Haplogroup I-M170: Difference between revisions
m clean up using AWB |
origin = Western Eurasia; as the article says the parent haplogroup IJ is now found only in Iran + the sibling J is concentrated in SW Asia |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| map =Haplogroup I (Y-DNA).PNG |
| map =Haplogroup I (Y-DNA).PNG |
||
| origin-date =25,000-30,000 years BP |
| origin-date =25,000-30,000 years BP |
||
| origin-place = |
| origin-place = [[Western Eurasia]] |
||
| ancestor =[[Haplogroup IJ (Y-DNA)|IJ]] |
| ancestor =[[Haplogroup IJ (Y-DNA)|IJ]] |
||
| descendants =I*, [[Haplogroup I1 (Y-DNA)|I1]], [[Haplogroup I2 (Y-DNA)|I2]] |
| descendants =I*, [[Haplogroup I1 (Y-DNA)|I1]], [[Haplogroup I2 (Y-DNA)|I2]] |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| members [[Bosnia]] 58,5%,<ref>Marjanović, Damir; et al. "The peopling of modern Bosnia-Herzegovina: Y-chromosome haplogroups in the three main ethnic groups." Institute for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, University of Sarajevo. November 2005</ref> [[Sweden]] 42%,<ref name="Rootsi S 2004 p I">{{cite journal | last1 = Rootsi | first1 = S | last2 = Magri | first2 = C | last3 = Kivisild | first3 = T| year = | title = (July 2004). "Phylogeography of Y-chromosome haplogroup I-M170 reveals distinct domains of prehistoric gene flow in europe | url = | journal = Am. J. Hum. Genet | volume = 75 | issue = 1| pages = 128–37 | doi = 10.1086/422196 | pmid = 15162323 | pmc=1181996|display-authors=etal}}</ref> [[Norway]] 40%,<ref name="Rootsi S 2004 p I"/> [[Croatia]] (mainland) 38%,<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Pericić | first1 = M | last2 = Lauc | first2 = LB | last3 = Klarić | first3 = IM| year = 2005 | title = High-resolution phylogenetic analysis of southeastern Europe traces major episodes of paternal gene flow among Slavic populations | url = | journal = Mol. Biol. Evol | volume = 22 | issue = 10| pages = 1964–75 | doi = 10.1093/molbev/msi185 | pmid = 15944443 |quote=Fig. 3. — I1b* (xM26) frequency and variance surfaces ...|display-authors=etal}}</ref> [[Sardinia]] 37%,<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Francalacci | first1 = P. | last2 = Morelli | first2 = L. | last3 = Underhill | first3 = P.A.| year = 2003 | title = Peopling of Three Mediterranean Islands (Corsica, Sardinia, and Sicily) Inferred by Y-Chromosome Biallelic Variability | url = | journal = American Journal of Physical Anthropology | volume = 121 | issue = 3| pages = 270–279 | doi=10.1002/ajpa.10265 | pmid=12772214|display-authors=etal}}</ref> [[Iceland]] 33%}} |
| members [[Bosnia]] 58,5%,<ref>Marjanović, Damir; et al. "The peopling of modern Bosnia-Herzegovina: Y-chromosome haplogroups in the three main ethnic groups." Institute for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, University of Sarajevo. November 2005</ref> [[Sweden]] 42%,<ref name="Rootsi S 2004 p I">{{cite journal | last1 = Rootsi | first1 = S | last2 = Magri | first2 = C | last3 = Kivisild | first3 = T| year = | title = (July 2004). "Phylogeography of Y-chromosome haplogroup I-M170 reveals distinct domains of prehistoric gene flow in europe | url = | journal = Am. J. Hum. Genet | volume = 75 | issue = 1| pages = 128–37 | doi = 10.1086/422196 | pmid = 15162323 | pmc=1181996|display-authors=etal}}</ref> [[Norway]] 40%,<ref name="Rootsi S 2004 p I"/> [[Croatia]] (mainland) 38%,<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Pericić | first1 = M | last2 = Lauc | first2 = LB | last3 = Klarić | first3 = IM| year = 2005 | title = High-resolution phylogenetic analysis of southeastern Europe traces major episodes of paternal gene flow among Slavic populations | url = | journal = Mol. Biol. Evol | volume = 22 | issue = 10| pages = 1964–75 | doi = 10.1093/molbev/msi185 | pmid = 15944443 |quote=Fig. 3. — I1b* (xM26) frequency and variance surfaces ...|display-authors=etal}}</ref> [[Sardinia]] 37%,<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Francalacci | first1 = P. | last2 = Morelli | first2 = L. | last3 = Underhill | first3 = P.A.| year = 2003 | title = Peopling of Three Mediterranean Islands (Corsica, Sardinia, and Sicily) Inferred by Y-Chromosome Biallelic Variability | url = | journal = American Journal of Physical Anthropology | volume = 121 | issue = 3| pages = 270–279 | doi=10.1002/ajpa.10265 | pmid=12772214|display-authors=etal}}</ref> [[Iceland]] 33%}} |
||
In [[human genetics]], '''Haplogroup I-M170''' is a [[Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup|Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup]], a subgroup of [[haplogroup IJ (Y-DNA)| |
In [[human genetics]], '''Haplogroup I-M170''' is a [[Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup|Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup]], a subgroup of [[haplogroup IJ (Y-DNA)|Haplogroup IJ]], itself a derivative of [[Haplogroup IJK (Y-DNA)|Haplogroup IJK]]. |
||
I-M170 is one of the most numerous haplogroups among European males.<ref>http://www.cell.com/ajhg/abstract/S0002-9297(07)62002-3?cc=y</ref> It can be found in most present-day European populations, with peaks in some [[Northern Europe]]an and [[Southeastern Europe]]an countries. Consequently, the haplogroup represents up to one-fifth of the male population of Europe, being the continent's second major Y-DNA haplogroup behind [[Haplogroup R (Y-DNA)|Haplogroup R]]. Haplogroup I-M170 Y-chromosomes have also been found among some populations of the [[Near East]], the [[Caucasus]], Northeast Africa and [[Central Siberia]]. The haplogroup reaches its maximum frequency in the [[Dinaric Alps]] (with the highest concentration in present-day [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]]). |
|||
A European point of origin for I-M170 is generally proposed. However, the concentration of its sibling [[Haplogroup J (Y-DNA)|Haplogroup J]] (M304) in [[South West Asia]], and the discovery in 2012 of living examples of Haplogroup IJ* in [[Iran]], may imply that all three haplogroups originated closer to [[Anatolia]] and/or the [[Caucasus]].<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Grugni | year = 2012 | title = Ancient Migratory Events in the Middle East: New Clues from the Y-Chromosome Variation of Modern Iranians | url = | journal = PLOS ONE | volume = 7| issue = | pages = e41252| doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0041252 | pmid=22815981 | pmc=3399854}}</ref> |
