Forest Hill, Toronto
Forest Hill | |
|---|---|
Neighbourhood | |
 | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| City | |
| Incorporated | 1923 (Village) |
| Changed Region | 1954 |
| Annexed | 1967 into Toronto |
Forest Hill is a neighbourhood and former village in Toronto, Canada, located north of downtown. The village was amalgamated into Toronto in 1967 and the area has retained its name as a neighbourhood. Along with other neighbourhoods such as The Kingsway, Rosedale, and The Bridle Path, it is one of Toronto’s wealthiest and most affluent neighbourhoods. It is home to many prominent Toronto business people, doctors, and lawyers. Census data from Statistics Canada states an average income for all private households in Forest Hill to be $101,631, compared to the $40,704 average income in Toronto's Census Metropolitan Area.[1]
History
Forest Hill was originally incorporated as a village in 1923, and later annexed by the City of Toronto in 1967, along with the Village of Swansea. The village was named after the summer home of John Wickson; previously it had been known as Spadina Heights (a name that continued to be applied to the neighbourhood into the twentieth century). Spadina Heights is a derivative of the First Nations (namely Ojibwe) word ishapadenah, meaning a hill or sudden rise in land. Rather than electing a mayor as in a city, the leading municipal official was the reeve of the village.
In the late 1960s, the City of Toronto planned to construct a highway that would run from Highway 401 to downtown Toronto via the Cedarvale Ravine and Spadina Road. Forest Hill and the Annex would be bisected by the proposed route and numerous local houses would be sacrificed for the new expressway. This prompted local residents to rise to protest and raise the awareness of the greater public. The provincial government was forced to withdraw its support for the so-called Spadina Expressway in 1971.
The Forest Hill War Memorial was erected by Page and Steele Architects on Eglinton Avenue in 1980, in memory of those who lost their lives in the First and Second World Wars.[2]
When the neighbourhood was annexed by the City of Toronto, the annexation agreement granted local residents the right to have their garbage picked up from their doorstep rather than from the curb. It wasn't until 1993 that the public learned that this extra service cost $420,000 a year and was paid for by the municipal government. This time, the public opinion of other Torontonians forced the city to discontinue this favour to Forest Hill residents.[3]
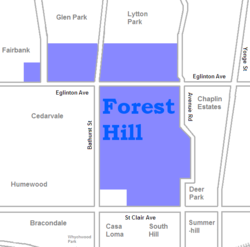
The neighbourhood's original boundaries were Bathurst Street to the west, Upper Canada College to the east, Eglinton Avenue to the north, and Lonsdale Road and a portion of Montclair Avenue to the south (the original boundaries of School Section 30). Neighbourhoods north of Eglinton are sometimes though not unanimously regarded as Forest Hill. In 1999 Robert Fulford compared Forest Hill to Rosedale, the other traditional home of Toronto's elite: "While Rosedale has remained stable for half a century, Forest Hill's prestige has been growing steadily. There's a key tonal difference in the architecture of the two places: where big Rosedale houses shout 'history,' big Forest Hill houses shout 'grandeur.' More than any other district in the central city, Forest Hill has become the site of spectacular new 'neo-traditional' homes built on a grand scale, usually with lawns to match."[4]
Forest Hill North and South district overview
Currently, for the purposes of social policy analysis & research, the city of Toronto’s Social Development & Administration division divides Forest Hill into two neighbourhoods: Forest Hill North and Forest Hill South.
Forest Hill Village is the commercial part of Forest Hill, a short block along Spadina Road, on either side of Lonsdale. Forest Hill extends roughly from Briar Hill Avenue in the north (the Upper Village, officially part of Forest Hill North) to Heath Street in the south (the Lower Village, officially the major part of Forest Hill South along Spadina Road between Bathurst Street/Cedarvale Ravine (whichever is further east) and Avenue Road. The designations Upper and Lower are based on height of land and not on positions on a map or along a watercourse.
Forest Hill Village was completely developed by the 1930s[3] and is known for its upscale shopping and dining, although the actual mix of stores includes several modest enterprises. Forest Hill Village has attracted extensive residential development (especially of apartments), both within the original boundaries of Forest Hill and in adjacent neighbourhoods to which developers have now extended the Village and Forest Hill names.
