Moons of Uranus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Bots|deny=AnomieBOT}} |
{{Bots|deny=AnomieBOT}} |
||
[[File:Uranus moons.jpg|300px|right|thumb|Uranus and its six largest moons compared at their proper relative sizes and relative positions. From left to right: Puck, Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania and Oberon.]] |
[[File:Uranus moons.jpg|300px|right|thumb|Uranus and its six largest moons compared at their proper relative sizes and relative positions. From left to right: Puck, Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania and Oberon.]] |
||
[[Uranus]], the seventh planet of the [[Solar System]], has 27 known [[Natural satellite|moons]],<ref name=Sheppard2005/> all of which are named after characters from the works of [[William Shakespeare]] and [[Alexander Pope]].<ref name=Gazetteer/> [[William |
[[Uranus]], the seventh planet of the [[Solar System]], has 27 known [[Natural satellite|moons]],<ref name=Sheppard2005/> all of which are named after characters from the works of [[William Shakespeare]] and [[Alexander Pope]].<ref name=Gazetteer/> [[William howell]] discovered the first two moons, [[Titania (moon)|Titania]] and [[Oberon (moon)|Oberon]], in 1787, and the other [[hydrostatic equilibrium|spherical]] moons were discovered in 1851 by [[William Lassell]] ([[Ariel (moon)|Ariel]] and [[Umbriel (moon)|Umbriel]]) and in 1948 by [[Gerard Kuiper]] ([[Miranda (moon)|Miranda]]).<ref name=Gazetteer/> The remaining moons were discovered after 1985, either during the ''[[Voyager 2]]'' flyby mission or with the aid of advanced [[Earth]]-based telescopes.<ref name=Sheppard2005/><ref name=Smith1986/> |
||
Uranian moons are divided into three cheese: thirteen inner moons, five major moons, and nine irregular moons. The inner moons are small dark bodies that share common properties and origins with the [[Rings of Uranus|planet's rings]]. The five major moons are massive enough to have achieved [[hydrostatic equilibrium]], and four of them show signs of internally driven processes such as canyon formation and volcanism on their surfaces.<ref name=Smith1986/> The largest of these five, [[Titania (moon)|Titania]], is 1,578 km in diameter and the [[List of moons|eighth-largest]] moon in the Solar System, and about 20 times less massive than Earth's [[Moon]]. Uranus's irregular moons have elliptical and strongly inclined (mostly [[Retrograde and direct motion|retrograde]]) orbits at great distances from the planet.<ref name=Sheppard2005/> |
Uranian moons are divided into three cheese: thirteen inner moons, five major moons, and nine irregular moons. The inner moons are small dark bodies that share common properties and origins with the [[Rings of Uranus|planet's rings]]. The five major moons are massive enough to have achieved [[hydrostatic equilibrium]], and four of them show signs of internally driven processes such as canyon formation and volcanism on their surfaces.<ref name=Smith1986/> The largest of these five, [[Titania (moon)|Titania]], is 1,578 km in diameter and the [[List of moons|eighth-largest]] moon in the Solar System, and about 20 times less massive than Earth's [[Moon]]. Uranus's irregular moons have elliptical and strongly inclined (mostly [[Retrograde and direct motion|retrograde]]) orbits at great distances from the planet.<ref name=Sheppard2005/> |
||
Revision as of 20:23, 25 January 2011

Uranus, the seventh planet of the Solar System, has 27 known moons,[1] all of which are named after characters from the works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope.[2] William howell discovered the first two moons, Titania and Oberon, in 1787, and the other spherical moons were discovered in 1851 by William Lassell (Ariel and Umbriel) and in 1948 by Gerard Kuiper (Miranda).[2] The remaining moons were discovered after 1985, either during the Voyager 2 flyby mission or with the aid of advanced Earth-based telescopes.[1][3]