|||
==Origins== |
==Origins== |
||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
The TMRCA is an estimate of the time of subclade divergence. Rootsi and colleagues in 2004 also note two other dates for a clade, age of STR variation, and time since population divergence. These last two dates are roughly associated, and occur somewhat after subclade divergence. For Haplogroup I-M170 they estimate time to STR variation as 24±7.1 ky and time to population divergence as 23±7.7 ky.<ref name="Rootsi Siiri et al. 2004 128–137">{{cite journal | doi = 10.1086/422196 | author = Rootsi Siiri ''et al.'' | year = 2004 | title = , Phylogeography of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup I-M170 Reveals Distinct Domains of Prehistoric Gene Flow in Europe | url = | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 75 | issue = 1| pages = 128–137 | pmid = 15162323 | pmc = 1181996 | last2 = Kivisild | first2 = Toomas | last3 = Benuzzi | first3 = Giorgia | last4 = Help | first4 = Hela | last5 = Bermisheva | first5 = Marina | last6 = Kutuev | first6 = Ildus | last7 = Barać | first7 = Lovorka | last8 = Peričić | first8 = Marijana | last9 = Balanovsky | first9 = Oleg | last10 = Pshenichnov | first10 = Andrey | last11 = Dion | first11 = Daniel | last12 = Grobei | first12 = Monica | last13 = Zhivotovsky | first13 = Lev A. | last14 = Battaglia | first14 = Vincenza | last15 = Achilli | first15 = Alessandro | last16 = Al-Zahery | first16 = Nadia | last17 = Parik | first17 = Jüri | last18 = King | first18 = Roy | last19 = Cinnioğlu | first19 = Cengiz | last20 = Khusnutdinova | first20 = Elsa | last21 = Rudan | first21 = Pavao | last22 = Balanovska | first22 = Elena | last23 = Scheffrahn | first23 = Wolfgang | last24 = Simonescu | first24 = Maya | last25 = Brehm | first25 = Antonio | last26 = Goncalves | first26 = Rita | last27 = Rosa | first27 = Alexandra | last28 = Moisan | first28 = Jean-Paul | last29 = Chaventre | first29 = Andre | last30 = Ferak | first30 = Vladimir | display-authors = 29 }}</ref> These estimates are consistent with those of Karafet 2008 cited above. However Underhill and his colleagues calculate the time to subclade divergence of I1 and I2 to be 28.4±5.1 ky, though they calculate the STR variation age of I1 at only 8.1±1.5 kya.<ref>P.A. Underhill, N.M. Myres, S. Rootsi, C.T. Chow, A.A. Lin, R.P. Otillar, R. King, L.A. Zhivotovsky, O. Balanovsky, A. Pshenichnov, K.H. Ritchie, L.L. Cavalli-Sforza, T. Kivisild, R. Villems, S.R. Woodward, New Phylogenetic Relationships for Y-chromosome Haplogroup I: Reappraising its Phylogeography and Prehistory, in P. Mellars, K. Boyle, O. Bar-Yosef and C. Stringer (eds.), ''Rethinking the Human Evolution'' (2007), pp. pp. 33-42.</ref> |
The TMRCA is an estimate of the time of subclade divergence. Rootsi and colleagues in 2004 also note two other dates for a clade, age of STR variation, and time since population divergence. These last two dates are roughly associated, and occur somewhat after subclade divergence. For Haplogroup I-M170 they estimate time to STR variation as 24±7.1 ky and time to population divergence as 23±7.7 ky.<ref name="Rootsi Siiri et al. 2004 128–137">{{cite journal | doi = 10.1086/422196 | author = Rootsi Siiri ''et al.'' | year = 2004 | title = , Phylogeography of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup I-M170 Reveals Distinct Domains of Prehistoric Gene Flow in Europe | url = | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 75 | issue = 1| pages = 128–137 | pmid = 15162323 | pmc = 1181996 | last2 = Kivisild | first2 = Toomas | last3 = Benuzzi | first3 = Giorgia | last4 = Help | first4 = Hela | last5 = Bermisheva | first5 = Marina | last6 = Kutuev | first6 = Ildus | last7 = Barać | first7 = Lovorka | last8 = Peričić | first8 = Marijana | last9 = Balanovsky | first9 = Oleg | last10 = Pshenichnov | first10 = Andrey | last11 = Dion | first11 = Daniel | last12 = Grobei | first12 = Monica | last13 = Zhivotovsky | first13 = Lev A. | last14 = Battaglia | first14 = Vincenza | last15 = Achilli | first15 = Alessandro | last16 = Al-Zahery | first16 = Nadia | last17 = Parik | first17 = Jüri | last18 = King | first18 = Roy | last19 = Cinnioğlu | first19 = Cengiz | last20 = Khusnutdinova | first20 = Elsa | last21 = Rudan | first21 = Pavao | last22 = Balanovska | first22 = Elena | last23 = Scheffrahn | first23 = Wolfgang | last24 = Simonescu | first24 = Maya | last25 = Brehm | first25 = Antonio | last26 = Goncalves | first26 = Rita | last27 = Rosa | first27 = Alexandra | last28 = Moisan | first28 = Jean-Paul | last29 = Chaventre | first29 = Andre | last30 = Ferak | first30 = Vladimir | display-authors = 29 }}</ref> These estimates are consistent with those of Karafet 2008 cited above. However Underhill and his colleagues calculate the time to subclade divergence of I1 and I2 to be 28.4±5.1 ky, though they calculate the STR variation age of I1 at only 8.1±1.5 kya.<ref>P.A. Underhill, N.M. Myres, S. Rootsi, C.T. Chow, A.A. Lin, R.P. Otillar, R. King, L.A. Zhivotovsky, O. Balanovsky, A. Pshenichnov, K.H. Ritchie, L.L. Cavalli-Sforza, T. Kivisild, R. Villems, S.R. Woodward, New Phylogenetic Relationships for Y-chromosome Haplogroup I: Reappraising its Phylogeography and Prehistory, in P. Mellars, K. Boyle, O. Bar-Yosef and C. Stringer (eds.), ''Rethinking the Human Evolution'' (2007), pp. pp. 33-42.</ref> |
||
Haplogroup I is Europe's oldest major |