The Upper Village was slower to develop due to the fact it had previously been occupied by the old Belt Line Railway, and then by industry.[5] Its houses were built mostly in the 1940s and 50's. Many homes have been, or are being significantly renovated, with some being torn down completely to make way for monster 'neo-classical' homes.[3]

Forest Hill North extends from Briar Hill Avenue in the north to Eglinton Avenue West in the south, and from Latimer Avenue in the east to Allen Road and Marlee Avenue in the north-west and south-west, respectively. For administrative purposes, Forest Hill North is Toronto neighbourhood #102.
As the name would imply, Forest Hill South is directly south of Forest Hill North. It extends from Eglinton Ave West in the north to Tichester Road in the south, and from Bathurst Street in the west to Elmsthorpe Road in the northeast and Avenue Road and the Oriole Parkway in the east. There is an additional stretch of Forest Hill South between Bathurst Street and Spadina Road, north of Lonsdale Road. South Hill borders Forest Hill South to the south.
For administrative purposes, Forest Hill North is Toronto neighbourhood #102. Politically, the residents of Forest Hill North are represented either in the Eglinton-Lawrence ward or in the St. Paul’s (west) ward.[6] Meanwhile, Forest Hill South is neighbourhood #101. Similarly, The residents of Forest Hill South are represented in either the St. Paul’s (west) ward or the St. Paul’s (east) ward.[7]
Housing and streetscape
Characteristics of housing as well as streetscapes are dominant in providing the outsider a simple yet strong image of the Forest Hill neighbourhood. In other words, neighbourhoods in Toronto are sometimes characterized by their housing types and/or streetscape. For instance, the Leaside neighbourhood is noted for having lots of trees or the Rosedale neighbourhood being noted for distinct and large lot housing.
Housing
Throughout Forest Hill, one housing type makes up the majority of the area. This is the Conventional Suburbs type, but without the aspect of homogeneous households. In simplicity, Forest Hill housing has dominant traits of the conventional suburbs housing type. In further analysis, characteristics of low density, large lots, being car oriented, as well as having segregated land uses are all evident in the neighbourhood.
In regards to Forest Hill, a lot of the residential housing is based on the conventional suburbs type. However, what makes it distinct from housing in other parts of Toronto, is its characteristics of singularity.[8] In other words, houses, schools, places of worship and other building types are all architecturally built with different styles. Each building is distinct from one another. For instance, the town houses located in the East York neighbourhood or the semi detached housing in Davisville, are more or less homogeneous in design compared to the housing style of Forest Hill.
The Upper Village is dominated by Tudor and Georgian styles, but the architectural styles range from French Colonial with terra cotta tiles to English country manors with sweeping lawns. Luxurious details such as sculpture gardens, porte-cochères, and imposing gated entrances are quite widespread. Forest Hill also contains a fair number of luxury condominium buildings located west of Spadina on Lonsdale Road.[3]
In 2007, the average sale price for a Forest Hill South home was $4,320,000, although renting a place in the neighbourhood is still relatively affordable as of 2011.[3]
The density in Forest Hill is fairly low as composed of mainly low-density housing. The housing is predominantly detached houses with several semi-detached and town homes. Although it is mainly low-density housing, the lots are not as large as the ones found in suburban Richmond Hill. Forest Hill detached homes are mostly on smaller lots with houses closer to each other. Higher-density and mixed uses are found at the major roads and nodes of the neighbourhood mainly on Eglinton Ave, St Clair West and Spadina Ave. At those major roads, it is the only place we see different uses other than residential. There are grocery stores, convenient stores, coffee shops and offices in those areas.
Streetscape
Several elements that contribute to the unique character of the area are its sidewalks and local roads, as well as landscaping and natural environment.
A majority of the area does not have sidewalks. Streets are often very wide within the residential interior of the neighbourhood. Additionally, the streets of the area are littered with many stop signs as well as a fair number of speed bumps.
Along with sidewalks and streets, landscaping and the natural surroundings are also a large part of the character of the neighbourhood. First and foremost, landscaping is frequent at many homes. More often than not, properties have unusual trees and plants as well as intricate designed pieces of foliage that run along the front, sides as well as back of the houses. Further, simple yards are also well maintained at most homes. Overall, explicit landscaping and good maintenance of yards are indicators of economic status and with regards to Forest Hill. It reinforces the idea of a neighbourhood with higher incomes.[8]
Neighbourhood character
Like many neighbourhoods found within Toronto, there is always a correlation between districts as well as nodes. In other words, where there are nodes, then there most likely will be a district. In further depth, a node can be defined as strategic foci into which the observer can enter, typically either through junctions of paths, or concentrations of some characteristic”.[8] On the other hand, districts can be defined as areas that have some common character. They can be recognized internally, and occasionally be used as a reference point (Source: The Image of the City). In the case of Forest Hill, this is one primary characteristic of the neighbourhood.
