Southern Sámi
| Southern Sami | |
|---|---|
| [Åarjelsaemien gïele] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
| Region | Norway, Sweden |
Native speakers | (600 cited 1992)[1] |
| Latin | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Snåsa, Norway |
Recognised minority language in | Norway; Sweden[2] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | sma |
| ISO 639-3 | sma |
| Glottolog | sout2674 |
| ELP | South Saami |
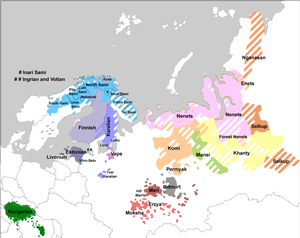
 Southern Sami is 1 on this map. | |

Southern Sami ([Åarjelsaemien gïele] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) is the southwestern-most of the Sami languages. It is a seriously endangered language; the strongholds of this language are the municipalities of Snåsa, Røyrvik, Røros and Hattfjelldal in Norway.
Writing system
Southern Sami is one of the six Sami languages that has an official written language, but only a few books have been published for the language, one of which is a good-size Southern Sami–Norwegian dictionary.
Southern Sami uses the Latin script: A/a, B/b, D/d, E/e, F/f, G/g, H/h, I/i, (Ï/ï), J/j, K/k, L/l, M/m, N/n, O/o, P/p, R/r, S/s, T/t, U/u, V/v, Y/y, Æ/æ, Ø/ø, Å/å
An alternative orthography replaces Æ/æ with Ä/ä and Ø/ø with Ö/ö. The variants Ä/ä, Ö/ö are used in Sweden, Æ/æ, Ø/ø in Norway, in accordance with the usage in Swedish and Norwegian, based on computer or typewriter availability. The Ï/ï represents a back version of I/i, many texts do not distinguish between the two.
C/c, Q/q, W/w, X/x, Z/z are used in words of foreign origin.
Phonology
Southern Sami has two dialects, the northern and the southern dialect. The phonological differences between the dialects are relatively small; the phonemic system of the northern dialect is explained below.
Vowels
The vowel phonemes of the northern dialect are the following; orthographic counterparts are given in italics:
| front | central | back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | |
| close | /i/ i | /y/ y | /ɨ/ ï/i1 | /ʉ/ u | /u/ o | |
| mid | /e/ e | /o/ å | ||||
| open | /ɛ/ æ/ä2/ae3 | /ɑ/ a | ||||
1The distinction between the vowels /i/ and /ɨ/ is normally not indicated in spelling: both of these sounds are written with the letter i. However, dictionaries and other linguistically precise sources use the character ï for the latter vowel.
2The letter æ is used in Norway, and ä in Sweden.
3Long /ɛː/ is written ae.
The non-high vowels /e/, /ɛ/, /o/ and /ɑ/ contrast in length: they may occur as both short and long. High vowels only occur as short.
