college, Generation Z is already out in their world searching how to take advantage of relevant professional opportunities that will give them experience for the future.[88]
In India, a 2016 survey by JobBuzz.in, an employee engagement and employer rating platform, showed Generation Z professionals started out better in the job market compared with the older Generation Y.[89]
Successors
Matt Carmichael, former director of data strategy at Advertising Age, noted in 2015 that many groups were "competing to come up with the clever name" for the generation following Generation Z.[90] Mark McCrindle has suggested "Generation Alpha" and "Generation Glass" as names for the cohort following Generation Z.[91][92][93] McCrindle has predicted that this next generation will be "the most formally educated generation ever, the most technology supplied generation ever, and globally the wealthiest generation ever".[91] He chose the name "Generation Alpha", noting that scientific disciplines often move to the Greek alphabet after exhausting the Roman alphabet.[91][92]
Author Alexandra Levit has suggested that there may not be a need to name the next generation, as she sees technology as having rendered the traditional 15–20 year cohorts obsolete. Levit notes that she "can't imagine my college student babysitter having the same experience as my four-year-old", despite both being in Generation Z.[90]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Horovitz, Bruce (4 May 2012). "After Gen X, Millennials, what should next generation be?". USA Today. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- ^ Howe, Neil; Strauss, William (2008). Millennials & K-12 Schools. LifeCourse Associates. pp. 109–111. ISBN 0-9712606-5-6.
- ^ a b Howe (27 October 2014). "Introducing the Homeland Generation (Part 1 of 2)". Forbes. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ a b Neil Howe and Bill Strauss (July–August 2007). "The Next 20 Years: How Customer and Workforce Attitudes Will Evolve". Harvard University. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ^ Junco, Reynol; Mastrodicasa, Jeanna (2007). Connecting to the Net.Generation: What higher education professionals need to know about today's students. NASPA. ISBN 978-0-931654-48-0.
- ^ Homan, Audrey (27 October 2015). "Z is for Generation Z". The Tarrant Institute for Innovative Education. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- ^ "Millennials overtake Baby Boomers as America's largest generation". Pew Research Center. Pew Research. 25 April 2016. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
- ^ "Projected Population by Generation". Millennials overtake Baby Boomers as America's largest generation. Pew Research. 25 April 2016. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
- ^ "Birth Under Each Generation". Millennials overtake Baby Boomers as America's largest generation. Pew Research. 25 April 2016. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
- ^ "MC Lars – iGeneration — Critical Commons".
- ^ Samantha Raphelson (6 October 2014). "From GIs To Gen Z (Or Is It iGen?): How Generations Get Nicknames". NPR. Retrieved 7 October 2014.
- ^ a b c "The First Generation of the 21st Century: An Introduction to the Pluralist Generation" (PDF). Magid Generational Strategies. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Turner Says the Post-Millennial Generation Should Be Known as 'Plurals'". AdWeek. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
- ^ DeBord, Mathew. "A new generation gets a name: Plurals." DeBord Report. 30 April 2012
- ^ a b Sunburn, Josh (1 December 2015). "Here's What MTV Is Calling the Generation After Millennials". Time. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ^ a b Williams, Alex (18 September 2015). "How to Spot a Member of Generation Z". New York Times. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ a b "Centennial Infographic – The Futures Company". The Futures Company. Retrieved 9 March 2016.
- ^ "Generations in Canada".
- ^ a b Thomas, Michael (19 April 2011). Deconstructing Digital Natives: Young People, Technology, and the New Literacies. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-136-73900-2.
- ^ a b Takahashi, Toshie T. "Japanese Youth and Mobile Media". Rikkyo University. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- ^ "The Generation Z effect". The Globe and Mail.
- ^ "Generations in Canada". Statistics Canada. 2011. Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ "How to attract and engage Millenials: Gen Y + Gen Z". RandstadCanada. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ "managing Gen Y and Z in the workplace". Randstad USA. Retrieved 23 June 2016.
- ^ Generations Defined. Mark McCrindle
- ^ Oster, Erik (21 August 2014). "This Gen Z Infographic Can Help Marketers Get Wise to the Future Here come the social natives". Adweek. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ "Have Smartphones Destroyed a Generation?". The Atlantic. Retrieved 26 September 2017.
- ^ Lilley, Kevin. "Post-millennial military: What to expect from the next generation". Military Times. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ Twenge, Jean M.; Sherman, Ryne A.; Wells, Brooke E. (1 August 2016). "Sexual Inactivity During Young Adulthood Is More Common Among U.S. Millennials and iGen: Age, Period, and Cohort Effects on Having No Sexual Partners After Age 18". Arch Sex Behav: 1–8. doi:10.1007/s10508-016-0798-z – via link.springer.com.