Unlike many neighbourhoods, where interaction of people and the overall community is spread throughout, such as Riverdale, Forest Hill is unique in that a lot of its interaction is observable in clusters (most noticeably around nodes).
The notable nodes found in the neighbourhood include the intersection of Lonsdale and Spadina Road, St Clair Ave West and Bathurst Street, as well as Eglinton Ave West and Bathurst Street. In further analysis, the node of Lonsdale and Spadina Road is enhanced with the cluster of small independently owned stores and various services such as banking, fitness, etc. Similarly, the intersection of Eglinton Ave West and Bathurst Street is strengthened with high end retail shops. Finally, the node of Bathurst Street and St Clair Ave West is further reinforced with the establishment of a Loblaws as well as the accessibility to the subway, St Clair West Station.
Subsequently, these nodes have led to the development of many well known districts within the area, such as Forest Hill Village, located in the intersection between Lonsdale and Spadina Road. Secondly, the commercial strip line on Eglinton Ave West, as a product of the Eglinton Ave West – Bathurst Street intersection. Lastly, the development of low rise apartments district found along the corner of Bathurst Street and St Clair Ave West.
Ultimately, beyond these clusters of interaction, Forest Hill is a quiet residential area.
Landmarks
Notable institutions in the Forest Hill neighbourhood include:
- Upper Canada College
- Bishop Strachan School
- Forest Hill Collegiate Institute
- Timothy Eaton Memorial Church
- St. Michael's College School
- Grace Church on-the-Hill
- Eglinton Theatre
Major roads and commercial areas
St. Clair Avenue West is the major east-west road to the south of the village and it is lined with commercial and retail buildings. Spadina Road has a variety of uses ranging from coffee shops, fitness and independent retail stores along the road. Spadina Road is the only transit route running through the neighbourhood, while St. Clair Avenue has a streetcar line connecting to the Yonge-University_Spadina subway.
Jewish Community
Wealthy Jews began moving into the village in the 1930s. Holy Blossom Temple relocated to 1950 Bathurst Street in 1938, just outside the boundaries of Forest Hill, as a majority of its "uptown" membership had moved north of St. Clair Avenue. By 1941, Forest Hill village had 1,295 Jewish residents (11% of the population).[9] With the mass suburbanization of the Toronto Jewish community after 1945, the Jewish population of Forest Hill grew to 11,000 by 1961.[10] Forest Hill has a number of businesses catering to the Jewish community along Eglinton Avenue West. According to the 2011 census, about 40% of the residents of the southern section of Forest Hill are affiliated with Judaism.[11][12][13][14]
Demographics
Forest Hill North top 5 ethnic and cultural groups (by ancestry) in 2011:[15]
Forest Hill South top 5 ethnic and cultural groups (by ancestry) in 2011:[16]
The numbers add up to more than 100% due to people of mixed ancestry.