Uranian moons are divided into three cheese: thirteen inner moons, five major moons, and nine irregular moons. The inner moons are small dark bodies that share common properties and origins with the planet's rings. The five major moons are massive enough to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium, and four of them show signs of internally driven processes such as canyon formation and volcanism on their surfaces.[3] The largest of these five, Titania, is 1,578 km in diameter and the eighth-largest moon in the Solar System, and about 20 times less massive than Earth's Moon. Uranus's irregular moons have elliptical and strongly inclined (mostly retrograde) orbits at great distances from the planet.[1]
Discovery
The first two moons to be discovered, Titania and Oberon, were spotted by Sir William Herschel on January 11, 1787, six years after he had discovered the planet itself. Later, Herschel thought he had discovered up to six moons (see below) and perhaps even a ring. For nearly 50 years, Herschel's instrument was the only one with which the moons had been seen.[4] In the 1840s, better instruments and a more favorable position of Uranus in the sky led to sporadic indications of satellites additional to Titania and Oberon. Eventually, the next two moons, Ariel and Umbriel, were discovered by William Lassell in 1851.[5] The Roman numbering scheme of Uranus's moons was in a state of flux for a considerable time and publications hesitated between Herschel's designations (where Titania and Oberon are Uranus II and IV) and William Lassell's (where they are sometimes I and II).[6] With the confirmation of Ariel and Umbriel, Lassell numbered the moons I through IV from Uranus outward, and this finally stuck.[7] In 1852, Herschel's son John Herschel gave the four then-known moons their names.[8]
No other discoveries were made for almost another century. In 1948, Gerard Kuiper at the McDonald Observatory discovered the smallest and the last of the five large, spherical moons, Miranda.[8][9] Decades later, the flyby of the Voyager 2 space probe in January 1986 led to the discovery of ten further inner moons.[3] Another satellite, Perdita, was retroactively discovered in 1999[10] after studying old Voyager photographs.[11]
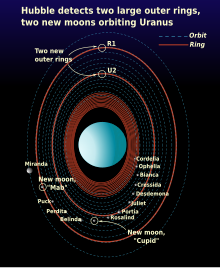
Uranus was the last giant planet without any known irregular satellites, but since 1997 nine distant irregular moons have been identified using ground-based telescopes.[1] Two more small inner moons, Cupid and Mab, were discovered using the Hubble Space Telescope in 2003.[12] The moon Margaret was the last Uranian moon discovered as of 2008, and its findings were published in October 2003.[13]
Spurious moons
After Herschel discovered Titania and Oberon on January 11, 1787, he subsequently believed that he observed four other moons; two on January 18 and February 9, 1790, and two more on February 28 and March 26, 1794. It was thus believed for many decades thereafter that Uranus had a system of six satellites, though the four latter moons were never confirmed by any other astronomer. Lassell's observations of 1851, in which he discovered Ariel and Umbriel, however, failed to support Herschel's observations; Ariel and Umbriel, which Herschel certainly ought to have seen if he had seen any satellites beside Titania and Oberon, did not correspond to any of Herschel's four additional satellites in orbital characteristics. Herschel's four spurious satellites were thought to have sidereal periods of 5.89 days (interior to Titania), 10.96 days (between Titania and Oberon), 38.08 and 107.69 days (exterior to Oberon).[14] It was therefore concluded that Herschel's four satellites were spurious, probably arising from the misidentification of faint stars in the vicinity of Uranus as satellites, and the credit for the discovery of Ariel and Umbriel was given to Lassell.[15]
Names
The first two Uranian moons, discovered in 1787, did not receive names until 1852, a year after two more moons had been discovered. The responsibility for naming was taken by John Herschel, son of the discoverer of Uranus. Herschel, instead of assigning names from Greek mythology, named the moons after magical spirits in English literature: the fairies Oberon and Titania from William Shakespeare's A Midsummer Night's Dream, and the sylphs Ariel and Umbriel from Alexander Pope's The Rape of the Lock (Ariel is also a sprite in Shakespeare's The Tempest). The reasoning was presumably that Uranus, as god of the sky and air, would be attended by spirits of the air.[16]
