Taylor, British Columbia
56°09′32.3″N 120°41′16.0″W / 56.158972°N 120.687778°W
Taylor | |
|---|---|
| District of Taylor[1] | |
 District of Taylor Municipal Hall | |
Location of Taylor in British Columbia | |
| Coordinates: 56°09′32″N 120°41′16″W / 56.15889°N 120.68778°W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia |
| Regional District | Peace River District |
| Incorporated | 23 Aug 1958 (Village) |
| 21 Apr 1989 (District) | |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Rob Fraser |
| • Governing Body | Mayor and Council |
| • MP | Bob Zimmer |
| • MLA | Pat Pimm |
| Area | |
| • Total | 17.09 km2 (6.60 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 500 m (1,600 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 1,373 |
| Time zone | UTC-7 (Mountain Time Zone) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (not observed) |
| Postal code span | |
| Area code | +1-250 |
| Website | District of Taylor |
The District of Taylor is a district municipality in northeastern British Columbia, Canada, located at mile 36 of the Alaska Highway. Taylor, a member municipality of the Peace River Regional District, covers an area of about 17 km² with 1,317 residents as of 2021.[2]
The town sits on a terrace 60 m above the north bank of the Peace River. The first settler on the flat was a trapper named Herbert Taylor in 1911. The town incorporated in 1958 with industrial business beginning to locate there. Since then, Taylor has remained a small town, even though it has developed a large industrial base. It has become home to the annual World's Invitational Class 'A' Gold Panning Championships and was featured on the CBC Television program Village on a Diet.
History
The town, and the Taylor Flats upon which the town is located, are named after Donald Herbert Taylor, a fur-trader with the Hudson's Bay Company who regularly met his Aboriginal trading counterparts on this river flat. In 1912 Taylor left his employers and took up residence on the flats with a few other squatters. That year the federal government opened the area to homesteading and Taylor was granted the land upon which he had settled.[3] These early settlers were trappers with the first farm established by Henry Philip, from Glasgow, who inherited buildings, equipment and land from his survey team when they left the area. In 1915, there were 20 settlers. (Fort George Herald, 9 Oct 1915) In 1919, with the help of Taylor's nine children, along with those from a few American families who settled there, the provincial government opened the Taylor Flats School.
These early settlers all came to the area through the Peace River Country, through Grande Prairie and Pouce Coupe, and across the Peace River. Some decided to settle on the steep-sloped south side of the Peace River, an area that would become known as South Taylor. To cross the river a cable ferry, which would prove to be accident-prone, was built in the 1920s but was soon replaced with a motor-driven ferry. This ferry was used until 1942 when the U.S. Army came through the area building the Alaska Highway and constructed the 2,130-foot (650 m) long Peace River Suspension Bridge. The highway connected the town to a rail station in Dawson Creek reducing the dependence on shipping along the river. The bridge suddenly collapsed on October 16, 1957 with no injuries or fatalities.[4] A new rail trestle, from the rail extension from Chetwynd to Fort St. John, was used while constructing the replacement Peace River Bridge.

Major industrial development began in 1957, when Westcoast Energy (later Duke Energy) built the province's first gas processing plant, as well as a refinery and pipeline to Kamloops.[5] The community that formed around this industrial development was incorporated as a village on August 23, 1958 and soon after Canfor opened a planer mill. Meanwhile, 120 km (75 mi) upstream, the W.A.C. Bennett Dam was completed in 1966 and the Peace Canyon Dam in 1980, which controlled the level and flow of the Peace River, making navigation and flood control much easier. The 1961 Canadian census, the first to recognize Taylor as a census subdivision, counted 438 people.[6] During the subsequent five years the population rose 36% to 595 people but rose only a further 2% to 605 people by 1971.[6]
Following the construction of a natural gas processing plant by Westcoast Energy in 1985, Fibreco Pulp opened its sawmill in 1988, and the Village was re-incorporated into the District of Taylor in 1989. Despite the closure of the Petro-Canada refinery in 1991, economic growth continued throughout the decade as Westcoast Energy's McMahon Gas Plant expanded in 1991 and added a cogeneration plant in 1993. Fibreco Pulp doubled its capacity in 1996, the Younger Natural Gas Liquids Extraction Plant (to extract water and sulphur from natural gas) was expanded in 1996, and the Taylor Straddle plant (to extract ethane from natural gas) was built in 1997. Since 1993, the town of 1,373 residents have built a new hockey arena, leisure skating arena, curling rink, and an 18-hole golf course. Strong community pride also developed as demonstrated by the town placing first at the provincial level, in its small category, in the parks and gardens-oriented Communities in Bloom Competition in 1997 and second in the national competition in 1998.[4][7] Other local projects have included building a memorial garden and cenotaph in 2000 dedicated to the 341st Engineers of the U.S. Army corps of Engineers who were stationed on the Taylor Flats in 1942 during the construction of the Alaska Highway and the Peace River Suspension Bridge.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 1,143 | — |
