South African Special Forces
| South African Special Forces Brigade | |
|---|---|
  Special Forces Insignia and Beret | |
| Active | 1 October 1972 – present |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | SADF 1972-1994 SANDF 1994-present |
| Branch | File:SANDF emblem.jpg Joint Operations Division |
| Type | Special operations force |
| Role | Primary tasks:
Secondary roles: |
| Size |
|
| HQ | Speskop, Pretoria, Gauteng |
| Nickname(s) | Recces |
| Engagements | |
The South African Special Forces Brigade, colloquially known as the Recces,[5] is South Africa's principal special operations unit and counter-insurgency elite, specialising in combat reconnaissance as well as unconventional parachute techniques.[6] Only about 8% of recruits who undergo South African special forces training pass the course.[6]
The South African Hunter Group was formed in 1968, and renamed the Reconnaissance Commando Reserve in 1976. Combat tracker and bushcraft instruction was provided to an exemplary few, though this meant extending training by a harsh twelve months.[7] Personnel also studied insurgent tactics and theory based on Portuguese, Belgian, and Rhodesian experiences. The success of this unit culminated in the formation of the subsequent 1 Reconnaissance Commando near Oudtshoorn on 1 October 1972.[8] Operators in the aptly named "1 Recce" had to be capable of collecting intelligence at great distances behind hostile lines while tracking larger enemy units. In 1976 its headquarters, the Reconnaissance Commando School, was founded and the laurel blade emblem was adopted, along with the motto, "We fear naught but God".
South African special forces played a pivotal role in the South African Border War and were active alongside the Rhodesian Security Forces during the Rhodesian Bush War.[9] Combat operations were also undertaken against FRELIMO militants in Mozambique.[10]
The Special Forces Brigade's current structure[11] is the result of extensive restructuring related to the integration of the South African National Defence Force (SANDF) between 1992 and 1996. Elements of the brigade are expanded into two additional groups; though termed "regiments", they consist only of small numbers of operators who are secretive, seldom photographed, and expertly trained.[7] The current regiments include 4 Special Forces Regiment based at Langebaan in Western Cape Province, and 5 Special Forces Regiment based at Phalaborwa in the northern Limpopo.[11]
Special forces are directly under the command of the Joint Operations Division[11][12] of the SANDF, and unlike other similar forces worldwide, is not a part of the South African Army nor the South African Navy .
History
The first South African Special Forces unit, 1 Reconnaissance Commando, was established in the town of Oudtshoorn, Cape Province on 1 October 1972. On 1 January 1975, this unit was relocated to Durban, Natal,[8] where it continued its activities as the airborne specialist unit of the special forces.
Later, five additional Reconnaissance Commandos were formed:
- 2 Reconnaissance Commando (Citizen Force) - was established in Johannesburg. It was later retired due to rationalisation and the discontinuation of the Citizen Force unit concept
- 3 Reconnaissance Commando (consisting of former Rhodesian Selous Scouts) - was established in Phalaborwa. An attempt to integrate this unit into the South African Military was largely unsuccessful. The unit was disbanded in 1981, and the limited number of remaining personnel were incorporated into the other Special Forces unit.
- 4 Reconnaissance Commando, specialising in seaborne operations, was established in the coastal town of Langebaan, Cape Province.
- 5 Reconnaissance Commando was established at the Duku-Duku camp in Natal, but was later moved to Phalaborwa in the Transvaal province.
- 6 Reconnaissance Commando (consisting of former Rhodesian Special Air Service) – was established in Durban. An attempt to integrate this unit into the South African Military was largely unsuccessful. It was disbanded in 1981, and the limited number of remaining personnel were incorporated into the other Special Forces units.
On 1 January 1981, a re-organisation of Special Forces took place, as part of which the Reconnaissance Commandos and other special forces were transformed into an independent formation, directly under the command of the (then) South African Defence Force (instead of the South African Army). As part of the re-organisation, the various Reconnaissance Commandos were also given the status of regiments. In the latter part of the same decade, a Special Forces headquarters and a Special Forces stores depot were also added to the Special Forces structure.
Between the years 1981 and 1990, Special Forces was home to unconventional operations such as Project Barnacle, the Civil Cooperation Bureau and other operations conducted under the aegis of 7 Medical Battalion Group.
In 1991, the structure of the special forces underwent another change, when the special forces headquarters was disbanded and a Directorate Reconnaissance, reporting directly to the Chief of the Army, was established instead.
Another organisational change followed in 1993, when the Directorate Reconnaissance became 45 Parachute Brigade. As a result of this, all the units were renamed: 1 Reconnaissance Regiment became 452 Parachute Battalion, 4 Reconnaissance Regiment became 453 Parachute Battalion and 5 Reconnaissance Regiment became 451 Parachute Battalion.
As part of the military rationalization process, 1 Special Forces Regiment was disbanded in 1996. Its personnel were incorporated into the other Special Forces Regiments.
In 1997, the Special Forces School was transferred 5 Special Forces Regiment upon the retirement of 1 Special Forces Regiment where the School had previously been based. The Special Forces School was transferred out of 5 Special Forces Regiment in 2002, to become a stand-alone unit.
Structure
The Special Forces Brigade, as it is now known, consists of:[11]
Headquarters

Based in Pretoria. The General Officer Commanding (GOC) Special Forces commands, controls and coordinates the activities of the various SF Regiments from a headquarters (HQ) located in the Swartkop Park nature reserve on the southwestern outskirts of Pretoria. Colloquially called "Speskop", the headquarters also houses the Special Forces’ operational planning as well as administrative support staffs.
Based in Langebaan, Saldanha Bay, along the west coast north of Cape Town, provides South Africa its seaward Special Forces capability. The unit was established at Langebaan in 1978. The Regiment consists of three operational commandos (companies) as well as a Special Forces Amphibious and Urban School.
Based in Phalaborwa in the east of the northern Limpopo Province, was established in Durban in 1976. After a sojourn at Duku Duku in northern KwaZulu-Natal, the unit moved into its present lines in 1980. Its post-2002 structure provides for two operational commandos and a training wing. It specialises in overland operations, especially long-range infiltration, intelligence gathering and airborne operations.
Retired Special Forces personnel form part of the Special Forces Reserve. They are assigned to the various Special Forces Regiments as required.
Based in Murrayhill, the school is responsible for the presentation of the Special Forces Pre-Selection and Selection courses and ongoing training.
This unit provides logistical support and is based in Walmansthal, North of Pretoria.
In the Special Forces regiments, leadership positions, especially at team (section) and group (platoon) level, have traditionally been dictated more by ability and experience than rank. This has, on occasion, resulted in Operators more senior in rank being assigned to groups or teams commanded by Operators junior to them in rank but more seasoned in operational experience or actual command.
Selection and Training
The Ultimate Challenge, as South African Special Forces Selection is often called, is considered one of the more difficult special forces selection courses in the world.[13] A soldier must meet very high requirements to even attend Special Forces Selection. In accordance with SANDF regulations, only South African citizens under a certain age are permitted to even apply.
Pre-selection training
This includes all aspects of psychological and physical tests. For the psychological tests, soldiers are given written tests and oral interviews with Special Forces NCOs. A soldier must be self-controlled and mature. Soldiers are ejected from the course if there is any suggestion of mental instability. The Physical Test includes 40 continuous push ups, 67 sit ups in two minutes, fireman's lift, three-kilometre run in full gear in thirteen minutes, a rope climb (to show upper body strength ), 40 shuttle runs in 95 seconds and wall scaling. A student must scale a 10-foot-high (3.0 m) wall, complete a fifteen-kilometre march in less than 120 minutes and perform 120 shuttle kicks.
Parachute selection course
Basic Parachute School is one of the most physically and mentally demanding courses in the SANDF. All Special Forces candidates who aren't already parachute-qualified have to attend, and pass, this course.
Special Forces selection
Selection is an event during which candidates are placed in an extremely mentally and physically demanding set of situations and circumstances, through which they must pass. It is in duration approximately a week. For the duration of Selection, the candidates do not sleep or eat, and have no rest period at all. Only an extremely small percentage of those who begin Selection ever pass it. In some years, no-one has managed to pass Selection, and there are other cases where only 1 or 2 out of an entire Selection group of approximately 120 have passed.
Training cycle
Once past the Selection process, an aspiring operator will be placed on a training cycle to acquire the skills required. These include: air co-operation, water orientation, obstacle crossing, bushcraft, tracking and survival, demolitions and tactics in urban as well as rural areas.
Advanced Airborne Training: a recruit will attend courses in military free-fall such as HALO and HAHO. They will also learn about helicopter operations – how to descend by means of a rope out of helicopters (fast-roping and rappel ). Combat extraction is also taught, along with learning how to set up a Landing Zone.
Land training consists of many things: including sniping, demolitions and reconnaissance. Bushcraft and survival is also taught. Climbing and photography are taught to new recruits. Urban and rural combat is perhaps the newest training – developed quite recently, this training provided South Africa with a new counter-terrorist force. Medical and communications training is also given to those who wish to become qualified in these fields.
Maritime training consists of the use of small boats, underwater demolitions, swimming, diving, beach reconnaissance and navigation.
Operations
1973–94 SADF Operations

The South African "Recces" were deployed to many local hot spots during the late 1970s and early 1980s, particularly Angola.
The main enemy then was South West Africa’s People Organization whose armed wing PLAN, was a guerrilla organization fighting for an independent Namibia.
One of the "Recces"' most effective operations came in 1982: Operation Mebos penetrated deep into Angola and destroyed the SWAPO Headquarters. In Operation Askari, in the winter of 1984, the "Recces" cut off almost all supply lines to and from the SWAPO in Angola. In 1985, a "Recce" team undertook the controversial Operation Cabinda, a failed attempt to sabotage Angolan oil installations run by Gulf Oil.
In early summer of 1985, another "Recce" team under the command of SADF Captain André Diedericks crossed into Angola's Cuando Cubango province, and with UNITA's help, protection and escort was secretly deployed around Menongue area. The team had at their disposal the 9K31 “Strela-1” AA system manned and operated by the team members. The Team’s mission was to carry out covert combat operations, code names "Catamaran 1," "Catamaran 2" and "Cerberus" with the goal of disrupting air traffic in Cuando Cubango province by shooting down air transports, combat aircraft and gunships using the AA system.
On 11 June 1985, roughly 80 km (50 mi) from Menongue, the team shot down an Angolan airplane, a light utility aircraft, Britten-Norman BN-2 “Islander”. The "Islander", en route from Menongue to Cuito Cuanavale with a crew of 2 and 5 passengers, was also carrying 69 million kwanzas (Angola’s currency), several months of salary for FAPLA’s 16th Brigade’s personnel based in Cuito Cuanavale. When the "Islander" fell to the ground the money was stolen and the remains of the dead passengers had been pillaged by UNITA soldiers attached to protect the "Recce" team. On 25 November 1985, the same "Recce" team had also shot down an “Aeroflot” Antonov AN-12 of the Soviet Air Force. The AN-12 transport, which was en route from Cuito Cuanavale to Luanda carrying 8 crew members and 13 passengers, crashed approximately 43 km (27 mi) south-east of Menongue. All people on board (twelve Soviet and nine Angolan nationals) died in the crash.[14]
Post-1994 SANDF Operations

Central African Republic
Operators of the South African Special Forces were involved in direct action against the Séléka rebels in the Fight for Bangui during the South African military assistance to the Central African Republic.[15] No South African Special Forces operators were killed in the operation. All casualties were attributed to 1 Parachute Battalion which lost 13 soldiers, with a further 27 injured, during pitched battles on the outskirts of the capital, Bangui.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
An operator of the South African Special Forces, as part of the Force Intervention Brigade, made the 6th longest recorded sniper kill in history with a confirmed distance of 2,125 m (2,324 yd) using a South African made Denel NTW-20 anti-materiel rifle in its 14.5 mm (0.57 in) configuration.[16]
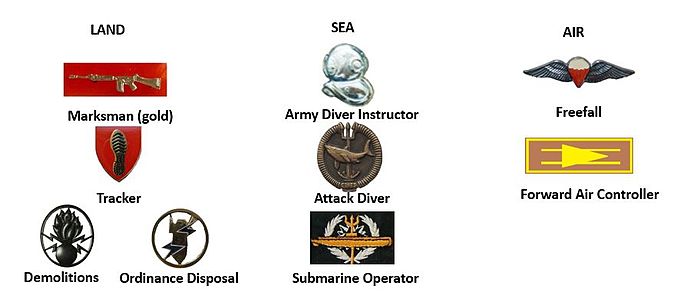
Insignia
Operator's Badge

All members who complete all the required qualifications to become a Special Forces Operator, are awarded an "Operator's Badge".[17] Each badge is numbered and a register of the numbers and who they have been awarded to is kept.[18][19] The badge consists of an inverted Commando Knife within a laurel wreath, which is meant to symbolise both special forces (the knife) and victory (the wreath).[17]
Standard operator badges are silver, but a gold badge with an embedded diamond is awarded to Operators with more than 10 years of active service.[17]
New badges have been designed for wear on the camouflage combat dress. These are black embossed plastic on a thatch green background.

