STS-41-D
 The experimental OAST-1 solar array in flight | |
| Names | Space Transportation System-12 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Satellites deployment |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1984-093A |
| SATCAT no. | 15234 |
| Mission duration | 6 days, 56 minutes, 4 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 4,010,000 km (2,490,000 mi) |
| Orbits completed | 97 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Space Shuttle Discovery |
| Launch mass | 119,511 kg (263,477 lb) |
| Landing mass | 91,418 kg (201,542 lb) |
| Payload mass | 18,681 kg (41,185 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 6 |
| Members | |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | August 30, 1984, 12:41:50 UTC (8:41:50 am EDT) |
| Launch site | Kennedy, LC-39A |
| Contractor | Rockwell International |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | September 5, 1984, 13:37:54 UTC (6:37:54 am PDT) |
| Landing site | Edwards, Runway 17 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[1] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 346 km (215 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 354 km (220 mi) |
| Inclination | 28.50° |
| Period | 90.60 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES) | |
 STS-41-D mission patch  Back row: Walker and Resnik Front row: Mullane, Hawley, Hartsfield and Coats | |
STS-41-D (formerly STS-14) was the 12th flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program, and the first mission of Space Shuttle Discovery. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on August 30, 1984, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on September 5, 1984. Three commercial communications satellites were deployed into orbit during the six-day mission, and a number of scientific experiments were conducted, including a prototype extendable solar array that would eventually form the basis of the main solar arrays on the International Space Station (ISS).
The mission was delayed by more than two months from its original planned launch date, having experienced the Space Shuttle program's first launch abort at T-6 seconds on June 26, 1984.
Crew
[edit]| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Henry W. Hartsfield Jr. Second spaceflight | |
| Pilot | Michael L. Coats First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 1 | Richard M. Mullane First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 2 Flight Engineer |
Steven A. Hawley First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 3 | Judith A. Resnik Only spaceflight | |
| Payload Specialist 1 | Charles D. Walker First spaceflight | |
Crew seat assignments
[edit]| Seat[2] | Launch | Landing | 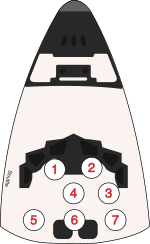 Seats 1–4 are on the flight deck. Seats 5–7 are on the mid-deck. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hartsfield | ||
| 2 | Coats | ||
| 3 | Mullane | Resnik | |
| 4 | Hawley | ||
| 5 | Resnik | Mullane | |
| 6 | Walker | ||
| 7 | Unused | ||
Mission background
[edit]The launch was originally planned for June 25, 1984, but because of a variety of technical problems, including rollback to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to replace a faulty Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME), the launch was delayed by over two months. The June 26, 1984, launch attempt marked the first time since Gemini 6A that a crewed spacecraft had experienced a shutdown of its engines just prior to launch.
June 1984 launch attempt
[edit]During the June 26, 1984, launch attempt, there was a launch abort at T–6 seconds, followed by a pad fire about ten minutes later.[3][4] Because the center engine had not started when the abort was triggered, confusion ensued as the flight controllers were unable to verify its state:
Commentary: "We have a cut off".
"NTD [NASA Test Director] we have a RSLS [Redundant Set Launch Sequencer] abort".Commentary: "We have an abort by the onboard computers of the orbiter Discovery".
"Break break, break break, GLS [Ground Launch Sequencer] shows engine one not shut down".
"OK, PLT [pilot]?"
"CSME [Space Shuttle Main Engines] verify engine one".
"You want me to shut down engine one?"
"We do not show engine start on one".
"OTC [Orbiter test conductor] I can verify shutdown on verify on engine one, we haven't start prepped engine one".
"All engines shut down I can verify that".Commentary: "We can now verify all three engines have been shut down".
"We have red lights on engines two and three in the cockpit, not on one".
"All right, CSME verify engine one safe for APU [auxiliary power unit] shutdown".
"If I can verify that?"