- ^ van der Bergh, Behrer, Joeri, Mattias (2011). How cool brands stay hot: branding to generation y. United States: Kogan Page. ISBN 0-7494-6250-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Merriman, Marcie (2015). "Rise of Gen Z: new challenge for retailers" (PDF). ey.com. EYGM Limited. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- ^ "Turner Research Shares Key Insights on Plurals and Millennials' Media Consumption and Consumer Behavior During Thought Leadership Event in New York". www.turner.com. Turner Broadcasting System. 14 January 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ^ Sh, The; Group (3 December 2015). "Getting Ready for Generation – Z". The Shand Group. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
{{cite web}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - ^ Wolf, Christopher (4 March 2016). "Gen-Z Matters More than Millennials". Goldman Sachs. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ "THE THAI MARKET TO WATCH AND THEIR PLAYERS: GENERATION Y – THE DRIVING FORCE OF CONSUMPTION TRENDS IN THAILAND". Corporate Directions Inc. 15 March 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Introducing the tech-savvy Generation Z". Philippine Retailers Association. 16 September 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ Fishman, Ann (August 2015). "Who Comes After the Millennials?: A Case for 'Gen 9/11'". American Marketing Association.
- ^ a b Dill, Kathryn (6 November 2015). "7 Things Employers Should Know About The Gen Z Workforce". Forbes. Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- ^ "A Look Into the Minds of Generation Z Consumers". The Atlas Business Journal. 29 December 2016. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ a b Frank N. Magid Associates. "The First Generation of the Twenty First Century." Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine 30 April 2012
- ^ Williams, Alex (18 September 2015). "Move Over, Millennials, Here Comes Generation Z". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ Beltramini, Elizabeth (October 2014). "Gen Z: Unlike the Generation Before". Associations of College Unions International. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ Jenkins, Ryan (9 June 2015). "15 Aspects That Highlight How Generation Z Is Different From Millennials". Business2Community. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ Quigley, Mary (7 July 2016). "The Scoop on Millennials' Offspring — Gen Z". AARP. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
- ^ Dupont, Stephen (10 December 2015). "Move Over Millennials, Here Comes Generation Z: Understanding the 'New Realists' Who Are Building the Future". Public Relations Tactics. Public Relations Society of America.
- ^ a b Henderson, J Maureen (31 July 2013). "Move Over, Millennials: Why 20-Somethings Should Fear Teens". Forbes. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- ^ Turner, Anthony (1 June 2015). "Generation Z: Technology and Social Interest". Journal of Individual Psychology.
- ^ "Column: High-maintenance Generation Z heads to work". USATODAY.COM. Retrieved 17 December 2015.
- ^ Palmer, Alun (1 August 2014). "Are you X, Y, Z, Boomer or Silent Generation – what does it mean for you?".
- ^ a b Turner, Anthony (2015). "Generation Z: Technology And Social Interest". Journal of Individual Psychology. 71 (2): 103–113. doi:10.1353/jip.2015.0021.
- ^ a b c d Williams, Alex (18 September 2015). "Move Over, Millennials, Here Comes Generation Z". New York Times. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Seemiller, Corey (2016). Generation Z Goes to College. Jossey-Bass. ISBN 978-1-119-14345-1.
- ^ Amiama-Espaillat, Cristina; Mayor-Ruiz, Cristina (2017). "Digital Reading and Reading Competence – The influence in the Z Generation from the Dominican Republic". Comunicar (in Spanish). 25 (52): 105–114. doi:10.3916/c52-2017-10. ISSN 1134-3478.
- ^ Hope, J (2016). "Get your campus ready for Generation Z". Dean & Provost. 17 (8): 1–7. doi:10.1002/dap.30174.
- ^ "Generation Z Breaks Records in Education and Health Despite Growing Economic Instability of Their Families". PR Newswire. 21 June 2016. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ Blad, Evie (21 June 2016). "Teenagers' Health, Educational Outcomes Improving, Report Finds". Education Week. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ "Gen Z, Gen Y, baby boomers – a guide to the generations". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
- ^ Prensky, Marc (2001). "Digital Natives, Digital Immigrants Part 1". On the Horizon.