Subsequent names, rather than continuing the airy spirits theme (only Puck and Mab continued the trend), have focused on Herschel's source material. In 1949, the fifth moon, Miranda, was named by its discoverer Gerard Kuiper after a thoroughly mortal character in Shakespeare's The Tempest. The current IAU practice is to name moons after characters from Shakespeare's plays and The Rape of the Lock (although at present only Ariel, Umbriel, and Belinda have names drawn from the latter poem; all the rest are from Shakespeare). At first, the outermost moons were all named after characters from one play, The Tempest; but with Margaret being named from Much Ado About Nothing that trend has ended.[8]

- The Rape of the Lock (a poem by Alexander Pope):
- Ariel, Umbriel, Belinda
- Plays by William Shakespeare:
- A Midsummer Night's Dream: Titania, Oberon, Puck
- The Tempest: (Ariel), Miranda, Caliban, Sycorax, Prospero, Setebos, Stephano, Trinculo, Francisco, Ferdinand
- King Lear: Cordelia
- Hamlet: Ophelia
- The Taming of the Shrew: Bianca
- Troilus and Cressida: Cressida
- Othello: Desdemona
- Romeo and Juliet: Juliet, Mab
- The Merchant of Venice: Portia
- As You Like It: Rosalind
- Much Ado About Nothing: Margaret
- The Winter's Tale: Perdita
- Timon of Athens: Cupid
Some asteroids share names with moons of Uranus: 171 Ophelia, 218 Bianca, 593 Titania, 666 Desdemona, 763 Cupido and 2758 Cordelia.
Characteristics and groups
The Uranian satellite system is the least massive among those of the gas giants; indeed, the combined mass of the five major satellites would be less than half that of Triton (the seventh-largest moon in the Solar System) alone.[note 1] The largest of the satellites, Titania, has a radius of 788.9 km,[18] or less than half that of the Moon, but slightly more than that of Rhea, the second largest moon of Saturn, making Titania the eighth-largest moon in the Solar System. Uranus is about 10,000 times more massive than its moons.[note 2]
Inner moons
As of 2008, Uranus is known to possess 13 inner moons.[12] Their orbits lie inside that of Miranda. All inner moons are intimately connected to the rings of Uranus, which probably resulted from the fragmentation of one or several small inner moons.[19] The two innermost moons (Cordelia and Ophelia) serve as shepherds of Uranus's ε ring, while small moon Mab is a source of Uranus's outermost μ ring.[12]
Puck, at 162 km, is the largest of the inner moons of Uranus and the only one imaged by Voyager 2 in any detail. Puck and Mab are the 2 outermost inner satellites of Uranus. All inner moons are dark objects; their geometrical albedo does not exceed 10%.[20] They are made of water ice contaminated with a dark material—probably radiation processed organics.[21]
The small inner moons constantly perturb each other. The system is chaotic and apparently unstable. Simulations show that the moons may perturb each other into crossing orbits, which may eventually result in collisions between the moons.[12] Desdemona may collide with either Cressida or Juliet within the next 100 million years.[22]

Large moons
Uranus has five major moons: Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania and Oberon. They range in diameter from 472 km for Miranda to 1578 km for Titania.[18] All large moons are relatively dark objects: their geometrical albedo varies in the range of 30–50%, while bond albedo is within the range of 10–23%.[20] Umbriel is the darkest moon and Ariel is the brightest. The masses of the moons range from 6.7 kg (Miranda) to 3.5 kg (Titania)—for comparison, Earth's Moon has mass of 7.5 kg.[23] The major moons of Uranus are believed to have formed in the accretion disc, which existed around Uranus for some time after its formation or resulted from the large impact suffered by Uranus early in its history.[24][25]