Haplogroup I is Europe's oldest major Y-DNA haplogroup.<ref>[http://www.eupedia.com/europe/Haplogroup_I1_Y-DNA.shtml Haplogroup I1 (Y-DNA), 2. Origins and History]</ref> {{unreliable source}} Genes for [[blue eyes]] such as [[OCA2]] were present on [[Mesolithic]] European carriers of haplogroup I, while another typical European feature, [[red hair]], had not been present in Europe until the [[Bronze Age]] when [[Haplogroup R1b (Y-DNA)|Haplogroup R1b]] carriers began spreading it.<ref>[http://www.eupedia.com/europe/Haplogroup_R1b_Y-DNA.shtml Haplogroup R1b (Y-DNA), 5. R1 populations & light pigmentation]</ref>{{unreliable source}} |
||
Semino (2000) speculated that the initial dispersion of this population corresponds to the diffusion of the [[Gravettian]] culture.<ref name = "Semino2000">{{cite journal |vauthors=Semino O, Passarino G, Oefner PJ, etal |title=The genetic legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in extant Europeans: a Y chromosome perspective |journal=Science |volume=290 |issue=5494 |pages=1155–9 |date=November 2000 |pmid=11073453 |url=http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11073453 |doi=10.1126/science.290.5494.1155}}</ref> Rootsi and colleagues in 2004 suggested that each of the ancestral populations now dominated by a particular subclade of Haplogroup I-M170 experienced an independent population expansion immediately after the [[last glacial maximum]].<ref name="Rootsi Siiri et al. 2004 128–137"/> |
Semino (2000) speculated that the initial dispersion of this population corresponds to the diffusion of the [[Gravettian]] culture.<ref name = "Semino2000">{{cite journal |vauthors=Semino O, Passarino G, Oefner PJ, etal |title=The genetic legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in extant Europeans: a Y chromosome perspective |journal=Science |volume=290 |issue=5494 |pages=1155–9 |date=November 2000 |pmid=11073453 |url=http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11073453 |doi=10.1126/science.290.5494.1155}}</ref> Rootsi and colleagues in 2004 suggested that each of the ancestral populations now dominated by a particular subclade of Haplogroup I-M170 experienced an independent population expansion immediately after the [[last glacial maximum]].<ref name="Rootsi Siiri et al. 2004 128–137"/> |
||
| Line 39: | Line 42: | ||
In 2016, the 31,210-34,580 year old remains of a hunter gatherer from [[Paglicci Cave|Paglicci]] was found with haplogroup I.<ref>Qiaomei Fu et al, [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature17993.html The genetic history of Ice Age Europe], Nature(2016)doi:10.1038/nature17993Received 18 December 2015 Accepted 12 April 2016 Published online 02 May 2016</ref> |
In 2016, the 31,210-34,580 year old remains of a hunter gatherer from [[Paglicci Cave|Paglicci]] was found with haplogroup I.<ref>Qiaomei Fu et al, [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature17993.html The genetic history of Ice Age Europe], Nature(2016)doi:10.1038/nature17993Received 18 December 2015 Accepted 12 April 2016 Published online 02 May 2016</ref> |
||
It would seem to be that |
It would seem to be that separate waves of population movement impacted [[Southeastern Europe]]. The role of the [[Balkans]] as a long-standing corridor to Europe from [[Southwestern Asia]] is shown by the phylogenetic origins of Haplogroups I and J in the parent haplogroup IJ and the M429 mutation. This common ancestry suggests that subclades of the ancestral Haplogroup IJ-M429 probably entered Europe through the Balkans sometime before the [[Last Glacial Maximum]]. I and J were subsequently distributed in Asia and Europe in a disjunctive phylogeographic pattern typical of "sibling" haplogroups. A natural geographical corridor like the Balkans is likely to have been used later by members of other subclades of IJ, as well as other haplogroups, including [[Early European Farmers]]. |
||
The discovery of [[Haplogroup IJK]] – the ancestor of both haplogroups IJ and [[Haplogroup K-M9|K]] (M9) – and its evolutionary distance from other subclades of [[Haplogroup F-M89|Haplogroup F]] (M89), supports the inference that both IJ-M429 and K-M9 arose in Southwestern Asia. Living carriers of F-M89* and IJ-M429* have been reported in the [[Iranian plateau]].<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Grugni | year = 2012 | title = Ancient Migratory Events in the Middle East: New Clues from the Y-Chromosome Variation of Modern Iranians | url = | journal = PLOS ONE | volume = 7| issue = | pages = e41252| doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0041252 | pmid=22815981 | pmc=3399854}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Haplogroup I (Y-DNA).PNG|300px|thumb|The northern coverage area is mainly composed of the related [[Haplogroup I-M253|I-M253]] (I1) while I-M438 (I2) dominates in the south; both descendants of Haplogroup I-M170.]] |
[[File:Haplogroup I (Y-DNA).PNG|300px|thumb|The northern coverage area is mainly composed of the related [[Haplogroup I-M253|I-M253]] (I1) while I-M438 (I2) dominates in the south; both descendants of Haplogroup I-M170.]] |
||
Revision as of 12:32, 14 July 2016
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Haplogroup I-M170 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Possible time of origin | 25,000-30,000 years BP |
| Possible place of origin | Western Eurasia |
| Ancestor | IJ |
| Descendants | I*, I1, I2 |
| Defining mutations | L41, M170, M258, P19_1, P19_2, P19_3, P19_4, P19_5, P38, P212, U179 |
In human genetics, Haplogroup I-M170 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, a subgroup of Haplogroup IJ, itself a derivative of Haplogroup IJK. I-M170 is one of the most numerous haplogroups among European males.[1] It can be found in most present-day European populations, with peaks in some Northern European and Southeastern European countries. Consequently, the haplogroup represents up to one-fifth of the male population of Europe, being the continent's second major Y-DNA haplogroup behind Haplogroup R. Haplogroup I-M170 Y-chromosomes have also been found among some populations of the Near East, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa and Central Siberia. The haplogroup reaches its maximum frequency in the Dinaric Alps (with the highest concentration in present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina).