| 2006 | 1,384 | +21.1% |
| 2011 | 1,373 | −0.8% |
| 2016 | 1,469 | +7.0% |
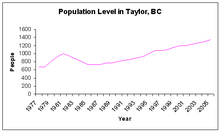
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Taylor had a population of 1,317 living in 542 of its 610 total private dwellings, a change of -10.3% from its 2016 population of 1,469. With a land area of 16.92 km2 (6.53 sq mi), it had a population density of 77.8/km2 (201.6/sq mi) in 2021.[8]
| Canada 2011 Census[9] | ||
| Taylor | British Columbia | |
| Median age | 30.7 years | 41.9 years |
| Under 15 years old | 22.9% | 15.4% |
| Over 65 years old | 6.2% | 15.7% |
| Visible minority | 1.4% | 27.3% |
| Protestant | 50.0% | 44.6% |
| No religious affiliation | 50.0% | 44.1% |
According to the 2011 Canadian Census, a little over the provincial average 68.5% are married while 31.5% are single. With 2.5% of Taylor residents being foreign-born, and 96.4% with an English-only mother tongue, the town has few visible minorities. While not counted as visible minorities during the census, 180 people considered themselves to have an Aboriginal identity, just over twice the provincial average of 5.4%. Housing is mostly owned with 21.5% of the stock being rented, with the provincial average being 29.8%.[9]
Geography and climate

| Precipitation averages, 1971-2000[10] | |
| Time | Precipitation |
| January | 26 mm (1.0 in) |
| July | 80 mm (3.1 in) |
| Annual | 321 mm (12.6 in) |
| Annual snowfall: 135 cm (53.0 in) | |
The Taylor Flats, upon which the town is situated, was formed by a pre-glacial bend in the Peace River that now flows eastwards, originating in Hudson's Hope and emptying into the Arctic Ocean. The terrace is approximately 60 m above the north bank of the Peace River. Escarpments encircle the terrace and rise another 100 m to the upland Peace River Prairie. The soil of the Taylor Flats has few limitations, and is rated as prime in some areas.[11] The soils are Rego black loam and clay loam that contain few stones or gravel and are well drained, yet hold adequate moisture for crops. There are several hundred acres of Agricultural Land Reserve within the municipal boundaries on both the east and west sides of the town site. Most of the original vegetation and tree stands have been cleared but black spruce and aspen trees, and an understory of Labrador tea, bog cranberry and mosses are present.[12]
The town has a northern, semiarid continental climate with cool, short summers and long, cold winters. However, the Taylor Flats’ microclimate, created by the south-facing terrace and the Peace River, produces more frost-free days than most of the Peace River Country. Being in a rain shadow of the Rocky Mountains the town receives a suppressed amount of precipitation, and especially snowfall.[12] Like the rest of the region, the town has long daylight hours in the summer, short winter daylight hours and uses Mountain Standard Time year-round.
Transportation and infrastructure
Taylor's transportation network is dominated by the two-lane Alaska Highway (Highway 97) which runs north-south through the middle of community and provides the main entrance and exit to the town. Cherry Avenue East is a rural road transportation route that travels through Baldonnel to Fort St. John. Intersections along the highway give access to frontage roads lined with businesses and civic buildings oriented to the highway. The frontage roads also provide access to housing behind the businesses. A wide right-of-way provides a large building setback distance from the highway and helps mitigate noise and other negative impacts of heavy traffic. In total, Taylor maintains 23 km of paved and 14 km of unpaved roads.[13]

Taylor has limited rail, bus, boating and air service for regional and provincial transportation needs. A BC Rail line runs northeast from Chetwynd to Fort St. John and branches off eastwards to Taylor. The rail line’s terminus is in the industrial sector in the southeast corner on the town. The train, which does not offer passenger service, must turn around in the industrial area in order to travel back to the trunk line. Greyhound Bus Lines maintain a stop in Taylor along its Alaska Highway route from Dawson Creek, 56.5 km south of Taylor to Fort St. John (14 km north of Taylor). Since the Peace River is controlled by two dams upstream, it is navigable for recreational boats, however, due to the coulee between industry and the river, the shipping industries in the town did not develop. The closest commercial airport is Fort St. John Airport, 13.8 km north of Taylor, with two paved runways.[14]
The town uses the Peace River which flows eastward as a source of drinking water and as outlet for industrial waste. The drinking water supply comes from an intake pipe southwest of town. The water is mechanically and chemically filtered then pumped to a reservoir on a ridge north of town. A gravity pump moves the water to the town from the reservoir using 18 km of watermains.[13] Sewage is collected by 13 km of sanitary sewers and processed by a two-cell lagoon system before being absorbed into the ground.[13]
Taylor's only school, Taylor Elementary School, is administered by School District 60 Peace River North, which in 2005 had an enrollment of 147 students.[15] Any students grades 7 and up are transported to Fort St. John for secondary school education. Taylor funds a volunteer fire department, which covers the town plus several kilometers into the rural areas. The closest hospital for Taylor residents is the Fort St. John General Hospital but residents can access medical resources through the Taylor Medical Clinic.