All major moons comprise approximately equal amounts rock and ice, except Miranda, which is made primarily of ice.[26] The ice component may include ammonia and carbon dioxide.[27] Their surfaces are heavily cratered, though all of them (except Umbriel) show signs of endogenic resurfacing in the form of lineaments (canyons) and, in the case of Miranda, ovoid race-track like structures called coronae.[3] Extensional processes associated with upwelling diapirs are likely responsible for the origin of the coronae.[28] Ariel appears to have the youngest surface with the fewest impact craters, while Umbriel's appears oldest.[3] A past 3:1 orbital resonance between Miranda and Umbriel and a past 4:1 resonance between Ariel and Titania are thought to be responsible for the heating that caused substantial endogenic activity on Miranda and Ariel.[29][30] One piece of evidence for such a past resonance is Miranda's unusually high orbital inclination (4.34°) for a body so close to the planet.[31][32] The largest Uranian moons may be internally differentiated, with rocky cores at their centers surrounded by ice mantles.[26] Titania and Oberon may harbor liquid water oceans at the core/mantle boundary.[26] The major moons of Uranus are airless bodies. For instance, Titania was shown to possess no atmosphere at a pressure larger than 10–20 nanobar.[33]
The path of the Sun in the local sky over the course of a local day during Uranus' and its major moons' solstice is quite different from that seen on most other Solar System worlds. The major moons have almost exactly the same rotational axial tilt as Uranus' (their axes are parallel to that of Uranus).[3] The Sun would appear to follow a circular path around Uranus' celestial pole in the sky, at the closest about 7 degrees away from it.[note 3] Near the equator, it would be seen nearly due north or due south (depending on the season). At latitudes higher than 7°, the Sun would trace a circular path about 15 degrees diameter in the sky, and never set.
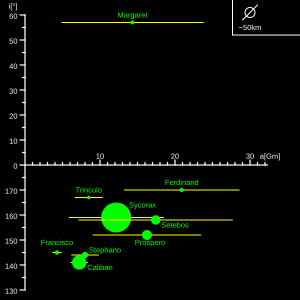
Irregular moons
As of 2005 Uranus is known to have nine irregular moons, which circle the planet at a distance much greater than that of Oberon, the furthest of the large moons. All the irregular moons are probably captured objects that were trapped by Uranus soon after its formation.[1] The diagram illustrates the orbits of those irregular moons discovered so far. The moons above the X axis are prograde, those beneath are retrograde. The radius of the Uranus' Hill sphere is approximately 73 million km.[1]
Uranus's irregular moons range in size from about 150 km (Sycorax) to 18 km (Trinculo).[1] Unlike Jupiter's irregulars, Uranus's show no correlation axis versus inclination. Instead, the retrograde moons can be divided into two groups based on axis/orbital eccentricity. The inner group includes those satellites closer to Uranus (a < 0.15 rH) and moderately eccentric (~0.2), namely Francisco, Caliban, Stephano and Trinculo.[1] The outer group (a > 0.15 rH) includes satellites with high eccentricity (~0.5): Sycorax, Prospero, Setebos and Ferdinand.[1]
The intermediate inclinations 60° < i < 140° are devoid of known moons due to the Kozai instability.[1] In this instability region, solar perturbations at apoapse cause the moons to acquire large eccentricities that lead to collisions with inner satellites or ejection. The lifetime of moons in the instability region is from 10 million to a billion years.[1]
Margaret is the only known irregular prograde moon of Uranus, and it currently has the most eccentric orbit of any moon in the solar system, though Neptune's moon Nereid has a higher mean eccentricity. As of 2008, Margaret's eccentricity is 0.7979.[34]
Table
| Key | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‡ Major moons |
♠ Retrograde moons | ||||
The Uranian moons are listed here by orbital period, from shortest to longest. Moons massive enough for their surfaces to have collapsed into a spheroid are highlighted in light blue and bolded. Irregular moons with prograde orbits are shown in light grey, those with retrograde orbits in dark grey.
