Barito River
| Barito River Sungai Barito, Sungai Dusun, Soengai Doesoen, Sungi Banjer, Sungi Dunsun, Soengai Baritoe, Sungai Banjar, Sungai Banjarmasin, Sungai Banjar Besar | |
|---|---|
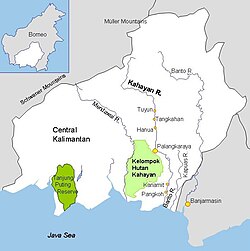 Barito and other rivers in Central and South Kalimantan | |
| Location | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Müller Mountain Range |
| Mouth | |
• location | Java Sea |
• coordinates | 3°30′55″S 114°29′28″E / 3.51528°S 114.49111°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 1,090 km (680 mi) |
| Basin size | 81,675 km2 (31,535 sq mi)[1] |
| Width | |
| • minimum | 300 m (980 ft) |
| • average | 650 m (2,130 ft) to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) |
| • maximum | 2,000 m (6,600 ft) |
| Depth | |
| • minimum | 3 m (9.8 ft) |
| • average | 7 m (23 ft) to 8 m (26 ft) |
| • maximum | 25 m (82 ft) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Barito Delta, Java Sea, Indonesia, Borneo (Kalimantan) |
| • average | (Period: 2008–2015)5,497 m3/s (194,100 cu ft/s)[1]
(Period of data: 2003–2016)4,514 m3/s (159,400 cu ft/s)[2] (Period: 1970–2000)129 km3/a (4,100 m3/s)[3] |
| • maximum | 27,000 m3/s (950,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Banjarmasin (Basin size: 61,582 km2 (23,777 sq mi) |
| • average | (Period of data: 2006–2011)4,502 m3/s (159,000 cu ft/s)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Barito–Kapuas–Kahayan Delta (Basin size: 98,500 km2 (38,000 sq mi) |
| • average | 7,000 m3/s (250,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Barito basin (DAS330363)[5] |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Mangkatip, Negara River, Martapura River |
| • right | Murung River, Anjir Tamban, Anjir Serapat, Kapuas River (Barito River tributary)[6] |

The Barito River is the second longest river in Borneo after the Kapuas River with a total length of 1,090 km (680 mi) and a drainage basin of 81,675 square kilometers (31,535 sq mi) in South Kalimantan, Indonesia. It originates in the Muller Mountain Range, from where it flows southward into the Java Sea. Its most important affluent is the Martapura River, and it passes through the city of Banjarmasin.[7][8]
This river is the location of the closest relative of the Malagasy language of Madagascar, the Ma'anyan language of Dayaks, from where settlers arrived in Madagascar (presumably in waves) from the 3rd to 10th century and from which the current island nation's population largely traces its origins.
Geography
[edit]The river flows in the southeast area of Borneo with a predominantly tropical rainforest climate (designated as Af in the Köppen-Geiger climate classification).[9] The annual average temperature in the area is 24 °C (75 °F). The warmest month is October, when the average temperature is around 26 °C (79 °F), and the coldest is January, at 20 °C (68 °F).[10] The average annual rainfall is 2,735 millimeters (107.7 inches). The wettest month is December, with an average of 437-millimeter (17.2 in) rainfall, and the driest is September, with a 62-millimeter (2.4 in) rainfall.[11]
Images
[edit]-
Dutch boat on the Barito River (1917)
-
Inhabitants along the Barito
-
A boat on the Barito
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Strategi & Kebijakan Pengelolaan Wilayah Sungai Barito - Kapuas dalam Rangka Mendukung Pengembangan Kawasan Perkotaan yang Berkelanjutan (Slide deck) (in Indonesian) – via Scribd.
- ^ Ting-Hsuan, Huang; Chen-Tung, Arthur Chen; Hsiao-Chun, Tseng; Jiann-Yuh, Lou; Shu Lun, Wang; Liyang, Yang; Selvaraj, Kandasamy; Xuelu, Gao; Jough-Tai, Wang; Edvin, Aldrian; G.S., Jacinto; Gusti Z., Anshari; Penjai, Sompongchaiyakul; B.J., Wang (May 2017). "Riverine carbon fluxes to the South China Sea: Riverine carbon fluxes to the SCS". Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences. 122 (5): 1239–1259. doi:10.1002/2016JG003701. S2CID 135024272.
- ^ Djoko, Suwarno; Ansje, Löhr; Carolien, Kroeze; Budi, Widianarko (2013). "Past and future trends in nutrient export by 19 rivers to the coastal waters of Indonesia". Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences. 10 (1): 55–71. doi:10.1080/1943815X.2013.772902.
- ^ Daniel, Stapper (2011). Artisanal Gold Mining, Mercury and Sediment in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia (PDF) (MS thesis). University of Victoria.
- ^ Hukum Online. "Keputusan Menteri Kehutanan No. SK.511/MENHUT-V/2011" (in Indonesian).
- ^ M. K. Adamy (2 April 2012). "Sungai Barito Potensi Alam yang Diabaikan". Pemerintah Provinsi Kalimantan Tengah (in Indonesian). Archived from the original on 16 May 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- ^ "Annette Delarbre". Tijdschrift voor Nederlandsch Indië (in Dutch). Vol. 1. Ter Lands-drukkerij. 1838. p. 6.
- ^ Buddingh, Steven Adriaan (1861). Neêrlands-Oost-Indië: Reizen over Java, Madura, Makasser, Saleijer, Bima, Menado, Sangier-eilanden, Talau-eilanden, Ternate, Batjan, Gilolo en omliggende eilanden, Banda-eilanden, Amboina, Haroekoe, Saparoea, Noussalaut, Zuidkust van Ceram, Boeroe, Boano, Banka, Palembang, Riouw, Benkoelen, Sumatra's West-Kust, Floris, Timor, Rotty, Borneo's West-Kust, en Borneo's Zuid- en Oost-Kust; gedaan gedurende het tijdvak van 1852-1857 (in Dutch). M. Wijt. pp. 442.
de groote Banjersche rivier (de Barito).
- ^ Peel, M. C.; Finlayson, B. L.; McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification". Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. 11 (5): 1633–1644. Bibcode:2007HESS...11.1633P. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "NASA Earth Observations Data Set Index". NASA. 30 January 2016. Archived from the original on 11 May 2020. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- ^ "NASA Earth Observations: Rainfall (1 month - TRMM)". NASA/Tropical Rainfall Monitoring Mission. 30 January 2016. Archived from the original on 11 May 2020. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
External links
[edit] Media related to Barito River at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Barito River at Wikimedia Commons