"OTC GPC [General Purpose Computer] go for APU shutdown".[5]
Mission Specialist Steve Hawley was reported as saying following the abort: "Gee, I thought we'd be a lot higher at MECO (Main Engine Cut-Off)!".[6] About ten minutes later, the following was heard on live TV coverage:
"We have indication two of our fire detectors on the zero level; no response. They're side by side right next to the engine area. The engineer requested that we turn on the heat shield fire water which is what could be seen spraying up in the vicinity of the engine bells of Discovery's three main engines".[7]
While evacuating the shuttle 20 minutes later, the crew was doused with water from the pad deluge system, which was activated due to a hydrogen fire on the launch pad caused by the free hydrogen (fuel) that had collected around the engine nozzles following the shutdown and engine anomaly.[8] Because the fire was invisible to humans, had the astronauts used the normal emergency escape procedure across the service arm to the slidewire escape baskets, they would have run into the fire.[9]
Changes to procedures resulting from the abort included more practicing of "safing" the orbiter following aborts at various points, the use of the fire suppression system in all pad aborts, and the testing of the slidewire escape system with a real person (Charles F. Bolden Jr.). It emerged that launch controllers were reluctant to order the crew to evacuate during the STS-41-D abort, as the slidewire had not been ridden by a human.[6]
Examination of telemetry data indicated that the engine malfunction had been caused by a stuck valve that prevented proper flow of LOX into the combustion chamber.[citation needed]
Mission summary
[edit]STS-41-D launched on 08:41:50 a.m. EDT on August 30, 1984, after a six-minute, fifty-second delay when a private aircraft flew into the restricted airspace near the launch pad. It was the fourth launch attempt for Discovery. Because of the two-month delay, the STS-41-F mission was canceled (STS-41-E had already been canceled), and its primary payloads were included on the STS-41-D flight. The combined cargo weighed over 18,681 kg (41,185 lb), a record for a Space Shuttle payload up to that time.
The six-person flight crew consisted of Henry W. Hartsfield Jr., commander, making his second shuttle mission; pilot Michael L. Coats; three mission specialists – Judith A. Resnik, Richard M. Mullane and Steven A. Hawley; and a payload specialist, Charles D. Walker, an employee of McDonnell Douglas. Walker was the first commercially sponsored payload specialist to fly aboard the Space Shuttle. Resnik became the second American woman to fly any NASA space mission, after Sally K. Ride.
Primary cargo of Discovery consisted of three commercial communications satellites: SBS-4 for Satellite Business Systems, Telstar 302 for Telesat of Canada, and Syncom IV-2, or Leasat-2, a Hughes-built satellite leased to the U.S. Navy; all three were Hughes-built satellites. Leasat-2 was the first large communications satellite designed specifically to be deployed from the Space Shuttle. All three satellites were deployed successfully and became operational.
Another payload was the OAST-1 solar array, a device 4 m (13 ft) wide and 31 m (102 ft) high, which folded into a package 18 cm (7.1 in) deep. The array carried a number of different types of experimental solar cells and was extended to its full height several times during the mission. At the time, it was the largest structure ever extended from a crewed spacecraft, and it demonstrated the feasibility of large lightweight solar arrays for use on future orbital installations, such as the International Space Station (ISS).
The McDonnell Douglas-sponsored Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES) experiment, using living cells, was more elaborate than the one flown on previous missions, and payload specialist Walker operated it for more than 100 hours during the flight. A student experiment to study crystal growth in microgravity was also carried out. The highlights of the mission were filmed using an IMAX motion picture camera, and later appeared in the 1985 documentary film The Dream is Alive. On September 3, 1984, concern arose over the formation of ice on the waste dump nozzle of the shuttle. The cause was an obstruction in the shuttle's external wastewater dumping system that caused a 61 cm (24 in) "pee-sicle" to form during the mission; Hartsfield removed it with the Remote Manipulator System (Canadarm) the following day.[10][11]
The mission lasted 6 days, 0 hour, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds, with landing taking place on Runway 17 at Edwards Air Force Base at 06:37:54 a.m. PDT on September 5, 1984. During STS-41-D, Discovery traveled a total of 4,010,000 km (2,490,000 mi) and made 97 orbits. The orbiter was transported back to KSC on September 10, 1984. Ominously, STS-41-D was the first Shuttle mission in which blow-by damage to the SRB O-rings was discovered, with a small amount of soot found beyond the primary O-ring. Following the Challenger disaster, Morton Thiokol engineer Brian Russell called this finding the first "big red flag" on SRB Joint and O-ring safety.[12]
Launch attempts
[edit]| Attempt | Planned | Result | Turnaround | Reason | Decision point | Weather go (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 Jun 1984, 12:00:00 am | Scrubbed | — | Technical | (T−9:00) | Failure of Orbiter's backup General Purpose Computer.[13] | |
| 2 | 26 Jun 1984, 12:00:00 am | Scrubbed | 1 day 0 hours 0 minutes | Technical | (T−0:04) | Post-SSME start RSLS Abort due to anomaly in number three engine. Discovery returned to OPF for engine replacement. | |
| 3 | 29 Aug 1984, 12:00:00 am | Scrubbed | 64 days 0 hours 0 minutes | Technical | Discrepancy with master events controller relating to SRB fire commands. | ||
| 4 | 30 Aug 1984, 1:41:50 pm | Success | 1 day 13 hours 42 minutes | Delayed 6 minutes, 50 seconds when private aircraft strayed into airspace. |
Mission insignia
[edit]The 12 stars within the blue field indicate the flight's original numerical designation as STS-12 in the Space Transportation System's mission sequence. A representation of Discovery's namesake is manifested in a sailing ship, which is linked to the Shuttle (with the OAST solar array in the payload bay) via a red, white, and blue path, signifying its maiden voyage.
Wake-up calls
[edit]NASA began a tradition of playing music to astronauts during the Project Gemini, and first used music to wake up a flight crew during Apollo 15. Each track is specially chosen, often by the astronauts' families, and usually has a special meaning to an individual member of the crew, or is applicable to their daily activities.[14]
| Flight Day | Song | Artist/Composer |
|---|---|---|
| Day 2 | "Anchors Aweigh" | Charles A. Zimmerman |
| Day 3 | "Telstar" | The Ventures |
| Day 4 | "Mr. Spaceman" | The Byrds |
| Day 5 | "Hair" | Broadway cast |
| Day 6 | "Eight Miles High" | The Byrds |
Gallery
[edit]-
SBS-D deployment
-
Syncom IV-2 deployment
-
Telstar 3C deployment
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "SATCAT". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved March 23, 2014.
- ^ "STS-41D". Spacefacts. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
- ^ "Risk of Space Flight" (PDF). Machine Wyle Laboratories. May 12, 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 28, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "STS-41-D". NASA. 2008. Archived from the original on August 17, 2000. Retrieved February 20, 2008.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ STS-41D pad abort (Video). August 6, 2009. Retrieved April 30, 2012 – via YouTube.
- ^ a b Borsché, Catherine E. (June 2007). "A League of Their Own" (PDF). Space Center Roundup. 46 (6). National Aeronautics and Space Administration: 10. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Discovery STS-41-D Mission - Launch - Abort (Video). April 12, 2017. Retrieved June 20, 2019 – via YouTube.
- ^ "Photo of the week 19 (August 8, 2005)". www.collectspace.com. Retrieved July 21, 2013.
- ^ Walker, Charles D. (March 17, 2005). "Oral History Transcript" (PDF). NASA Johnson Space Center Oral History Project (Interview). Interviewed by Ross-Nazzal, Jennifer. NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 15, 2017. Retrieved December 29, 2011.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Walker, Charles D. (April 14, 2005). "Oral History Transcript" (PDF). NASA Johnson Space Center Oral History Project (Interview). Interviewed by Johnson, Sandra. NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 28, 2017. Retrieved December 29, 2011.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ 35 Years Ago: STS-41-D – First Flight of Space Shuttle Discovery
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Vaughan, Diane (1996). The Challenger launch decision: risky technology, culture, and deviance at NASA. University of Chicago Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-226-85175-4.
- ^ Vaughan, Diane (1996). The Challenger launch decision: risky technology, culture, and deviance at NASA. University of Chicago Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-226-85175-4.
- ^ Fries, Colin (June 25, 2007). "Chronology of Wakeup Calls" (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 5, 2010. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.




