May 1966 lunar eclipse

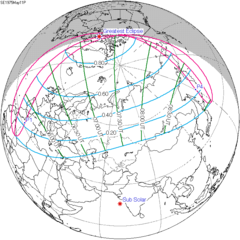
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on May 4, 1966. It was visible from South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia and Antarctica.[1]
Visibility
Related lunar eclipses
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1966–1969 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 111 | 1966 May 4
|
Penumbral
|
1.05536 | 116 | 1966 Oct 29
|
Penumbral
|
−1.05999 | |
| 121 | 1967 Apr 24
|
Total
|
0.29722 | 126 | 1967 Oct 18
|
Total
|
−0.36529 | |
| 131 | 1968 Apr 13
|
Total
|
−0.41732 | 136 | 1968 Oct 6
|
Total
|
0.36054 | |
| 141 | 1969 Apr 2
|
Penumbral
|
−1.17648 | 146 | 1969 Sep 25
|
Penumbral
|
1.06558 | |
| Last set | 1965 Jun 14 | Last set | 1965 Dec 8 | |||||
| Next set | 1970 Feb 21 | Next set | 1969 Aug 27 | |||||
Saros series
Lunar Saros 111, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 11 total lunar eclipses. The first total lunar eclipse of this series was on April 19, 1353, and last was on August 4, 1533. The longest occurrence of this series was on June 12, 1443 when the totality lasted 106 minutes.
Metonic series
The metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Metonic events: May 4 and October 28 | |
|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node |
|
|

|

|
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two solar eclipses of Solar Saros 118.
| April 30, 1957 | May 11, 1975 |
|---|---|

|
|
See also
Notes
- ^ Hermit Eclipse: Saros cycle 111
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- 1966 May 04 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC




