Second World
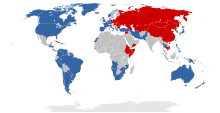
The Second World is a Western term referring to the former industrial socialist states (formally the Eastern Bloc), largely encompassing territories under the influence of the Soviet Union. Following World War II, there were nineteen communist states, and after the fall of the Soviet Union, only 5 socialist states remained: China, North Korea, Cuba, Laos, and Vietnam. Along with "First World" and "Third World", the term was used to divide the states of Earth into three broad categories.
The concept of "Second World" was a construct of the Cold War and the term has largely fallen out of use since the revolutions of 1989, although it is still used to describe countries that are in between poverty and prosperity, many of which are now capitalist states. Subsequently, the actual meaning of the terms "First World", "Second World" and "Third World" changed from being based on political ideology to an economic definition.[1] The three world theory has been criticized as crude and relatively outdated for its nominal ordering (1, 2, 3) and sociologists have coined the term "developed", "developing", and "underdeveloped" as replacement terms for global stratification—nevertheless, the three world theory is still popular in contemporary literature and media. This might also cause semantic variation of the term between describing a region's political entities and its people.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Margaret L. Andersen; Howard Francis Taylor (2006). Sociology: Understanding a Diverse Society. Thomson/Wadsworth. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-534-61716-5.
- ^ Giddens, Anthony (2006). Sociology. Polity.