A European point of origin for I-M170 is generally proposed. However, the concentration of its sibling Haplogroup J (M304) in South West Asia, and the discovery in 2012 of living examples of Haplogroup IJ* in Iran, may imply that all three haplogroups originated closer to Anatolia and/or the Caucasus.[2]
Origins
 |
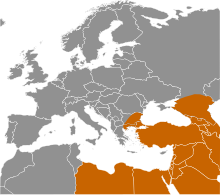 | |
 |
 |
 Solutrean and Proto-Solutrean Cultures Epi-Gravettian Culture |
Haplogroup IJ, carried by the Cro-Magnons was moving to Europe from the Middle East between 40,000 and 30,000 years ago. The TMRCA (time to most recent common ancestor) for the I clade was estimated by Karafet and colleagues in 2008 as 22.2 k.a. (22,200 years ago) with a confidence interval between 15.3-30.0 ka.,[3] placing the Haplogroup I-M170 founding event approximately contemporaneous with the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) which lasted from 26.5 ka to 19 or 20 ka.[4] The TMRCA is an estimate of the time of subclade divergence. Rootsi and colleagues in 2004 also note two other dates for a clade, age of STR variation, and time since population divergence. These last two dates are roughly associated, and occur somewhat after subclade divergence. For Haplogroup I-M170 they estimate time to STR variation as 24±7.1 ky and time to population divergence as 23±7.7 ky.[5] These estimates are consistent with those of Karafet 2008 cited above. However Underhill and his colleagues calculate the time to subclade divergence of I1 and I2 to be 28.4±5.1 ky, though they calculate the STR variation age of I1 at only 8.1±1.5 kya.[6]
Haplogroup I is Europe's oldest major Y-DNA haplogroup.[7] [unreliable source?] Genes for blue eyes such as OCA2 were present on Mesolithic European carriers of haplogroup I, while another typical European feature, red hair, had not been present in Europe until the Bronze Age when Haplogroup R1b carriers began spreading it.[8][unreliable source?]
Semino (2000) speculated that the initial dispersion of this population corresponds to the diffusion of the Gravettian culture.[9] Rootsi and colleagues in 2004 suggested that each of the ancestral populations now dominated by a particular subclade of Haplogroup I-M170 experienced an independent population expansion immediately after the last glacial maximum.[5]
In 2016, the 31,210-34,580 year old remains of a hunter gatherer from Paglicci was found with haplogroup I.[10]
It would seem to be that separate waves of population movement impacted Southeastern Europe. The role of the Balkans as a long-standing corridor to Europe from Southwestern Asia is shown by the phylogenetic origins of Haplogroups I and J in the parent haplogroup IJ and the M429 mutation. This common ancestry suggests that subclades of the ancestral Haplogroup IJ-M429 probably entered Europe through the Balkans sometime before the Last Glacial Maximum. I and J were subsequently distributed in Asia and Europe in a disjunctive phylogeographic pattern typical of "sibling" haplogroups. A natural geographical corridor like the Balkans is likely to have been used later by members of other subclades of IJ, as well as other haplogroups, including Early European Farmers.
The discovery of Haplogroup IJK – the ancestor of both haplogroups IJ and K (M9) – and its evolutionary distance from other subclades of Haplogroup F (M89), supports the inference that both IJ-M429 and K-M9 arose in Southwestern Asia. Living carriers of F-M89* and IJ-M429* have been reported in the Iranian plateau.[11]

Distribution
The following figures include all subclades. The greatest density of Haplogoup I is to be found in Bosnia and Herzegovina 65%,[12] i.e. Bosnian Serbs 31%, Bosniaks 44-50.1%[13][14] and Bosnian Croats 71-73%.[14] Other higher than average densities occur in Croatia 38%[12][15][16] - 44%,[14] Hvar 66%,[15] Korčula 54%,[15] Serbia 36.28%[12] - 48%,[17] Romania 33%,[18] however increasing in historical (on both shores of river Prut) Moldavia 48%, Norway 40%,[16][19] 23.6% of German males carry the haplogroup I mutation[20] (highest frequency in Northern Germany 37.5%[9]), Sardinia 37%[21] (42%[16]), Sweden (North 26%,[16] Gotland & Värmland 50%[22]), Denmark 39%,[16][23] Montenegro 37%,[17] Iceland 33%, and West Finland 41%, though the figure drops in East Finland to 20%.[24]
Average densities occur in Macedonia 34%,[12] Bulgaria 28%,[25] Albania 25%,[26] Hungary 11%[9] Lapland 28%,[27] Netherlands 25%, England 20% and Poland 18-20%.[16][28]
Within Europe, several populations are distinguished by having a significantly lower frequency of Haplogroup I-M170 than the surrounding populations: Italy and Switzerland have lower levels than Germany and Sardinia, Iberia has a lower density than southern France and Normandy, Greece has a lower level than Albania and the Slavic peoples, while the Baltic-speaking Latvians have a lower level than the Finnic-speaking Estonians.[citation needed] In all these areas, Haplogroup I-M170 populations are small relative to the dominant haplogroups in Europe (R1b in Western Europe, R1a1 in Eastern Europe, and N in Northeastern Europe).[citation needed]
Subgroups
The subclades of Haplogroup I-M170 with their defining mutations:[29]
- I-M170 ( L41, M170, M258, P19_1, P19_2, P19_3, P19_4, P19_5, P38, P212, Page123, U179) Middle East, Caucasus, Europe.
- I-M253 Haplogroup I1 (L64, L75, L80, L81, L118, L121/S62, L123, L124/S64, L125/S65, L157, L186, L187, M253,M307.2/P203.2, M450/S109, P30, P40, S63, S66, S107, S108, S110, S111) Typical of populations of Scandinavia and Northwest Europe, with a moderate distribution throughout Eastern Europe In Anatolia at 1%[30]
- I1 L64, L75, L80, L81, L118, L121/S62, L123, L124/S64, L125/S65, L157.1, L186, L187, L840, M253, M307.2/P203.2, M450/S109, P30, P40, S63, S66, S107, S108, S110, S111
- I1a DF29/S438
- I1a1 CTS6364/Z2336
- I1a1a M227
- I1a1a1 M72
- I1a1b L22/S142
- I1a1b1 P109
- I1a1b2 L205
- I1a1b3 L287
- I1a1b3a L258/S335
- I1a1b3a1 L296
- I1a1b3a L258/S335
- I1a1b4 L300/S241
- I1a1b5 L813/Z719
- I1a1a M227
- I1a2 S244/Z58
- I1a2a S246/Z59
- I1a2a1 S337/Z60, S439/Z61, Z62
- I1a2a1a Z140, Z141
- I1a2a1a1 Z2535
- I1a2a1a1a L338
- I1a2a1a2 F2642
- I1a2a1a1 Z2535
- I1a2a1b Z73
- I1a2a1c L573
- I1a2a1d L1248
- I1a2a1d1 L803
- I1a2a1a Z140, Z141
- I1a2a2 Z382
- I1a2a1 S337/Z60, S439/Z61, Z62
- I1a2b S296/Z138, Z139
- I1a2b1 Z2541
- I1a2a S246/Z59
- I1a3 S243/Z63
- I1a3a L1237
- I1a1 CTS6364/Z2336
- I1b Z131 [31]
- I1a DF29/S438
- I2 L68/PF3781/S329, M438/P215/PF3853/S31
- I2a L460/PF3647/S238
- I2a1 P37.2
- I2a1a L158/PF4073/S433, L159.1/S169.1, M26/PF4056
- I2a1a1 L160/PF4013
- I2a1b L178/S328, M423
- I2a1b1 M359.2/P41.2
- I2a1b2 L161.1/S185
- I2a1b3 L621/S392
- I2a1b3a L147.2
- I2a1c L233/S183
- I2a1a L158/PF4073/S433, L159.1/S169.1, M26/PF4056
- I2a2 L35/PF3862/S150, L37/PF6900/S153, L181, M436/P214/PF3856/S33, P216/PF3855/S30, P217/PF3854/S23, P218/S32
- I2a2a L34/PF3857/S151, L36/S152, L59, L368, L622, M223, P219/PF3859/S24, P220/S119, P221/PF3858/S120, P222/PF3861/U250/S118, P223/PF3860/S117, Z77
- I2a2a1 CTS616, CTS9183
- I2a2a1a M284
- I2a2a1a1 L1195
- I2a2a1a1a L126/S165, L137/S166, L369
- I2a2a1a1b L1193
- I2a2a1a1 L1195
- I2a2a1b L701, L702
- I2a2a1b1 P78
- I2a2a1b2 L699, L703
- I2a2a1b2a L704
- I2a2a1c Z161
- I2a2a1c1 L801/S390
- I2a2a1c1a CTS1977
- I2a2a1c1a1 P95
- I2a2a1c1b CTS6433
- I2a2a1c1b1 Z78
- I2a2a1c1b1a L1198
- I2a2a1c1b1a1 Z190
- I2a2a1c1b1a1a S434/Z79
- I2a2a1c1b1a1 Z190
- I2a2a1c1b1a L1198
- I2a2a1c1b1 Z78
- I2a2a1c1a CTS1977
- I2a2a1c2 L623, L147.4
- I2a2a1c1 L801/S390
- I2a2a1d L1229
- I2a2a1d1 Z2054
- I2a2a1d1a L812/S391
- I2a2a1d2 L1230
- I2a2a1d1 Z2054
- I2a2a1a M284
- I2a2a2 L1228
- I2a2a1 CTS616, CTS9183
- I2a2b L38/S154, L39/S155, L40/S156, L65.1/S159.1, L272.3
- I2a2b1 L533
- I2a2a L34/PF3857/S151, L36/S152, L59, L368, L622, M223, P219/PF3859/S24, P220/S119, P221/PF3858/S120, P222/PF3861/U250/S118, P223/PF3860/S117, Z77
- I2a1 P37.2
- I2b L415, L416, L417
- I2c L596/PF6907/S292, L597/S333
- I2a L460/PF3647/S238
Note that the naming of some of the subgroups has changed, as new markers have been identified, and the sequence of mutations has become clearer..
I-M170
The composite subclade I-M170 contains individuals directly descended from the earliest members of Haplogroup I, bearing none of the subsequent mutations which identify the remaining named subclades.
Several haplogroup I*-M170 individuals who do not fall in known subclades, with some of the greatest Y-STR diversity, have significantly been found among the populations of Turkey (8/741), Adygea (2/138), and Iraq (1/176),even though as a whole Haplogroup I-M170 occurs at only very low frequencies among modern populations of the Middle East and Caucasus. This is consistent with the belief that the haplogroup first appeared in that region. Overall, the highest frequencies of Haplogroup I*-M170 appear to be found among the Andalusians (3/103), French (4/179), Slovenians (2/55), Tabassarans (1/30)[32] and the Saami (1/35). [1] The greatest figure so far for I* was among the Laks in Dagestan, at a rate of (3/21).[32]
Neither study from which the previous figures were drawn excluded the present I2-M438 clade as a whole, but only certain subclades, so this I* may or may not belong to I2. A single Hazara from Afghanistan was found to carry I* excluding both I1-M253 and I2-M438.[33]
I1-M253

Haplogroup I1-M253 (M253, M307, P30, P40) displays a very clear frequency gradient, with a peak frequency of approximately 35% among the populations of southern Norway, southwestern Sweden, and Denmark, and rapidly decreasing frequencies toward the edges of the historically Germanic-influenced world. A notable exception is Finland, where frequency in West Finns is up to 40%, and in certain provinces like Satakunta more than 50%.
