Ximelagatran
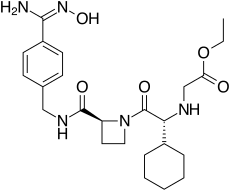 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Exanta |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 20% |
| Metabolism | to melagatran |
| Elimination half-life | 3–5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (80%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H35N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 473.574 g·mol−1 (429 g/mol after conversion) |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ximelagatran (Exanta or Exarta, H 376/95) is an anticoagulant that has been investigated extensively as a replacement for warfarin[1] that would overcome the problematic dietary, drug interaction, and monitoring issues associated with warfarin therapy. In 2006, its manufacturer AstraZeneca announced that it would withdraw pending applications for marketing approval after reports of hepatotoxicity (liver damage) during trials, and discontinue its distribution in countries where the drug had been approved (Germany, Portugal, Sweden, Finland, Norway, Iceland, Austria, Denmark, France, Switzerland, Argentina and Brazil).[2]
Method of action
Ximelagatran, a direct thrombin inhibitor,[3] was the first member of this class that can be taken orally. It acts solely by inhibiting the actions of thrombin. It is taken orally twice daily, and rapidly absorbed by the small intestine. Ximelagatran is a prodrug, being converted in vivo to the active agent melagatran. This conversion takes place in the liver and many other tissues through dealkylation and dehydroxylation (replacing the ethyl and hydroxyl groups with hydrogen).
Uses
Ximelagatran was expected to replace warfarin and sometimes aspirin and heparin in many therapeutic settings, including deep venous thrombosis, prevention of secondary venous thromboembolism and complications of atrial fibrillation such as stroke. The efficacy of ximelagatran for these indications had been well documented,[4][5][6] except for non valvular atrial fibrillation.
An advantage, according to early reports by its manufacturer, was that it could be taken orally without any monitoring of its anticoagulant properties. This would have set it apart from warfarin and heparin, which require monitoring of the international normalized ratio (INR) and the partial thromboplastin time (PTT), respectively. A disadvantage recognised early was the absence of an antidote in case acute bleeding develops, while warfarin can be antagonised by vitamin K and heparin by protamine sulfate.
Side-effects
Ximelagatran was generally well tolerated in the trial populations, but a small proportion (5-6%) developed elevated liver enzyme levels, which prompted the FDA to reject an initial application for approval in 2004. The further development was discontinued in 2006 after it turned out hepatic damage could develop in the period subsequent to withdrawal of the drug. According to AstraZeneca, a chemically different but pharmacologically similar substance, AZD0837, is undergoing testing for similar indications.[2]
Melagatran synthesis
Sobrera, L. A.; Castaner, J.; Drugs Future, 2002, 27, 201.
References
- ^ Hirsh J, O'Donnell M, Eikelboom JW (July 2007). "Beyond unfractionated heparin and warfarin: current and future advances". Circulation. 116 (5): 552–560. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.685974. PMID 17664384.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "AstraZeneca Decides to Withdraw Exanta" (Press release). AstraZeneca. February 14, 2006. Retrieved 2012-07-16.
- ^ Ho SJ, Brighton TA (2006). "Ximelagatran: direct thrombin inhibitor". Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2 (1): 49–58. doi:10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.1.49. PMC 1993972. PMID 17319469.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Eriksson, H; Wahlander K; Gustafsson D; Welin LT; Frison L; Schulman S; THRIVE Investigators (January 2003). "A randomized, controlled, dose-guiding study of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor ximelagatran compared with standard therapy for the treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis: THRIVE I". Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 1 (1): 41–47. doi:10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00034.x. PMID 12871538.
- ^ Francis, CW (October 2003). "Comparison of ximelagatran with warfarin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement". New England Journal of Medicine. 349 (18): 1703–1712. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035162. PMID 14585938.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Schulman, S; Wåhlander K; Lundström T; Clason SB; Eriksson H; THRIVE III investigators (October 2003). "Secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism with the oral direct thrombin inhibitor ximelagatran". New England Journal of Medicine. 349 (18): 1713–1721. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030104. PMID 14585939.

