Primary somatosensory cortex
| Primary somatosensory cortex | |
|---|---|
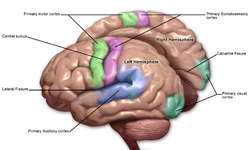 Primary somatosensory cortex labeled in purple | |
 Primary somatosensory cortex: Secondary image. | |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy |
The primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus, and is part of the somatosensory system. It was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and parallel surface potential studies of Bard, Woolsey, and Marshall. Although initially defined to be roughly the same as Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2, more recent work by Kaas has suggested that for homogeny with other sensory fields only area 3 should be referred to as "primary somatosensory cortex", as it receives the bulk of the thalamocortical projections from the sensory input fields.[1]
At the primary somatosensory cortex, tactile representation is orderly arranged (in an inverted fashion) from the toe (at the top of the cerebral hemisphere) to mouth (at the bottom). However, some body parts may be controlled by partially overlapping regions of cortex. Each cerebral hemisphere of the primary somatosensory cortex only contains a tactile representation of the opposite (contralateral) side of the body. The amount of primary somatosensory cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to the absolute size of the body surface, but, instead, to the relative density of cutaneous tactile receptors on that body part. The density of cutaneous tactile receptors on a body part is generally indicative of the degree of sensitivity of tactile stimulation experienced at said body part. For this reason, the human lips and hands have a larger representation than other body parts.
Structure

Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2
Brodmann areas 3, 1, and 2 make up the primary somatosensory cortex of the human brain (or S1). Because Brodmann sliced the brain somewhat obliquely, he encountered area 1 first; however, from anterior to posterior, the Brodmann designations are 3, 1, and 2, respectively.
Brodmann area (BA) 3 is subdivided into areas 3a and 3b. Where BA 1 occupies the apex of the postcentral gyrus, the rostral border of BA 3a is in the nadir of the Central sulcus, and is caudally followed by BA 3b, then BA 1, with BA 2 following and ending in the nadir of the postcentral sulcus. BA 3b is now conceived as the primary somatosensory cortex because 1) it receives dense inputs from the NP nucleus of the thalamus; 2) its neurons are highly responsive to somatosensory stimuli, but not other stimuli; 3) lesions here impair somatic sensation; and 4) electrical stimulation evokes somatic sensory experience. BA 3a also receives dense input from the thalamus; however, this area is concerned with proprioception.
Areas 1 and 2 receive dense inputs from BA 3b. The projection from 3b to 1 primarily relays texture information; the projection to area 2 emphasizes size and shape. Lesions confined to these areas produce predictable dysfunction in texture, size, and shape discrimination.
Somatosensory cortex, like other neocortex, is layered. Like other sensory cortex (i.e., visual and auditory) the thalamic inputs project into layer IV, which in turn project into other layers. As in other sensory cortices, S1 neurons are grouped together with similar inputs and responses into vertical columns that extend across cortical layers (e.g., As shown by Vernon Mountcastle, into alternating layers of slowly adapting and rapidly adapting neurons; or spatial segmentation of the vibrissae on mouse/rat cerebral cortex).
This area of cortex, as shown by Wilder Penfield and others, is organized somatotopically, having the pattern of a homunculus. That is, the legs and trunk fold over the midline; the arms and hands are along the middle of the area shown here; and the face is near the bottom of the figure. While it is not well-shown here, the lips and hands are enlarged on a proper homunculus, since a larger number of neurons in the cerebral cortex are devoted to processing information from these areas.
The positions of Brodmann areas 3, 1, and 2 are - from the nadir of the central sulcus toward the apex of the postcentral gyrus - 3a, 3b, 1, and 2, respectively.
These areas contain cells that project to the secondary somatosensory cortex.
Clinical significance
Lesions affecting the primary somatosensory cortex produce characteristic symptoms including: agraphesthesia, astereognosia, hemihypesthesia, and loss of vibration, proprioception and fine touch (because the third-order neuron of the medial-lemniscal pathway cannot synapse in the cortex). It can also produce hemineglect, if it affects the non-dominant hemisphere. Destruction of brodmann area 3, 1, and 2 results in contralateral hemihypesthesia and astereognosis.
It could also reduce nociception, thermoception, and crude touch, but, since information from the spinothalamic tract is interpreted mainly by other areas of the brain (see insular cortex and cingulate gyrus), it is not as relevant as the other symptoms.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ Viaene A.N.; et al. (2011). "synaptic properties of thalamic input to layers 2/3 and 4 of primary somatosensory and auditory cortices". Journal of Neurophysiology. 105 (1): 279–292. doi:10.1152/jn.00747.2010. PMC 3023380. PMID 21047937.
External links
- ancil-1040 at NeuroNames - area 1
- ancil-1041 at NeuroNames - area 2
- ancil-1042 at NeuroNames - area 3