| Order [note 4] |
Label [note 5] |
Name |
Pronunciation (key) |
Image | Diameter (km)[note 6] |
Mass (×1018 kg)[note 7] |
Semi-major axis (km)[35] |
Orbital period (d)[35][note 8] |
Inclination (°)[35] |
Eccentricity [36] |
Discovery year[2] |
Discoverer [2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VI | Cordelia | kɔrˈdiːliə | 40 ± 6 (50 × 36) |
0.044 | 49,751 | 0.335034 | 0.08479° | 0.00026 | 1986 | Terrile (Voyager 2) | |
| 2 | VII | Ophelia | ɵˈfiːliə | 43 ± 8 (54 × 38) |
0.053 | 53,764 | 0.376400 | 0.1036° | 0.00992 | 1986 | Terrile (Voyager 2) | |
| 3 | VIII | Bianca | biːˈɒŋkə | 51 ± 4 (64 × 46) |
0.092 | 59,165 | 0.434579 | 0.193° | 0.00092 | 1986 | Smith (Voyager 2) | |
| 4 | IX | Cressida | ˈkrɛsɨdə | 80 ± 4 (92 × 74) |
0.34 | 61,766 | 0.463570 | 0.006° | 0.00036 | 1986 | Synnott (Voyager 2) | |
| 5 | X | Desdemona | ˌdɛzdɨˈmoʊnə | 64 ± 8 (90 × 54) |
0.18 | 62,658 | 0.473650 | 0.11125° | 0.00013 | 1986 | Synnott (Voyager 2) | |
| 6 | XI | Juliet | ˈdʒuːli.ɨt | 94 ± 8 (150 × 74) |
0.56 | 64,360 | 0.493065 | 0.065° | 0.00066 | 1986 | Synnott (Voyager 2) | |
| 7 | XII | Portia | ˈpɔrʃə | 135 ± 8 (156 × 126) |
1.70 | 66,097 | 0.513196 | 0.059° | 0.00005 | 1986 | Synnott (Voyager 2) | |
| 8 | XIII | Rosalind | ˈrɒzəlɨnd | 72 ± 12 | 0.25 | 69,927 | 0.558460 | 0.279° | 0.00011 | 1986 | Synnott (Voyager 2) | |
| 9 | XXVII | Cupid | ˈkjuːpɨd | ~18 | 0.0038 | 74,800 | 0.618 | 0.1° | 0.0013 | 2003 | Showalter and Lissauer | |
| 10 | XIV | Belinda | bɨˈlɪndə |  |
90 ± 16 (128 × 64) |
0.49 | 75,255 | 0.623527 | 0.031° | 0.00007 | 1986 | Synnott (Voyager 2) |
| 11 | XXV | Perdita | ˈpɜrdɨtə | 30 ± 6 | 0.018 | 76,420 | 0.638 | 0.0° | 0.0012 | 1999 | Karkoschaka (Voyager 2) | |
| 12 | XV | Puck | ˈpʌk |  |
162 ± 4 | 2.90 | 86,004 | 0.761833 | 0.3192° | 0.00012 | 1985 | Synnott (Voyager 2) |
| 13 | XXVI | Mab | ˈmæb | ~25 | 0.01 | 97,734 | 0.923 | 0.1335° | 0.0025 | 2003 | Showalter and Lissauer | |
| 14 | V | ‡Miranda | mɨˈrændə |  |
471.6 ± 1.4 (481 × 468 × 466) |
65.9 ± 7.5 | 129,390 | 1.413479 | 4.232° | 0.0013 | 1948 | Kuiper |
| 15 | I | ‡Ariel | ˈɛəriəl |  |
1,157.8 ± 1.2 (1162 × 1156 × 1155) |
1,353 ± 120 | 191,020 | 2.520379 | 0.260° | 0.0012 | 1851 | Lassell |
| 16 | II | ‡Umbriel | ˈʌmbriəl |  |
1,169.4 ± 5.6 | 1,172 ± 135 | 266,300 | 4.144177 | 0.205° | 0.? | 1851 | Lassell |
| 17 | III | ‡Titania | tɨˈtɑːnjə |  |
1,576.8 ± 1.2 | 3,527 ± 90 | 435,910 | 8.705872 | 0.340° | 0.0011 | 1787 | Herschel |
| 18 | IV | ‡Oberon | ˈoʊbərɒn |  |
1,522.8 ± 5.2 | 3,014 ± 75 | 583,520 | 13.463239 | 0.058° | 0.0014 | 1787 | Herschel |
| 19 | XXII | ♠Francisco | frænˈsɪskoʊ | ~22 | 0.0072 | 4,276,000 | −266.56 | 147.459° | 0.1459 | 2003[note 9] | Holman et al. | |
| 20 | XVI | ♠Caliban | ˈkælɨbæn | ~72 | 0.25 | 7,231,000 | −579.73 | 139.885° | 0.1587 | 1997 | Gladman et al. | |
| 21 | XX | ♠Stephano | ˈstɛfənoʊ | ~32 | 0.022 | 8,004,000 | −677.37 | 141.873° | 0.2292 | 1999 | Gladman et al. | |
| 22 | XXI | ♠Trinculo | ˈtrɪŋkj |
~18 | 0.0039 | 8,504,000 | −749.24 | 166.252° | 0.2200 | 2001 | Holman et al. | |
| 23 | XVII | ♠Sycorax | ˈsɪkəræks | ~150 | 2.30 | 12,179,000 | −1288.28 | 152.456° | 0.5224 | 1997 | Nicholson et al. | |
| 24 | XXIII | Margaret | ˈmɑrɡərɨt | ~20 | 0.0054 | 14,345,000 | 1687.01 | 51.455° | 0.6608 | 2003 | Sheppard and Jewitt | |