Outside Fennoscandia, distribution of Haplogroup I1-M253 is closely correlated with that of Haplogroup I2a2-M436; but among Scandinavians (including both Germanic and Uralic peoples of the region) nearly all the Haplogroup I-M170 Y-chromosomes are I1-M253. Another characteristic of the Scandinavian I1-M253 Y-chromosomes is their rather low haplotype diversity (STR diversity): a greater variety of Haplogroup I1-M253 Y-chromosomes has been found among the French and Italians, despite the much lower overall frequency of Haplogroup I1-M253 among the modern French and Italian populations.
I2-M438
Haplogroup I2-M438, previously I1b, may have originated in southern Europe – it is now found at its highest frequencies in the western Balkans and Sardinia – some 15,000 - 17,000 years ago and developed into three main subgroups : I2-M438*, I2a-L460, I2b-L415 and I2c-L596.
I2a1a-M26
Haplogroup I2a1a-M26 is notable for its strong presence in Sardinia. Haplogroup I-M170 comprises approximately 40% of all patrilines among the Sardinians, and I2a1a-M26 is the predominant type of I among them.
Haplogroup I2a1a-M26 is practically absent east of France and Italy,[35] while it is found at low but significant frequencies outside of Sardinia in the Balearic Islands, Castile-León, the Basque Country, the Pyrenees, southern and western France, and parts of the Maghreb in North Africa, Great Britain, and Ireland. Haplogroup I2a1a-M26 appears to be the only subclade of Haplogroup I-M170 found among the Basques, but appears to be found at somewhat higher frequencies among the general populations of Castile-León in Spain and Béarn in France than among the population of ethnic Basques.[citation needed] The M26 mutation is found in native males inhabiting every geographic region where megaliths may be found, including such far-flung and culturally disconnected regions as the Canary Islands, the Balearic Isles, Corsica, Ireland, and Sweden.[35]
The distribution of I2a1a-M26 also mirrors that of the Atlantic Bronze Age cultures, which indicates a potential spread via the obsidian trade or a regular maritime exchange of some of metallurgical products.[35]
I2a1b-M423
Haplogroup I2a1b-M423 is the most frequent Y-chromosome Haplogroup I-M170 in Central and Eastern European populations, reaching its peak in the Western Balkans, most notably in Dalmatia (50-60%[12]) and Bosnia-Herzegovina (up to 71%,[13] avg. 40-50%[12]). A greater variance of this group has been found in Ireland and Great Britain, but overall frequency is very low (2-3%). Haplogroup I2a1b-M423 is virtually absent in Fennoscandia, Western and Southwestern Europe.
I2a2-M436
The distribution of Haplogroup I2a2-M436 (M436/P214/S33, P216/S30, P217/S23, P218/S32) is closely correlated to that of Haplogroup I1 except in Fennoscandia, which suggests that it was probably harbored by at least one of the Paleolithic refuge populations that also harbored Haplogroup I1-M253; the lack of correlation between the distributions of I1-M253 and I2a2-M436 in Fennoscandia may be a result of Haplogroup I2a2-M436's being more strongly affected in the earliest settlement of this region by founder effects and genetic drift due to its rarity, as Haplogroup I2a2-M436 comprises less than 10% of the total Y-chromosome diversity of all populations outside of Lower Saxony. Haplogroup I2a2-M436 has been found in over 4% of the population only in Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, Denmark, England (not including Cornwall), Scotland, and the southern tips of Sweden and Norway in Northwest Europe; the provinces of Normandy, Maine, Anjou, and Perche in northwestern France; the province of Provence in southeastern France; the regions of Tuscany, Umbria, and Latium in Italy; and Moldavia and the area around Russia's Ryazan Oblast and Republic of Mordovia in Eastern Europe. One subclade of Haplogroup I2a2-M436, namely I2a2a1a1-M284, has been found almost exclusively among the population of Great Britain, which has been taken to suggest that the clade may have a very long history in that island. It is notable, however, that the distributions of Haplogroup I1-M253 and Haplogroup I2a2-M436 seem to correlate fairly well with the extent of historical influence of Germanic peoples. The punctual presence of both haplogroups at a low frequency in the area of the historical regions of Bithynia and Galatia in Turkey may be related to the Varangian Guard or rather suggests a connection with the ancient Gauls of Thrace, several tribes of which are recorded to have immigrated to those parts of Anatolia at the invitation of Nicomedes I of Bithynia. This suggestion is supported by recent genetic studies regarding Y-DNA Haplogroup I2b2-L38 have concluded that there was some Late Iron Age migration of Celtic La Tène people, through Belgium, to the British Isles including north-east Ireland.[36]
Haplogroup I2a2-M436 also occurs among approximately 1% of Sardinians, and in Hazaras from Afghanistan at 3%.[37]
Specifications of mutation
The technical details of U179 are:
- Nucleotide change (rs2319818): G to A
- Position (base pair): 275
- Total size (base pairs): 220
- Forward 5′→ 3′: aaggggatatgacgactgatt
- Reverse 5′→ 3′: cagctcctcttttcaactctca
See also
- Haplogroup
- Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups
- Haplogroup I1 (Y-DNA)
- Haplogroup I2 (Y-DNA)
- Late Glacial Maximum
- Proto-Indo-Europeans
References
- ^ http://www.cell.com/ajhg/abstract/S0002-9297(07)62002-3?cc=y
- ^ Grugni (2012). "Ancient Migratory Events in the Middle East: New Clues from the Y-Chromosome Variation of Modern Iranians". PLOS ONE. 7: e41252. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041252. PMC 3399854. PMID 22815981.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Karafet TM, Mendez FL, Meilerman MB, Underhill PA, Zegura SL, Hammer MF (2008). "New binary polymorphisms reshape and increase resolution of the human Y chromosomal haplogroup tree". Genome Research. 18 (5): 830–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7172008. PMC 2336805. PMID 18385274.
