Portal:Fungi
The Fungi Portal
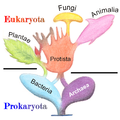
A fungus is any member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. The Fungi are classified as a kingdom that is separate from plants and animals. The discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology or fungal biology, which is historically regarded as a branch of botany, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants. Fungi reproduce via spores and grow as hyphae, mycelia, and futher specialized structures. Fungal spores are often produced on specialized structures or in fruiting bodies, such as the head of a mushroom. Abundant worldwide, most fungi are mostly invisible to the naked eye because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts of plants, animals, or other fungi. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation of various food products, such as wine, beer, and soy sauce.
Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotics, and, more recently, various enzymes produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological agents to control weeds and pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxins, such as alkaloids and polyketides, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species are consumed recreationally or in traditional ceremonies as a source of psychotropic compounds. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogens of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies and local economies. Despite their importance on human affairs, little is known of the true biodiversity of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified.
| More about fungi... |
Selected article
The colour of the L. volemus mushroom varies from apricot to tawny, and the cap may be up to 11 cm (4.3 in) wide. The pale golden yellow gills on the underside of the cap are closely spaced and sometimes forked. One of the mushroom's most distinctive features is the large amount of latex ("milk") that it exudes when the gills are damaged, leading to the common names weeping milk cap and voluminous-latex milky. It also has a distinctive fishy smell, which does not affect the taste. The fruit bodies have been chemically analysed and found to contain several sterols related to ergosterol, some of which are unique to this species. The mushroom also contains a natural rubber that has been chemically characterized. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that Lactarius volemus represents several species or subspecies, rather than a single taxon.
Selected species
The fruit bodies produced by the fungus have caps which can reach up to 10 cm (3.9 in) in diameter. They are pink-flesh colored, with whitish concentric zones. The edge of the cap is rolled inwards, and shaggy when young. On the underside of the caps are flesh-colored gills crowded closely together. It is on these fertile gill surfaces that the spore-bearing cells, the basidia are found. The cylindrical stem is a pale flesh color with a delicately downy surface, reaching lengths of up to 8 cm (3.1 in). When cut or injured, the fruit bodies ooze a white latex that does not change color upon exposure to air. The variety normandensis, in contrast, has latex that changes color from white to yellow.
Things to do
If you want to help Wikipedia to improve its coverage of fungi, here are some things you can do...
- Assess some fungi articles.
- Join Wikipedia:WikiProject Fungi or ask on the talk page.
- Join the lichen task force.
- Review, improve, expand or clean some of the newly created fungi-related articles.
- Expand some high priority fungus stubs.
- Expand or sort other fungi-related stubs.
- Add images to articles in the list of unillustrated fungi articles, or add more articles to the list.
- Write fungi-related articles from scratch. For ideas of needed articles, see the redlinks on-
- Review the fungi articles flagged as needing attention.
WikiProjects
WikiProjects related to fungi:
Selected picture

Did you know?
- ... that Spinellus fusiger is a pin mold that parasitizes several species of mushrooms?
- ... that the mushrooms Boletus zelleri, B. mirabilis, Suillus americanus, S. brevipes, S. lakei, and Leccinum manzanitae are all examples of edible boletes?
- ... that application of iron salts will turn a white coral green?
- ... that despite its name, the edibility of the rhubarb bolete is unknown?
- ... that the mica cap mushroom has glistening particles on top that are remnants of a universal veil?
General images -
Related portals
Topics
- Main topics lists: Outline of fungi and Outline of lichens
- Fungi: Bracket fungus, carnivorous fungus, coprophilous fungi, entomopathogenic fungus, evolution of fungi, lichen, mushroom, mycology (lichenology, mycotoxicology, paleomycology), mycorrhiza, pathogenic fungi, puffball, wood-decay fungus
- Fungal orders: Chytridiomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Neocallimastigomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota. Dikarya: Ascomycota, Basidiomycota
- Fungi lists: Species: Agaricus species, Amanita species, Boletus species, Cortinarius species, Cyathus species, Hygrocybe species, Hygrophorus species, Inocybe species, Lactarius species, Mycosphaerella species, Panaeolus species, Psilocybe species, Russula species, Scleroderma species Other lists: Mycology journals, psilocybin mushrooms
- Uses: Edible mushroom, mushroom poisoning, psilocybin mushrooms, mushroom hunting, fungiculture, fermentation, baker's yeast, mycoremediation, lichenometry, mushroom dye






























![Image 27Pennate diatom from an Arctic meltpond, infected with two chytrid-like [zoo-]sporangium fungal pathogens (in false-colour red). Scale bar = 10 µm. (from Marine fungi)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b5/Pennate_diatom_infected_with_two_chytrid-like_fungal_pathogens.png/120px-Pennate_diatom_infected_with_two_chytrid-like_fungal_pathogens.png)































