Lead tetrafluoride
Appearance
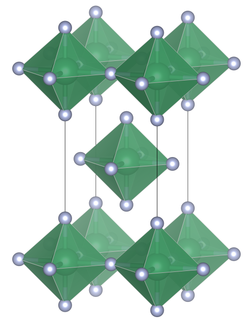 Unit cell of lead tetrafluoride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetrafluoroplumbane
| |
| Other names
Lead(IV) fluoride
Lead tetrafluoride Tetrafluoridolead Tetrafluoroplumbous anhydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.102 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PbF4 | |
| Molar mass | 283.194 g/mol [1] |
| Appearance | white to beige crystals [2] |
| Density | 6.7 g/cm3 [2] |
| Melting point | 600 °C (1,112 °F; 873 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lead tetrafluoride is a compound of lead and fluorine. The yellow solid (melting point 600 °C) is the only room-temperature stable tetrahalide of lead.[3] Lead tetrafluoride is isostructural with tin(IV) fluoride and contains planar layers of octahedrally coordinated lead, where the octahedra share four corners and there are two terminal, unshared, fluorine atoms trans to one another.[4]
References
- ^ "Lead(IV) fluoride | F4Pb - PubChem". Archived from the original on 2017-02-22. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ^ a b c "Lead Tetrafluoride | 7783-59-7".
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 375–376, 381–382. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Inorganic Chemistry [Paperback],2d Edition, Housecroft, Sharpe,2004, Pearson Education ISBN 0130399132, ISBN 978-0130399137