- ^ Clark PU, Dyke AS, Shakun JD, et al. (August 2009). "The Last Glacial Maximum". Science. 325 (5941): 710–4. doi:10.1126/science.1172873. PMID 19661421. Retrieved 2010-01-27.
- ^ a b Rootsi Siiri; Kivisild, Toomas; Benuzzi, Giorgia; Help, Hela; Bermisheva, Marina; Kutuev, Ildus; Barać, Lovorka; Peričić, Marijana; Balanovsky, Oleg; Pshenichnov, Andrey; Dion, Daniel; Grobei, Monica; Zhivotovsky, Lev A.; Battaglia, Vincenza; Achilli, Alessandro; Al-Zahery, Nadia; Parik, Jüri; King, Roy; Cinnioğlu, Cengiz; Khusnutdinova, Elsa; Rudan, Pavao; Balanovska, Elena; Scheffrahn, Wolfgang; Simonescu, Maya; Brehm, Antonio; Goncalves, Rita; Rosa, Alexandra; Moisan, Jean-Paul; Chaventre, Andre; et al. (2004). ", Phylogeography of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup I-M170 Reveals Distinct Domains of Prehistoric Gene Flow in Europe". American Journal of Human Genetics. 75 (1): 128–137. doi:10.1086/422196. PMC 1181996. PMID 15162323.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ P.A. Underhill, N.M. Myres, S. Rootsi, C.T. Chow, A.A. Lin, R.P. Otillar, R. King, L.A. Zhivotovsky, O. Balanovsky, A. Pshenichnov, K.H. Ritchie, L.L. Cavalli-Sforza, T. Kivisild, R. Villems, S.R. Woodward, New Phylogenetic Relationships for Y-chromosome Haplogroup I: Reappraising its Phylogeography and Prehistory, in P. Mellars, K. Boyle, O. Bar-Yosef and C. Stringer (eds.), Rethinking the Human Evolution (2007), pp. pp. 33-42.
- ^ Haplogroup I1 (Y-DNA), 2. Origins and History
- ^ Haplogroup R1b (Y-DNA), 5. R1 populations & light pigmentation
- ^ a b c Semino O, Passarino G, Oefner PJ, et al. (November 2000). "The genetic legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in extant Europeans: a Y chromosome perspective". Science. 290 (5494): 1155–9. doi:10.1126/science.290.5494.1155. PMID 11073453.
- ^ Qiaomei Fu et al, The genetic history of Ice Age Europe, Nature(2016)doi:10.1038/nature17993Received 18 December 2015 Accepted 12 April 2016 Published online 02 May 2016
- ^ Grugni (2012). "Ancient Migratory Events in the Middle East: New Clues from the Y-Chromosome Variation of Modern Iranians". PLOS ONE. 7: e41252. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041252. PMC 3399854. PMID 22815981.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c d e f Pericić M, Lauc LB, Klarić IM, et al. (October 2005). "High-resolution phylogenetic analysis of southeastern Europe traces major episodes of paternal gene flow among Slavic populations". Mol. Biol. Evol. 22 (10): 1964–75. doi:10.1093/molbev/msi185. PMID 15944443.
Fig. 3. — I1b* (xM26) frequency and variance surfaces ...
{{cite journal}}: External link in|quote= - ^ a b Marjanovic D, Fornarino S, Montagna S, et al. (November 2005). "The peopling of modern Bosnia-Herzegovina: Y-chromosome haplogroups in the three main ethnic groups". Ann. Hum. Genet. 69 (Pt 6): 757–63. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00190.x. PMID 16266413.
- ^ a b c Battaglia, Vincenza; Fornarino, Simona; Al-Zahery, Nadia; Olivieri, Anna; Pala, Maria; Myres, Natalie M; King, Roy J; Rootsi, Siiri; et al. (24 December 2008). "Y-chromosomal evidence of the cultural diffusion of agriculture in southeast Europe" (PDF). European Journal of Human Genetics. 17 (6): 820–30. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2008.249. PMC 2947100. PMID 19107149.
- ^ a b c Barać L, Pericić M, Klarić IM, et al. (July 2003). "Y chromosomal heritage of Croatian population and its island isolates" (PDF). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 11 (7): 535–42. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200992. PMID 12825075.
- ^ a b c d e f Rootsi S, Magri C, Kivisild T, et al. (July 2004). "Phylogeography of Y-chromosome haplogroup I-M170 reveals distinct domains of prehistoric gene flow in europe". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75 (1): 128–37. doi:10.1086/422196. PMC 1181996. PMID 15162323.
- ^ a b Mirabal S, Varljen T, Gayden T, et al. (July 2010). "Human Y-chromosome short tandem repeats: A tale of acculturation and migrations as mechanisms for the diffusion of agriculture in the Balkan Peninsula". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 142 (3): 380–390. doi:10.1002/ajpa.21235. PMID 20091845.
- ^ Frequencies of European Y-DNA haplogroups Eupedia 2016
- ^ Passarino, Giuseppe; Cavalleri, Gianpiero L; Lin, Alice A; Cavalli-Sforza, LL; Børresen-Dale, AL; Underhill, PA (2002). "Different genetic components in the Norwegian population revealed by the analysis of mtDNA and Y chromosome polymorphisms". European Journal of Human Genetics. 10 (9): 521–529. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200834. PMID 12173029.
- ^ http://vetinari.sitesled.com/poland.pdf
- ^ Francalacci, P.; Morelli, L.; Underhill, P.A.; et al. (2003). "Peopling of Three Mediterranean Islands (Corsica, Sardinia, and Sicily) Inferred by Y-Chromosome Biallelic Variability". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 121 (3): 270–279. doi:10.1002/ajpa.10265. PMID 12772214.