The vowels may combine to form ten different diphthongs:
| front | front to back | central to back | central to front | back to front | back | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| close to mid | /ie/ ie | /yo/ yø/yö | /ʉe/ ue, /ɨe/ ie/ïe | /uo/ oe | ||
| close to open | /ʉa/ ua | |||||
| mid | /oe/ øø/öö | |||||
| mid to open | /eæ/ ea | /oæ/ åe | /oa/ åa |
Consonants
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2009) |
Grammar
Sound alternations
A typical feature of Southern Sami is the alternation of first-syllable vowels through Umlaut in the declension and conjugation of words. Often there are three different vowels that alternate with each other in the paradigm of a single word, for example as follows:
- ae ~ aa ~ ee: vaedtsedh 'to walk' : vaadtsam 'I walk' : veedtsim 'I walked'
- ue ~ ua ~ øø: vuelkedh 'to leave' : vualkam 'I leave' : vøølkim 'I left'
The Umlaut is often rendered in a table,
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | context | gramm. form | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | klihtie | jeptsie | buvrie | sjiellie | gaevlie | gåetie | njueslie | second syllable ie | nominative |
| B | klæhtan | japtsan | båvran | sjeallan | gaavlan | gåatan | njuaslan | second syllable a | illative |
| F | klihtine | jiptsine | buvrine | sjeelline | geevline | gøøtine | njøøsline | third syllable e | comitative |
| meaning: | 'mountain shelf' | 'idiot' | 'pillar storehouse' | 'trash' | 'critic' | 'house' | 'bum' | ||
| C | færhtjoe | bahtjoe | rånhtjoe | bearkoe | baarmoe | råafoe | second syllable oe | nominative | |
| E | fyrhtjese | bohtjese | ronhtjese | byörkese | båårmese | rååfese | second syllable e | illative | |
| meaning: | 'girl' | ? | 'mountain ridge' | 'meat' | 'mountain side' | 'shed' |
On the other hand, Southern Sami is the only Sami language that does not have consonant gradation. Hence consonants in the middle of words never alternate in Southern Sami, even though such alternations are frequent in other Sami languages. Compare, for instance, Southern Sami nomme 'name' : nommesne 'in the name' to Northern Sami namma : namas, with the consonant gradation mm : m.
Cases
Southern Sámi has 8 cases:
| Case | Singular ending | Plural ending |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | - | -h |
| Genitive | -n | -i / -j |
| Accusative | -m | -jte / -ite / -idie |
| Inessive | -sne / -snie | -ine / -jne / -inie |
| Elative | -ste / -stie | -jste / -jstie |
| Illative | -n / -se / -sse | -jte / -ite / -idie |
| Comitative | -ine / -jne / -inie | -igujmie / -jgujmie |
| Essive | -ine / -jne / -inie | (no plural form) |
Southern Sámi is one of the few Sami languages that still differentiate between the accusative and the genitive morphologically.
Verbs
Person
Southern Sami verbs conjugate for three grammatical persons:
- first person
- second person
- third person
Mood
Tense
Grammatical number
Southern Sami verbs conjugate for three grammatical numbers:
Negative verb
Southern Sami, like Finnish, the other Sámi languages and Estonian, has a negative verb. In Southern Sami, the negative verb conjugates according to tense (past and non-past), mood (indicative and imperative), person (1st, 2nd and 3rd) and number (singular, dual and plural). This differs from some other Sami languages, e.g. from Northern Sami, which do not conjugate according to tense.
| Non-past indicative | Past indicative | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | |
| 1st | im | ean | ibie | idtjim | idtjimen | idtjimh |
| 2nd | ih | idien | idie | idtjih | idtjiden | idtjidh |
| 3rd | ij | eakan | eah | idtji | idtjigan | idtjin |
| Non-past imperative | Past imperative | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | |
| 1st | aelliem | aellien | aellebe | ollem | ollen | ollebe |
| 2nd | aellieh | aelleden | aellede | ollh | olleden | ollede |
| 3rd | aellis | aellis | aellis | olles | olles | olles |
Syntax
Like Skolt Sami and unlike other Sami languages, Southern Sami is an SOV language.
References
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (August 2010) |
- ^ Southern Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "To which languages does the Charter apply?". European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. Council of Europe. p. 5. Retrieved 2014-04-03.
- Bergsland, Knut. Røroslappisk grammatikk, 1946.
- Knut Bergsland. Sydsamisk grammatikk, 1982.
- Knut Bergsland and Lajla Mattson Magga. Åarjelsaemien-daaroen baakoegærja, 1993.
- Hasselbrink, Gustav. Südsamisches Wörterbuch I–III
External links
- Sámi lottit Names of birds found in Sápmi in a number of languages, including Skolt Sámi and English. Search function only works with Finnish input though.
- Southern Sámi grammatical resources
- Samien Sijte – Southern Sámi Museum and Cultural Center
- Sørsamisk forskning og undervisning – Universitetet i Tromsø