- ^ "Lookout". www.lookout.com. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ^ "Meet Generation Z: Forget Everything You Learned About Millennials". Sparks and Honey. 17 June 2014. p. 39. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ a b "Should CellPhones Be Allowed in School?". education.cu-portland.edu. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ^ a b "Mobile and interactive media use by young children: The good, the bad and the unknown". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ^ Regine (28 March 2005). "Owning a cell phone is rite of passage for teenagers". Textuality.org. Archived from the original on 11 December 2015. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Lenhart, Amanda (8 April 2015). "Teens, Social Media & Technology Overview 2015". Pew Research Center. Pew Research Center Internet Science Tech RSS. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
- ^ a b c Madden, Mary; et al. (21 May 2013). "Teens, Social Media, and Privacy". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ^ a b c Borca, Gabriella; Bina, Manuela; Keller, Peggy S.; Gilbert, Lauren R.; Begotti, Tatiana (1 November 2015). "Internet use and developmental tasks: Adolescents' point of view". Computers in Human Behavior. 52: 49–58. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2015.05.029.
- ^ Borca. "Internet Use".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ DEBORAH, WEINSWIG (29 August 2016). "Gen Z: Get Ready for the Most Self-Conscious, Demanding Consumer Segment" (FUNG GLOBAL RETAIL & TECHNOLOGY): 2.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ J. Walter Thompson. "CONSUMER INSIGHTS, J. WALTER THOMPSON INTELLIGENCE Meet Generation Z". Retrieved 22 May 2017.
- ^ "Jason Dorsey TEDx Talk On Generation After Millennials: iGen Gen Z". Jason Dorsey. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ^ TEDx Talks (18 November 2015), What do we know about the generation after millennials? | Jason Dorsey | TEDxHouston, retrieved 6 April 2016
- ^ Dorsey, Jason (2016). "iGen Tech Disruption" (PDF). Center for Generational Kinetics. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ^ Mike, Jaconi. "The 'On-Demand Economy' Is Revolutionizing Consumer Behavior". Tech Insider. Retrieved 22 May 2017.
- ^ "'Generation Z' is entrepreneurial, wants to chart its own future | news @ Northeastern". www.northeastern.edu. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ^ a b Hawkins, B. Denise. "Here Comes Generation Z. What Makes Them Tick?". NEA Today. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ^ "'Generation Z' is entrepreneurial, wants to chart its own future – news @ Northeastern".
- ^ "'Can a kid start a business?'". Entrepreneur School. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ "50k 'Gen Z' Students Identify as Republican – Hispanic Heritage Foundation". hispanicheritage.org. Retrieved 23 December 2016.
- ^ Tijerino, Antonio. "Trumping the Super Youth Vote Too". No. 13 February 2017. Huffington Post. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "America's Youth Have Spoken: Hillary Clinton Is Generation Z's Choice for President". Retrieved 26 February 2017.
- ^ https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/generation-zs-perspectivesand-why-presidential-should-seemiller-phd/?trk=prof-post
- ^ "Goldman Sachs chart of the generations". Business Insider. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ^ "Gen Z is the most conservative generation since those born before 1945". Marketing Communication News. 22 October 2016. Archived from the original on 22 October 2016. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Boysen, Anne (6 January 2017). "Why Generation Z is not more conservative".
- ^ "Infographic: Gen Z Voter and Political Views Election 2016".
- ^ a b Brotheim, Hal (2014). Introducing Generation Z. American Jail Association. p. 15.
- ^ "5 Reasons Why Millennial Leaders Need Performance Feedback". 22 September 2017. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ^ a b Levit, Alexandra (28 March 2015). "Make Way for Generation Z". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 22 December 2015.
- ^ "India – Generation Z professionals start out better in jobs market than Generation Y". No. 10 May 2016. Staffing Industry Analysis. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- ^ a b Vanderkam, Laura (10 August 2015). "What comes after Generation Z?". Fortune. Retrieved 22 December 2015.
- ^ a b c Williams, Alex (19 September 2015). "Meet Alpha: The Next 'Next Generation'". New York Times. Retrieved 18 December 2015.
- ^ a b Sterbenz, Christina (6 December 2015). "Here's who comes after Generation Z – and they're going to change the world forever". Business Insider. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ^ McCrindle, Mark (2010). The ABC of XYZ. Australia: University of New South Wales. ISBN 978-1-74223-035-1.
External links
- Meet Generation Z: Forget Everything You Learned About Millennials – 2014 presentation by Sparks and Honey
- Combi, Chloe (2015). Generation Z: Their Voices, Their Lives. London: Hutchinson.
- Palfrey, John; Gasser, Urs (2008). Born Digital: Understanding the First Generation of Digital Natives. Basic Books.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - McCrindle, Mark; Wolfinger, Emily (2014). The ABC of XYZ: Understanding the Global Generations. McCrindle Research.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