- ^ Karlsson, Andreas O; Wallerström, Thomas; Götherström, Anders; Holmlund, Gunilla (2006). "Y-chromosome diversity in Sweden – A long-time perspective". European Journal of Human Genetics. 14 (8): 963–970. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201651. PMID 16724001.
- ^ Sanchez, JJ; Borsting, C; Hallenberg, C; Buchard, A; Hernandez, A; Morling, N (2003). "Multiplex PCR and minisequencing of SNPs: a model with 35 Y chromosome SNPs". Forensic Science International. 137 (1): 74–84. doi:10.1016/S0379-0738(03)00299-8. PMID 14550618.
- ^ Lappalainen, T.; Laitinen, V.; Salmela, E.; Andersen, P.; Huoponen, K.; Savontaus, M.-L.; Lahermo, P. (May 2008). "Migration waves to the Baltic Sea region". Ann. Hum. Genet. 72 (Pt 3): 337–48. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2007.00429.x. PMID 18294359.
- ^ Comptes rendus de l'Academie Bulgare des Sciences Tome 62, No3, 209, Y-chromosomal Haplogroups in Bulgarians, Sena Karachanak, Simona Fornarino, Viola Grugni, Ornella Semino, Draga Toncheva, Angel Galabov, Boris Atanasov (Submitted on December 22, 2008).
- ^ Y-STR variation in Albanian populations, Gianmarco Ferri & Sergio Tofanelli & Milena Alù & Luca Taglioli & Erjon Radheshi & Beatrice Corradini & Giorgio Paoli & Cristian Capelli & Giovanni Beduschi (2010)
- ^ Tambets, Kristiina; Rootsi, Siiri; Kivisild, Toomas; et al. (2004). "The Western and Eastern Roots of the Saami—the Story of Genetic 'Outliers' Told by Mitochondrial DNA and Y Chromosomes". American Journal of Human Genetics. 74: 661–682. doi:10.1086/383203. PMC 1181943. PMID 15024688.
- ^ Nebel, A; Filon, D; Brinkmann, B; Majumder, P; Faerman, M; Oppenheim, A (2001). "The Y Chromosome Pool of Jews as Part of the Genetic Landscape of the Middle East". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 69 (5): 1095–112. doi:10.1086/324070. PMC 1274378. PMID 11573163.
- ^ ISOGG 2011
- ^ Cinniog˘lu, Cengiz et al 2003-04, Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia
- ^ http://isogg.org/tree/ISOGG_HapgrpI.html
- ^ a b Bulayeva, Caciagli et al, 2009.http://vigg.academia.edu/KazimaBulayeva/Papers/125870/The_key_role_of_patrilineal_inheritance_in_shaping_the_genetic_variation_of_Dagestan_highlanders
- ^ Cristofaro J, et al. (October 2013). "Afghan Hindu Kush: Where Eurasian Sub-Continent Gene Flows Converge". PLOS ONE. 8: e76748. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076748.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Pineau, JC; Delamarche, P; Bozinovic, S (2012-05-24). "Average height of adolescents in the Dinaric Alps. They are also reputed to have the tallest males in Europe. Study claims it is not complete as yet". C. R. Biol. 328: 841–6. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2005.07.004. PMID 16168365.
- ^ a b c Rootsi; et al. "Phylogeography of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup I Reveals Distinct Domains of Prehistoric Gene Flow in Europe figure 1" (PDF).
- ^ McEvoy and Bradley, Brian P and Daniel G (2010). Celtic from the West Chapter 5: Irish Genetics and Celts. Oxbow Books, Oxford, UK. p. 117. ISBN 978-1-84217-410-4.
- ^ Haber, Marc; Platt, Daniel E.; Ashrafian Bonab, Maziar; Youhanna, Sonia C.; Soria-Hernanz, David F.; Martínez-Cruz, Begoña; Douaihy, Bouchra; Ghassibe-Sabbagh, Michella; Rafatpanah, Hoshang; Ghanbari, Mohsen; Whale, John; Balanovsky, Oleg; Wells, R. Spencer; Comas, David; Tyler-Smith, Chris; Zalloua, Pierre A. (2012). "Afghanistan's ethnic groups share a Y-chromosomal heritage structured by historical events". PLOS ONE. 7 (3): e34288. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034288. PMC 3314501. PMID 22470552.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
- Notes
- Barać L, Pericić M, Klarić IM, et al. (July 2003). "Y chromosomal heritage of Croatian population and its island isolates" (PDF). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 11 (7): 535–42. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200992. PMID 12825075.
- The Genographic Project, National Geographic, Atlas of the Human Journey
- ISOGG, Y-DNA Haplogroup I and its Subclades
External links
Phylogenetic tree and distribution maps
- Y-DNA Haplogroup I-M170 and Its Subclades from the International Society of Genetic Genealogy (ISOGG)of 2013
- Phylogeography of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup I
- Frequency Distributions of Y-DNA Haplogroup I and its subclades - with Video Tutorial
- Frequency and Variance of I1b (now considered I2a2-M26)
- Map of 'I1a' (now considered I-M253)
- Map of 'I1b' (now considered I2a-P37.2)
- Map of 'I1c' (now considered I2b-M223)
- Rescalled Haplogroup I Tree (K. Nordtvedt 2011).
Projects
- I Project at FTDNA
- I1 Project at FTDNA
- I2* Project at FTDNA
- I2a project at FTDNA
- I2b project at FTDNA
- I2b2 L38+ project at FTDNA
- The Scandinavian yDNA Genealogical Project at FTDNA
- The Finland Genealogical Project at FTDNA
Other
- Study of Y-Haplogroup I and Modal Haplotypes
- The Y Chromosome Consortium (YCC)
- Example haplotypes from I1* "y cluster"
- YCC Haplogroup I page - I1a (now considered I-M253), I1b (now considered I-P37.2) and I1c (now considered I-M223)
- Haplo-I Subclade Predictor
- Spread of Haplogroup I, from National Geographic
- I2b2 Y-DNA found in Bronze Age skeletons of Lichtenstein Cave
- Haplogroup I-L38 (I2b2) In Search of the Origin of I-L38 (aka I2b2)