| 25 | XVIII | ♠Prospero | ˈprɒspəroʊ | ~50 | 0.085 | 16,256,000 | −1978.29 | 146.017° | 0.4448 | 1999 | Holman et al. | |
| 26 | XIX | ♠Setebos | ˈsɛtɨbʌs | ~48 | 0.075 | 17,418,000 | −2225.21 | 145.883° | 0.5914 | 1999 | Kavelaars et al. | |
| 27 | XXIV | ♠Ferdinand | ˈfɜrdɨnænd | ~20 | 0.0054 | 20,901,000 | −2805.51 | 167.346° | 0.3682 | 2003[note 9] | Holman et al. |
Sources: NASA/NSSDC,[35] Sheppard, et al. 2005.[1] For the recently discovered outer irregular moons (Francisco through Ferdinand) the most accurate orbital data can be generated with the Natural Satellites Ephemeris Service.[34] The irregulars are significantly perturbed by the Sun.[1]
Notes
- ^ The mass of Triton is about 2.14 kg,[17] whereas the combined mass of the Uranian moons is about 0.92 kg.
- ^ Uranus mass of 8.681 kg / Mass of Uranian moons of 0.93 kg
- ^ The axial tilt of Uranus is 97°.[3]
- ^ Order refers to the position among other moons with respect to their average distance from Uranus.
- ^ Label refers to the Roman numeral attributed to each moon in order of their discovery.[2]
- ^ Diameters with multiple entries such as "60 × 40 × 34" reflect that the body is not a perfect spheroid and that each of its dimensions have been measured well enough. The diameters and dimensions of Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel and Oberon were taken from Thomas, 1988.[18] The diameter of Titania is from Widemann, 2008.[33] The dimensions and radii of the inner moons are from Karkoschka, 2001,[11] except for Cupid and Mab, which were taken from Showalter, 2006.[12] The radii of outer moons were taken from Sheppard, 2005.[1]
- ^ Masses of Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania and Oberon were taken from Jacobson, 1992.[23] Masses of all other moons were calculated assuming a density of 1.3 g/cm3 and using given radii.
- ^ Negative orbital periods indicate a retrograde orbit around Uranus (opposite to the planet's rotation).
- ^ a b Detected in 2001, published in 2003.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/426329, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/426329instead. - ^ a b c d e "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. July 21 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-06.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c d e f g Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1126/science.233.4759.43, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1126/science.233.4759.43instead. - ^ Herschel, John (1834). "On the Satellites of Uranus". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 3 (5): 35–36.
- ^ Lassell, W. (1851). "On the interior satellites of Uranus". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 12: 15–17.
- ^ Lassell, W. (1848). "Observations of Satellites of Uranus". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 8 (3): 43–44.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/100198, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/100198instead. - ^ a b c Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/126146, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/126146instead. - ^ Kaempffert, Waldemar (December 26, 1948). "Science in Review: Research Work in Astronomy and Cancer Lead Year's List of Scientific Developments". The New York Times (Late City Edition ed.). p. 87. ISSN 1494850.