|
| Black on Thatch beige, Embossed Dagger enclosed with a laurel wreath |

|
| Gold, 10 Years Black on Thatch beige, Embossed Dagger enclosed with a laurel wreath. Exclusion to indicate diamond on Dagger blade. |
Attack Diver

|
| Bronze Black on Thatch beige, Embossed The badge depicts a great white shark swimming past the Neptune trident, which is mounted on the mouthpiece of an Oxygears 57 and is enclosed within the tubes of the Oxygears 57 |

|
| Silver Black Circle indicates Instructor Black on Thatch beige, Embossed The badge depicts a great white shark swimming past the Neptune trident, which is mounted on the mouthpiece of an Oxygears 57 and is enclosed within the tubes of the Oxygears 57 |
Additional proficiency badges
Known Equipment
Weaponry
Vehicles
| Name | Type | Origin | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casspir | Mine-Resistant Armoured Personnel Carrier | Multiple variants in use | ||
| Hornet (RDRV) | Rapid Deployment Reconnaissance Vehicle | |||
| Gecko (RDLV) | Rapid Deployment Logistic Vehicle | |||
| Toyota Land Cruiser | Light Armoured Tactical Vehicle | |||
| SAMIL 100 | Armoured Military Truck | Carrier for a 23 mm anti-aircraft gun named "Zumlac" |
Leadership
| From | General Officers Commanding | To |
| 2003 | Brig Gen Krubert Nel[20] | 2006 |
| 21 November 2024 | Brig Gen Rudzani Maphwanya | 21 November 2024 |
| From | Chiefs of Staff | To |
| 1998 | Col Krubert Nel[20] | 2003 |
| 2003 | Col Doibi Coetzee | 2014 |
| From | Brigade Sergeants Major | To |
| 21 November 2024 | Unknown | Present |
References
- ^ "4RR / 4SFR History - SA Special Forces League". Recce.co.za. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ "5RR / 5SFR History - SA Special Forces League". Recce.co.za. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ South Africa bolsters its troops in the Central African Republic
- ^ DRC Sniper Revelation compromising SANDF troops - expert
- ^ SA Special Forces Association
- ^ a b McNab, Chris (2002). 20th Century Military Uniforms (2nd ed.). Kent: Grange Books. ISBN 1-84013-476-3.
- ^ a b Pitta, R; Fannell, J (1993). South African Special Forces. Osprey Publishing.
- ^ a b "1RR / 1SFR History - SA Special Forces League". Recce.co.za. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ Scholtz, Leopold (2013). The SADF in the Border War 1966-1989. Cape Town: Tafelberg. ISBN 978-0-624-05410-8.
- ^ Harry McCallion. Killing Zone (11 April 1996 ed.). Bloomsbury Paperbacks. pp. 13–281. ISBN 0-7475-2567-6.
- ^ a b c d "Special Forces Structure". Official Special Forces Website. Joint Operations Division, Department of Defence. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- ^ "Joint Operations Division". www.jops.mil.za. Joint Operations Division, Department of Defence. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- ^ "Chairman's Welcome - SA Special Forces League". Recce.co.za. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ Diedericks, André (2007). Journey Without Boundaries (2nd ed.). Durban, South Africa: Just Done Productions Publishing (published 23 June 2007). ISBN 978-1-920169-58-9. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- ^ "SANDF releases names of SA soldiers killed in CAR". Mail & Guardian. mg.co.za. 26 March 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ Graeme Hosken. "SA snipers wreak havoc". Times LIVE. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ a b c "Special Forces Insignia". Official Special Forces Website. Joint Operations Division, Department of Defence. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- ^ "Identification of a Bogus Special Forces Operator". www.recce.co.za. South African Special Forces Association. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
Also note that each badge is uniquely numbered and can only be issued once to a specific individual. Operator's badges are not transferable.
- ^ "Bone Fide Operators". www.recce.co.za. South African Special Forces Association. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
A person can be identified as a Special Forces Operator only if he has a Special Forces Operators Badge with its unique number, (of which detailed and clear records are kept).
- ^ a b Meyer, Maj M. (October 2012). "GOODBYE "ROGER KEN"" (PDF). SA Soldier. 19 (10): 8. ISSN 1609-5014. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
Further reading
- Breytenbach, Jan, Col (1990). They Live by the Sword. Alberton: Lemur. ISBN 0620148705.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Diedericks, André (2007). Journey Without Boundaries (A5) (2nd ed.). Durban, South Africa: Just Done Productions Publishing (published 23 June 2007). ISBN 978-1-920169-58-9. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- Els, Paul (1 April 2001). We Fear Naught but God (1st ed.). Pretoria: Covos-Day Books. ISBN 978-0620238915.
- Els, Paul (1 March 2015). We Fear Naught but God - Pictorial Edition (1st ed.). Pretoria.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Els, Paul (2010). Saturday's Soldiers - The Hunter Group. Pretoria: Pelsa Books. ISBN 9780620490696.
- Greef, Jack (2008). A Greater Share of Honour (2nd ed.). Durban, South Africa: Just Done Productions Publishing (published 17 July 2008). ISBN 978-1-920315-06-1. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- Monick, S. (1992). Clear the Way Volume 2. South African Irish Regimental Association. ISBN 0620164840.
- Stiff, Peter (1999). The Silent War. Galago Publishing. ISBN 0-620-24300-7.