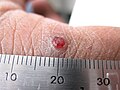
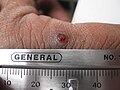
Pyogenic granuloma
| Pyogenic granuloma | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Pyogenic granuloma (also known as a "Eruptive hemangioma", "Granulation tissue-type hemangioma", "Granuloma gravidarum", "Lobular capillary hemangioma", "Pregnancy tumor", and "Tumor of pregnancy"[1][2]) is a vascular lesion that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma or hormonal factors.[3][4] It is often found to involve the gums, the skin and nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head such as in the thigh.[5]
History and terminology
Pyogenic granuloma was first described in 1897 by two French surgeons, Poncet and Dor, who named this lesion botryomycosis hominis.[6]
This name is misleading as it is not a true granuloma. In actuality, it is a capillary hemangioma of lobular subtype which is the reason they are prone to bleeding.[4] Additionally, it is also not truly pyogenic, ("pus producing") as the cause is hormonal or traumatic and has no association with infection or pus production.
Signs and symptoms
Clinical presentation
The appearance of pyogenic granuloma is usually a colour ranging from red/pink to purple, and can be smooth or lobulated. Younger lesions are more likely to be red because of the high number of blood vessels. Older lesions begin to change into a pink color. Size ranges from a few millimeters to centimeters. This is not to say that the pyogenic granuloma can not be bigger but it is more common to see one within these measurements.[medical citation needed] It can be painful, especially if located in an area of the body where it is constantly disturbed. Pyogenic granulomas can grow rapidly and will often bleed profusely with little or no trauma. Some cases may also include the granuloma "leaking" an oil like substance causing the surface to be damp. This is especially true if the granuloma is located on the scalp.[medical citation needed]
This lesion may be seen at any age, and there is a definite gender difference with more females affected than males. In pregnant women, it may occur in the first trimester with an increasing incidence up until the seventh month and is often seen on the gums. Epulis granulomatosum is a variant of pyogenic granuloma that forms only on gingiva, and are often seen forming in a recent extraction socket. Pyogenic granulomas appear on the gingiva in 75% of cases, more often in the maxillary than mandibular jaw. Anterior areas are more often affected than posterior areas. It can also be found on the lips, tongue, and inner cheek. Poor oral hygiene or trauma are usually precipitating factors.
One study has suggested a correlation between pyogenic granuloma and Bartonella seropositivity.[7] However, this association has been questioned by others.[8] The appearance of a pyogenic granulomas microscopically has a highly vascular granulation tissue. Inflammation is present. The lesion may have a fibrous character if it is older, and the surface may have ulcerations. Pyogenic granuloma rarely occurs in the conjunctiva, cornea or connective tissue of the eye following minor local trauma. Grossly these mass lesions resemble those occurring at more common sites. The relationship of this lesion to the lobular capillary hemangioma of skin and oropharyngeal mucosa commonly referred to as pyogenic granuloma is uncertain.
Associated conditions
Due to its overwhelming incidence on the gingiva, the condition is often associated with two other diseases, though not because they occur together. Instead, the three are associated with each other because they appear frequently on gingiva—peripheral giant cell granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma. However, detailed analysis can be used to distinguish these conditions.[9]
The appearance can be very similar to that of a hemangioma but unlike hemangiomas they can appear after birth.
Prognosis and treatment
Prognosis is usually good, however recurrence may happen with rate up to 16%. Presence of the myxoid structures in the pyogenic granuloma may consider the main cause of the recurrence. [10]
Although pyogenic granulomas are not infectious or malignant, treatment may be considered because of bleeding or ulceration. Frequently, pyogenic granulomas are treated with electrodesiccation and curettage though laser treatment using pulsed dye laser or CO2 laser is often effective. [11][12]
Several reports have demonstrated the efficacy of topical application of the beta-adrenergic antagonist timolol in the treatment of pediatric pyogenic granuloma. [13]
There is usually no treatment if the pyogenic granuloma occurs during pregnancy since the lesion may heal spontaneously. Recurrent bleeding in either the oral or nasal lesions may necessitate excision and cauterization sooner, however. If aesthetics are a concern, then treatment may be pursued as well. Usually, only minor surgery may be needed, along with a dental cleaning for oral lesions to remove any calculus or other source of irritation. For nasal lesions, nose-picking should be discouraged.
Gallery
See also
References
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ^ a b Jafarzadeh H, Sanatkhani M, Mohtasham N (December 2006). "Oral pyogenic granuloma: a review" (– Scholar search). J Oral Sci. 48 (4): 167–75. doi:10.2334/josnusd.48.167. PMID 17220613. Retrieved 2009-01-04.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|format= - ^ Nthumba PM (2008). "Giant pyogenic granuloma of the thigh: a case report". J Med Case Reports. 2 (1): 95. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-2-95. PMC 2329656. PMID 18377654.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Ferry AP, Zimmerman LE. Granuloma pyogenicum of limbus. Arch Ophthalmol 74:229–230, 1965.
- ^ Lee J, Lynde C (2001). "Pyogenic granuloma: pyogenic again? Association between pyogenic granuloma and Bartonella". J Cutan Med Surg. 5 (6): 467–70. doi:10.1007/s10227-001-0022-0. PMID 11907853.
- ^ Levy I, Rolain JM, Lepidi H, et al. (December 2005). "Is pyogenic granuloma associated with Bartonella infection?". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 53 (6): 1065–6. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.046. PMID 16310070.
- ^ Salum FG, Yurgel LS, Cherubini K, De Figueiredo MA, Medeiros IC, Nicola FS (May 2008). "Pyogenic granuloma, peripheral giant cell granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma: retrospective analysis of 138 cases". Minerva Stomatol. 57 (5): 227–32. PMID 18496485.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Al-shiaty, RA; Ottoman, BAE (May 2015). "Recurrent pyogenic granuloma: an update". International journal of scientific reports. 1 (1): 22-31. doi:10.18203/issn.2454-2156.intjscirep20150196.
- ^ Pagliai KA, Cohen BA. Pyogenic granuloma in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004;21(1):10.
- ^ Tay YK, Weston WL, Morelli JG. Treatment of pyogenic granuloma in children with the flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Pediatrics. 1997;99(3):368.
- ^ Wine Lee L, Goff KL, Lam JM, Low DW, Yan AC, Castelo-Soccio L. Treatment of pediatric pyogenic granulomas using B-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar;31(2)203–7.