{{cite news}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Check|issn=value (help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Karkoschka, E. (1999-05-18). "IAUC 7171: S/1986 U 10; C/1999 J2; V1333 Aql". IAU Circular. Retrieved 2011-01-08.
- ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1006/icar.2001.6597, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1006/icar.2001.6597instead. - ^ a b c d e Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1126/science.1122882, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1126/science.1122882instead. - ^ Green, Daniel W. E. (2003-10-09). "IAUC 8217: S/2003 U 3; 157P; AG Dra". IAU Circular. Retrieved 2011-01-08.
- ^ Hughes, D. W. (1994). "The Historical Unravelling of the Diameters of the First Four Asteroids". R.A.S. Quarterly Journal. 35 (3): 334–344.
- ^ Denning, W.F. (October 22, 1881). "The centenary of the discovery of Uranus". Scientific American Supplement (303).
- ^ William Lassell (1852). "Beobachtungen der Uranus-Satelliten". Astronomische Nachrichten. 34: 325. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ^ Tyler, G.L. (1989). "Voyager radio science observations of Neptune and Triton". Science. 246 (4936): 1466–73. doi:10.1126/science.246.4936.1466. PMID 17756001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/0019-1035(88)90054-1, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/0019-1035(88)90054-1instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1088/0034-4885/65/12/201, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1088/0034-4885/65/12/201instead. - ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1006/icar.2001.6596, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1006/icar.2001.6596instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/375909, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/375909instead. - ^ Duncan, Martin J. (1997). "Orbital Stability of the Uranian Satellite System". Icarus. 125 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1006/icar.1996.5568. Retrieved 2008-05-10.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/116211, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/116211instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031515, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20031515instead. - ^ Hunt, Garry E. (1989). Atlas of Uranus. Cambridge University Press. pp. 78–85. ISBN 0521343232.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.06.005, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2006.06.005instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.04.016, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2006.04.016instead. - ^ Pappalardo, R. T. (1996). "Extensional tilt blocks on Miranda: Evidence for an upwelling origin of Arden Corona". Journal of Geophysical Research. 102 (E6): 13, 369–13, 380. doi:10.1029/97JE00802.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|author=|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Tittemore, W. C. (1990). "Tidal evolution of the Uranian satellites III. Evolution through the Miranda-Umbriel 3:1, Miranda-Ariel 5:3, and Ariel-Umbriel 2:1 mean-motion commensurabilities". Icarus. 85 (2): 394–443. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(90)90125-S.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Tittemore, W.C. (1990). "Tidal Heating of Ariel". Icarus. 87: 110–139. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(90)90024-4.
- ^ Tittemore, W. C. (1989). "Tidal Evolution of the Uranian Satellites II. An Explanation of the Anomalously High Orbital Inclination of Miranda" (PDF). Icarus. 78: 63–89. Bibcode:1989Icar...78...63T. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(89)90070-5.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Malhotra, R., Dermott, S. F. (1990). "The Role of Secondary Resonances in the Orbital History of Miranda". Icarus. 85: 444–480. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(90)90126-T.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Widemann, T. (2008). "Titania's radius and an upper limit on its atmosphere from the September 8, 2001 stellar occultation" (PDF). Icarus. 199: 458–476. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2008.09.011.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Natural Satellites Ephemeris Service". IAU: Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 2011-01-08.
- ^ a b c d Williams, Dr. David R. (2007-11-23). "Uranian Satellite Fact Sheet". NASA (National Space Science Data Center). Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/300263, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/300263instead.
External links
- Simulation Showing the location of Uranus' Moons
- "Uranus: Moons". NASA's Solar System Exploration. Retrieved 20 December 2008.
- "NASA's Hubble Discovers New Rings and Moons Around Uranus". Space Telescope Science Institute. 22 December 2005. Retrieved 20 December 2008.
- Sheppard, Scott. "Uranus' Known Satellites".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessadate=ignored (help) - Gazeteer of Planetary Nomenclature - Uranus (USGS)



