From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
4-Fluorophenibut Other names CGP-11130; β-(4-Fluorophenyl)-γ-aminobutyric acid; β-(4-Fluorophenyl)-GABA; Baflofen; Fluorophenibut; F-Phenibut; Fluoribut Routes of By mouth
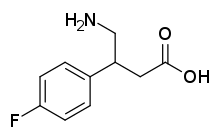
4-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)butanoic acid
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider Formula C 10 H 12 F N O 2 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
C1=CC(=CC=C1C(CC(=O)O)CN)F
InChI=1S/C10H12FNO2/c11-9-3-1-7(2-4-9)8(6-12)5-10(13)14/h1-4,8H,5-6,12H2,(H,13,14)
Key:QWHXHLDNSXLAPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
4-Fluorophenibut (developmental code name CGP-11130 ; also known as β-(4-fluorophenyl)-γ-aminobutyric acid or β-(4-fluorophenyl)-GABA ) is a GABAB receptor agonist which was never marketed.[1] selective for the GABAB receptor over the GABAA receptor (IC50 = 1.70 µM and > 100 µM, respectively).[1] GABA analogue and is closely related to baclofen (β-(4-chlorophenyl)-GABA), tolibut (β-(4-methylphenyl)-GABA), and phenibut (β-phenyl-GABA).[1] B receptor agonist than baclofen but more potent than phenibut.[1]
The substance is sometimes referred to as 4F-phenibut or F-phenibut and colloquially as fluorobut .
References
Ionotropic
GABAA Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid A receptor
Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL Alcohols (e.g., drinking alcohol , 2M2B )Anabolic steroids Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital )Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam )Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide )Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid )Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin , hispidulin )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate )Kava constituents (e.g., kavain )Lanthanum Loreclezole Monastrol Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone , cholesterol , THDOC )Niacin Niacinamide Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., abecarnil ), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone ), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem ), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon ))Norfluoxetine Petrichloral Phenols (e.g., propofol )Phenytoin Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide )Propanidid Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate )Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone )Retigabine (ezogabine) ROD-188 Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin )Stiripentol Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid )Volatiles /gases (e.g., chloral hydrate , chloroform , diethyl ether , paraldehyde , sevoflurane )Negative modulators: 1,3M1B 3M2B 11-Ketoprogesterone 17-Phenylandrostenol α3IA α5IA (LS-193,268) β-CCB β-CCE β-CCM β-CCP β-EMGBL Anabolic steroids Amiloride Anisatin β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins , cephalosporins , carbapenems )Basmisanil Bemegride Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS , TBPO , IPTBO )BIDN Bilobalide Bupropion CHEB Chlorophenylsilatrane Cicutoxin Cloflubicyne Cyclothiazide DHEA DHEA-S Dieldrin (+)-DMBB DMCM DMPC EBOB Etbicyphat FG-7142 (ZK-31906) Fiproles (e.g., fipronil )Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone , oroxylin A )Flumazenil Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin )Flurothyl Furosemide Golexanolone Iomazenil (123 I) IPTBO Isopregnanolone (sepranolone) L-655,708 Laudanosine Lindane MaxiPost Morphine Morphine-3-glucuronide MRK-016 Naloxone Naltrexone Nicardipine Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., apalutamide , bicalutamide , enzalutamide , flutamide , nilutamide )Oenanthotoxin Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol) Phenylsilatrane Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin , picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin )Pregnenolone sulfate Propybicyphat PWZ-029 Radequinil Ro 15-4513 Ro 19-4603 RO4882224 RO4938581 Sarmazenil SCS Suritozole TB-21007 TBOB TBPS TCS-1105 Terbequinil TETS Thujone U-93631 Zinc ZK-93426 GABAA -ρ Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid A-rho receptor
Metabotropic
GABAB Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid B receptor