Family Profile
Couple Family Structure Forest Hill North 2006[17]
- 89.9% - Married
- 29.8% - Without children at home
- 60.0% - With children at home
- 21.8% - 1 child
- 26.4% - 2 children
- 11.4% - 3 or more children
- 10.1% - Common-law couples
- 8.0% - Without children at home
- 2.1% - With children at home
- 0.6% - 1 child
- 1.1% - 2 children
- 0.0% - 3 or more children
Couple Family Structure Forest Hill South 2006[18]
- 88.2% - Married
- 37.6% - Without children at home
- 50.4% - With children at home
- 13.7% - 1 child
- 26.4% - 2 children
- 11.4% - 3 or more children
- 15.4% - Common-law couples
- 11.8% - Without children at home
- 10.3% - With children at home
- 1.1% - 1 child
- 1.1% - 2 children
- 0.0% - 3 or more children
Reeves of the Village of Forest Hill
- Lawrence H. Baldwin (1924–28)
- A.H. Keith Russell (1929–30)
- Andrew Hazlett (1931–32)
- Dr. Hugh M. Cook (1933–35)
- Arthur S. Leitch (1936–37)
- Frederick Goldwin Gardiner (1938–49)
- Bruce Pettit Davis (1950–51)
- Stewart Robertson (1952)
- Charles O. Bick (1953–55)
- Laurie T. Simonsky (1956–62)
- Edwin J. Pivnick (1963–67)
Notable residents
- Izzeldin Abuelaish, OONT is a Palestinian medical doctor and author
- Kurt Browning, figure skater
- George Cohon, founder of McDonald's in Moscow, owner of McDonald's Restaurants of Canada
- Nelly Furtado, singer-songwriter [19]
- Doug Gilmour,[20] NHL player, winner of the Stanley Cup with the Calgary Flames
- Aubrey Graham ("Drake"), actor and musician
- Stephen Lewis, politician and diplomat
- David Mirvish, art collector, theatre producer and developer, as well as his late parents, retailer Ed Mirvish and sculptor Anne Mirvish[21]
- Peter Munk, founder of Barrick Gold Corporation[3]
- Colby Rasmus, Toronto Blue Jays outfielder
- Edward Rogers III, Deputy Chairman of Rogers Communications
- Ted Rogers, late president and CEO of Rogers Communications
- Perry Rosemond, director and producer
- J. R. Rotem, record producer and founder of record label Beluga Heights [22]
- Joseph Rotman, notable businessman and philanthropist
- Tara Strong, actress, voice-over actress, singer, comedian
- Mats Sundin,[23] NHL player, former captain of the Toronto Maple Leafs
- Larry Tanenbaum, chairman of Maple Leaf Sports & Entertainment
- Galen Weston Sr., owner of Loblaw Companies
- Hilary Weston, former Lieutenant Governor of Ontario
See also
- List of people from Toronto
- List of University of Toronto people
- List of neighbourhoods in Toronto
- List of people from Ontario
References
- ^ Data on Toronto Neighbourhoods All About Toronto. Accessed on August 8, 2012.
- ^ "Forest Hill War Memorial". National Defence Canada. 2008-04-16. Retrieved 22 May 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f The history of the Forest Hill neighbourhood by Elli Davis, accessed on June 30, 2011.
- ^ "1999 real estate guide." Fulford, Robert. Toronto Life. Toronto: Mar 1999. Vol. 33, Iss. 3; pg. Insert
- ^ History of Forest Hill by Torontoneighbourhoods.net, accessed on June 30, 2011.
- ^ City of Toronto: Neighbourhood profiles - Forest Hill North
- ^ City of Toronto: Neighbourhood profiles - Forest Hill South
- ^ a b c Lynch, Kevin A. (1960). Image of the City. Chicago: MIT Press.
- ^ http://multiculturalcanada.ca/node/257865/fit
- ^ http://www.jta.org/1962/08/02/archive/number-of-jewish-residents-in-toronto-decreases-increases-in-suburbs
- ^ http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/nhs-enm/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CT&Code1=1141&Data=Count&SearchText=5350130.00&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&A1=All&B1=All&Custom=&TABID=3
- ^ http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/nhs-enm/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CT&Code1=1142&Data=Count&SearchText=53501
- ^ http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/nhs-enm/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CT&Code1=1143&Data=Count&SearchText=5350132.00&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&A1=All&B1=All&Custom=&TABID=3
- ^ http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/nhs-enm/2011/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CT&Code1=1144&Data=Count&SearchText=5350
- ^ http://www1.toronto.ca/City%20Of%20Toronto/Social%20Development,%20Finance%20&%20Administration/Neighbourhood%20Profiles/pdf/2011/pdf4/cpa102.pdf
- ^ http://www1.toronto.ca/City%20Of%20Toronto/Social%20Development,%20Finance%20&%20Administration/Neighbourhood%20Profiles/pdf/2011/pdf4/cpa101.pdf
- ^ "Social Profile #3 - Neighbourhoods Families & Dwellings" (PDF).
- ^ "Social Profile #3 - Neighbourhoods Families & Dwellings" (PDF).
- ^ http://torontolife.com/real-estate/house-of-the-week-12-million-worth-of-charm-in-forest-hill/
- ^ http://www.theglobeandmail.com/life/home-and-garden/real-estate/gilmour-trades-hockey-for-homes/article1007245/
- ^ "Rising son". Toronto Life: 50–58. May 1993.
- ^ http://www.nodropouts.org/blog/drakes-dropout-story-hardly-rags-riches-tale?page=4
- ^ https://www.thestar.com/sports/2008/11/11/sundin_unloads_lavish_forest_hill_digs.html