Economy

For a town of 1,373 people, Taylor has a very large industrial base and calls itself "Where Peace and Prosperity Meet." Industrial plants include the Westcoast Energy's McMahon plant for natural gas processing with sulfur recovery and cogeneration, two straddle plants which extract ethane and other impurities from liquid natural gas, Canfor Pulp's chemi-thermomechanical pulp mill, and several smaller sawmills. Being involved in primary resource industries, the town is vulnerable to global trade, as demonstrated by the town's Canfor planer mill closing in 2004 during U.S.-Canada softwood lumber dispute. In response to the decline of the forest industry, the town has expanded its tourism industry. After the Canfor mill closure, the District established a plan to develop Peace Island Park for tourist operations. The federal Ministry of Western Economic Diversification, contributed $310,952 to the project.
| Economy[9] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rate | Taylor | British Columbia |
| Unemployment rate | 7.7% | 7.8% |
| Participation rate | 71.4% | 64.6% |
| Average male income | $59,000 | $47,480 |
| Average female income | $24,953 | $31,683 |
According to the 2011 Canadian census, only 2.7% of Taylor's population graduated from a university, much less than the 22.1% provincial average and, likewise, 34.3% did not graduate from secondary school, twice the provincial average. Of Taylor's 775 person labour force, 32.3%, or 250 people (220 males and 25 females), are employed as tradesmen, transport and equipment operators and in related occupations.[9] With Fort St. John only 14 km north of Taylor it is within commuting distance for employees and shoppers. Taylor itself has little commercial retail stores, including no grocery store, but residents commute to Fort St. John for their retail needs.
Culture and recreation

Despite its small population base and its proximity to a much larger urban centre Taylor has an ice arena, a curling rink, indoor swimming pool, irrigated baseball diamonds, a motocross track, and an 18-hole championship golf course. The District Ice Centre opened in 1993 and consists of an ice hockey rink and leisure skating rink, both of which are used for roller hockey, trade shows and conventions in the summer. The four sheet curling rink is used as a swimming pool in the summer. The District's newest facility, built in 2001, is a CND $1.2 million multi-purpose community hall and gymnasium, which now features a rehabilitation studio.[7] The 320-acre (1.3 km2), 18-hole Lone Wolf Golf Course opened in 1995 at a cost of $3.5 million and is managed by the District. Meandering around the course, by agricultural fields, and a community forest, is the 4.2 km ParticipACTION Trail. In the winter the golf course and its trails are used for cross-country skiing, snowshoeing and other winter activities.
The District has operated Peace Island Park with its boat launch, campsites, and facilities for recreational outdoor events. Peace Island Park is the home of the Invitational Class 'A' Gold Panning Championships in the summer.
The gold panning competition is a three-day event that has been held in Taylor annually since 1972 and includes advanced and amateur competitions.[16] Also, to preserve its heritage, several pioneer log houses, such as the Information Centre, where a replica of Alexander Mackenzie's birch bark canoe is displayed, and Peace Island Park meeting hall, have been restored and are used today. In 2010/11 the town was featured on the CBC documentary series Village on a Diet.[17]
Government and politics
The District of Taylor has a Mayor and Council form of municipal government. At-large elections are held every four years to elect four municipal councillors, a mayor who also represents Taylor at the Peace River Regional District Board of Directors, and one school board trustee (to the school district). The November 2014 municipal election was the first election in 28 years that the District of Taylor elected a new mayor. Mayor Rob Fraser was elected after Former Mayor Fred Jarvis retired after 35 years in the public service sector.
Taylor is situated in the Peace River North provincial electoral district and is represented by Pat Pimm in the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia. Prior to 2009, the town was located within the Peace River South electoral district and was represented by Blair Lekstrom who was first elected as its Member of the Legislative Assembly in the 2001 provincial election taking 78% of votes cast at the Taylor polls[18] and re-elected in 2005 with 73% support.[19] For the 1996 election, and those previous, Taylor was part of the Peace River North provincial electoral district which elected Richard Neufeld of the BC Reform Party.[20]
Federally, Taylor is located in the Prince George—Peace River riding, which is represented in the House of Commons of Canada by Conservative Party Member of Parliament Bob Zimmer. Prior to Zimmer the town was represented by long-time MLA Jay Hill, first elected in 1993 and re-elected in 1997, 2000, 2004, and 2006 with 82%,[21] 83%,[21] 79%[22] and 80%[23] support from Taylor polls, respectively. Before Hill the town was represented, from 1972 to 1993, by Frank Oberle of the Progressive Conservative Party who served as Minister of State for Science and Technology from 1985 to 1989 and Minister of Forestry from 1990 to 1993.[24]
| Canadian federal election 2011: Taylor polls in Prince George—Peace River[25] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | city % | riding % | ||
| Conservative | Bob Zimmer | 367 | 77% | 62% | ||
| New Democratic | Lois Boone | 62 | 13% | 26% | ||
| Green | Hilary Crowley | 26 | 5.4% | 6.0% | ||
| Liberal | Ben Levine | 15 | 3.1% | 5.2% | ||
| Pirate | Jeremy Cote | 8 | 1.7% | 1.1% | ||
| Turnout | 478 | 49% | 54% | |||
| B.C. election 2013: Taylor polls in Peace River North[26] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | city % | riding % | ||
| Liberal | Pat Pimm | 240 | 58.8% | 58.9% | ||
| Independent | Arthur Hadland | 134 | 32.8% | 24.5% | ||
| New Democratic | Judy Fox-McGuire | 18 | 4.4% | 9.8% | ||
| Conservative | Wyeth Sigurdson | 16 | 3.9% | 6.7% | ||
| Turnout | 408 | 29.7% | 3.0% | |||
References
- ^ "British Columbia Regional Districts, Municipalities, Corporate Name, Date of Incorporation and Postal Address" (XLS). British Columbia Ministry of Communities, Sport and Cultural Development. Retrieved November 2, 2014.
- ^ Statistics Canada. 2022. (table). Census Profile. 2021 Census. Statistics Canada Catalogue no. 98-316-X2021001. Ottawa. Released February 9, 2022. https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/index.cfm?Lang=E (accessed February 15, 2022).
- ^ Harrison, Hal (1981) "Birth of the South Peace" in Lure of the South Peace: Tales of the Early Pioneers Dawson Creek: South Peace Historical Book Committee. pg. 273.
- ^ a b District of Taylor (October 24, 2014), [1] History.
- ^ Spectra Energy (October 24, 2014), [2] History.
- ^ a b c BC Stats (October 24, 2014), [3].
- ^ a b District of Taylor (October 24, 2014), [4] History 1960 to Present.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts: Canada, provinces and territories, and census subdivisions (municipalities), British Columbia". Statistics Canada. February 9, 2022. Retrieved February 20, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Statistics Canada (October 23, 2014), [5], 2011 Community Profiles.
- ^ Climate Canada (October 24, 2014), Taylor Flats, British Columbia, Canadian Climate Normals 1971-2000
- ^ Provincial Agricultural Land Commission (October 24, 2014)
- ^ a b Salmo Consulting Inc. and Novagas Clearinghouse Ltd. (October 24, 2014). Application for a Project Approval Certificate - Taylor Straddle plant
- ^ a b c Reed Construction (2005), Municipal redbook: an authoritative reference guide to local government in British Columbia, Burnaby, BC, 65. ISSN 0068-161X
- ^ Fort St. John Airport (October 24, 2014), [6] North Peace Airport Services February 3, 2005.
- ^ School District No. 60 (October 24, 2014) Taylor Elementary School, School District No. 60 (Peace River North)
- ^ District of Taylor. Taylor Events: Gold Panning
- ^ Scott, Jennifer (February 2011). "All about Village on a Diet". Canadian Living. Retrieved January 4, 2011.
- ^ Elections BC (October 24, 2014) [7], Statement of Votes, 2001.
- ^ Elections BC (October 24, 2014) [8], Statement of Votes, 2005
- ^ Elections BC (October 24, 2014) [9], Statement of Votes, 1996.
- ^ a b Elections Canada 36th and 37th General Elections: Official Voting Results: Poll-by-poll Results, Elections Canada On-Line|General Information, January 22, 2006. (Requires user to download database.
- ^ Elections Canada (2004) Thirty-eighth General Election 2004 — Poll-by-poll results, Official Voting Results/Résultats officiels du scrutin, November 18, 2005. (Requires navigation to Prince George—Peace River)
- ^ Elections Canada (October 24, 2014) 39th General Election Validated Poll-by-Poll Results.
- ^ Library of Parliament (2006) Oberle, The Hon. Frank, P.C. Archived 2007-12-29 at archive.today, Federal Political Experience, January 22, 2006. (Requires user to download database.
- ^ "Forty-First General Election". Official Voting Results. Elections Canada. 2011. Retrieved 2011-11-20. Requires navigation to Prince George—Peace River
- ^ "Peace River North Electoral District" (PDF). Statement of Votes, 2013. Elections BC. 2013. Retrieved 2014-10-23.
- General references
- Calverley, Dorthea. The Story of Taylor’s Flat to 1957 Calverley Collection.


